Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
F9FM-Session09 d08
Hochgeladen von
ErclanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
F9FM-Session09 d08
Hochgeladen von
ErclanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
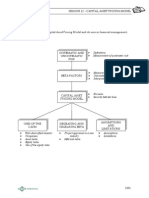
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0901
OVERVIEW
Objective
To appreciate the options available to a company for long, medium and short-term debt
finance.
LONG-TERM
FINANCE
OTHER SOURCES
SHORT-TERM
FINANCE
Preference shares
Debentures
Deep discount bonds
Zero coupon bonds
Tax relief on interest
MEDIUM-TERM
FINANCE
Bank loans
Leasing
Sale and leaseback
Mortgage loans
Bank overdraft
Trade credit
Bills of exchange
Commercial paper
Grants
Loan guarantee
scheme
Business angels
CONVERTIBLES
AND WARRANTS
Convertibles
Effect on EPS of convertible debt
Warrants
DEBT
FINANCE
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0902
1 LONG-TERM FINANCE
1.1 Preference shares
Definition
Shares with a fixed rate of dividend having a prior claim on profits available
for distribution.
Whilst legally equity, they are often treated as debt as they are similar in nature to debt.
1.1.1 Features
Shares which have a fixed percentage dividend payable before ordinary dividend.
The dividend is only payable if there are sufficient distributable profits. However if the
shares are cumulative preference shares the right of dividend is carried forward. Any
arrears of dividend are then payable before ordinary dividends.
As with ordinary dividends, preference dividends are not deductible for corporate tax
purposes they are a distribution of profit rather than an expense.
On liquidation of the company, preference shareholders rank before ordinary
shareholders.
1.1.2 Advantages
No voting rights; therefore no dilution of control.
Compared to the issue of debt:
Dividends do not have to be paid if profits are poor;
Not secured on company assets;
Non-payment of dividend does not give holders the right to appoint a liquidator.
1.1.3 Disadvantages
Dividends are not tax deductible (unlike interest on debt).
To attract investors the company needs to pay a higher return to compensate for
additional risk compared to debt.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0903
1.2 Debentures
Definition
A written acknowledgement of a debt, usually given under the companys seal,
containing provisions for payment of interest and repayment of principal. The
debt may be secured on some or all of the companys assets
Type Secured debentures Unsecured debentures
Security and
voting rights
Can be secured on one or more
specific assets - a fixed charge e.g.
over property
Or a floating charge can be offered
over a class of assets e.g. over net
current assets (working capital)
On default the assets are sold and
debt repaid
No voting rights.
No security.
Holders have the same rights as
ordinary creditors.
No voting rights.
Income A fixed annual amount, usually
expressed as a % of nominal value.
A fixed annual amount, usually
expressed as a % of nominal value.
Amount of
capital
A fixed amount per unit of loan stock
or debenture.
A fixed amount per unit of loan
stock or debenture.
In the UK debentures are usually issued with a face value of 100. They can then be traded
on the bond market and reach a market price. Hence, if a debenture is said to be selling at a
premium of 15%, this means that a debenture with a face value of 100 is currently selling
for 115. This indicates that the rate of interest on this debenture is attractive when
compared with current market rates, creating demand for the debenture and a rise in price.
In the US the face value of each debenture is usually $1000.
Note the terms debenture, loan stock and bond all basically refer to the same thing
i.e. a written acknowledgement of a companys debt which can then be traded. Also face
value can also be referred to as par value of nominal value.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0904
1.3 Deep discount bonds
Definition
Loan stock issued at a large discount to nominal value redeemable at par on
maturity
Investors receive large capital gain on redemption, but low rate of interest during term
of the loan.
Cash flow advantage to the borrower useful for financing projects which produce
weak cash flows in early years.
Illustration 1
A five year $1000 3% Bond issued at $800 would generate the following cash
inflows/(outflows) for the issuing company:
t0 t1 t2 t3 t4 t5
Issue price 800
Interest (30) (30) (30) (30) (30)
Redemption (1000)
1.4 Zero coupon bonds
Definition
Bonds issued at a discount to face value and which pay zero annual interest
No interest is paid.
Investors gain from the difference between issue and redemption price.
Advantages to borrowers:
No cash payout until maturity;
Cost of redemption known at time of issue.
1.5 Tax relief on debt interest
Interest expense is tax deductible and therefore reduces corporate tax payments.
Regarding the tax system the Issue of debt is preferable to the issue of shares as
dividends are not allowable for tax.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0905
Illustration 2
CoA CoB
Profit before tax 100 100
Interest (10)
___ ___
100 90
Corporation tax 30% (30) (27)
___ ___
70 63
Effective cost of debt in CoB
Interest 10
Less Tax relief (3)
___
$7
___
$7 difference
After-tax cost of debt = Pre-tax cost of debt (1 Tax rate)
The fact that interest on debt is tax allowable is referred to as the tax shield
2 CONVERTIBLES AND WARRANTS
2.1 Convertibles
Definition
Bonds or preference shares that can be converted into ordinary shares.
Pay fixed interest or dividend until converted.
They may be:
converted into ordinary shares;
on a pre-determined date;
at a pre-determined rate;
at the option of the holder.
Conversion ratio may change during the period of convertibility to stimulate early
conversion.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0906
Advantages to investors a relatively low risk investment with the opportunity to make
high returns upon converting to ordinary shares.
Advantages to issuing company can offer a lower rate of interest than on straight
debentures.
2.2 Effect on EPS (Earnings Per Share) of convertible debt
Convertible debentures require a fully diluted EPS to be calculated to indicate what EPS
might be if debt is converted into equity.
Method
Increase earnings by the loan interest saved, net of tax.
Increase the number of shares due to conversion.
Recalculate EPS
2.3 Warrants
Definition
A right given to an investor to subscribe cash for new shares at a future date at
a fixed price the exercise price.
Warrants are sometimes attached to loan stock, to make the loan stock more attractive.
Warrants are basically share options
The holder of the warrants may sell them rather than keep them.
Advantages to issuing company
The warrants themselves do not involve the payment of any interest or dividends.
When they are initially attached to loan stock, the interest rate on the loan stock will be
lower than for comparable straight debt. This due to the additional benefit for the
investor of potential equity shares at an attractive price.
May make an issue of unsecured loan stock possible where no adequate security exists.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0907
3 MEDIUM-TERM FINANCE
3.1 Bank loans
3.1.1 Advantages
The loan will be for a fixed term: no risk of early recall;
Interest rate may be fixed.
3.1.2 Disadvantages
Inflexible;
May require security,
May require covenants restrictions on the company e.g. limits on dividend
payments, limits on further borrowing.
3.2 Leasing
3.2.1 Advantages
Many willing providers;
Remains off-balance sheet if an operating lease;
Matches finance to the asset ;
Very flexible packages available, some of which include maintenance.
3.2.2 Disadvantage
Can be costly.
3.3 Sale and leaseback
Property is sold to an institution, such as a pension fund, and then leased back to the
company.
3.3.1 Advantages
Releases significant funds;
May improve ratios such as ROCE (Return on Capital Employed).
3.3.2 Disadvantages
No longer own property and hence cannot participate in any future increase in value;
Risk of lease payments increasing.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0908
3.4 Mortgage loan a loan secured on property.
3.4.1 Advantages
Given the security, the loan will attract a lower interest rate than other debt;
Institutions will be willing to lend over a longer term;
Still participate in the growth in value of the property.
3.4.2 Disadvantage
Default may result in a key asset being liquidated
4 SHORT-TERM FINANCE
4.1 Bank overdraft
4.1.1 Advantages
Flexible;
Provides instant finance.
4.1.2 Disadvantages
Repayable on call, unless the bank offers a revolving line of credit
High and variable interest rate.
4.2 Trade credit
4.2.1 Advantages
Generally cheap;
Flexible.
4.2.2 Disadvantages
May lose settlement (quick payment) discounts;
May lose suppliers goodwill.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0909
4.3 Bills of exchange
Definition
An acknowledgement of a debt to be paid at some time in the future e.g. by a
customer. Such a bill may then be discounted i.e. sold to a third party for a %
of face value
4.3.1 Advantages
Improves cash flow.
Flexible.
4.3.2 Disadvantages
Fees.
Illustration 3
X sells $2m worth of goods to Y. X writes out (draws) a bill of exchange for
$2m payable in 2 months (say) which it sends to Y. Y signs the bill to
acknowledge the debt and returns it to X.
X can hold on to the bill for 2 months until Y pays the debtor sell it at a
discount e.g. at 98%of face value. The buyer of the bill then receives the $2m
and makes a gain.
4.4 Commercial Paper
Definition
Commercial paper is short-term (usually less than 270 days) unsecured debt
issued by high quality companies. The paper can then be traded by investors
on the bond markets.
4.4.1 Advantages
Large sums can be raised and relatively cheaply
No security required
4.4.2 Disadvantages
Only available to large companies with very good credit ratings
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0910
5 OTHER SOURCES
Commentary
The following are particularly suitable for small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs)
which are of particular interest to the examiner as they often have difficulty finding
debt finance. Such difficulties may be caused byasymmetry of information where
banks fear making loans to companies which are not well known and without published
credit ratings.
5.1 Grants
Depending upon the location and nature of the business local, regional, national or
European grant assistance may be available.
5.2 Loan guarantee scheme
Just as small/medium sized companies find it hard to raise equity, they can also find it hard
to raise debt, due to their high perceived risk. The Loan Guarantee Scheme is a UK
government-backed scheme where, for a fee, a substantial proportion of the loan may be
guaranteed. Hence potential providers of that loan are willing to lend, as most of their risk
has been eliminated.
5.3 Business angels
Business angels are rich individuals who are prepared to invest money in small companies if
they see high potential for growth
Such angels are often retired businesspeople who became wealthy as entrepreneurs in the
high-tech sector.
They may also give useful advice as well as finance and may even be able to use their
contacts to obtain new business for the companies they invest in.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0911
Key points
Preference shares are in substance debt as they pay a fixed committed
dividend in priority to any ordinary dividend. They also rank ahead of
ordinary shareholders upon liquidation (although after real debt such as
bank loans and debentures)
Preference shareholders therefore face lower risk than ordinary
shareholders and require lower returns
However banks and bondholders take even lower risks, as they rank
ahead of preference shareholders upon bankruptcy, and their debts may
be secured by fixed or floating charge over assets. Providers of loans
therefore require lower returns than other providers of finance.
Hence loans are the least expensive source of finance for a company,
particularly if the effect of the tax system is introduced (loan interest is a
tax allowable expense, unlike dividends.)
Unfortunately debt also has a dark side too much debt may increase the
risks faced by shareholders to unacceptable levels.
FOCUS
You should now be able to:
explain the features of preference shares and the reasons for their issue;
explain the features of different types of long-term straight debt and the reasons for
their issue;
explain the features of convertible debt and warrants and the reasons for their issue;
assess the effect on EPS of conversion and option rights;
suggest appropriate sources of debt finance for SMEs e.g. leasing, loan guarantee
scheme, and business angels.
SESSION 09 DEBT FINANCE
0912
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- F9FM RQB Qs - j09kj NDokument64 SeitenF9FM RQB Qs - j09kj NErclan0% (1)
- Goldman Sachs Global Strategy Paper The Post Modern Cycle PositioningDokument32 SeitenGoldman Sachs Global Strategy Paper The Post Modern Cycle PositioningRoadtosuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 31 An Introduction To Debt Policy and ValueDokument8 SeitenCase 31 An Introduction To Debt Policy and ValueChittisa CharoenpanichNoch keine Bewertungen
- WACC, Gearing and Capital Structure TheoriesDokument16 SeitenWACC, Gearing and Capital Structure TheoriesMuhammadAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exemplar Company. SuicoDokument4 SeitenExemplar Company. SuicoSofia Russel Mae SuicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equity Investments PPT PresentationDokument80 SeitenEquity Investments PPT PresentationRupal Rohan Dalal100% (1)
- Synergy Average Price Bar PDFDokument7 SeitenSynergy Average Price Bar PDFomonisha100% (2)
- F9 Financial Management: Revision Question BankDokument1 SeiteF9 Financial Management: Revision Question BankMuhammadAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working Capital Management: Assessing Liquidity and Optimizing CycleDokument10 SeitenWorking Capital Management: Assessing Liquidity and Optimizing CycleErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9 Financial Management: Study SystemDokument1 SeiteF9 Financial Management: Study SystemMuhammadAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9 Financial Management: Study Question BankDokument1 SeiteF9 Financial Management: Study Question BankMuhammadAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session17 d08xsxDokument16 SeitenF9FM-Session17 d08xsxErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM SQBsasDokument92 SeitenF9FM SQBsasErclan100% (1)
- Financial Management NPV AnalysisDokument40 SeitenFinancial Management NPV AnalysisErclan50% (2)
- F9FM SQB Conts - d07Dokument8 SeitenF9FM SQB Conts - d07ErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session16 D08sweeDokument12 SeitenF9FM-Session16 D08sweeErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session19 d08Dokument0 SeitenF9FM-Session19 d08Glendon JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session10 d08vzzxDokument26 SeitenF9FM-Session10 d08vzzxErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM Session20IndexsxsDokument4 SeitenF9FM Session20IndexsxsErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session18 d08Dokument18 SeitenF9FM-Session18 d08ErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session15 D08qasDokument12 SeitenF9FM-Session15 D08qasErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session14 d08Dokument14 SeitenF9FM-Session14 d08MuhammadAliNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session05 d08jkbnDokument30 SeitenF9FM-Session05 d08jkbnErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Options for Raising Equity CapitalDokument12 SeitenOptions for Raising Equity CapitalErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session06 D08kjnhoijnDokument14 SeitenF9FM-Session06 D08kjnhoijnErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session04 d08jnknDokument22 SeitenF9FM-Session04 d08jnknErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session12 D08qasDokument12 SeitenF9FM-Session12 D08qasErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session07 D08iojimDokument12 SeitenF9FM-Session07 D08iojimErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session03 D08oinopinDokument8 SeitenF9FM-Session03 D08oinopinErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session02 D08jnonDokument24 SeitenF9FM-Session02 D08jnonErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session01 d07 PDokument8 SeitenF9FM-Session01 d07 PMadalina CiupercaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM-Session00 D08onoip (Dokument14 SeitenF9FM-Session00 D08onoip (ErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM RQB Conts - j09klDokument8 SeitenF9FM RQB Conts - j09klErclanNoch keine Bewertungen
- F9FM RQB Qs - D08ojnpDokument62 SeitenF9FM RQB Qs - D08ojnpErclan25% (4)
- Nifty Intra Day TradingDokument20 SeitenNifty Intra Day Tradingvarun vasurendranNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study of Consumer Behavior in Real Estate Sector: Inderpreet SinghDokument17 SeitenA Study of Consumer Behavior in Real Estate Sector: Inderpreet SinghMahesh KhadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Association for Financial Markets in Europe proposes changes to CVA and CS01 formulasDokument4 SeitenAssociation for Financial Markets in Europe proposes changes to CVA and CS01 formulasRenu MundhraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nike Case AnalysisDokument10 SeitenNike Case AnalysisFarhan SoepraptoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guerrilla Marketing ExcellenceDokument8 SeitenGuerrilla Marketing ExcellenceWarren BuffetNoch keine Bewertungen
- C14 - Tutorial Answer PDFDokument5 SeitenC14 - Tutorial Answer PDFJilynn SeahNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS-44J (Working Capital Management)Dokument13 SeitenMS-44J (Working Capital Management)juleslovefenNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEC-OGCOpinionNo.09-04 - Public Offering of SecuritiesDokument4 SeitenSEC-OGCOpinionNo.09-04 - Public Offering of SecuritiesHannah Keziah Dela CernaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equitas - Results PresentationDokument35 SeitenEquitas - Results PresentationsherwinmitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fas95 PDFDokument66 SeitenFas95 PDFNaamir Wahiyd BeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Statements and Ratio AnalysisDokument81 SeitenFinancial Statements and Ratio AnalysisHattori HanzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxpnl FY2023 2024Dokument31 SeitenTaxpnl FY2023 2024sumitthakur17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nvestment Consulting: A Conversation With Peter BernsteinDokument13 SeitenNvestment Consulting: A Conversation With Peter BernsteinPavankumar KaredlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long-Term Liabilities: QuestionsDokument74 SeitenLong-Term Liabilities: QuestionsChu Thị ThủyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin in The Game Producer OffsetDokument28 SeitenSkin in The Game Producer OffsetAmol PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mr. Loqueloque Will Contribute The Amount 3,795,250Dokument6 SeitenMr. Loqueloque Will Contribute The Amount 3,795,250John ManatadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Germany Industry Overview AutomotiveDokument16 SeitenGermany Industry Overview AutomotiveChatzianagnostou George0% (1)
- Geographical Pricing Strategy FinalDokument10 SeitenGeographical Pricing Strategy FinalSeif ElkhoulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Study Financial Performance Analysis of Lakshmi Vilas BankDokument12 SeitenTo Study Financial Performance Analysis of Lakshmi Vilas BankVel MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Finance Major OutputDokument3 SeitenBasic Finance Major OutputKazia PerinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forecasting and Valuing Cash FlowDokument31 SeitenForecasting and Valuing Cash FlowIshitta SardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mun. Ord. No. 14-001 - Local Investment Incentive Code of PinanDokument13 SeitenMun. Ord. No. 14-001 - Local Investment Incentive Code of PinanChrysmae FloraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profit Planning with Three WheelsDokument28 SeitenProfit Planning with Three Wheelssiyeni100% (2)
- Financial Statement Analysis RatiosDokument90 SeitenFinancial Statement Analysis RatiosAlayou TeferaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal entries for partnership capital accountsDokument3 SeitenJournal entries for partnership capital accountsSam VNoch keine Bewertungen