Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
1DPHYS - QUIZ1 (Electrostatics)
Hochgeladen von
Krishnaveni Subramani S0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
198 Ansichten2 SeitenThis document contains a quiz on electrostatics with multiple choice and matching questions. It tests concepts like:
- Which particles are electrically charged
- How charged and neutral objects interact
- Methods of charging and discharging objects
- Applications of electrostatics like in oil refineries
It contains diagrams to illustrate concepts and questions that require explaining charging processes and predicting interactions between charged objects. The quiz covers key topics in electrostatics and assesses understanding through different question types.
Originalbeschreibung:
k
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document contains a quiz on electrostatics with multiple choice and matching questions. It tests concepts like:
- Which particles are electrically charged
- How charged and neutral objects interact
- Methods of charging and discharging objects
- Applications of electrostatics like in oil refineries
It contains diagrams to illustrate concepts and questions that require explaining charging processes and predicting interactions between charged objects. The quiz covers key topics in electrostatics and assesses understanding through different question types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
198 Ansichten2 Seiten1DPHYS - QUIZ1 (Electrostatics)
Hochgeladen von
Krishnaveni Subramani SThis document contains a quiz on electrostatics with multiple choice and matching questions. It tests concepts like:
- Which particles are electrically charged
- How charged and neutral objects interact
- Methods of charging and discharging objects
- Applications of electrostatics like in oil refineries
It contains diagrams to illustrate concepts and questions that require explaining charging processes and predicting interactions between charged objects. The quiz covers key topics in electrostatics and assesses understanding through different question types.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
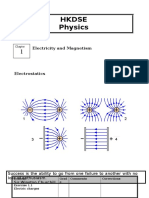
SNC1D PHYSICS: ELECTROSTATICS QUIZ#1
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (10 MARKS)
Choose the best response in each case and place your answer in the appropriate space on your answer sheet.
1. Which atomic particles are electrically charged?
(a) both electrons and protons
(b) both electrons and neutrons
(c) both protons and neutrons
2. A neutral pith ball is:
(a) attracted by another uncharged pith ball.
(b) repelled by a charged glass rod.
(c) attracted by a charged glass rod.
3. A piece of fur is negatively charged when:
(a) the electrons become positively charged.
(b) it has a deficit of electrons.
(c) it has an excess of electrons.
4. 4 objects (R, S, T, U) are brought together. S has a
positive charge. The following is observed:
Sphere S attracts all the other spheres.
Spheres T and U repel each other.
Sphere R attracts all the other spheres.
It can be concluded that sphere R is:
(a) neutral
(b) positive.
(c) negative.
5. When a positively charged object is brought close to
(but not touching) the knob of a neutral metal-leaf
electroscope, the leaves will separate because:
(a) both leaves are negative & the knob is positive.
(b) both leaves are positive & the knob is negative.
(c) none of the above.
6. If X attracts Y but repels Z, then X must be:
(a) charged only.
(b) neutral only.
(c) either neutral or charged.
7. A glass rod becomes negatively charged when rubbed
with acetate. This means that after rubbing:
(a) the glass rod lost electrons while the acetate
gained electrons.
(b) the glass rod gained electrons while the acetate
lost electrons.
(c) none of the above.
8. When the knob of a neutral metal-leaf electroscope is
touched with a positively charged rod:
(a) no electron flow takes place.
(b) electrons move from the rod to the knob.
(c) electrons move from the knob to rod.
9. When a positively charged rod is brought close to a
neutral pith ball which is free to move, the pith ball
will:
(a) be repelled by the rod.
(b) be attracted by the rod.
(c) do nothing.
10. Whenever a net charge is placed on an object by
contact, the kind of charge on the object:
(a) is the same as the charge on the charging agent.
(b) is opposite to the charge on the charging agent.
(c) depends on the kind of material of the object.
PART B: MATCH (5 MARKS)
Match the definition from the 1 column to the best term in the 2 column and place the matching letter in the
st nd
appropriate space on your answer sheet.
1. Study of electric charges that move very little.
2. Substance in which the movement of electrons is restricted.
3. Method of charging which involves touching the object with a charged object.
4. Consists of two thin metal leaves suspended from a conductive metal rod.
5. Method of charging where two different neutral objects are rubbed together.
A) conductor
B) contact
C) electrostatics
D) friction
E) ground
F) induction
G) insulator
H) metal-leaf electroscope
I) photoconductor
J) pith-ball electroscope
SNC1D PHYSICS: ELECTROSTATICS QUIZ#1
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (10 MARKS)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
PART B: MATCH (5 MARKS)
1 2 3 4 5
PART C: SHORT ANSWER (45 MARKS)
Answer questions 1 to 6 in the space provided. Answer questions 7 and 8 on the back of this sheet.
{3} 1. State the law of electric charges
{3} 2. Consider the following interactions between 3 pith-
balls (A,B,C). B is repelled by a positively charged
rod; A is attracted to B; and there is no interaction
between A and C. Determine the electrostatic
charge(s) on each of the spheres.
A L B L C L
{6} 3. Complete the following chart that summarizes the
properties for the 3 atomic particles.
Name Charge Location
neutron
nucleus
-1
{4} 4. List 2 ways to (i) charge a
neutral object & (ii) discharge a
charged object.
(i)
(ii)
{10} 5. If the B = es, what
charge (# & type) is
on the:
(a) pith-ball?
(b) vinylite?
Redraw the objects after
they have touched.
What charge (# & type) is
now on the:
(a) pith-ball?
(b) vinylite?
Would these objects attract or repel? Explain.
Do these objects now attract or repel? Explain.
{3} 6. List 3 practical applications of electrostatics.
7. Use the electrostatic chart to the right to help answer this question.
{3} (a) A wool sweater is worn under a plastic raincoat. Assuming both objects are
neutral to begin with, what charge will appear on the sweater when it rubs against
the raincoat? Explain why?
{4} (b) With the aid of properly labelled diagrams explain how (a) occurs. What method
of charging is used?
{5} (c) The raincoat is now brought near but not touching a neutral pith ball. With the aid
of properly labelled diagrams explain what will happen? What is this called?
Weak hold on es L
increasing
tendency
to gain
electrons
Strong hold on es L
acetate
wool
fur/hair
silk
cotton
ebonite
plastic
rubber
{4} 8. What makes oil refineries and gas stations among the most dangerous places to work? What precautions are taken?
Why?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Honors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayDokument8 SeitenHonors Physics Midterm Review: Exam DayEarl averzosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFDokument11 SeitenPHYS 211 Exam 1 Sample 2 With Key PDFAndrew TrolioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Origin of The UniverseDokument37 Seiten1 - Origin of The UniverseMa'am Geneizzel GotuatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Law of Thermo WorksheetDokument2 Seiten1st Law of Thermo WorksheetAngelica Calamba CalicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lightning InjuriesDokument33 SeitenLightning InjuriesKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar Junction Transistor CharacteristicsDokument5 SeitenBipolar Junction Transistor CharacteristicsKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- TestDokument361 SeitenTestJake Sy100% (1)
- BASPHYS Kinematics ReviewerDokument14 SeitenBASPHYS Kinematics ReviewerJulian Clement TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatics MCQDokument5 SeitenElectrostatics MCQMohan Raj100% (1)
- 1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticeDokument12 Seiten1 .2013 El Force and El Field Hw-PracticerbgrossNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms First Chapter 6 Lewis StructuresDokument58 SeitenAtoms First Chapter 6 Lewis StructuresJaya Chitra Degala Ramalu100% (1)
- Physics 2 Quarter 3 Module 5Dokument53 SeitenPhysics 2 Quarter 3 Module 5Bea Lha Zandra BesingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1H ProjectilesDokument22 Seiten2.1H ProjectilesVictor KwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GNPHYS 2 - WORKTEXT - Week 7 - Unit 7Dokument8 SeitenGNPHYS 2 - WORKTEXT - Week 7 - Unit 7Nad dlanyer LatigidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity: Flows in Only One Direction Through A WireDokument3 SeitenElectricity: Flows in Only One Direction Through A WiresaintEmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Phy Un7Dokument10 SeitenGrade 9 Phy Un7Mahammad Aarif UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Field Phs122Dokument52 SeitenElectric Field Phs122Danika LoavesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatic 3Dokument26 SeitenElectrostatic 3nozel77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDokument68 SeitenMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentBiprodeep14Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Force & Electric Field IDokument60 SeitenElectric Force & Electric Field IImran ParvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21: The Electric Field I: Discrete Charge DistributionsDokument114 SeitenChapter 21: The Electric Field I: Discrete Charge Distributionsjclv.youknow8373Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Worksheet Page 2Dokument1 SeiteElectricity Worksheet Page 2Laura LucumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential WorksheetDokument2 SeitenElectric Potential Energy and Electric Potential WorksheetMero MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialDokument12 SeitenElectric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialMarquee Mae EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BDokument39 SeitenPhysics 1653 Exam 3 - Review Questions: Sphere A Sphere BPi PoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free FallDokument7 SeitenFree FallFatin Naqiya Roslan50% (2)
- Long Quiz Physics 1 Newton Laws of MotionDokument1 SeiteLong Quiz Physics 1 Newton Laws of MotionK-Cube MorongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 4 - Electrostatic Force WorksheetDokument1 SeiteLesson 4 - Electrostatic Force WorksheetAnonymous jDrrLjraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric charGE AND ELECTRIC FIELDDokument20 SeitenElectric charGE AND ELECTRIC FIELDsiddhartha2862Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14 Electrostatics PDFDokument29 SeitenChapter 14 Electrostatics PDFAvik DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsDokument1 SeiteElectric Potential Energy Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 2 Module 1Dokument32 SeitenGeneral Physics 2 Module 1GNC Tricia Faye DeleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson - Plan - Sobosobo - CG - Electric FluxDokument4 SeitenLesson - Plan - Sobosobo - CG - Electric FluxAllyza Alimeos SobosoboNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics2 Lesson 2 PDFDokument4 SeitenGeneral Physics2 Lesson 2 PDFJohn Renzo MolinarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ XII Physics Chapter 2Dokument31 SeitenMCQ XII Physics Chapter 2Mayank ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics E/M Charges and Coulomb's Law QuestDokument19 SeitenAP Physics E/M Charges and Coulomb's Law QuestJanice ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work and EnergyDokument28 SeitenWork and EnergyMir'atun Nissa QuinalendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers Electric Forces and FieldsDokument6 SeitenChapter Test A: Teacher Notes and Answers Electric Forces and Fieldsmahsan abbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 2 Quarter 3: Week 2: Module 2: Gauss's LawDokument11 SeitenGeneral Physics 2 Quarter 3: Week 2: Module 2: Gauss's LawBryan OndajareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric FieldsDokument8 SeitenElectric FieldsrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.01 Static ElectricityDokument38 Seiten9.01 Static ElectricitychristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Chapter 1 and 2) : Anaphy Quiz Reviewer (Chapters 1-3)Dokument20 Seiten(Chapter 1 and 2) : Anaphy Quiz Reviewer (Chapters 1-3)Mariam GamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- C4-Dynamics Newton's Law of MotionDokument13 SeitenC4-Dynamics Newton's Law of MotionHisyammudin RoslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - MomentumDokument44 SeitenChapter 8 - MomentumGabriel R GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity PracticeDokument108 SeitenElectricity PracticeVarshLokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Midterm 1 Practice With AnswersDokument5 SeitenChemistry Midterm 1 Practice With Answerskashaf93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Resistors in Series and ParallelDokument4 SeitenResistors in Series and Parallelmarilujane100% (3)
- Two DimensionsDokument7 SeitenTwo Dimensionsalex murker100% (1)
- Chemistry Final Exam Review KEY: Practice ProblemsDokument7 SeitenChemistry Final Exam Review KEY: Practice ProblemsZetrix JensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric PotentialDokument10 SeitenElectric Potentialzakibrant230% (1)
- General Physics 1 LessonDokument170 SeitenGeneral Physics 1 LessonEunice AquinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Momenum Ws 3 - Elastic and Inelastic CollisionsDokument2 SeitenMomenum Ws 3 - Elastic and Inelastic Collisionsdilini0% (1)
- Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDokument24 SeitenElectric Forces and Electric FieldsLara WadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- POGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumDokument5 SeitenPOGIL: Dynamic Equilibrium: Name - Regents Chemistry Unit 7: Part C: EquilibriumsydNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Law of MotionDokument25 SeitenFirst Law of MotionErwin CipresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen - Physics II LP Day#3Dokument3 SeitenGen - Physics II LP Day#3MIKENoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2 Gauss LawDokument60 SeitenLecture 2 Gauss LawDamianDailisan100% (1)
- Lab 3 - Electric Field ReportDokument4 SeitenLab 3 - Electric Field ReportfloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatic ForceDokument22 SeitenElectrostatic ForceHuzefa ZoaibNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Thermal Expansion Practice ProblemDokument6 Seiten02 Thermal Expansion Practice Problemprem19999100% (1)
- Dr. Pedro Julio Villegas AguilarDokument48 SeitenDr. Pedro Julio Villegas AguilarCt0% (1)
- Multiple ChoiceDokument3 SeitenMultiple Choiceprince adilan planasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise 1.1 Electric ChargesDokument22 SeitenExercise 1.1 Electric ChargesKarvin LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity and Magnetism - I: Ans. (A) (I) Negative Charge Is Produced On Ebonite RodDokument18 SeitenElectricity and Magnetism - I: Ans. (A) (I) Negative Charge Is Produced On Ebonite RodTajiriMollelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 15: Some Natural PhenomenaDokument28 SeitenChapter - 15: Some Natural PhenomenaKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal of Electrostatics: Sadhana Talele, Paul Gaynor, Michael J. Cree, Jethro Van EkeranDokument14 SeitenJournal of Electrostatics: Sadhana Talele, Paul Gaynor, Michael J. Cree, Jethro Van EkeranKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reversed Switch-On Dynistor Switches of Gigawatt Power Microsecond PulsesDokument10 SeitenReversed Switch-On Dynistor Switches of Gigawatt Power Microsecond PulsesKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulsed Electric Field Processing in Food Technology: Yashwant Kumar, Krishna Kumar Patel and Vivek KumarDokument12 SeitenPulsed Electric Field Processing in Food Technology: Yashwant Kumar, Krishna Kumar Patel and Vivek KumarKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid-State Electronics: Lei Lin, Jian H. ZhaoDokument5 SeitenSolid-State Electronics: Lei Lin, Jian H. ZhaoKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of ElectricityDokument29 SeitenBasics of ElectricityKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Modeling of The Influence of Medium Conductivity On ElectroporationDokument23 SeitenElectrical Modeling of The Influence of Medium Conductivity On ElectroporationKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theory of Impedance Networks: The Two-Point Impedance and LC ResonancesDokument21 SeitenTheory of Impedance Networks: The Two-Point Impedance and LC ResonancesKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Compass Oscillating in A Background FieldDokument1 SeiteA Compass Oscillating in A Background FieldKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average Current Mode Control For LLC SeriesDokument8 SeitenAverage Current Mode Control For LLC SeriesKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Charge Near Microbes During Pulsed Electric Field Pasteurization Liquid FoodsDokument4 SeitenSpace Charge Near Microbes During Pulsed Electric Field Pasteurization Liquid FoodsKrishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Chapter 5Dokument14 Seiten10 - Chapter 5Krishnaveni Subramani SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet MP2380DNDokument11 SeitenDatasheet MP2380DNchevicitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report: Rocket Experiment 2017Dokument20 SeitenLab Report: Rocket Experiment 2017api-343596257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Manual Solar Controller PDFDokument11 SeitenInstallation Manual Solar Controller PDFLhenzCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Day Wise Lesson PlanDokument34 SeitenDay Wise Lesson PlanSatyajit PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LBYEC3P - Exp02 - Prelim ReportDokument9 SeitenLBYEC3P - Exp02 - Prelim ReportJob BumanlagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece Labmanual With VivaDokument58 SeitenEce Labmanual With VivasathwikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes For The Course General Relativity V 2.4: Luca AmendolaDokument109 SeitenNotes For The Course General Relativity V 2.4: Luca AmendolaJosepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Casio Qw5239Dokument9 SeitenManual Casio Qw5239Radu Cosmin TudorNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Publication 1MRK509015-BEN C en High Impedance Differential Relay RADHADokument5 SeitenABB Publication 1MRK509015-BEN C en High Impedance Differential Relay RADHAjavedsmg1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2466 To 2470 EDC MicroprojectDokument20 Seiten2466 To 2470 EDC MicroprojectAkash AkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic Properties of Materials PDFDokument31 SeitenMagnetic Properties of Materials PDFPavan_yoyo100% (1)
- Wiley - Power System Relaying, 4th Edition - 978!1!118-66200-7Dokument2 SeitenWiley - Power System Relaying, 4th Edition - 978!1!118-66200-7Aung Kyaw KhineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Note - Chapter 1Dokument30 SeitenLecture Note - Chapter 1zamspaceklNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA PHY2H W QP JUN08u PDFDokument16 SeitenAQA PHY2H W QP JUN08u PDFdadajee420Noch keine Bewertungen
- LADS Modular 1K Online UPS ManualDokument27 SeitenLADS Modular 1K Online UPS ManualSab BahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Guide: VLT Micro Drive FC 51Dokument99 SeitenDesign Guide: VLT Micro Drive FC 51Giang BùiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growatt Min 5000tlxDokument2 SeitenGrowatt Min 5000tlxMatheus FariasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Data Sheet Glastic Laminates®Dokument1 SeiteTechnical Data Sheet Glastic Laminates®Tim NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 Work Energy PowerDokument7 SeitenModule 4 Work Energy PowerGreen BrainNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Extended Writing Question ChecklistDokument1 SeiteA2 Extended Writing Question ChecklisthaudinihaudiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humiseal 1C49Lv Silicone Conformal Coating Technical Data SheetDokument2 SeitenHumiseal 1C49Lv Silicone Conformal Coating Technical Data Sheetmario230991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ed Ual Er Mini Chiller Inv 201801Dokument50 SeitenEd Ual Er Mini Chiller Inv 201801fiqrinovelNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBM MW TableDokument1 SeiteDBM MW TablenarayanbscribidNoch keine Bewertungen
- ErrorsDokument8 SeitenErrorsnorhazli ibrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mi3290 Earth Analyser DatasheetDokument4 SeitenMi3290 Earth Analyser DatasheetErick LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2-1Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 2-1Ananthi JeyarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Thermal Capacity Used - How Does The Relay Know PDFDokument14 SeitenMotor Thermal Capacity Used - How Does The Relay Know PDFdusktodawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank-III Semester: EEE 223 - Electrical Machines & DrivesDokument29 SeitenQuestion Bank-III Semester: EEE 223 - Electrical Machines & DrivesKalaiselvan PunniyamoorthyNoch keine Bewertungen