Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry SPM Module Form 4 Chapter 3
Hochgeladen von
ShobanaKumaranOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry SPM Module Form 4 Chapter 3
Hochgeladen von
ShobanaKumaranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CHAPTER 3: CHEMICAL FORMULAE AND
EQUATIONS
Concept of moles
1. One mole is the amount of substance which contains the same number of particles
as there are in 12 grams of carbon-12
2. The number of atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12 is 6.02 X 10
23
3. This 6.02 X 10
23
is called Avogadro's number or Avogadro's constant (NA)
4. Particles can be
a) atoms,
b) ions
c) molecules
5. Molar mass and relative molecular mass is same meaning
6. Calculation molar mass (RAM refer to periodic table)
a) What is the molar mass for glucose, C6H12O6? [RAM of C=12, H=1, O= 16]
(12x6) + (1x12) + (16x6)
=180
b) The molecular mass of M(OH)2 is 98. What is the relative atomic mass of atom
M [RAM of H=1, O= 16]
M + (16+1)2 = 98
M = 98 34
M = 64
c) Molar mass of Mn(NO3)2 ? [RAM of Mn=55, N=14, O= 16]
55 + (14x2) + (16x6)
= 179
7. Calculate the mass (RAM refer to periodic table):
If number of mole is given
and remember RMM/molar mass always can be found
use above formula to find mass by number mole multiply with RMM
a) 0.05 mol of KMnO4 [answer: 7.9g]
b) 0.1 mol CuSO4 [answer: 16g]
c) 0.08 mol of ascorbic acid, C6H8O6 [answer: 14.08g]
8. Calculate the number of mole for: (RAM refer to periodic table)
If number of mass is given
and remember RMM/molar mass always can be found
use above formula to find number mole by mass divide with RMM
a) 2.8g iron [answer: 0.05 mol]
b) 4.05g of nicotine, C10H14N2 [answer: 0.025 mol]
c) 1.49g of (NH4)3PO4 [answer: 0.01 mol]
d) 2.3g of ethanol, C2H5OH [answer: 0.05 mol]
e) 23.5g of copper(II) nitrate, Cu(NO3)2 [answer: 0.125 mol]
9. Calculate the number of particles in: (RAM refer to periodic table)
[(Assume NA= 6.02 x 10
23
mol
-1
]
Particles can be
i. atoms,
ii. ions
iii. molecules
Based on above formula to find number particles must have number of
mole and Avogadros constant, NA
and remember RMM/molar mass always can be found
find number of mole first
a) 0.75 mol of Aluminum atoms, Al [answer: 4.52 x 10
23
Aluminum atoms]
Number of moles x NA
= 0.75 X 6.02 x 10
23
= 4.52 x 10
23
Aluminum atoms (atoms also number of particles)
b) 1.2 mol of chloride ions, Cl
-
[answer: 7.22 x 10
23
chloride ions]
Number of moles x NA
= 1.2 X 6.02 x 10
23
= 7.22 x 10
23
chloride ions (ions also number of particles)
c) 0.07 mol of carbon dioxide molecules, CO2 [answer: 4.21 x 10
22
carbon
dioxide molecules
Number of moles x NA
= 0.07 X 6.02 x 10
23
= 4.21 x 10
22
carbon dioxide molecules (molecules also number of particles)
10. Calculate the number of atoms in: (RAM refer to periodic table)
[Assume NA= 6.02 x 10
23
mol
-1
]
Given is molecules but they asked number atoms
Find number of particles first
Find number of atoms in that molecules
Multiply number of particle with the atoms
a) 0.2 mol of sulphur dioxide gas, SO2 [answer: 3.61 x 10
23
atoms]
Number paticles = 0.2 x 6.02 x 10
23
= 1.204 x 10
23
Number of atoms in SO2 = 1 Sulphur and 2 Oxygen
= 3 atoms
Number of atoms = 1.204 x 10
23
x 3
= 3.61 x 10
23
atoms
b) 0.125 mol of methane gas CH4 [answer: 3.76 x 10
23
atoms]
Number paticles = 0.125 x 6.02 x 10
23
= 7.525 x 10
22
Number of atoms in CH4 = 1 Carbon and 5 hydrogen
= 5 atoms
Number of atoms = 7.525 x 10
22
x 5
= 3.76 x 10
23
atoms
11. Calculate the number of particles in: (RAM refer to periodic table)
a) 12.8g of copper [answer: 1.2x 10
23
atoms]
b) 8.5g of ammonia, NH3 [answer: 3.01 x 10
23
atoms]
c) 2g of hydrogen gas, H2 [answer: 6.02 x 10
23
atoms]
d) 5g of nitrogen dioxide gas NO2 [answer: 6.54 x 10
22
atoms ]
e) 6.6g of ethane C2H6 [answer: 1.32 x 10
23
atoms]
(Assume NA= 6 x 10
23
mol
-1
)
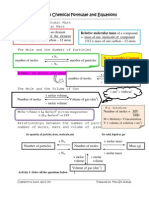
Relationship between Number of moles of a gas and its
volume
1. 1 mol of any gas at room temperature (25
0
C) and pressure of 1 atmosphere occupies
24 dm
3
(24 000 cm
3
)
2. At standard temperature and pressure (s.t.p) which at 0
0
C and 1 atmosphere, 1 mol
of gas occupies 22.4 dm
3
(22 400 cm
3
)
3. 1 dm
3
= 1000 cm
3
4. Calculate the volume of: (RAM refer to periodic table, s.t.p= 22.4dm
3
, r.t.p = 24.0 dm
3
)
Based on above formula, to find volume, number mole is required
Multiply with stp or rtp based on the question [always given]
a) 0.75 mol nitrogen gas at s.t.p [answer: 16.8 dm
3
]
b) 0.55 mol of oxygen gas at room temperature and pressure [answer: 13.2 dm
3
]
5. Calculate the no. of moles of the following gases at room temperature and pressure
(RAM refer to periodic table, s.t.p= 22.4dm
3
, r.t.p = 24.0 dm
3
)
Based on above formula, to find number mole, volume is required
Multiply with stp or rtp based on the question
a) 4.8 dm
3
of chlorine gas [answer: 0.2 mol]
b) 1200 cm
3
of methane gas [answer: 0.05 mol]
6. Calculate the number of moles of:
(RAM refer to periodic table, s.t.p= 22.4dm
3
, r.t.p = 24.0 dm
3
)
a. 672 cm
3
carbon dioxide at s.t.p [answer: 0.03 mol] (convert to dm
3
first)
b. 50 dm
3
oxygen gas at s.t.p and r.t.p [answer: 2.2 mol, 2.1 mol]
7. Calculate the volume occupied by:
(RAM refer to periodic table, s.t.p= 22.4dm
3
, r.t.p = 24.0 dm
3
)
a) Based on above formula, to find volume, MUST GO PASS NUMBER OF
MOLE
b) Find number mole first
c) Then, Multiply with stp or rtp based on the question
a. 1.4g of ethene gas, C2H4 at s.t.p [answer: 1.12 dm
3
]
b. 2.5g of oxygen gas at room temperature and pressure [answer: 1.88 dm
3
]
c. 4g of carbon dioxide gas at room temperature and pressure [answer: 2.09 dm
3
]
8. Calculate the mass of the following
(RAM refer to periodic table, s.t.p= 22.4dm
3
, r.t.p = 24.0 dm
3
)
a) Based on above formula, to find mass, MUST GO PASS NUMBER OF
MOLE
b) Find number mole first
c) Then, Multiply with RMM
a. 16.8 dm
3
of methane gas CH4 at s.t.p [answer: 12g]
b. 6720 cm
3
of carbon monoxide gas, CO at s.t.p [answer: 8.4g]
Empirical and molecular formula
1. Empirical formula is the simplest ratio of the atoms of the
elements that combine to form compound
2. Molecular formula is the actual numbers of the atoms of the
elements to form the compound
REMEMBER: IF YOU GET SIMPLEST RATIO SUCH AS 0.5, 1.5, 2.5, 3.5,
Please make as whole number by multiplying with 2. DONT EVER LEAVE
IT IN DECIMAL PLACES
IN Calculating empirical formula
1. Write mass or percentage
2. Calculate no of mole
3. Divide with smallest number of mole
4. Get simplest ratio
Calculation
1. A compound has element X and Y.
a. Mass of X is 2.4g and mass of Y is 1.6g.
b. (RAM: X=48; Y=16). Calculate the empirical formula
Empirical formula is X1Y2 but written as XY2
2. A compound has 4.8% of hydrogen, 17.7% of boron and the rest is oxygen
a. (RAM; H=1; B=11; O=16)
b. Calculate the empirical formula
Empirical formula is H3BO3
Element X Y
Mass (step 1) 2.4g 1.6g
Number of
moles
(step 2)
2.4
48
= 0.05 mol
1.6
16
=0.1 mol
Simplest ratio
(step 3)
0.05
0.05
= 1
0.10
0.05
= 2
Element H B O
Mass (step 1) 4.8% 17.7% 100- 4.8- 17.7 = 77.5
Number of
moles
(step 2)
4.8
1
= 4.8 mol
17.7
11
=1.6 mol
77.5
16
= 4.8 mol
Simplest ratio
(step 3)
4.8
1.6
= 3
1.6
1.6
= 1
4.8
1.6
= 3
3. A hydrocarbon has 85.7% of carbon. The rest are hydrogen. The molar mass is 28
a. (RAM: H=1; C=12)
b. Determine the empirical formula
c. Determine the molecular formula
Empirical formula is CH2
Molecular formula is (CH2)n = molar mass
[12 + (1 x 2)]n = 28
14n = 28
n = 2
Replace n =2 into (CH2)n, the molecular formula is C2H4
4. 2.5g of X combined with 4g of Y to form a compound with formula XY2 . If the RAM of
Y is 80, determine the relative atomic mass of X
5. 1.04g of element X reacted with 0.48g of oxygen to form an oxide with empirical formula
X2O3. Determine the relative atomic mass of X
Element C H
Mass (step 1) 85.7% 100- 85.7 = 14.3
Number of
moles
(step 2)
85.7
12
= 7.1 mol
14.3
1
=14.3 mol
Simplest ratio
(step 3)
7.1
7.1
= 1
14.3
7.1
= 2
CRUCIBLE LID METHOD IS SUITABLE FOR MAGNESIUM BECAUSE IT IS HIGHER IN
ECS AND VERY REACTIVE COMPARED TO COPPER WHICH IS LESS REACTIVE AND
USES REDUCTION BY HYDROGEN
Crucible lid need to open from time to time to allow oxygen gas to enter and to
react
the hydrogen gas must be passed through first before experiment to remove
all the air in the combustion tube
mixture of air and hydrogen can cause explosion when ignited
weight should be measured from time to time until constant weight is
obtained to assume the reaction completed
hydrogen gas is continuously flow through during cooling process to prevent
any gas to enter again and react with the metal
this causes constant weight could not achieved
Calcium chloride to dry the hydrogen gas
HCl/ H
2
SO
4
and Zinc to produce hydrogen gas
CaCl
Reduction by hydrogen method
Crucible lid method
SOLVING CHEMISTRY QUESTION RULES
1. Write chemical equation
2. Balance the equation
3. Find number of mole of any compound that information
given
4. Dont calculate the excess compounds
(Relative Atomic Mass PLEASE REFER TO PERIODIC TABLE)
QUESTIONS
1. If 0.12g of magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid, calculate
a. The mass of magnesium chloride formed
b. The volume of hydrogen gas evolved at room temperature and pressure
c. (RAM; Mg=24, Cl=35.5; 1 mol of gas occupies a volume of 24 dm
3
at rtp)
Step 1 (Equation): Mg + HCl MgCl2 + H2
Step 2 (Balance the equation): Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
Step 3 (Find number of mole of any compound that information given):
Information given is for magnesium which has mass and RAM so,
Number of mole = Mass/RAM 0.12g / 24 = 0.005 mole
a) Already found which is 0.005 mole
b) Based on the equation, Mg + 2HCl MgCl2 + H2
So number of mole of hydrogen gas is 0.005 mol,
0.005 mol x 24 dm
3
(given) = 0.12 dm
3
Mg
2+
Cl
-
MgCl2
0.005 0.01 0.005 0.005
2. 3.2g of copper(II) oxide powder reacted with excess of nitric acid
a. Cu0 + HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + H2O
b. Calculate the mass of copper(II) nitrate formed
c. (RAM; N=14, O=16, Cu=64)
3. Ethanol burns in air as below
a. C2H5OH +3O2 2CO2 + 3H2O
b. Calculate the mass of ethanol burnt if 2.4dm
3
of carbon dioxide is produced at
room temperature
c. (RAM; H=1, C=12, O=16; 1 mol of gas occupies a volume of 24 dm
3
at rtp)
4. A hydrocarbon X contains 82.76% carbon by mass. 2.9g of hydrocarbon X occupies a
volume of 1.2 dm
3
at room temperature and pressure. (RAM: H=1, C=12, O=16; 1 mol of
gas occupies a 24dm
3
at rtp; NA = 6 X 10
23
mol
-1
)
a. Determine the empirical formula of hydrocarbon X
b. Determine the molecular formula of hydrocarbon X
c. Combustion of X in air produces carbon dioxide and water. Write chemical
equation
d. If 11.6g of X burnt
e. The mass of water formed
f. The number of carbon dioxide molecules produced at room temperature
5. K + O2 K2O
a. Calculate the mass number of mole for potassium oxide if 23.5g of potassium
oxide is used
b. Calculate the number of mole of potassium used
c. Calculate the mass of potassium used
d. Calculate the volume of oxygen used
e. (STP: 22.4dm
3
)
6. H2O2 H2O + O2
a. (rtp: 24dm
3
)
b. Calculate the number mole of oxygen produced if 11.2dm
3
oxygen produced
c. Calculate the number of mole of H2O2 used
d. Calculate the mass of H2O2 used
7. 8.0g of copper (II) oxide powder is added to excess dilute nitric acid and heated. Find the
mass of copper (II) nitrate formed
8. 1.3g of zinc reacts with excess dilute sulphuric acid. The product formed are zinc
sulphate and hydrogen gas. Find the volume of hydrogen released at STP
9. C3H8 + O2 CO2 + H2O
a. 720 cm
3
of propane gas at rtp burns in excess oxygen. Calculate the mass of
carbon dioxide formed
10. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes according to the following equation:
2
2 2
O H (l) 2 O H
2
(l) +
2
O (g)
a. Calculate the volume of oxygen gas,
2
O measured at STP that can be obtained
from the decomposition of 34 g of hydrogen peroxide,
2 2
O H . [Relative atomic
mass : H, 1 ; O, 16. Molar volume : 22.4
3
dm
1
mol at STP] (Ans:
11.2 dm
3
)
11. Silver carbonate Ag2CO3 breaks down easily when heated to produce silver metal
2 Ag2CO3(l) 4 Ag (s) + 2
2
CO (g) +
2
O
a. Find the mass of silver carbonate that is required to produce 10 g of silver
[Relative atomic mass: C, 12 ; O, 16 ; Ag, 108]
(Ans : 12.77g)
12. 16 g of copper (II) oxide, CuO is reacted with excess methane,
4
CH . Using the equation
below, find the mass of copper that is produced.
[Relative atomic mass: Cu, 64; O, 16]
4 CuO(s) +
4
CH (g) 4 Cu (s) +
2
CO (g) + 2 O H
2
(l)
(Ans : 12.8 g)
13. A student heats 20 g of calcium carbonate
3
CaCO strongly. It decomposes according to
the equation below:
3
CaCO (s) CaO (s) +
2
CO (g).
(a). If the carbon dioxide produced is collected at room conditions, what is its volume?
(b). Calculate the mass of calcium oxide, CaO produced.
[Relative atomic mass: C, 12 ; O, 16; Ca, 40. Molar volume : 24 dm
3
1
mol at
room conditions]
(Ans : (a). 4.8 dm
3
(b) 11.2 g)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsDokument6 SeitenChapter 3 Chemical Formulae and EquationsArif AyepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Form 4 - LisDokument30 SeitenChapter 3 Form 4 - LisStephenie Nilus Richard KulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsVon EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- MF008 Fhs LNT 002 May11Dokument32 SeitenMF008 Fhs LNT 002 May11Lim Shu YingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemistry Xi 2011Dokument134 SeitenChemistry Xi 2011Mini PGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Chem'l QuantitiesDokument52 Seiten2013 Chem'l Quantitiesapi-266061131Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATDokument29 SeitenTopic 1, Fundamental Concepts First Year MCATKhubaib Khan100% (1)
- Heterogeneous Catalysis at Nanoscale for Energy ApplicationsVon EverandHeterogeneous Catalysis at Nanoscale for Energy ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Dokument101 SeitenChap 3 f4 KSSM - Student 2021Koo Rui CheeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conventional and Alternative Power Generation: Thermodynamics, Mitigation and SustainabilityVon EverandConventional and Alternative Power Generation: Thermodynamics, Mitigation and SustainabilityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter3problems-Bursoln 25362232Dokument11 SeitenChapter3problems-Bursoln 25362232leoriza mae salapareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Kimia Skor ADokument9 SeitenModul Kimia Skor Aacik5596Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hyrdogen Storage TechnologiesVon EverandHyrdogen Storage TechnologiesMehmet SankirNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch5 6 7Dokument1 Seitech5 6 7Jeff MartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample AQA AS ChemistryDokument30 SeitenSample AQA AS ChemistryDarlingtinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4Dokument53 SeitenCH 4JayelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- StiochiometryDokument11 SeitenStiochiometryIndrojyoti MondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Lecture NotesDokument10 SeitenChapter 3 Lecture NotesAhmad KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATTER (1.2 Mole Concept)Dokument101 SeitenMATTER (1.2 Mole Concept)Supia NazmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equations - LATIHAN PENGUKUHANDokument4 SeitenChapter 3 Chemical Formulae and Equations - LATIHAN PENGUKUHANSiti Aishah AzmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Calculations ADokument8 SeitenChemistry Calculations AKasunDilshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05athemole 101129173016 Phpapp01Dokument28 Seiten05athemole 101129173016 Phpapp01Karm VeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3 CompleteDokument48 SeitenCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3 CompleteDokument48 SeitenCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moles and Stoich-07 PDFDokument16 SeitenMoles and Stoich-07 PDFNabila Hanim100% (1)
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokument32 SeitenChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (3)
- Chemistry PDFDokument22 SeitenChemistry PDFcarlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Test 2 Revision 1: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDokument7 SeitenChemistry Test 2 Revision 1: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDaniel BerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole Concept PDFDokument26 SeitenMole Concept PDFPrashant Kumar67% (3)
- 5B - Stoichiometry 2Dokument41 Seiten5B - Stoichiometry 2Vimanan A/L S. VelangganiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument43 SeitenScienceHemang NityantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole Concept: Relative Atomic, Molecular and Formula Masses Relative Atomic Mass (RAM)Dokument7 SeitenMole Concept: Relative Atomic, Molecular and Formula Masses Relative Atomic Mass (RAM)Aria PersaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry in EnglishDokument149 SeitenChemistry in EnglishSabuj JanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 24 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsDokument14 Seiten1 24 Calculations and Chemical ReactionsSabina SabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drill For An A: TEST 1 (JULY 2011)Dokument11 SeitenDrill For An A: TEST 1 (JULY 2011)enzyxNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Relative Atomic MassDokument7 Seiten1 Relative Atomic MassHooi YingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3 CompleteDokument48 SeitenCh3 CompleteAN NGUYENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kimia Bab 3 Part1 (Bambang S.)Dokument9 SeitenKimia Bab 3 Part1 (Bambang S.)Ardianyogi SaputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Revision 2 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDokument7 SeitenChemistry Revision 2 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDaniel BerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 1A Chapter5 Exercises PDFDokument5 SeitenChem 1A Chapter5 Exercises PDFJoela Faith Ming GongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul 4-Basic ChemDokument10 SeitenModul 4-Basic ChemSaravanan ManiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuizDokument4 SeitenQuizsololexzibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms & Molecules SolutionsDokument11 SeitenAtoms & Molecules Solutionshkush78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mole ConceptDokument32 SeitenMole ConceptFatin ComelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Claz (Holiday)Dokument8 SeitenChemistry Claz (Holiday)agg4652100% (1)
- Chem Formulae and EquationDokument5 SeitenChem Formulae and EquationrvinrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsDokument7 SeitenSPM Form 4 Terminology and Concepts Chemical Formulae and EquationsJedidah JongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem 1Dokument9 SeitenProblem 1Prince Isaiah JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Revision 3 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDokument8 SeitenChemistry Revision 3 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDaniel BerryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFDokument50 Seiten20171101131106chapter 5b - Mole and Stoichiometry PDFShah100% (1)
- Mole ConceptDokument59 SeitenMole ConceptGlen Mangali100% (1)
- Formula, Equations and MolesDokument4 SeitenFormula, Equations and MolesyasinrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molar Mass For ChemistryDokument31 SeitenMolar Mass For ChemistryHajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsVon EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableVon EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeVon EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (90)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincVon EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (137)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactVon EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolVon EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideVon EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsVon EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Water-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Von EverandWater-Based Paint Formulations, Vol. 3Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Transformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathVon EverandTransformer: The Deep Chemistry of Life and DeathBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (13)