Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Worksheet 26 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Vijay BhaskarOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Worksheet 26 PDF
Hochgeladen von
Vijay BhaskarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 1
26 Worksheet (A2)
Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet.
1 Calculate the force experienced by an oil droplet with a charge of 3.2 10
19
C due to a
uniform electric field of strength 5.0 10
5
V m
1
. [2]
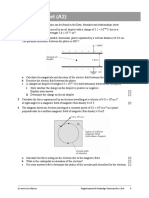
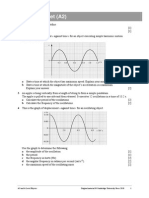
2 The diagram shows two parallel, horizontal plates separated by a vertical distance of 3.0 cm.
The potential difference between the plates is 600 V.
a Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electric field between the plates. [3]
b Describe the electric field between the plates. [2]
c A charged oil droplet of weight 6.4 10
15
N is held stationary between the two plates.
i State whether the charge on the droplet is positive or negative.
Explain your answer. [2]
ii Determine the charge on the oil droplet. [2]
3 Calculate the force experienced by an electron travelling at a velocity of 4.0 10
6
m s
1
at right angles to a magnetic field of magnetic flux density 0.18 T. [3]
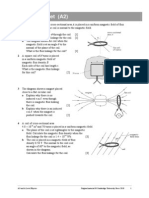
4 The diagram shows an electron moving at a constant speed of 8.0 10
6
m s
1
in a plane
perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of magnetic flux density 4.0 mT.
a Calculate the force acting on the electron due to the magnetic field. [3]
b What is the centripetal acceleration of the electron? [2]
c Use your answer to b to determine the radius of the circular path described by the electron. [2]
26 Worksheet (A2)
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 2
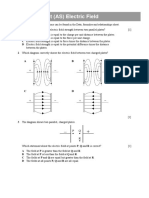
5 The diagram shows the trajectory of an electron travelling into a region of uniform magnetic
field of flux density 2.0 mT. The electron enters the region of magnetic field at 90.
a Draw the direction of the force experienced by the electron at points A and B. [1]
b Explain why the electron describes part of a circular path while in the region of the
magnetic field. [1]
c The radius of curvature of the path of the electron in the magnetic field is 5.0 cm.
Calculate the speed v of the electron. [5]
d Explain how your answer to c would change if the electron described a circular path
of radius 2.5 cm. [2]
6 A proton of kinetic energy 15 keV travelling at right angles to a magnetic field describes
a circle of radius of 5.0 cm. The mass of a proton is 1.7 10
27
kg.
a Show that the speed of the proton is 1.7 10
6
m s
1
. [3]
b For this proton, calculate the centripetal force provided by the magnetic field. [3]
c Determine the magnetic flux density of the magnetic field that keeps the proton moving
in its circular orbit. [3]
d How long does it take for the proton to complete one orbit? [2]
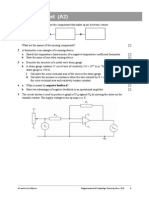
7 The diagram shows a velocity-selector for charged ions. Ions of speed v emerge from the slit.
a The parallel plates have a separation of 2.4 cm and are connected to a 5.0 kV supply.
A magnetic field is applied at right angles to the electric field between the plates such
that the positively charged ions emerge from the slit of the velocity-selector at a speed of
6.0 10
6
m s
1
. Calculate the magnetic flux density of the magnetic field. [6]
b Ions from the velocity-selector pass into a mass spectrometer which contains another magnetic
field, of flux density B. The ions all have charge Q but either have mass m
1
or mass m
2
. Show
that the difference in the radius of the two isotopes in the magnetic field is given by:
r =
BQ
v m m ) (
2 1
[2]
26 Worksheet (A2)
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 3
8 An electron describes a circular orbit in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field.
a Show that the time T taken by an electron to complete one orbit in the magnetic field is
independent of its speed and its radius, and is given by:
T =
Be
m 2
where B is the magnetic flux density of the magnetic field, e is the charge on an electron
and m is the mass of an electron. [5]
b Explain in words how a faster electron takes the same time to complete one orbit as a slower
electron. [1]
Total:
55
Score: %
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Worksheet 26Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 26Subarna Lamsal100% (1)
- 5.1.2 Worksheet 2Dokument3 Seiten5.1.2 Worksheet 2Ali AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 23 PDFDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 23 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 18 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 18 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitational Forces and FieldsDokument3 SeitenGravitational Forces and FieldsPathmanathan Nadeson0% (2)
- 22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Dokument3 Seiten22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 19Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 19Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 05 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 05 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 02 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 02 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersDokument1 SeiteCH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersAmberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 07 PDFDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 07 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 13Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet 13Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23 Laws of Electromagnetic InductionDokument64 SeitenChapter 23 Laws of Electromagnetic InductionPathmanathan NadesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics DC CircuitsDokument24 SeitenPhysics DC CircuitsJenessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 04 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 04 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Fields and Circuits Study GuideDokument22 SeitenElectric Fields and Circuits Study GuideLawrence Onthuga100% (1)
- Chapter20pp181 190Dokument10 SeitenChapter20pp181 190InderMaheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 09Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 09Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Momentum QPDokument6 SeitenMomentum QPXandws -IOS tips and trick and gamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Physics PracticalDokument56 SeitenA2 Physics PracticalFathmath AthfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 18Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet 18Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kirchoff's Laws Part 2Dokument13 SeitenKirchoff's Laws Part 2alexobama100% (1)
- Edexcel Physics A2 Answers Student S Book PDFDokument12 SeitenEdexcel Physics A2 Answers Student S Book PDFWaqasKhan100% (1)
- Parallelogram Law ExperimentDokument9 SeitenParallelogram Law ExperimentcthomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 SuperpositionDokument75 Seiten11 SuperpositionRonnie QuekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 14Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet 14Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01 Physical Quantities and UnitsDokument4 SeitenChapter 01 Physical Quantities and UnitsPathmanathan NadesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answers To Examination-Style Questions: Answers Marks Examiner's TipsDokument7 SeitenAnswers To Examination-Style Questions: Answers Marks Examiner's TipsjasbirsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrostatic ForceDokument3 SeitenElectrostatic ForceAlyssa Cole100% (1)
- Unit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyDokument12 SeitenUnit 5 - Physics From Creation To Collapse: Thermal EnergyShivani MajithiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11Dokument16 SeitenCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/11AdeenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Module Form 5 Electric Current RelationshipDokument26 SeitenPhysics Module Form 5 Electric Current RelationshipjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDEXCEL MODEL PHYSICS ANSWERS 1995-2001 (04-Oct-10)Dokument265 SeitenEDEXCEL MODEL PHYSICS ANSWERS 1995-2001 (04-Oct-10)Radiant ree100% (1)
- 14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14Dokument4 Seiten14 - Waves General Waves and Wave Intensity - 14dil19860209Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet (AS) PDFDokument1 SeiteWorksheet (AS) PDFMahad AsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet (AS) PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet (AS) PDFMahad AsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 24 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 24 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniform Circular Motion Experiment AnalysisDokument13 SeitenUniform Circular Motion Experiment AnalysisJohndoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 31Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 31Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- M Schemes 01Dokument2 SeitenM Schemes 01Pathmanathan NadesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Worksheet (AS) : What Is The Current X ?Dokument4 Seiten11 Worksheet (AS) : What Is The Current X ?Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MagnetsDokument26 SeitenMagnetsapi-422428700Noch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Physics NotesDokument3 SeitenA2 Physics NotesZain ImranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 20 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 30 PDFDokument4 SeitenWorksheet 30 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Astrophysics and Cosmology NotesDokument6 SeitenAstrophysics and Cosmology NotesJTBTeddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 2008 ALL JC Prelims Questions (2013)Dokument47 SeitenH2 2008 ALL JC Prelims Questions (2013)Indrik WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 02Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 02Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A2 Physics Monthly Test January 2017Dokument3 SeitenA2 Physics Monthly Test January 2017AbhiKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1 Lab | Determine Time Constant of RC CircuitDokument5 SeitenPhysics 1 Lab | Determine Time Constant of RC Circuitf wNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resolution of Vectors (Student Worksheet)Dokument4 SeitenResolution of Vectors (Student Worksheet)Tan Kok Kim0% (1)
- Worksheet 26 CombineDokument24 SeitenWorksheet 26 CombineCleo Poulos0% (1)
- Charged Particle in Magnetic Field-Worksheet - 26Dokument3 SeitenCharged Particle in Magnetic Field-Worksheet - 26rizwansiddiqui1970Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 26Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 26Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- g485 5 1 2 Magnetic Fields BDokument10 Seiteng485 5 1 2 Magnetic Fields Bapi-236179294Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH - 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism PYQDokument4 SeitenCH - 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism PYQKrishna ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 961019Dokument11 SeitenQuestion 961019rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 PHY2 CLC Problems BaitapDokument13 Seiten2021 PHY2 CLC Problems BaitapThinh Nguyen100% (1)
- Print Question PaperDokument8 SeitenPrint Question PaperSaniya MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformationsclassifieds PDFDokument35 SeitenTransformationsclassifieds PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 33Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 33Pathmanathan NadesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 33A LevelDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 33A LevelVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 30Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet 30Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 28 PDFDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 32Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 32Pathmanathan NadesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 32Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 32Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 30 PDFDokument4 SeitenWorksheet 30 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 31Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 31Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 31 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 31 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 29Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet 29Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 29 PDFDokument4 SeitenWorksheet 29 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 24 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 24 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 27Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 27Vijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 28Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 28Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 21Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 21Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Dokument3 Seiten27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Syed Abdul Rehman ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 26Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 26Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 22Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 22Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 25Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 25Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 24Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 24Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 25 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 25 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (2)
- Worksheet 21 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 21 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 23Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 23Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 20 PDFDokument3 SeitenWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Dokument3 Seiten22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 20Dokument3 SeitenWorksheet 20Vijay BhaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 19Dokument2 SeitenWorksheet 19etud3cl100% (1)
- Gearless Mill Drives in Mining Industry PDFDokument7 SeitenGearless Mill Drives in Mining Industry PDFRadu BabauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercises For TFFY54Dokument25 SeitenExercises For TFFY54sattar28Noch keine Bewertungen
- DeforestationDokument4 SeitenDeforestationPeggopoulouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distillation DesignDokument30 SeitenDistillation Designfdc20062340100% (2)
- Unit 1.1 - EV IntroDokument68 SeitenUnit 1.1 - EV IntroPilar Martinez Gonzalez100% (1)
- 64L - Coffee - Table - Book (1) (1) (1) - 032Dokument1 Seite64L - Coffee - Table - Book (1) (1) (1) - 032Nilda Ester RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me6603 Fea - 2 MarksDokument15 SeitenMe6603 Fea - 2 MarksPrabha KaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- PedgkDokument32 SeitenPedgkGokulakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Fiber-Dispersion SP 2014Dokument19 SeitenOptical Fiber-Dispersion SP 2014Ajay DillikarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chaudhry2021 Does Culture Affect Energy PovertyDokument16 SeitenChaudhry2021 Does Culture Affect Energy PovertyRaul MJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Tertiary and Quaternary StructureDokument18 SeitenProtein Tertiary and Quaternary Structuremaryscribd241Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 Facilities Standards (P100) PDFDokument358 Seiten2017 Facilities Standards (P100) PDFBhingle Abellera100% (1)
- Energy Recharge Calculator - Energy Recharge CalculatorDokument12 SeitenEnergy Recharge Calculator - Energy Recharge Calculatorsubit timalsinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DCA0012601P0001 Dca0012601p0001Dokument7 SeitenDCA0012601P0001 Dca0012601p0001Sakahi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEY's IED Sustainable DevelopmentDokument236 SeitenDEY's IED Sustainable DevelopmentHemaline Rose100% (1)
- Control SystemsDokument77 SeitenControl SystemsLuis Portillo Ogbe BaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalog CHESTERTON - MRO - 2017 - eDokument96 SeitenCatalog CHESTERTON - MRO - 2017 - eNanda PerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FP 238Dokument32 SeitenFP 238Mahmoud Atia100% (2)
- Sustainable Energy TechnologyDokument89 SeitenSustainable Energy Technologyyonas fentahunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sintech Make Pumps For Power Generation IndustryDokument16 SeitenSintech Make Pumps For Power Generation Industrysahildhingra0% (1)
- Harris ER90S B3Dokument2 SeitenHarris ER90S B3Mingo EvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy Recovery Heat Exchanger Steam Cogeneration Steam Turbine Combined CycleDokument4 SeitenEnergy Recovery Heat Exchanger Steam Cogeneration Steam Turbine Combined CycleprathapNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Lesson LogDokument4 SeitenSchool Lesson LogLudy Lyn80% (5)
- PAPER SIDIQ ICOS FixDokument7 SeitenPAPER SIDIQ ICOS FixAtika AssalafiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varsani JayDokument33 SeitenVarsani JayBHAVESH KERAI100% (1)
- NE104 EXP 7 NotesDokument2 SeitenNE104 EXP 7 Notesudaymehta94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yanmar 3TNV76-DWL Engine Parts CatalogDokument20 SeitenYanmar 3TNV76-DWL Engine Parts CatalogDarryl CareyNoch keine Bewertungen
- HONOMOBO Canada Email Package 2016-June-1 PG 1 / 7Dokument9 SeitenHONOMOBO Canada Email Package 2016-June-1 PG 1 / 7Daniel StaveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Garnituri DIN 2697Dokument12 SeitenGarnituri DIN 2697Dumitru SorinaNoch keine Bewertungen