Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
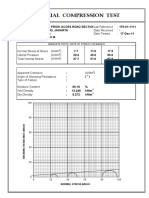
Soil Thermal Properties PDF
Hochgeladen von
IaraFerreiradeRezendeOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Soil Thermal Properties PDF
Hochgeladen von
IaraFerreiradeRezendeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Soil thermal properties
Ref.: Mitchell & Soga (2005):
Thermal Conductivity () (W.m
-1
.K
-1
) in SI units
Measurement thermal needle method (ASTM, 2000)
Typical values:
Air - 0,024
Water - 0,60
Soil - 0,25 2,5 (~ 1,7)
Thermal Resistivity (1/) (K.m.W
-1
)
There is a critical water content below which the soil resistivity increases
exponentially:
Heat Capacity or Specific Heat (c) (kJ.kg
-1
.K
-1
)
Typical values:
Water - 4,186
Minerals 0,710
Rocks - 0,80 2,20
Volumetric Heat Capacity (C = .c) (kJ.m
-3
.K
-1
)
Typical values:
Water - 4,186
Soil -
d
(72,4 + 427.w/100) where
d
(kN/m
3
)
Ref.: SSSA Book Series: 5 Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 4 (2002):
Chapter 5 Soil Heat, p.1183-1252.
J.H. Dane & G.C. Topp (Co-editors). Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 4 Physical
Methods. Soil Science Society of America Book Series Number 5, SSSA, Inc.,
Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 2002.
5.2. Heat Capacity and Specific Heat, p.1201-1208. (G.J. KLUITENBERG)
Soil Heat Capacity (C) characterizes the quantity of heat that can be added to or
removed from soil per unit change in temperature.
(the higher the soil heat capacity, the greater will be the soil capacity of storing energy
or, in other words, lower temperature variations will be experienced by the soil for a
given amount of heat)
Definition: ( ) P T f
dT
dQ
C , = =
Related parameters:
Specific Heat heat capacity expressed on a mass unit basis, usually
measured at constant pressure in soils (c) (kJ.kg
-1
.K
-1
)
Volumetric Heat Capacity heat capacity expressed on a unit volume basis
(c) (kJ.m
-3
.K
-1
)
Typical values: (van Wijk & de Vries, 1963)
Soil minerals
s
= 2,65 (Mg/m
3
) c = 0,73 (kJ/kg/K) C = 1,9 (MJ/m
3
/K)
Soil organic matter
s
= 1,3 (Mg/m
3
) c = 1,9 (kJ/kg/K) C = 2,5 (MJ/m
3
/K)
Water
w
= 1,0 (Mg/m
3
) c = 4,18 (kJ/kg/K) C = 4,18 (MJ/m
3
/K)
Air
a
= 0,0012 (Mg/m
3
) c = 1,0 (kJ/kg/K) C = 0,0012 (MJ/m
3
/K)
The Volumetric Heat Capacity (c) can be calculated based on soil composition as
follows:
( ) w c c c C
w o o m m d
. . . . + + = | | where
d
soil dry density (Mg/m
3
)
|
m
, |
o
- dry mass fractions of minerals and organic matter, respectively (-)
w gravimetric water content (-)
c
m
, c
o
, c
w
specific heat of each component in soil (kJ/kg/K)
5.3. Thermal Conductivity, p.1209-1226. (K.L. BRISTOW)
Soil Thermal Conductivity () (W.m
-1
.K
-1
) soils ability to transmit heat
Soil Volumetric Heat Capacity (c) (J/m
3
/K) soils ability to store heat
Soil Thermal Diffusivity (o) (m
2
/s) rate of transmission of temperature change
within the soil.
Definition:
) ( c
o =
Typical values:
Quartz - = 8,8 (W/m/K)
Granite - = 2,0 (W/m/K)
Basalt - = 2,2 (W/m/K)
Clay Minerals - = 2,9 (W/m/K)
Soil OM - = 0,25 (W/m/K)
Water - ( ) ( )
2 5 3
. 10 1 , 1 . 10 34 , 2 552 , 0 T T
+ = (T in C)
Air - T . 00064 , 0 0237 , 0 + = (T in C)
T = 30C; 50C; 70C; 90C
OBS: O efeito da temperatura sobre a condutividade trmica do solo grande para o
solo mido, mas irrelevante para o solo na proximidade da saturao (quando a
condutividade trmica comandada pela gua) e quando seco (quando a resistividade
trmica aumenta exponencialmente).
Approximate relationship between the soil constituents thermal conductivities:
Solids >> Water >> Air
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sed - Calculation PadDokument5 SeitenSed - Calculation PadTarek AbulailNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPM Dial Reading True Yield Taza de Corte (Y) Sec-1 Shear Stress T (lb/100ft2) Apparent Viscosity CPDokument38 SeitenRPM Dial Reading True Yield Taza de Corte (Y) Sec-1 Shear Stress T (lb/100ft2) Apparent Viscosity CPErika TanakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TP02L 12Dokument1 SeiteTP02L 12sunartililikNoch keine Bewertungen
- DensityDokument2 SeitenDensityEngineeri TadiyosNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Highways Authority of IndiaDokument2 SeitenNational Highways Authority of IndiajitendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBR Empty FormDokument24 SeitenCBR Empty FormJosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Shear 26112018Dokument24 SeitenDirect Shear 26112018O'cond DioraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile Load TestDokument2 SeitenPile Load TestKhaled MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 23 - Vane Shear Test ResultsDokument5 SeitenFigure 23 - Vane Shear Test ResultsHamza NadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrometer Analysis Reference: IS:2720 (Part 4) - 1985: Sr. No. Description SampleDokument4 SeitenHydrometer Analysis Reference: IS:2720 (Part 4) - 1985: Sr. No. Description SampleRakesh7770Noch keine Bewertungen
- Direct Shear Kel. 1Dokument5 SeitenDirect Shear Kel. 1Sita Auliyah RahmasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Required For Cement TestsDokument2 SeitenWater Required For Cement TestsdhwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Use WashersDokument14 SeitenWhy Use WashersAPGENCO EENoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Test ResultDokument4 SeitenLab Test ResultPrabha KaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pumping Cooper JacobDokument22 SeitenPumping Cooper JacobNaim ZeinounNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeoVES - V1 VES SoftwareDokument5 SeitenGeoVES - V1 VES SoftwareAurangzeb JadoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrometer No. Average Temperature (°C) R R' - C +CDokument3 SeitenHydrometer No. Average Temperature (°C) R R' - C +CRafiq MirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atterberg Limits. DSDokument18 SeitenAtterberg Limits. DSGhulam Quadir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Testing 25-08-2011Dokument14 SeitenSoil Testing 25-08-2011PiyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is456 2000Dokument8 SeitenIs456 2000gyanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Large Strain Consolidation: TitleDokument41 SeitenLarge Strain Consolidation: Titlerelu59Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supplied Parameters From A Lab Report: Problem: Porosity, Effective Porosity, Density, Saturation 72.50 152.00Dokument31 SeitenSupplied Parameters From A Lab Report: Problem: Porosity, Effective Porosity, Density, Saturation 72.50 152.00Cole NathanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elements of Soil Mechanics, 8th Edition Bearing Capacity FactorsDokument14 SeitenElements of Soil Mechanics, 8th Edition Bearing Capacity FactorsdiditjayacuteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matix GeocalculationsDokument8 SeitenMatix Geocalculationsraghav abudhabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grain Size Distribution CurveDokument1 SeiteGrain Size Distribution CurveDetjan JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBR YeneDokument8 SeitenCBR YenehizbawisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ballast FormatsDokument12 SeitenBallast Formats906rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Field Permeability Test-2Dokument1 SeiteField Permeability Test-2Ignatius PathulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7-Modified Proctor TestDokument8 Seiten7-Modified Proctor TestElimar Alvarado MirandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Borehole LogDokument5 SeitenBorehole LogMark Iliw-Iliw RelingadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10:32:30 Am 10:33:00 Am 10:34:00 Am 10:36:00 Am 10:40:00 Am 10:47:00 Am 11:00:00 Am 11:32:00 Am 12:32:00 PM 2:32:00 PM 6:02:30 PM 10:32:00 Am 10:32:00 Am 10:32:00 AmDokument48 Seiten10:32:30 Am 10:33:00 Am 10:34:00 Am 10:36:00 Am 10:40:00 Am 10:47:00 Am 11:00:00 Am 11:32:00 Am 12:32:00 PM 2:32:00 PM 6:02:30 PM 10:32:00 Am 10:32:00 Am 10:32:00 AmAnonymous 0JPCPZHNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooper-Jakob V2 Todd 2005-441Dokument8 SeitenCooper-Jakob V2 Todd 2005-441Park IlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dial Gauge Reading (DGR) Proving Ring Reading (PRR) XC Strain % Deviator Load WD PRR CF Corrected Area Deviator Stress, KG/CM CF C Ao 1 - (DL/L)Dokument12 SeitenDial Gauge Reading (DGR) Proving Ring Reading (PRR) XC Strain % Deviator Load WD PRR CF Corrected Area Deviator Stress, KG/CM CF C Ao 1 - (DL/L)Shreyans DodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- As3 Triaxial SG-SJ ValoresDokument39 SeitenAs3 Triaxial SG-SJ ValoresSantiago Maldonado LeoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Classification ChartDokument2 SeitenSoil Classification ChartTiny WOnderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Triaxial Test ResultsDokument1 SeiteAnalysis of Triaxial Test ResultsGents HeydNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shallow Footing Bearing CapacityDokument1 SeiteShallow Footing Bearing CapacityMalayKumarDebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deep - Foundations Ex 14.4Dokument13 SeitenDeep - Foundations Ex 14.4Rohan JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation: Formula For Moisture Content W (Weight of Water/ Weight of Soil) X 100Dokument8 SeitenCalculation: Formula For Moisture Content W (Weight of Water/ Weight of Soil) X 100SilverfangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oedometer Raw DataDokument14 SeitenOedometer Raw Datamastergeo35Noch keine Bewertungen
- For 30 Sq. CM Area Before TestDokument45 SeitenFor 30 Sq. CM Area Before TestFairyssa Duron AfinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atterberg LimitDokument2 SeitenAtterberg LimitAshraf KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plate Load Test: Land-Drill Geotechnics LTDDokument5 SeitenPlate Load Test: Land-Drill Geotechnics LTDJimmy MollonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Bearing Capacity: E.C.P Bearing Capacity Factors Bearing Capacity Factors GraphDokument6 SeitenSoil Bearing Capacity: E.C.P Bearing Capacity Factors Bearing Capacity Factors GraphMohamed HagrassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sieve Analysis GraphDokument6 SeitenSieve Analysis GraphDeserie JoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPT Correlation n60 and n'60 To Odst As Per AashtoDokument4 SeitenSPT Correlation n60 and n'60 To Odst As Per AashtoAstrid AubryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Stress 8Dokument1 SeiteSoil Stress 8Akhtar BahramNoch keine Bewertungen
- C (Kpa) 60 F 30 Depth of The Pile (M) 20 Dia of The Pile (M) 0.5 D/B 40 A 0.45 0.7 F/D 0.6 Fos (Skin) 2.5 Fos (Base) 2.5 KS/KDokument6 SeitenC (Kpa) 60 F 30 Depth of The Pile (M) 20 Dia of The Pile (M) 0.5 D/B 40 A 0.45 0.7 F/D 0.6 Fos (Skin) 2.5 Fos (Base) 2.5 KS/KNita NabanitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation Test Specimen DataDokument6 SeitenConsolidation Test Specimen DataSyafrizal ThaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil GSB WMM by Sand Replacement MethodDokument2 SeitenSoil GSB WMM by Sand Replacement MethodBrahammanand BairwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grain Size Analysis For SoilsDokument11 SeitenGrain Size Analysis For SoilsyogananthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corrected SPT 1Dokument7 SeitenCorrected SPT 1Mohamed YasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA TerzaghiDokument15 SeitenQA TerzaghiErnesto BencosmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 5249 1992 PDFDokument16 SeitenIs 5249 1992 PDFrentu skNoch keine Bewertungen
- SBC Mixed FailureDokument1 SeiteSBC Mixed Failuresatheb319429Noch keine Bewertungen
- Consolidation 15 16Dokument30 SeitenConsolidation 15 16magfirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEO Rock Mass Mapping ProformaDokument1 SeiteGEO Rock Mass Mapping Proformaklau avNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Cutter TestDokument6 SeitenCore Cutter TestMian M KhurramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Temperature and Heat Flow: CE/ENVE 320 - Vadose Zone Hydrology/Soil Physics Spring 2004Dokument37 SeitenSoil Temperature and Heat Flow: CE/ENVE 320 - Vadose Zone Hydrology/Soil Physics Spring 2004shubanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Properties of Representative Soils of The Czech RepublicDokument10 SeitenThermal Properties of Representative Soils of The Czech RepublicAlejandra VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBE Thermal Comfort Tool For ASHRAE-55 80 42 PDFDokument1 SeiteCBE Thermal Comfort Tool For ASHRAE-55 80 42 PDFIaraFerreiradeRezendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBE Thermal Comfort Tool For ASHRAE-55 80 42Dokument1 SeiteCBE Thermal Comfort Tool For ASHRAE-55 80 42IaraFerreiradeRezendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- KD2 Pro - WebDokument71 SeitenKD2 Pro - WebIaraFerreiradeRezendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uan 2006 Soil Tillage ResearchDokument28 SeitenUan 2006 Soil Tillage ResearchNikhil100% (1)
- 2018 Agrawal 3rd SEEC Conference IIT Roorkee (Paper 11)Dokument4 Seiten2018 Agrawal 3rd SEEC Conference IIT Roorkee (Paper 11)Kamal Kumar AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011, Ongoing Aspects in Geotechnical Engineering, O. Leibniz, S. Semprich, K. Gell PDFDokument135 Seiten2011, Ongoing Aspects in Geotechnical Engineering, O. Leibniz, S. Semprich, K. Gell PDFVasile BudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Temperature and Heat Flow: CE/ENVE 320 - Vadose Zone Hydrology/Soil Physics Spring 2004Dokument37 SeitenSoil Temperature and Heat Flow: CE/ENVE 320 - Vadose Zone Hydrology/Soil Physics Spring 2004shubanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SoilThermalResistivity PDFDokument29 SeitenSoilThermalResistivity PDFgnklol3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soil Thermal Properties PDFDokument3 SeitenSoil Thermal Properties PDFIaraFerreiradeRezendeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Resistivity Tests June 26 June 2016Dokument5 SeitenThermal Resistivity Tests June 26 June 2016AliAl-naqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Performance Analysis of Earth-Air-Pipe-Heat Exchanger System With Different Backfilling MaterialsDokument5 SeitenThermal Performance Analysis of Earth-Air-Pipe-Heat Exchanger System With Different Backfilling MaterialsKamal Kumar AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen