Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A 823 - 99 R03 Qtgymw - PDF
Hochgeladen von
Mung Duong Xuan0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten7 SeitenThis standard covers gray iron castings that are statically cast in permanent molds. No precise quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties of the iron in various locations of the same casting. Castings ordered and produced under this standard are classified into a number of grades based on the properties of separately cast test bars.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
A 823 _ 99 R03 ;QTGYMW__.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis standard covers gray iron castings that are statically cast in permanent molds. No precise quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties of the iron in various locations of the same casting. Castings ordered and produced under this standard are classified into a number of grades based on the properties of separately cast test bars.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
9 Ansichten7 SeitenA 823 - 99 R03 Qtgymw - PDF
Hochgeladen von
Mung Duong XuanThis standard covers gray iron castings that are statically cast in permanent molds. No precise quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties of the iron in various locations of the same casting. Castings ordered and produced under this standard are classified into a number of grades based on the properties of separately cast test bars.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 7
Designation: A 823 99 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard Specication for
Statically Cast Permanent Mold Gray Iron Castings
1
This standard is issued under the xed designation A 823; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This specication covers gray iron castings that are
statically cast in permanent molds.
1.2 No precise quantitative relationship can be stated be-
tween the properties of the iron in various locations of the same
casting or between the properties of a casting and those of a test
specimen cast from the same iron (see Appendix X1).
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as the standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
A 247 Test Method for Evaluating the Microstructure of
Graphite in Iron Castings
A 644 Terminology Relating to Iron Castings
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E 10 Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materi-
als
2.2 Federal Standard:
Fed. Std. No. 123 Marking for Shipment
3
2.3 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
3
3. Terminology
3.1 Denitions for many terms common to iron castings are
found in Terminology A 644. A classication of graphite
structure is found in Test Method A 247.
4. Classication
4.1 Castings ordered and produced under this specication
are classied into a number of grades based on the properties
of separately cast test bars. The test bar shall be selected on the
basis of the controlling section size of the casting (see 9.1 and
9.2 and Table 1).
4.2 Castings may be produced in the as cast state provided
the requirements of this standard in Table 1 are met. However,
annealing or normalizing heat treatments are usual and cus-
tomary and are a basis for classication.
4.3 The grades are designated A for annealed or N for
normalized. This is followed by an S or a C to designate a solid
or a cored casting, followed by an A, B, C, or S to designate the
test bar to be poured with the castings. Examples of proper
designations are as follows:
Permanent Mold Castings, ASTM Specication A 823,
Grade N-SB
Permanent Mold Castings, ASTM Specication A 823,
Grade A-CC
5. Ordering Information
5.1 Orders for material to this specication shall include the
following information:
5.1.1 ASTM designation number and year of issue.
5.1.2 Grade of iron required (see Section 4 and Table 1).
5.1.3 The size of the separately cast test bar (letter classi-
cation A, B, C, or S) which best represents the thickness of the
controlling section of the casting (see 4.1 and Table 2).
5.1.4 Location for Brinell Hardness determination (see
10.1.1).
1
This specication is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.01 on Gray Iron
Castings.
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1999. Published November 1999. Originally
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as A 823 99.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standards Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, Bldg. 4 Section D, 700
Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094, Attn: NPODS.
TABLE 1 Permanent Mold Gray Iron Specications
Grade Tensile Strength, min, ksi
(MPa)
A
BHN
UncoredAnnealed
A-SA 30 000 (207) 163207
A-SB 25 000 (172) 163207
A-SC 20 000 (138) 163207
A-SS 18 000 (124) 143207
CoredAnnealed
A-CA 30 000 (207) 143207
A-CB 25 000 (172) 143207
A-CC 20 000 (138) 143207
UncoredNormalized
N-SA 30 000 (207) 170229
N-SB 25 000 (172) 170229
N-SC 20 000 (138) 170229
N-SS 18 000 (124) 149229
CoredNormalized
N-CA 30 000 (207) 170229
N-CB 25 000 (172) 149229
N-CC 20 000 (138) 149229
A
Refer to Fig. X1.1 for the relationship between tensile strength and section
size.
1
Copyright ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
5.1.5 Lot size (see Section 16).
5.1.6 Special requirements (see Section 17).
5.1.7 Special preparation for delivery (see Section 22).
5.1.8 Saving tested specimens or unbroken test bars (see
19.1.1).
6. Chemical Composition
6.1 The chemical composition shall be such as to produce
the mechanical properties required by this specication. As a
reference, typical compositions covering all grades are shown
in Table X1.1 in Appendix X1.
6.2 By agreement between the manufacturer and purchaser,
chemical composition requirements may be specied.
7. Heat Treatment
7.1 Although castings may be provided in the as cast
condition, when necessary, heat treatment shall be such as to
produce the mechanical properties required in this standard.
8. Tensile Requirements
8.1 Test bars representing castings conforming to this speci-
cation shall meet the requirements for tensile strength de-
scribed in Table 1.
9. Cast Test Bars
9.1 Test bars shall be separate castings poured from the
same iron as the castings they represent and shall have
dimensions as shown in Table 2. Allowance may be made for
reasonable pattern draft within the tolerances shown in Table 2.
Test bars A, B, and C are all standard test bars in the form of
simple cylinders. Test bar S is special and is intended for use
where the controlling section of the casting is over 2 in.
9.2 The test bar selected shall be based on the controlling
section size of the casting. This shall be determined by the
dimensions of the largest cylinder that will t into the control-
ling section of the casting with the additional requirement that
the height of the cylinder must be at least equal to its diameter.
9.3 The test bars shall be cast in a permanent mold. The
mold shall be of similar material, design, and construction as
that used to make the production castings. The test bar
permanent mold shall be preheated with three consecutive
pours, after which, starting with the fourth pour, the bars can be
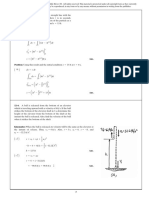
used for the tension test. A suitable design for a mold is shown
in Fig. 1.
9.4 By specic agreement between the manufacturer and the
purchaser, test bars removed from the castings may be substi-
tuted for separately cast test bars. The location from which the
bars are taken shall be as agreed between the parties and
indicated on the casting drawing or data base equivalent.
TABLE 2 Diameters and Lengths of Cast Test Bars
Test
Bar
As-Cast Diameter, in. (mm)
A
Length, in. (mm)
Nominal
(Mid-Length)
Minimum
(Bottom)
Maximum
(Top)
Minimum
(Specied)
Maximum
(Recommended)
A 0.88 (22.4) 0.85 (21.6) 0.96 (24.4) 5.0 (125) 6.0 (150)
B 1.20 (30.5) 1.14 (29.0) 1.32 (33.5) 6.0 (150) 9.0 (230)
C 2.00 (50.8) 1.90 (48.3) 2.10 (53.3) 7.0 (175) 10.0 (255)
S
B
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A
The diameter is the controlling section for the appropriate permanent mold
specication (see Section 9).
B
All dimensions of test bar S shall be agreed upon by the manufacturer and the
purchaser.
Required Features:
1. MaterialPermanent molds.
2. PositionBars vertical.
3. LSee Table 2.
4. DSee Table 2.
FIG. 1 Suitable Design and Dimensions for Mold for Separately Cast Cylindrical Test Bars for Gray Iron
A 823 99 (2003)
2
9.5 Where test specimens are to represent heat treated
castings, they shall accompany the castings in the same heat
treat lot(s), or by agreement, be subjected to the same thermal
cycle that the castings undergo.
10. Hardness Requirements
10.1 Brinell hardness readings taken on the castings shall
conform to the requirements in Table 1.
10.1.1 The area or areas on the castings where the hardness
is to be determined shall be established by agreement between
manufacturer and purchaser and shall be shown on the casting
drawing.
10.1.2 Brinell hardness shall be determined in accordance
with Test Method E 10. Sufficient surface material shall be
removed (generally 0.010 to 0.030 in.) to ensure that the
measured hardness is representative of the basic iron structure.
10.1.3 Brinell hardness measurements shall be undertaken
at room temperature, dened as 5095 F (1035 C).
11. Dimensional Requirements
11.1 The castings shall conform to the dimensions or
drawings furnished by the purchaser, or, if there are no
drawings, to the dimensions predicted by the pattern equipment
supplied by the purchaser.
12. Workmanship and Finish
12.1 The surface of the casting shall be inspected visually,
particularly in critical areas, for such surface defects as cracks,
hot tears, adhering sand and scale, cold shuts, and gas holes.
12.2 No repairing by plugging or welding of any kind shall
be permitted unless written permission is granted by the
purchaser.
13. Number of Tests and Retests
13.1 The manufacturer shall cast and prepare at least three
test bars for each lot of castings intended to conform to this
specication. The manufacturer shall conduct the specied
tests unless the manufacturer and purchaser agree that the tests
shall be made by another qualied laboratory. Only one bar
need be tested if the results conform to the property require-
ments of this specication. If any test specimen shows defec-
tive or improper machining, or obvious lack of continuity of
metal, it may be discarded and replaced by another specimen
from another test bar from the same lot.
13.2 If after testing, a test specimen shows evidence of a
defect, the results of the test may be invalidated and another
made on a specimen from the same lot.
13.3 If the results of a valid test fail to conform to the
requirements of this specication, two retests shall be made. If
either retest fails to meet the specication requirements, the
castings represented by these test specimens shall be rejected.
A valid test is one wherein the specimen has been properly
prepared and appears to be sound and on which the approved
test procedure has been followed.
13.4 If sufficient separately cast test pieces are not available,
the manufacturer shall have the option of removing a test
specimen from a location of representative casting, as agreed
upon between the manufacturer and purchaser.
13.5 If the rst test results indicate that a heat treatment or
an additional heat treatment is needed to meet the test
requirements, the entire lot of castings and the representative
test specimens shall be heat treated or reheat treated together.
Testing shall proceed in accordance with 13.1,13.2,13.3, and
13.4 .
14. Tension Test Specimens
14.1 For test bar A, the tension test specimen A, as shown in
Fig. 2, shall be machined concentric with the axis of the test
bar.
14.2 For test bar B, the tension test specimen B, as shown in
Fig. 2, shall be machined concentric with the axis of the test
bar.
14.3 For test bar C, tension test specimen C, as shown in
Fig. 2, shall be machined concentric with the axis of the test
bar. Unless the size of the tensile test specimen to be machined
from test bar C is specied in writing by the purchaser, the
decision whether to use tension test specimen B or C shall be
made by the manufacturer of the castings.
14.4 For test bar S, the nature and dimensions of the tension
test specimen shall be determined by agreement between the
manufacturer and the purchaser. Test bar S is to be used
whenever the controlling section exceeds 2 in.
15. Tension Test
15.1 Tension testing shall be determined in accordance with
Test Methods E 8.
15.2 The tension test specimens shall t the holders of the
testing machine in such a way that the load shall be axial.
15.3 The elapsed time from the beginning of loading in the
tension test to the instant of fracture shall be not less than 15
s for test specimen A and not less than 20 s for test specimens
B or C.
16. Description of a Lot
16.1 The manufacturer may dene a lot as any of the
following:
16.1.1 A lot size may be established by agreement between
the manufacturer and the purchaser.
16.1.2 Absent such an agreement as described in 16.1.1, a
lot shall be a group of castings weighing less than 2000 lb (910
kg) each when the total weight of the group does not exceed
8000 lb (3600 kg) and when poured continuously within 4 h
from the same melt and from consecutive charges of essentially
the same percentages and types of materials.
17. Special Requirements
17.1 When agreed upon in writing by the manufacturer and
the purchaser, it may be necessary for the castings to meet
special requirements as to hardness, chemical composition,
microstructure, pressure tightness, radiographic soundness,
dimensions, surface nish, etc.
18. Identication Marking
18.1 When the size of the casting permits, each casting shall
bear the identifying mark of the manufacturer and the part or
A 823 99 (2003)
3
pattern number at a location shown on the covering drawing or,
if not shown on the drawing, at a location at the discretion of
the producer.
19. Responsibility for Inspection
19.1 Unless otherwise specied in the contract or purchase
order, the manufacturer shall be responsible for carrying out all
the tests and inspections required by this specication, using
his own or other reliable facilities, and he shall maintain
complete records of all such tests and inspections. Such records
shall be available for review by the purchaser.
19.1.1 When agreed upon between manufacturer and pur-
chaser, tested specimens or unbroken test bars from the same
lot shall be saved for a period for 3 months after the date of the
test report.
19.2 The purchaser reserves the right to perform any of the
inspections set forth in the specication where such inspections
are deemed necessary to assure that supplies and services
conform to the prescribed requirements.
20. Rejection and Resubmission
20.1 Any castings or lot of castings failing to comply with
the requirements of this specication may, where possible, be
reprocessed, retested, and reinspected. If the tests and inspec-
tions on the reprocessed casting(s) show compliance with this
specication, the castings shall be acceptable; if they do not,
they shall be rejected.
20.2 If the purchaser should nd that a casting or lot of
castings fails to comply with this specication subsequent to
receipt at his facility, he shall so notify the manufacturer
promptly and in no case later than 6 weeks after receipt of the
shipment, stating clearly the basis for rejection.
21. Certication
21.1 When specied by the purchasers order or contract, a
manufacturers certication or compliance statement that the
casting or lot of castings was made, sampled, tested, and
inspected in accordance with this specication, including a
report of test results signed by an authorized agent of the
manufacturer, shall be furnished at the time of shipment, and
such certication or compliance statement shall be the basis for
acceptance of the casting or lot of castings.
22. Preparation for Delivery
22.1 Unless otherwise stated in the contract or order, the
cleaning, preservation, and packing of castings for shipment
shall be in accordance with the manufacturers commercial
practice. Packaging and marking shall also be adequate to
identify the contents and to ensure acceptance and safe delivery
by the carrier for the mode of transportation employed.
22.2 U.S. Government ProcurementWhen specied in the
contract or purchase order, marking for shipment shall be in
accordance with the requirements of Fed. Std. No. 123 for civil
agencies and MIL-STD-129 for military activities.
Tension Tension Tension
Dimensions, in. (mm) Test Specimen A Test Specimen B Test Specimen C
GLength of parallel, min 0.50 (13) 0.75 (19) 1.25 (32)
DDiameter 0.500 6 0.010 0.750 6 0.015 1.25 6 0.025
(12.7 6 0.25) (19.1 x6 0.4) (32 6 0.6)
RRadius of llet, min 1 (25) 1 (25) 2 (50)
ALength of reduced section, min 1
1
4 (32) 1
21
32 (42) 2
17
32 (64)
LOverall length, min 3
3
4 (95) 4
5
32 (106) 6
3
8 (160)
CDiameter of end section, approx
7
8 (22.2) 1
1
4 (31.8) 1
7
8 (47)
ELength of shoulder, min
1
4 (6)
1
4 (6)
5
16 (8)
FDiameter of shoulder
5
8 6
1
64
15
16 6
1
64 1
7
16 6
1
64
(16 6 0.5) (25 6 0.5) (36 6 0.5)
BLength of end section
A A A
A
Optional to t holders on testing machine. If threaded, root diameter shall not be less than dimension F.
FIG. 2 Tension Test Specimens
A 823 99 (2003)
4
23. Keywords
23.1 chemical composition; gray iron; hardness; heat treat-
ment; iron castings; statically cast permanent mold; tensile
strength
APPENDIXES
(Nonmandatory Information)
X1. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF CASTINGS
X1.1 The mechanical properties of iron castings are inu-
enced by the cooling rate during and after solidication, by
chemical composition (particularly carbon equivalent)(see
Table X1.1), by the design of the casting, by the design and
nature of the mold, by the location and effectiveness of gates
and risers, and by certain other factors.
X1.2 The cooling rate in the mold and, hence, the proper-
ties developed in any particular section are inuenced by the
presence of cores, chills and chaplets, changes in section
thickness, and the existence of bosses, projections, and inter-
sections, such as junctions of ribs and bosses. Because of the
complexity of the interactions of these factors, no precise
quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties
of the iron in various locations of the same casting or between
the properties of a casting and those of a test specimen cast
from the same iron. When such a relationship is important and
must be known for a specic application, it may be determined
by appropriate experimentation.
X1.3 When reliable information is unavailable on the
relationship between properties in a casting and those in a
separately cast test specimen and where experimentation would
be unfeasible, the size of the test casting should be so selected
as to approximate the thickness of the main or controlling
section of the casting (see Fig. X1.1).
X1.4 If iron castings are welded, (see 12.2), the microstruc-
ture of the iron is usually altered, particularly in the vicinity of
the weldment. Therefore, the properties of the casting may be
adversely affected by welding. Where practical, appropriate
post weld heat treatment may reduce this effect of the welding.
TABLE X1.1 Typical Chemical CompositionsAll Grades
Carbon 3.303.70 %
Silicon 2.202.80 %
Manganese 0.401.00 %
Phosphorus 0.45 % max
Sulfur 0.15 % max
A 823 99 (2003)
5
NOTEThe relationship of permanent mold gray iron tensile strength versus section size is shown above. Castings with controlling section up to 0.875
in. will have a minimum tensile strength of 30 000 psi (207 MPa). Castings with controlling section between 0.875 and 1.2 in. will have a minimum tensile
strength of 25 000 psi (172 MPa). Castings with controlling section between 1.2 and 2.0 in. will have a minimum tensile strength of 20 000 psi (138 MPa).
FIG. X1.1 Tensile Strength versus Section Size of Permanent Mold Gray Iron
A 823 99 (2003)
6
X2. MICROSTRUCTURE
X2.1 Information on microstructure is given in Table
X2.1.
X3. HEAT TREATMENT
X3.1 Castings may be in the as-cast, annealed, or normal-
ized conditions.
X3.2 When needed to achieve the requirements of this
standard, the annealing or normalizing heat treatment cycles
may be determined by the manufacturer.
ASTM International takes no position respecting the validity of any patent rights asserted in connection with any item mentioned
in this standard. Users of this standard are expressly advised that determination of the validity of any such patent rights, and the risk
of infringement of such rights, are entirely their own responsibility.
This standard is subject to revision at any time by the responsible technical committee and must be reviewed every ve years and
if not revised, either reapproved or withdrawn. Your comments are invited either for revision of this standard or for additional standards
and should be addressed to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
responsible technical committee, which you may attend. If you feel that your comments have not received a fair hearing you should
make your views known to the ASTM Committee on Standards, at the address shown below.
This standard is copyrighted by ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959,
United States. Individual reprints (single or multiple copies) of this standard may be obtained by contacting ASTM at the above
address or at 610-832-9585 (phone), 610-832-9555 (fax), or service@astm.org (e-mail); or through the ASTM website
(www.astm.org).
TABLE X2.1 Permanent Mold Gray Iron Graphite and Matrix Information
Grade Graphite
A
Matrix
UncoredAnnealed
A-SA, A-SB, A-SC Predominantly type D, size 5-8, some type A, size 4-6 Essentially ferrite
A-SS Type D, size 5-8 with type A, size 3-6 and some type C
CoredAnnealed
A-CA, A-CB Predominantly type D, size 5-8 and some type A, size 4-6 Essentially ferrite
A-CC Type D, size 5-8, type A and B, size 3-6
UncoredNormalized
N-SA, N-SB Predominantly type D, size 5-8, some type A, size 4-6 Ferrite plus 1020 % pearlite
N-SC Type D, size 5-8 and type A, size 3-6, some type C Ferrite plus 1025 % pearlite at surface, up to 50 % at center
N-SS Type D, size 5-8, type A, size 3-6, some type C Ferrite plus 10 % pearlite at surface, up to 60 % at center
CoredNormalized
N-CA, N-CB Predominantly type D, size 5-8, some type A, size 4-6. Ferrite plus 1020 % pearlite
Ferrite plus 1020 % pearlite near core
N-CC Type D, size 5-8, type A and B, size 3-6 Ferrite plus 10 % pearlite at surface and 50 % pearlite at center
A
Graphite type and size in accordance with Test Method A 247.
A 823 99 (2003)
7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ts619 PDFDokument12 Seitents619 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts606 PDFDokument33 Seitents606 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ts611 2011-01 Rules Class Hull Monitoring SysDokument18 SeitenTs611 2011-01 Rules Class Hull Monitoring SysAdriano CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts615 PDFDokument12 Seitents615 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts617 PDFDokument34 Seitents617 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts618 PDFDokument17 Seitents618 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAV-O Class Notation: ShipsDokument11 SeitenNAV-O Class Notation: ShipsMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts609 PDFDokument18 Seitents609 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts603 PDFDokument35 Seitents603 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ts 614 CDokument11 SeitenTs 614 CGoran JurisicNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts501 PDFDokument162 Seitents501 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts513 PDFDokument6 Seitents513 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts613 PDFDokument44 Seitents613 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts610 PDFDokument18 Seitents610 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts602 PDFDokument15 Seitents602 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotating Machinery, Driven Units: Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface CraftDokument39 SeitenRotating Machinery, Driven Units: Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface Craftjoaofelipe.msNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts402 PDFDokument12 Seitents402 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts502 PDFDokument152 Seitents502 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slop Reception and Processing Facilities: ShipsDokument10 SeitenSlop Reception and Processing Facilities: ShipsMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts102 PDFDokument35 Seitents102 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Vessels: Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface CraftDokument81 SeitenPressure Vessels: Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface Craftjoaofelipe.msNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Safety: ShipsDokument11 SeitenFire Safety: ShipspwkannonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts511 PDFDokument30 Seitents511 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ts510 PDFDokument31 Seitents510 PDFMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNV 100 Above Hull StructuralDokument187 SeitenDNV 100 Above Hull StructuralDaniela AleidanNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Requirements For Materials: Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface CraftDokument14 SeitenGeneral Requirements For Materials: Ships / High Speed, Light Craft and Naval Surface CraftWeverthon BeiralNoch keine Bewertungen
- RULES FOR CLASSIFICATION OF Ships - PART 0 CHAPTER 2Dokument8 SeitenRULES FOR CLASSIFICATION OF Ships - PART 0 CHAPTER 2PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hull Structural Design - Ships With Length Less Than 100 MetresDokument107 SeitenHull Structural Design - Ships With Length Less Than 100 MetresMung Duong XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ts 403Dokument88 SeitenTs 403joaofelipe.msNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Tough Turkish TBM Moves Through Fractured and Faulted Rock: Issue 1 + 2014Dokument8 SeitenTough Turkish TBM Moves Through Fractured and Faulted Rock: Issue 1 + 2014sCoRPion_trNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyna PDFDokument12 SeitenDyna PDFVernadette VenturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azubuko v. Motor Vehicles, 95 F.3d 1146, 1st Cir. (1996)Dokument2 SeitenAzubuko v. Motor Vehicles, 95 F.3d 1146, 1st Cir. (1996)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 3 Evidence Act 1950Dokument3 SeitenSection 3 Evidence Act 1950ayesyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 8 Introduction To XML: Exercise 1Dokument4 SeitenLab 8 Introduction To XML: Exercise 1HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PfizerDokument4 SeitenPfizerliqu1dcourageNoch keine Bewertungen
- SafeCargo PDFDokument76 SeitenSafeCargo PDFSyukry MaulidyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Álogo de Peças de Reposi ÇÃO: Trator 6125JDokument636 SeitenCAT Álogo de Peças de Reposi ÇÃO: Trator 6125Jmussi oficinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Damayan Benefit PolicyDokument2 SeitenDamayan Benefit PolicyMSWDO STA. MAGDALENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Specifications For Metro Ethernet 13-Sdms-10Dokument30 SeitenSpecifications For Metro Ethernet 13-Sdms-10ashrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13Dokument20 SeitenThe Strategy of IB: International Business - Chapter 13Yến Ngô HoàngNoch keine Bewertungen
- US20170335223A1Dokument18 SeitenUS20170335223A1hugo vignoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArraysDokument36 SeitenArraysKAMBAULAYA NKANDANoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Takaful CREDIT & DEBIT CARD AUTOPAY Authorization Form V1.0 2018Dokument2 Seiten02 Takaful CREDIT & DEBIT CARD AUTOPAY Authorization Form V1.0 2018UstazFaizalAriffinOriginalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generator Exciter & Voltage ExciterDokument34 SeitenGenerator Exciter & Voltage ExciterYasir MehmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cobas B 123 POC System: Instructions For Use, Version 13.0 Software Version 4.17Dokument354 SeitenCobas B 123 POC System: Instructions For Use, Version 13.0 Software Version 4.17zelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample MCQ - Facility Location and LayoutDokument3 SeitenSample MCQ - Facility Location and LayoutJITENDRA SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Arrest Report For 22jan2016Dokument4 SeitenPublic Arrest Report For 22jan2016api-214091549Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet 3VA2225-5HL32-0AA0: ModelDokument7 SeitenData Sheet 3VA2225-5HL32-0AA0: ModelJENNYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Announcement: Inter-And Intra-Sectoral Dynamics For Transforming Indian AgricultureDokument8 SeitenAnnouncement: Inter-And Intra-Sectoral Dynamics For Transforming Indian AgricultureEnamul HaqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study ExamplesDokument18 SeitenCase Study ExamplesSujeet Singh BaghelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Masonary Retaining Wall - SteppedDokument3 SeitenDesign of Masonary Retaining Wall - Steppedmeenu100% (1)
- Real Estate Merger Motives PDFDokument13 SeitenReal Estate Merger Motives PDFadonisghlNoch keine Bewertungen
- GostDokument29 SeitenGostMoldoveanu Teodor80% (5)
- AcctIS10E - Ch04 - CE - PART 1 - FOR CLASSDokument32 SeitenAcctIS10E - Ch04 - CE - PART 1 - FOR CLASSLance CaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- TopGearDokument188 SeitenTopGearbarborina10% (1)
- Good Story Company Submission Cheat SheetDokument28 SeitenGood Story Company Submission Cheat SheetRoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logiq 180 UsuarioDokument414 SeitenLogiq 180 UsuariolaboratorioelectroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relocation Guide Version 5.6 - New BrandingDokument29 SeitenRelocation Guide Version 5.6 - New BrandingEndika AbiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Ethernet Switch at-FS705L (Data Sheet) - EngDokument2 SeitenFast Ethernet Switch at-FS705L (Data Sheet) - EngBaroszNoch keine Bewertungen