Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Amt026 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Jeremiah GallowayOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Amt026 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Jeremiah GallowayCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
www.NewCircuits.
com
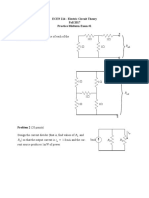
R L C circuit with one switch
Problem #1
#1) In the circuit showed in figure 1, answer the questions below:
#1-1) Find so that voltage of the capacitor becomes critically damped.
1
R
#1-2) Find so that
2
R (0) 100 V v =
#1-1) Find ( ) v t in the point 1ms t =
Figure 1
(Solution in the next page)
Solution:
For the current source delivers 0 Ampere and the switch is closed (see
figure 2). For the current source has been delivering 0.5 Amperes for a
long time to the circuit (see figure 3).
0 t >
0 t <
Figure 2
Figure 3
To find , see figure 2:
1
R
1
0
1
1
C
L
L L
R
dv
I C
dt
dI
v v L I v dt I
dt L
v
I
R
=
= = = +
=
And,
1
0
C L R
I I I + + =
0
1
1
0
dv v
C v dt I
dt L R
+ + + =
2
2
1
1 1
0
d v dv
C v
dt L R dt
+ + =
2
2
1
1 1
0
d v dv
v
dt R C dt LC
+ + = (1)
So the characteristic equation is as below:
1
1 1
0 v v v
R C LC
+ + =
2
1
1 1
0 p p
R C LC
+ + = (2)
If we want the voltage of the capacitor becomes critically damped, the equation
(1) must have one root,
2
1
1 1
4 0
R C LC
=
1 1
6
4
1000
4 4 10
L
R R
C
= = =
To find , see figure 3, because the current source has been delivering a fixed
amount of current for a very long time, so the voltage across the inductor, and
the current of the capacitor is equal to zero, so two resistors are parallel and all
the current is passing through the equal resistor. On the other hand, we have the
condition
2
R
(0) 100 V v = , so:
1
1
1 2
1000
1 2
1 2 1 2
1 2
2 2
2
100
(0) 100 0.5
0.5
1 1 100
200
0.5
200 200 200
1000 200 1000 200
250
eq eq
eq
R
v R R
R
R R
R R
R R R R
R R
R R
R
=
= = =
= + = =
= = +
+
= +
=
To find ( ) v t in the point , the equation (1) must be solved for . At
first, substitute the values and into (1) and rewrite the equation,
1 ms t = 0 t >
1
R
2
R
( )
2
2 3 6 6
2
3 3
2
2 3 3
2
1 1
0
10 10 4 10
10 250 10 0
10 250 10 0
500 0
500
d v dv
v
dt dt
d v dv
v
dt dt
p p
p
p
+ +
+ + =
+ + =
+ =
=
=
So the homogeneous response becomes,
( )
500
1 2
( )
t
v t A A t e
= + (3)
There are two conditions, the first one is (0) 100 V v = ,
( )
500 0
1 2 1
(0) 100 0 100 v A A e A
= = + =
For the second condition,
6 500
2
6 500 500
2 2
6 500 0 500 0
2 2
10 (100 )
( ) 10 500(100 )
(0 ) 10 500(100 0)
t
C
t t
C
C
dv d
I C A t e
dt dt
I t A e A t e
I A e A e
+
= = +
= +
= +
6 3
2
(0 ) 10 50 10
C
I A
+
=
(4)
Here we need to discuss about the value of (0 )
C
I
+
. Although its value is
definitely zero for , but is it zero for 0 0 t <
+
? First, we calculate the (0 )
L
I
and
:
1
(0 )
R
I
1
(0 ) (0 ) (0 ) 0.5
C L R
I I I A
+ + =
A
1
0 (0 ) (0 ) 0.5
L R
I I
+ + = (5)
And,
1
2 1
(0 ) (0 )
L R
R I R I
=
1
250 (0 ) 1000 (0 )
L R
I I
= (6)
(5) and (6) yield,
1
(0 ) 0.4
(0 ) 0.1
L
R
I A
I A
=
=
We know that the current of an inductor won't change immediately. Let's say
the current of the resistor for 0
1
R
+
can be changed so that the current of the
capacitor remains zero for 0 , in this case the current of the inductor must pass
through the resistor so we will lose 0.1 Amperes in the circuit immediately
and this is not possible. Therefore the currents
+
1
R
(0 )
L
I
and cannot be
changed and must pass through the capacitor, so
1
(0 )
R
I
1
(0 ) (0 ) (0 ) 0.5
C L R
I I I
+ + +
= + = A (7)
(4) and (7) yield,
6 3
2
0.5 10 50 10 A
=
3
2
450 10 A =
Then,
( )
3 50
( ) 100 450 10
t 0
v t t
= e
For t=1 ms,
( )
3
3 3 500 10
(1ms) 100 450 10 10 v e
=
0.5
(1ms) 350 v e
=
(1 ) 212V v ms =
Last updated on April 9, 2009
Rasoul Mojtahedzadeh
Back to Articles
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- DAC Seminar ReportDokument28 SeitenDAC Seminar ReportAshutosh BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Datasheet Isl62882-BDokument42 SeitenDatasheet Isl62882-BSkander NomaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- (291882886) Et-Lab-ManualDokument31 Seiten(291882886) Et-Lab-ManualvpzfarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- DFGDokument14 SeitenDFGian jheferNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- ETE 1112 - Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDokument27 SeitenETE 1112 - Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualSabuj Ahmed100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Chapter 3 SingelstageamplifierDokument41 SeitenChapter 3 SingelstageamplifieraramshishmanyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Voltage Conveyor Based Applications: B.E. Project OnDokument20 SeitenVoltage Conveyor Based Applications: B.E. Project OnSaketKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Op-Amp DesignDokument11 SeitenOp-Amp DesignSOHAN DEBNATHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Chapter 2.6 - Thevenin's Theorem-2Dokument21 SeitenChapter 2.6 - Thevenin's Theorem-2geosltdNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Nodal AnalysisDokument30 SeitenNodal AnalysisPuji LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMOS CM & Biasing CircuitsDokument50 SeitenCMOS CM & Biasing Circuitsabhi_jNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Apgenco Set A1880Dokument16 SeitenApgenco Set A1880Srimannarayana NandamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zen of Analog Circuit Design - Anand UdupaDokument78 SeitenZen of Analog Circuit Design - Anand Udupaashishmanyan100% (3)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Particle Swarm Optimization For Improved Performance of PID Controller On Buck ConverterDokument5 SeitenParticle Swarm Optimization For Improved Performance of PID Controller On Buck ConverterjamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Feedback AmplifiersDokument43 SeitenFeedback AmplifiersMuraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Avr400 Service ManualDokument34 SeitenAvr400 Service ManualwatteaucarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Analysis & Synthesis - WatermarkDokument217 SeitenNetwork Analysis & Synthesis - WatermarkNitya MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Problems On TheveninDokument16 SeitenSolved Problems On TheveninsathyaeceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- CX-1010 Installation/ Wiring Guide: SK1659 Rev ADokument54 SeitenCX-1010 Installation/ Wiring Guide: SK1659 Rev AJulio FerminNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Gate Cloud NETWORK ANALYSIS Vol 1 by KanodiaDokument127 SeitenGate Cloud NETWORK ANALYSIS Vol 1 by KanodiaSujeet Kumar100% (1)
- Problem 4.8 Pspice - Multisim: Ee 211/212 Sp15 HW #04 - Nodal Analysis, Mesh AnalysisDokument16 SeitenProblem 4.8 Pspice - Multisim: Ee 211/212 Sp15 HW #04 - Nodal Analysis, Mesh AnalysisAyaz AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question BankDokument4 SeitenQuestion BankKetan SalviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sol 2Dokument21 SeitenSol 2Candice Xie100% (3)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- IEEE Harmonics Test SystemsDokument9 SeitenIEEE Harmonics Test SystemsezequielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam 1 Fall 2017Dokument2 SeitenPractice Exam 1 Fall 2017Allie JuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP Journal 1975-03Dokument24 SeitenHP Journal 1975-03dwisselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits 10th Edition Nilsson Solutions ManualDokument37 SeitenElectric Circuits 10th Edition Nilsson Solutions ManualVernon Hilton100% (36)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- AN04 Thermistor Calibration IXDokument12 SeitenAN04 Thermistor Calibration IXDDragos GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions To Homework 1: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)Dokument8 SeitenSolutions To Homework 1: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)joa91189100% (1)
- Input-Controlled Buck Converter For Photovoltaic Applications: Modeling and DesignDokument5 SeitenInput-Controlled Buck Converter For Photovoltaic Applications: Modeling and DesignIlva Leandro ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)