Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Requirement For Branch Connection at Flare Header
Hochgeladen von
gpskumar220 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
569 Ansichten3 Seiten1
Originaltitel
Requirement for Branch Connection at Flare Header
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument melden1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
569 Ansichten3 SeitenRequirement For Branch Connection at Flare Header
Hochgeladen von
gpskumar221
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Requirement for branch connection at flare header
Branch Requirement at Flare Header
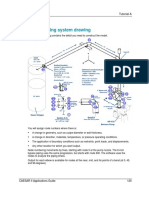
What is flare system?
In simple word, the waste gases from all the services in the process
plant are directed to flare headers made of piping that run around the
process plant carries up to the chimney to burn it before exposing to
atmosphere.
Requirement for branch:
When taking a branch from the flare system, the connection shall be at
45 degree inclined in line with flow direction of the header. The flow
direction of branch line at the point of contact on header shall be the
flow direction of the header. Reason to have an inclination at the branch
line is to disseminate the hammering effect of thrust comes from branch
cause reverse flow in the header when the branch is at 90 degree
pointing perpendicular to the axis of the header.
Recommended tapping orientation:
Preferred : Tapping on top of the header.
A general practice for all the connections made in flare system.
Accepted : Tapping from side of header
This orientation is also fairly accepted in gaseous service where
impurities at the header are quiet less. This practice is not suitable for 2-
phase medium where condensates are expected to be more in quantity
in which connection from side could cause the fluid flow from header to
the branch. It is advisable to have a healthy discussion with process
engineers to understand flow, density, condensate quantity, or other
impurities before choosing this option.
Avoid : Tapping from bottom
Reaction forces and Remedies:
Flare system is one of the critical systems to be given vital importance in
the process plant. The process lines of different temperatures and
pressures are connected with flare headers that cause serious impact on
piping which needs to be considered carefully. Basically a stress analysis
is required to balance the forces and moments acting on it. Here you
find the basic requirement to full fill the branch connection.
In process plant, all the PSV discharge lines are sent to flare header. The
discharge condition of PSV is the point at which the pressure exceeds
the maximum set pressure and exposed to discharge line which in turn
generates reaction force and that transferred to the flare header. The
force due to psv reaction force , vibration, expansion of discharge acts
at the joint that connects branch and header. Therefore, the weakest
point is the point of contact of the branch with the header. The force
acting at this point could damage the header pipe. Hence it is necessary
to provide reinforcement at the joint.
Thumb Rule for Reinforcement pad sizing:
Reinforcement area = 3 times X Diameter of the branch pipe
Pad thickness shall be same as the header pipe thickness (schedule).
Reinforcement calculation shown here gives value more than the actual
requirement. To find out actual area Refer ASME 31.3 chapter II (Design)
section 304.3.3 nomenclature for detail calculation. The calculation based
on ASME comes around twice the diameter of the branch that means it
is one time less than the above shown thumb rule . Hence it is helpful in
a large scale project to minimize the material cost.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ControTrace Vs Jacketed Piping enDokument3 SeitenControTrace Vs Jacketed Piping enYoung-seok Hwang100% (1)
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsVon EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Routing InstructionsDokument37 SeitenPipe Routing InstructionsDANLIN ENGINEERS100% (1)
- Offshore Piping Design: Technical Design Procedures & Mechanical Piping MethodsVon EverandOffshore Piping Design: Technical Design Procedures & Mechanical Piping MethodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Writing A-Z: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, Second Edition, British English: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, U.S. English Second EditionVon EverandTechnical Writing A-Z: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, Second Edition, British English: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, U.S. English Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLR Strainer Data Sheet PDFDokument7 SeitenSLR Strainer Data Sheet PDFKailas NimbalkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Design Considerations For Centrifugal Compressor Piping SystemsDokument5 SeitenThermal Design Considerations For Centrifugal Compressor Piping SystemsSerge Rinaudo100% (1)
- RPS Support CatalogueDokument49 SeitenRPS Support Catalogueravivarmadatla2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Samss 006Dokument17 Seiten02 Samss 006inatt101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supporting of Piping SystemsDokument3 SeitenSupporting of Piping Systemsaap150% (2)
- Slug Flow Analysis Using Dynamic Spectrum Method in Caesar II Part 2 of 2Dokument4 SeitenSlug Flow Analysis Using Dynamic Spectrum Method in Caesar II Part 2 of 2Romner Cordova100% (2)
- 357-PressureEquivalentMethod 2007ASMESectionVIIIDivision2Dokument4 Seiten357-PressureEquivalentMethod 2007ASMESectionVIIIDivision2ZAZZERA125Noch keine Bewertungen
- Span Limits For Elevated Temperature PipingDokument4 SeitenSpan Limits For Elevated Temperature PipingDushyant Varshney100% (2)
- Increase Allowable Stress CodeDokument9 SeitenIncrease Allowable Stress Codewenny_tpdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Offshore Piping Design CriteriaDokument1 SeiteOffshore Piping Design CriteriaDhakshina K100% (1)
- Piping Class SpecificationDokument6 SeitenPiping Class Specificationcitra puspita sariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isometrics For Jacketed Piping SymbolsDokument1 SeiteIsometrics For Jacketed Piping SymbolsQiuniuNoch keine Bewertungen
- FRP Flange DesignDokument29 SeitenFRP Flange DesignSubhadip RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Temperature Characteristics of Stainless Steels: A Designers' Handbook Series N 9004Dokument47 SeitenHigh-Temperature Characteristics of Stainless Steels: A Designers' Handbook Series N 9004aemis2010Noch keine Bewertungen
- S-G000-535Z-001 - Specification Nozzle Loads On Mechanical EquipmentDokument13 SeitenS-G000-535Z-001 - Specification Nozzle Loads On Mechanical Equipment전아진Noch keine Bewertungen
- CAESAR II PIPING Tutorial A Pages 120 To 157 From C2APDokument38 SeitenCAESAR II PIPING Tutorial A Pages 120 To 157 From C2APLuis OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01SA0S02Dokument5 Seiten01SA0S02raobabar21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Input and OutputDokument7 SeitenPiping Input and OutputpraneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expansion Calculation and Loop Sizing001Dokument2 SeitenExpansion Calculation and Loop Sizing001Joseph R. F. DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cryogenic PipingDokument34 SeitenCryogenic PipingDilip100% (3)
- Points To Be Considered During Stress AnalysisDokument24 SeitenPoints To Be Considered During Stress AnalysismishtinilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floating Unit Piping Stress AnalysisDokument4 SeitenFloating Unit Piping Stress AnalysisRagerishcire Kanaalaq100% (1)
- Piping Design (Revised)Dokument22 SeitenPiping Design (Revised)Yash PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intsallation of Hot Tap FittingsSAEP0311Dokument25 SeitenIntsallation of Hot Tap FittingsSAEP0311Ehab SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN10 Critical Line List SampleDokument2 SeitenTN10 Critical Line List Sampleyulianus_srNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01NC0B02Dokument4 Seiten01NC0B02raobabar21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Load CasesDokument15 SeitenLoad CasesVishnu Menon100% (1)
- Dynamic Load in Piping SystemDokument3 SeitenDynamic Load in Piping SystemAMITDEWANGAN1991100% (1)
- Underground Piping Installation (GRP Pipe)Dokument9 SeitenUnderground Piping Installation (GRP Pipe)Cristi DemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2150 Attachment 13 - Minimum Piping DesiDokument24 Seiten2150 Attachment 13 - Minimum Piping Desidimdaliak_985662241100% (1)
- Stress Critical Line ListDokument1 SeiteStress Critical Line ListJitendraSurveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping SpecificationDokument3 SeitenPiping SpecificationArun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Material SpecificationDokument18 SeitenPiping Material SpecificationAmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expansion Loop DesignDokument61 SeitenExpansion Loop DesignTauqueerAhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jord Y-Type Strainer DatasheetDokument1 SeiteJord Y-Type Strainer DatasheetSpoonful BurnsideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typical Arrangement of Air Cooler PipingDokument4 SeitenTypical Arrangement of Air Cooler Pipingvedadon100% (1)
- To-HQ-02-037 Rev 00 Philosophy For Piping Design - OnshoreDokument41 SeitenTo-HQ-02-037 Rev 00 Philosophy For Piping Design - OnshoreHedi Ben MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column Piping Study Layout NoDokument21 SeitenColumn Piping Study Layout NoTAMIZHKARTHIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Analysis Report FormatDokument9 SeitenStress Analysis Report FormatPinak Projects100% (2)
- Air Cooled Heat ExchangerDokument24 SeitenAir Cooled Heat Exchangeriaft100% (2)
- Pipe Stress Analysis - FWDokument32 SeitenPipe Stress Analysis - FWmasoud132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist For Chapter VIII of ASME B31.3 Piping For Category M Fluid ServiceDokument5 SeitenChecklist For Chapter VIII of ASME B31.3 Piping For Category M Fluid ServiceiaftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On SPRING HANGERDokument113 SeitenPresentation On SPRING HANGERvishal MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Intensification - Flexibility in Pipe Stress Analysis PDFDokument6 SeitenStress Intensification - Flexibility in Pipe Stress Analysis PDFcelermNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compr Piping SHXHDJDNDDokument12 SeitenCompr Piping SHXHDJDNDSkr9143 ShivNoch keine Bewertungen
- PN03CL1S01Dokument4 SeitenPN03CL1S01Amreusit SaschimbnumeleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Wall Thickness CalculationDokument79 SeitenPipe Wall Thickness CalculationRaj Bindas100% (1)
- Plot Plan Development 19822mon TwuwDokument9 SeitenPlot Plan Development 19822mon TwuwTom0% (1)
- Sanitary Waste and Vent Piping 15150Dokument15 SeitenSanitary Waste and Vent Piping 15150Munir RasheedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rack PipingDokument6 SeitenRack PipingMayank Sethi100% (1)
- Piping Spring HangersDokument2 SeitenPiping Spring HangersyogacruiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Containment EDokument43 SeitenDouble Containment EDavid FonsecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP Lined PipeDokument68 SeitenPP Lined Pipegilbert4285Noch keine Bewertungen
- PipingDokument15 SeitenPipingDerick Mendoza100% (1)
- Anvil 1Dokument1 SeiteAnvil 1gpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- SIF For Y-ConnectionsDokument3 SeitenSIF For Y-Connectionsgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Vibration ExamplesDokument4 SeitenPiping Vibration Examplesgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Foamproport Bladder TankDokument6 SeitenFoamproport Bladder Tankgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- U.S. Regional Service Centers: Corporate Offices Anvil International Worldwide Customer Service CenterDokument1 SeiteU.S. Regional Service Centers: Corporate Offices Anvil International Worldwide Customer Service Centergpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical EngineeringDokument3 SeitenMechanical Engineeringgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anvil Sample ProblemDokument1 SeiteAnvil Sample Problemgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allowable Hot StressDokument1 SeiteAllowable Hot Stressgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circumferential StressDokument1 SeiteCircumferential Stressgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Piping Code ComplianceDokument1 SeitePiping Code Compliancegpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Triflex Windows: Figure 1 Cold Spring DrawingDokument1 SeiteTriflex Windows: Figure 1 Cold Spring Drawinggpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Std10 Tamil 1 PDFDokument125 SeitenStd10 Tamil 1 PDFsasikumar rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expansion Stress RangeDokument2 SeitenExpansion Stress Rangegpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anvil Sample ProblemDokument1 SeiteAnvil Sample Problemgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flexibility Analysis of The Vessel-Piping Interface: Martin M. SchwarzDokument9 SeitenFlexibility Analysis of The Vessel-Piping Interface: Martin M. Schwarzgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Acoustic Induced Vibration (AIV), Flow Induced Vibration (FIV) AnalysisDokument8 SeitenGuidelines For Acoustic Induced Vibration (AIV), Flow Induced Vibration (FIV) Analysisgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Acoustic Induced Vibration (AIV), Flow Induced Vibration (FIV) AnalysisDokument8 SeitenGuidelines For Acoustic Induced Vibration (AIV), Flow Induced Vibration (FIV) Analysisgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Schedule PDFDokument1 SeitePipe Schedule PDFSrinivasan SeenuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elbows Returns B 169Dokument1 SeiteElbows Returns B 169gpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- GD&T - Print Reading For ManufacturingDokument207 SeitenGD&T - Print Reading For Manufacturingpatdh1028100% (2)
- Design of Structural Steel Pipe Racks PDFDokument12 SeitenDesign of Structural Steel Pipe Racks PDFmobin1978100% (3)
- Elbows Returns B 169Dokument1 SeiteElbows Returns B 169gpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Printed: 8/21/2014 6:53:35 AM Model: F:/PIPING STRESS ANALYSIS/01. STATIC ANALYSIS... /PUMP MANIFOLDDokument1 SeitePrinted: 8/21/2014 6:53:35 AM Model: F:/PIPING STRESS ANALYSIS/01. STATIC ANALYSIS... /PUMP MANIFOLDgpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Std10 Tamil 2Dokument131 SeitenStd10 Tamil 2gpskumar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- TNPSC Vao Exam 20 02 2011 Keys DetailedDokument5 SeitenTNPSC Vao Exam 20 02 2011 Keys DetailedVenkata Raman VNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Biology TNPSC Exam Question Answer Download ModelDokument12 Seiten7th Biology TNPSC Exam Question Answer Download ModelMathan NaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- CWE Advertisement RRBs Phase IIIDokument27 SeitenCWE Advertisement RRBs Phase IIIAnsh OzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CWE Advertisement RRBs Phase IIIDokument27 SeitenCWE Advertisement RRBs Phase IIIAnsh OzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEBINAR: Ballast Water Management - Be Ready For The Discharge Standard D-2Dokument32 SeitenWEBINAR: Ballast Water Management - Be Ready For The Discharge Standard D-2sukhjit78Noch keine Bewertungen
- COOLANT Komatsu PDFDokument16 SeitenCOOLANT Komatsu PDFdarwin100% (1)
- Tappi 0502-17 Papermaker FormulaDokument19 SeitenTappi 0502-17 Papermaker FormulaMulyadi Moel86% (21)
- Duty Engineer: Grand Mercure & Ibis Yogyakarta Adi SuciptoDokument1 SeiteDuty Engineer: Grand Mercure & Ibis Yogyakarta Adi Suciptoali maulana yuthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P287 SCIL Programming BasicsDokument78 SeitenP287 SCIL Programming BasicsOscar GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cilindros Hid. CK ATOSDokument8 SeitenCilindros Hid. CK ATOSAntonio LopesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predictive Analytics in Warranty ClaimsDokument6 SeitenPredictive Analytics in Warranty ClaimsRaj SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tkinter GUI Programming by ExampleDokument374 SeitenTkinter GUI Programming by ExampleArphan Desoja100% (5)
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiDokument26 SeitenChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, BhilaiSK BeharNoch keine Bewertungen
- A140Dokument104 SeitenA140hungchagia1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Btech Trainings GuideDokument26 SeitenBtech Trainings GuideAlfian Pamungkas SakawigunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4X Stainless Steel Laser Sensor: Instruction ManualDokument42 SeitenQ4X Stainless Steel Laser Sensor: Instruction Manualtigres1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group 7 - Mumhdsakjbai Monorail - Project Management ReportDokument21 SeitenGroup 7 - Mumhdsakjbai Monorail - Project Management ReportYogesh Parate100% (1)
- 46 50Dokument1 Seite46 50isturmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- QAch 02Dokument13 SeitenQAch 02Rami Alnajjar100% (1)
- TM 9-792 M21 AMMUNITION TRAILERDokument128 SeitenTM 9-792 M21 AMMUNITION TRAILERAdvocate100% (1)
- Harden's Spices Model For Biochemistry in Medical CurriculumDokument10 SeitenHarden's Spices Model For Biochemistry in Medical CurriculumGlobal Research and Development Services100% (1)
- NAD Factory Default and Software CheckDokument13 SeitenNAD Factory Default and Software CheckNorma FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- HartfordDokument7 SeitenHartfordapi-443631703Noch keine Bewertungen
- Barrett Light 50Dokument23 SeitenBarrett Light 50Zayd Iskandar Dzolkarnain Al-HadramiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addressing Corrosion Under Pipe Supports (CUPS) (PRS200a)Dokument2 SeitenAddressing Corrosion Under Pipe Supports (CUPS) (PRS200a)Trajko GorgievskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Truck Parking Areas 2009Dokument147 SeitenTruck Parking Areas 2009IRUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Foam From SFPE HandbookDokument10 SeitenNotes On Foam From SFPE HandbookkdsessionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trane VAV Equipment SpecificationsDokument52 SeitenTrane VAV Equipment Specificationsyu4212Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Slickline OperationsDokument302 Seiten6 Slickline OperationsAntonio Bevilacqua100% (4)
- Careers 2Dokument1 SeiteCareers 2CityPressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation Operation Maintenance 7200CB en USDokument140 SeitenInstallation Operation Maintenance 7200CB en USEleno RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asme b16.5Dokument246 SeitenAsme b16.5hugo_siqueira_11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qs Iar MB PT Mega Pratama UnggulDokument7 SeitenQs Iar MB PT Mega Pratama UnggulNaufal MuljonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorado Brand GuidelinesDokument63 SeitenColorado Brand GuidelineszpweeksNoch keine Bewertungen