Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Leb12 05 PDF
Hochgeladen von
yamilmamani1230 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten5 SeitenConductivity measurements enable the rate of hydrolysis of urea by the enzyme urease to be determined. The addition of an appropriate inhibitor poisons the enzyme so that it no longer converts substrate.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
LEB12_05.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenConductivity measurements enable the rate of hydrolysis of urea by the enzyme urease to be determined. The addition of an appropriate inhibitor poisons the enzyme so that it no longer converts substrate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
20 Ansichten5 SeitenLeb12 05 PDF
Hochgeladen von
yamilmamani123Conductivity measurements enable the rate of hydrolysis of urea by the enzyme urease to be determined. The addition of an appropriate inhibitor poisons the enzyme so that it no longer converts substrate.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 5
76 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co.
KG D-37070 Gttingen Laboratory Experiments, Biology
12.05 Enzyme inhibition (poisoning of enzymes)
Biochemistry LEB 12
Principle and tasks:
The enzymatic hydrolysis of urea in
aqueous solution liberates carbon
dioxide and ammonia. The ions of
these compounds increase the con-
ductivity of the solution. Conductivi-
ty measurements enable the rate of
hydrolysis of urea by the enzyme
urease to be determined. The addi-
tion of an appropriate inhibitor poi-
sons the enzyme, so that it no longer
converts substrate.
Conductivity-time plot for the hydrolysis of urea with urease before and after
poisoning
What you can learn about
Poisoning of enzymes
Enzymatic hydrolysis of urea
Silver nitrate inhibition of
urease
Conductivity measurement
Equipment (for the experimental procedure using the CHEM-UNIT)
Cobra3 CHEM-UNIT 12153.00 * 1
Power supply, 12 V 12151.99 1
Data cable 2 x SUB-D, 9 pin 14602.00 1
Software Cobra3 CHEM-UNIT 14520.61 * 1
Conductivity-temperature electrode 13701.01 * 1
Magnetic stirrer mini, plastic (ABS) 47334.93 1
Magnetic stirring rod, cylindrical, l = 30 mm 46299.02 1
Magnetic bar separator made of PTFE 35680.03 1
Balance SAS 51, 200 g / 0.01 g, RS232 45990.93 1
Support rod, l = 500 mm, stainless steel 02032.00 1
Support base, variable 02001.00 1
Right angle clamp (bosshead) 02043.00 1
Universal clamp 37715.00 1
Beaker, DURAN, tall form, 100 ml 36002.00 8
Beaker, low form, 250 ml, plastic 36013.01 1
Volumetric pipette, 1 ml 36575.00 1
Volumetric pipette, 20 ml 36579.00 1
Safety pipettor Flip 36592.00 1
Microliter syringe, 100 ml 02606.00 1
Pasteur pipettes, l = 145 mm, 250 off 36590.00 1
Rubber caps, 10 pcs 39275.03 1
Spoon with spatula end, l = 150 mm, steel, micro 33393.00 1
Wash bottle, 500 ml 33931.00 1
Urea, 250 g 30086.25 1
Urease solution in 50% glycerine, 1000 U/ml, 10 ml 31924.03 1
Silver nitrate, 15 g 30222.00 1
Distilled water, 5 l 31246.81 1
PC, Windows 95 or higher
Changes in the equipment required for use of the Basic-Unit:
(Instead of * above-mentioned)
Cobra3 Basic-Unit 12150.00 1
Software Cobra3 conductivity 14508.61 1
Measuring module conductivity 12108.00 1
Conductivity probe, glass shaft l = 12 cm 18151.02 1
Temperature sensor, semiconductor type 12120.00 1
What you need:
Enzyme inhibition (poisoning of enzymes)
with Cobra3 Basic-Unit P4120511
Experimental set-up using the Basic-Unit (P4120540)
Enzyme inhibition (poisoning of enzymes)
with Cobra3 Chem-Unit P4120540
Related topics
Poisoning of enzymes, enzymatic hydrolysis of urea, silver
nitrate inhibition of urease, conductivity measurement
Principle and task
The enzymatic hydrolysis of urea in aqueous solution lib-
erates carbon dioxide and ammonia. The ions of these
compounds increase the conductivity of the solution.
Conductivity measurements enable the rate of hydrolysis
of urea by the enzyme urease to be determined. The addi-
tion of an appropriate inhibitor poisons the enzyme, so
that it no longer converts substrate.
Equipment (for the experimental procedure using the
CHEM-UNIT)
Cobra3 CHEM-UNIT 12153.00* 1
Cobra3 power supply 12151.99 1
Data cable 2 x SUB-D, 9 pin 14602.00 1
Software Cobra3 CHEM-UNIT 14520.61* 1
Conductivity-temperature electrode 13701.01* 1
Magnetic stirrer mini, plastic (ABS) 47334.93 1
Magnetic stirring rod, cylindrical, l = 30 mm 46299.02 1
Magnetic bar separator made of PTFE 35680.03 1
Balance SAS 51, 200 g / 0.01 g, RS232 45990.93 1
Support rod, l = 500 mm, stainless steel 02032.00 1
Support base, variable 02001.00 1
Right angle clamp (bosshead) 02043.00 1
Universal clamp 37715.00 1
Beaker, DURAN, tall form, 100 ml 36002.00 8
Beaker, low form, 250 ml, plastic 36013.01 1
Volumetric pipette, 1 ml 36575.00 1
Volumetric pipette, 20 ml 36579.00 1
Safety pipettor Flip 36592.00 1
Microliter syringe, 100 l 02606.00 1
Pasteur pipettes, l = 145 mm, 250 off 36590.00 1
Rubber caps, 10 pcs 39275.03 1
Spoon with spatula end, l = 150 mm,
steel, micro 33393.00 1
Wash bottle, 500 ml 33931.00 1
Urea, 250 g 30086.25 1
Urease solution in 50% glycerine,
1000 U/ml, 10 ml 31924.03 1
Silver nitrate, 15 g 30222.00 1
Distilled water, 5 l 31246.81 1
Hazards and safety measures
Silver nitrate is a highly corrosive solid substance. Dust
from it irritates the respiratory organs. It liberates nitric
acid under the influence of moisture and light. The silver
which is so formed causes typical black stains. In the case
of fire, silver nitrate acts fire promoting by liberating oxy-
gen.
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41205 149
LEB
12.05
Enzyme inhibition (poisoning of enzymes)
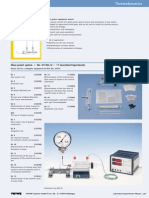
Fig. 1: Experimental set-up using the Chem-Unit
Do not inhale dust. Avoid contact with eyes and skin.
When working with it, wear appropriate protective appar-
el, protective gloves and safety glasses. Store it dry and
excluded from light.
Must be kept out of the reach of children.
First aid: Thoroughly rinse the affected skin or eyes
(opened wide) with plenty of water. When eyes are affect-
ed, seek immediate medical attention. After accidents or
on feeling unwell, fetch medical attention at once. When
inhaled: Fresh air, keep respiratory tract free. On respira-
tory distress: Transport to medical attention in a half-sit-
ting position.
Waste disposal: Collect solutions containing silver ions in
a correspondingly labelled container and submit them for
recycling or suitable waste disposal.
Preparatory work
Prepare the solutions required for the experiment as fol-
lows:
1.6% urea solution: Weigh 2.00 g of urea into a 250 ml
beaker and dissolve it in 123.00 g of distilled water
(prepare this fresh before each experiment).
1% silver nitrate solution: Weigh 0.5 g of silver nitrate
tion into a 100 ml beaker and dissolve it in 49.5 g of
distilled water.
Note: The urease solution must always be kept in a re-
frigerator.
Set-up and procedure (using the Chem-Unit)
Set the apparatus up as shown in Fig. 1
Connect the conductivity-temperature probe to the
appropriate input of the Chem-Unit
Call up the Cobra3 Measure programme in Windows
and assign the Chem-Unit as measuring instrument
Set the measurement parameters as shown in Fig. 2.
In the <Displays...> menu, set both Digital display 1
and Diagram 1a (range 0-600 s) to conductivity (range
0 to 1000 S/cm)
Set the temperature compensation in the <Preferen-
ces / Conductivity> menu to linear with Pt 1000 tem-
perature probe
Fix the universal clamp to the rod of the support stand
with a right angle clamp
Use the 20 ml volumetric pipette twice to pipette
40 ml of the 1.6% urea solution into a 100 ml beaker
and add a magnetic stirrer rod
Place the beaker on the magnetic stirrer and immerse
the conductivity electrode in the solution
Adjust the stirrer to a medium stirring speed (Take
care: Do not allow the magnetic stirring rod to hit
against the pH electrode)
Add 50 l of the urease solution with the microliter
pipette and then start the measurement without any
delay by clicking on <Continue> and <Start measure-
ment>
The course of the reaction with time can be visually
followed on the screen
300 seconds after the start of the reaction, use the
volumetric pipette to add 1 ml of 1% silver nitrate to
the solution in the beaker and wait until the pro-
gramme ends the measurement after 600 seconds
At the end of the measurement, save the data in menu
<File> <Save measurement as...>
Results and evaluation
Fig. 3 shows an example of a conductivity-time plot, as is
displayed by the programme after ending the measure-
ment.
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41205 150
LEB
12.05
Enzyme inhibition (poisoning of enzymes)
Fig. 2: Measurement parameters (Chem-Unit) Fig. 3: Conductivity-time plot for the hydrolysis of urea
with urease before and after poisoning
Urease acts on urea to decompose the substrate to car-
bon dioxide and ammonia. The ions so released into the
aqueous solution enable the progress of the reaction over
time to be followed by measuring the conductivity of the
solution. During the first 300 seconds, the conductivity
continually increases as a result of the enzymatic activity.
The addition of silver nitrate first leads to a drastic
increase in the conductivity, because of the silver and
nitrate ions. The continuing course of the reaction curve
shows no further increase in conductivity, however. The
reason for this is the irreversible inhibition of urease by sil-
ver ions, i.e. the enzyme has been poisoned. No further
transformation of substrate is possible.
Experimental procedure using the Basic-Unit
The experiment using the Chem-Unit described above
can be analogously carried out using the Basic-Unit. For
this, the entries in the list of materials which are marked
with an asterisk must be replaced by the materials listed
below. The set-up and procedure are then also slightly dif-
ferent (see below, in particular Fig. 4 and Fig. 5).
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41205 151
LEB
12.05
Enzyme inhibition (poisoning of enzymes)
Fig. 4: Experimental set-up using the Basic-Unit
Fig. 5: Measurement parameters (Basic-Unit)
Changes in the equipment required for use of the Basic-Unit:
Cobra3 Basic-Unit 12150.00 1
Software Cobra3 conductivity 14508.61 1
Measuring module conductivity 12108.00 1
Conductivity probe, glass shaft l = 12 cm 18151.02 1
Temperature sensor, semiconductor type 12120.00 1
Set-up and procedure using the Basic-Unit
Prepare the set-up as in Fig. 4
Connect the conductivity electrode to the conductivi-
ty measuring module and the temperature sensor to
input S2 of the Basic-Unit
Call up the Cobra3 Measure programme in Windows
and assign Cobra3 conductivity as measuring instru-
ment
Set the measurement parameters as shown in Fig. 5
Carry on from here as with the Chem-Unit
Note
The measurement can also be carried out without a tem-
perature probe, but then the temperature of the solution
must be entered by hand in the menu <Preferences /
Conductivity>, or, when using the Basic-Unit, in the field
<Temperature compensation>.
This experiment can also be carried out using hand-held
measuring instrument conductivity 07138.00, conductivi-
ty/temperature probe 13701.01, conductivity software
14418.61 and data cable 07157.01.
Phywe Series of publication Laboratory Experiments Biology PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Gttingen 41205 152
LEB
12.05
Enzyme inhibition (poisoning of enzymes)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 4.1.01-15 Ohm's Law With FG-Module: What You NeedDokument1 Seite4.1.01-15 Ohm's Law With FG-Module: What You Needyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Glass Jacket System No. 01196.12 17 Described ExperimentsDokument3 SeitenGlass Jacket System No. 01196.12 17 Described Experimentsyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leb01 06 PDFDokument3 SeitenLeb01 06 PDFyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- LEP LaserDokument6 SeitenLEP Laseryamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lep1101 00 PDFDokument5 SeitenLep1101 00 PDFyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Demonstration Experiments - Magnet Board OpticsDokument3 SeitenPhysics Demonstration Experiments - Magnet Board Opticsyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leb12 06 PDFDokument5 SeitenLeb12 06 PDFyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phonocardiography: Cardiac and Vascular Sonic Measurement (PCG) 02.02Dokument3 SeitenPhonocardiography: Cardiac and Vascular Sonic Measurement (PCG) 02.02yamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Demonstration Experiments Physics - Magnetic Board HeatDokument3 SeitenDemonstration Experiments Physics - Magnetic Board Heatyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- LEP LaserDokument6 SeitenLEP Laseryamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Laboratory ExperimentsDokument16 SeitenBiology: Laboratory Experimentsyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phywe Systeme GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Göttingen Federal Republic of GermanyDokument1 SeitePhywe Systeme GMBH & Co. KG D-37070 Göttingen Federal Republic of Germanyyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec01 01Dokument3 SeitenLec01 01yamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Demonstration Experiments - Magnet Board OpticsDokument3 SeitenPhysics Demonstration Experiments - Magnet Board Opticsyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Laboratory ExperimentsDokument16 SeitenBiology: Laboratory Experimentsyamilmamani123Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- My New ResumeDokument4 SeitenMy New ResumeSurajNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUGMENTIN Syrup: What Is in This Leaflet?Dokument5 SeitenAUGMENTIN Syrup: What Is in This Leaflet?Rafaela LennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPC F1 IS Unit 2 Water - TeacherEdDokument29 SeitenSPC F1 IS Unit 2 Water - TeacherEdFor BackupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irganox® 1010 Sds en SGDokument10 SeitenIrganox® 1010 Sds en SGPrototypeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal-Chemical Modified Rice Husk-Based Porous Adsorbents For Cu (II), PB (II), ZN (II), MN (II) and Fe (III) AdsorptionDokument14 SeitenThermal-Chemical Modified Rice Husk-Based Porous Adsorbents For Cu (II), PB (II), ZN (II), MN (II) and Fe (III) AdsorptionzallaishzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regular chimney inspections extend plant operationsDokument6 SeitenRegular chimney inspections extend plant operationstecvidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saudi Aramco Test Report: Internal Tank Bottom Testing 30-Oct-17 CP-SATR-X-3205Dokument8 SeitenSaudi Aramco Test Report: Internal Tank Bottom Testing 30-Oct-17 CP-SATR-X-3205Tayyab AchakzaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Hydrotreating Reactors Cocurrent Versus Countercurrent Operations - Art5Dokument14 Seiten2-Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Hydrotreating Reactors Cocurrent Versus Countercurrent Operations - Art5Vicente SosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Pt. Musim MasDokument6 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Pt. Musim MasAydilover AydinousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activated CarbonDokument34 SeitenActivated CarbonSanjeeva YedavalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 11 Infrared SpectrosDokument5 SeitenLab Manual 11 Infrared SpectrosLuca Selva CampobassoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline Repeated Dose Toxicity Revision 1 - enDokument9 SeitenGuideline Repeated Dose Toxicity Revision 1 - ennimirani2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 20220411175616686155Dokument52 SeitenDPP 20220411175616686155Ronit NigamNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP 10th CBSE Week 1 of JulyDokument6 SeitenDPP 10th CBSE Week 1 of JulyYash KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objectives Identify The Two Main Classes of Vitamins. List Seven Minerals Your Body Needs inDokument28 SeitenObjectives Identify The Two Main Classes of Vitamins. List Seven Minerals Your Body Needs inyosysilalahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isobutane Butane Fractionator PDFDokument7 SeitenIsobutane Butane Fractionator PDFhoustonmathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wear Plate SpecsDokument4 SeitenWear Plate SpecsJuan Carlos EspinozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Control Methods PDFDokument10 SeitenWell Control Methods PDFrobert5castillo-5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Based Thermosetting Resins For FuturDokument34 SeitenBio Based Thermosetting Resins For Futursatish kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- WoW Gold Guide v2Dokument20 SeitenWoW Gold Guide v2ZontirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbocharger Service InstructionsDokument4 SeitenTurbocharger Service Instructionskarol1177Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary - Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)Dokument1 SeitePreliminary - Welding Procedure Specification (WPS)Rudi DaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2: Problem Set CH148/A32: Camacho, Ocampo, Patuto, Rodenas, TizonDokument5 SeitenModule 2: Problem Set CH148/A32: Camacho, Ocampo, Patuto, Rodenas, TizonZhane TizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe and Fitting ChartDokument12 SeitenPipe and Fitting Chartyulianus_sr100% (2)
- UPSEE Full-Paper 2006Dokument40 SeitenUPSEE Full-Paper 2006AditiBhatnagar1100% (1)
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Progression Test: Science Paper 2Dokument16 SeitenCambridge Lower Secondary Progression Test: Science Paper 2mahdi hassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotamat® Rok 4 Pumping Stations Screen: WasteDokument4 SeitenRotamat® Rok 4 Pumping Stations Screen: WastecrvenicajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1 Biology F4Dokument12 SeitenTest 1 Biology F4Nurfatin JamaludinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jess 106Dokument16 SeitenJess 106Tej Krishan SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final PG Sby 0024Dokument3 SeitenFinal PG Sby 0024Afwa Wildan RomadhonNoch keine Bewertungen