Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture17sec - Midmidterm 2 Review PDF
Hochgeladen von
jasminetsoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture17sec - Midmidterm 2 Review PDF
Hochgeladen von
jasminetsoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Midterm II Review
15.501/516 Accounting
Spring 2004
Professor S. Roychowdhury
Sloan School of Management
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
April 12, 2004
2
z
i
z
z
z
z i
Exam Structure
Ques 1:
Long L ved Assets
Ques 2:
Marketable Securities
Ques 3
Bond Accounting
Ques 4
Lease Accounting
Expect to be tested on anything d scussed in class
3
z ini
z i i
z
z
z
z
z i i
z
z
Key Issues in Long-Lived Assets
Determ ng acquisition cost
Sett ng up depreciat on schedule
Estimating Salvage Value
Estimating useful life
Determining a depreciation method, in most cases, straight
line for financial reporting purposes
Depreciation per year =
(Acquisition Cost Salvage Value)/ (Useful Life)
Changes in depreciat on est mates
Asset disposal
Deferred taxes
Page 1
Change in Depreciation
Estimates
z Apply the change prospectively, i.e., to future
years (no restatement of past years results)
z Check example already done in class
4
Disposal (retirement): Gain or
Loss
z Computation:
z Gain (Loss) = Proceeds from selling the asset - book value,
z where BV = Acquisition cost - Accumulated Depreciation
associated with the asset
z Bookkeeping: Remove assets historical cost and accumulated
depreciation from the balance sheet and record Gain (Loss).
z Gain/Loss on sale of asset included in Income Statement, often as
part of Other Income
z In Indirect Cash Flow statement, gain/loss on asset sale is
explicitly subtracted/added back to Net Income, respectively, to
arrive at Cash Flow from Operations.
z Proceeds from sale are reported in the Investing section of Cash
Flow Statement
5
Deferred Tax Accounting
z Differences between the tax rate of depreciation and
the book rate of depreciation will give rise to
deferred tax liabilities
z In any year, change in deferred tax liability =
(Tax depreciation Book depreciation)*tax rate
z Above also called deferred tax expense
z Income tax expense = Tax expense recorded in
income statement
z Income tax payable = actual taxes that have to be
paid to government
6
Page 2
Marketable Securities
z Three classes of securities
z Held to maturity (debt only)
z Acquired with ability and intent to hold to maturity
z No changes in market value reported in the income statement, thus
investment carried at historical cost in the balance sheet
z Interest income reported in operating section of SCF
z Trading securities (debt and equity)
z Acquired for short-term profit potential
z Changes in market value reported in the income statement (net of taxes),
investment marked to market in the balance sheet
z Purchases and disposals reported in operating section of SCF
z Available for sale (debt and equity)
z Securities not classified as either of above
z Changes in market value reported in Other Equity (net of taxes), instead of
the income statement!
z Purchases and disposals reported in investing section of SCF
7
Marking to market
z For both Trading and AFS securities
z Book value of security investments tracks market value
z Done via a Marketable Securities Adjunct Account
z Balance sheet effects are the same! Marketable Securities and total
Stockholders Equity will be the same.
z Balance in Deferred Tax Liability Account will be the same
z What is different?
z Income statement effects
z For trading securities, gains or losses recognized in Income Statement
track changes in market value
z For AFS securities, gains or losses net of taxes are cumulatively
recorded in Other Equity till securities are sold
z At that time, all gains and losses are recognized in Income Statement
and the Other Equity account as well as Deferred Tax Liability
account is cleared off.
z Important work through detailed numerical example done in class
8
Present Values and Bonds
z Present Value Concepts will not be tested
directly, only through bond and lease accounting
z Three kinds of bond structure discussed in class
z Coupon Bond
z At par, discount or premium
z Zero Coupon Bond
z Bond structured as mortgage/annuity relatively
infrequent
9
Page 3
Key Common Features of
Bond Accounting
z Net Bonds Payable issued by a company is always recorded at the present
value of future cash outflows promised to bond investors or the market
value at issuance
z Bonds Payable is recorded at Face Value. A Discount/Premium account
is set up to capture the difference between market value at time of issuance
and Face Value
z Cash payment before and at maturity is as specified in the terms of the
bond will vary by bond structure (see last slide)
z Interest payment in any year =
(Market interest rate at time of issuance) * (Net Bonds Payable at the
beginning of the year)
z The difference between Cash Payment and Interest Expense reduces the
Discount/Premium Account
10
Early Retirement of Debt
You repurchase Zero-Coupon bonds (Face Value = $ 11,910) in the
open market at the start of 2002 (2 years to maturity) when the market
rate is 5%. Market rate at time of issuance is 6%.
What is the market price of the bonds at that time?
PV
0
= FV
n
/ (1+r)
n
PV
0
= 11,910 / (1.05)
2
= 10,803
What is the effect on the BSE and financial statements?
Cash (A) = Bond Principal - Discount + RE
BB 11,910 - 1,310
(10,803) (11,910) (1,310) (203)
The gain or loss on early retirement of debt is reported as an
extraordinary item on the income statement.
What is the journal entry?
11
On Bond Accounting
z If you have the terms of the bond, you should
be able to calculate book value of the bond at
the end of any period, interest rate at time of
issuance, etc.
12
Page 4
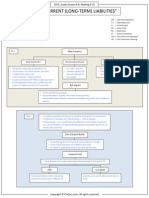
Lease accounting
z Differences between operating lease and capital
lease
z What conditions are used to classify a lease as a
capital lease?
z Lease footnotes what they do and dont tell you
z Lease liability at the end of any year = Present value
of future lease payments at the lease capitalization
rate (or effective interest rate)
z Is it possible to work out lease liability if operating
leases were instead classified as capital leases?
13
Summary
z Read Question Carefully answer all parts
z You will probably see questions on Journal Entries
or T-accounts involving any of the topics for this
midterm
z Do Not Panic If its on the exam, you have seen it
before
z Good Luck
14
Page 5
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Intermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideVon EverandIntermediate Accounting 2: a QuickStudy Digital Reference GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- PAT + Depreciation + Interest On Term CommitmentsDokument4 SeitenPAT + Depreciation + Interest On Term CommitmentsarunapecNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Von EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (17)
- Chapter - 7 Income Statements Learning Objectives: Dr. Trading A/C CRDokument14 SeitenChapter - 7 Income Statements Learning Objectives: Dr. Trading A/C CRSaket_srv2100% (1)
- Bond Yields DurationDokument18 SeitenBond Yields DurationKaranbir Singh RandhawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Com 5 Sem Advance Financial Accounting 1Dokument9 SeitenB. Com 5 Sem Advance Financial Accounting 1AlankritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Bond Prices and YieldsDokument36 SeitenChapter 11 Bond Prices and Yieldssharktale2828Noch keine Bewertungen
- Long-Term Debt: 15.515 2003 Session 13Dokument7 SeitenLong-Term Debt: 15.515 2003 Session 13krissh_87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesDokument7 SeitenChapter 1 - Current LiabilitiesAnton LauretaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fa4e SM Ch09Dokument36 SeitenFa4e SM Ch09michaelkwok1100% (1)
- Investment AccountsDokument7 SeitenInvestment AccountsRiju Varkey ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- English For The Financial Sector: Mohamed - Diab@univ-Msila - DZDokument5 SeitenEnglish For The Financial Sector: Mohamed - Diab@univ-Msila - DZAli KerbabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bloomberg Professional For Bond Pricing & Yield To MaturityDokument5 SeitenBloomberg Professional For Bond Pricing & Yield To MaturityjujonetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investment New ScopeDokument19 SeitenInvestment New ScopeayinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slide 2 Learning ObjectiveDokument11 SeitenSlide 2 Learning ObjectiveHaikal Nur FahreziNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 12 Powerpoint A334Dokument62 SeitenCH 12 Powerpoint A334ThiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACCA F7 SummaryDokument10 SeitenACCA F7 SummaryLai AndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 32Dokument6 SeitenFinQuiz - Smart Summary - Study Session 9 - Reading 32RafaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Libby 4ce Solutions Manual - Ch11Dokument59 SeitenLibby 4ce Solutions Manual - Ch117595522Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial TermsDokument35 SeitenFinancial TermsJosafat BasurtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting StandardDokument93 SeitenAccounting Standardsiddhi1234pedNoch keine Bewertungen
- NISM ModuleDokument222 SeitenNISM ModulepiyushpritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Assets at Amortized CostDokument8 SeitenFinancial Assets at Amortized CostbluemajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Investments in Debt Securities and Other Non-Current Financial AssetsDokument56 SeitenChapter 3 - Investments in Debt Securities and Other Non-Current Financial AssetsYel75% (4)
- BA 141 RatiosDokument14 SeitenBA 141 RatiosNigelT.LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIN 408 - Ch.10Dokument26 SeitenFIN 408 - Ch.10Shohidul Islam SaykatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Global Bond InvestmentDokument51 SeitenChapter 5 Global Bond InvestmentThư Trần Thị AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap012 - InvestmentsDokument46 SeitenChap012 - InvestmentsShynara MuzapbarovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (A+F) NYU OutlineDokument14 Seiten(A+F) NYU OutlineShawn BuskovichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actuarial Society of India: ExaminationsDokument8 SeitenActuarial Society of India: ExaminationsRewa ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bond Market Maths: Group Members Swarana Biyani - 01 Sanket Desai - 02 Rohan Jadhav - 08 Shama Lonare - 14Dokument74 SeitenBond Market Maths: Group Members Swarana Biyani - 01 Sanket Desai - 02 Rohan Jadhav - 08 Shama Lonare - 14Namrata KolteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Final Review NotesDokument8 SeitenAccounting Final Review NotesARHistoryHubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaire IntactDokument10 SeitenQuestionnaire Intact?????Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter6 - Trial balance and Preparation of Final Accounts яDokument13 SeitenChapter6 - Trial balance and Preparation of Final Accounts яshreya taluja100% (1)
- ACCA Financial InstrumentsDokument8 SeitenACCA Financial Instrumentsyung kenNoch keine Bewertungen
- IA Chap. 19, 20, and 22Dokument31 SeitenIA Chap. 19, 20, and 22Pitel O'shoppeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interest Rate Swap ValuationDokument7 SeitenInterest Rate Swap Valuationamanmanji2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Retained EarningsDokument6 SeitenRetained EarningsLeslie FaustinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plugin Ifrs Investment Funds Issue 1b 686Dokument0 SeitenPlugin Ifrs Investment Funds Issue 1b 686xuhaibimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intercorporate Investments and Accounting For International OperationsDokument23 SeitenIntercorporate Investments and Accounting For International Operationsarshad mNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Bond Market - For BSAISDokument63 SeitenThe Bond Market - For BSAISAngela Dela PeñaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Strength of Southeast Bank LimitedDokument7 SeitenFinancial Strength of Southeast Bank LimitedEasin Mohammad RomanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Standard 11Dokument5 SeitenAccounting Standard 11Gmd NizamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment: Ques1. What Is Beta?Dokument5 SeitenAssignment: Ques1. What Is Beta?Richa MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting and Interpreting Bonds: Answers To QuestionsDokument43 SeitenReporting and Interpreting Bonds: Answers To QuestionsceojiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kaplan - SBR Simplest SummaryDokument13 SeitenKaplan - SBR Simplest Summarymuazzam.danganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bonds, Bond Valuation, Interest Rates - Session 7 - 8Dokument19 SeitenBonds, Bond Valuation, Interest Rates - Session 7 - 8anon_974035635Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting For InvestmentDokument14 SeitenAccounting For Investmentefe davidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin 4828 CH 1-7Dokument4 SeitenFin 4828 CH 1-7Heather KellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 413sol3 04Dokument17 Seiten413sol3 04drtoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial Balance To Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet For Corporate & Non-Corporate EntitiesDokument24 SeitenTrial Balance To Profit & Loss A/c and Balance Sheet For Corporate & Non-Corporate EntitiesChintan PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- As-22 Accounting For Taxes On Income - Brief NoteDokument5 SeitenAs-22 Accounting For Taxes On Income - Brief NoteKaran KhatriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Flow ProjectionsDokument36 SeitenCash Flow ProjectionsJoy FaruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit V: Financial AccountingDokument31 SeitenUnit V: Financial AccountingAbhishek Bose100% (2)
- 4 Bond and StockDokument32 Seiten4 Bond and Stockmahwish111Noch keine Bewertungen
- 395 33 Powerpoint Slides 6 Valuation Management Bonds CHAPTER 6Dokument41 Seiten395 33 Powerpoint Slides 6 Valuation Management Bonds CHAPTER 6Parlikad JayaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- SwapsDokument44 SeitenSwapsAditya Paul SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Investments in Debt SecuritiesDokument24 SeitenChapter 10 Investments in Debt SecuritiesChristian Jade Lumasag NavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investments and AcquisitionsDokument5 SeitenInvestments and AcquisitionsBurhan Al MessiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bs en Iso 1 1:2012 4064Dokument32 SeitenBs en Iso 1 1:2012 4064jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorldGBC ANZ Status Report 2021 - FINALDokument25 SeitenWorldGBC ANZ Status Report 2021 - FINALjasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Standard: Risk Management - GuidelinesDokument24 SeitenInternational Standard: Risk Management - Guidelinesjasminetso100% (14)
- 01 GasolineDokument9 Seiten01 GasolineYarin HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graduate STEM Education For The 21st CenturyDokument203 SeitenGraduate STEM Education For The 21st CenturyJuan PobleteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inspect The BuildingDokument5 SeitenInspect The BuildingjasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Note For Finance CommitteeDokument8 SeitenNote For Finance CommitteejasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Research ProposalDokument8 SeitenExample Research ProposalMarco BarretoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ultimate Guide To Benchmarking Construction WorkflowsDokument13 SeitenThe Ultimate Guide To Benchmarking Construction WorkflowsjasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Next Normal in ConstructionDokument90 SeitenThe Next Normal in ConstructionRodrigo Giorgi100% (1)
- BIM International Edition 2020Dokument36 SeitenBIM International Edition 2020Edward C100% (1)
- Revised RODP 500x500Dokument1 SeiteRevised RODP 500x500jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Solucionario Quimica La Ciencia Central 9na Edicion BrownDokument2 SeitenPDF Solucionario Quimica La Ciencia Central 9na Edicion BrownSofia VelásquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Certificate in Principles of New Engineering Contract (NEC)Dokument1 SeiteCertificate in Principles of New Engineering Contract (NEC)jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Sample Template of WI Preambles To Specifications V1.0 201610Dokument5 Seiten11 Sample Template of WI Preambles To Specifications V1.0 201610Bruce WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Sample Template For BQ Preambles V1!1!201703Dokument7 Seiten13 Sample Template For BQ Preambles V1!1!201703Jasmine TsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEC Collaboration CLLB Ti: Practice NotesDokument122 SeitenNEC Collaboration CLLB Ti: Practice NotesCT0011Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Format of Grand Summary of The Activity Schedule / Bill of Quantities in NEC ECC ContractsDokument1 SeiteSample Format of Grand Summary of The Activity Schedule / Bill of Quantities in NEC ECC ContractsjasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEC3 Delegate Handbook v2 - Sept2018Dokument39 SeitenNEC3 Delegate Handbook v2 - Sept2018jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Nec Ecc PN V1.0 201610 PDFDokument120 Seiten01 Nec Ecc PN V1.0 201610 PDFghjtyu0% (1)
- CWDCS Web Basic 20210129Dokument1.050 SeitenCWDCS Web Basic 20210129jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix To The General Conditions of Tender Correction Rules For Tender Errors (General Conditions of Tender Clause GCT 11)Dokument15 SeitenAppendix To The General Conditions of Tender Correction Rules For Tender Errors (General Conditions of Tender Clause GCT 11)Jasmine TsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contract Clause "Hired and Hire-Purchase Constructional Plant". The Project Offices ShouldDokument17 SeitenContract Clause "Hired and Hire-Purchase Constructional Plant". The Project Offices ShouldjasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emp 1201Dokument12 SeitenEmp 1201jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fig 22-10 Experiments: Experiment A Experiment E +++++ +++++ +++++ +++ ++ ++ ++ +Dokument1 SeiteFig 22-10 Experiments: Experiment A Experiment E +++++ +++++ +++++ +++ ++ ++ ++ +jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CWDCS Web Basic 20210129Dokument1.050 SeitenCWDCS Web Basic 20210129jasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICNIRPemfgdl 1Dokument38 SeitenICNIRPemfgdl 1lukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Register of Rics Accredited MediatorsDokument3 SeitenRegister of Rics Accredited MediatorsjasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architecture Design Handbook - Fundamentals - Radio Frequency ShieldingDokument1 SeiteArchitecture Design Handbook - Fundamentals - Radio Frequency ShieldingjasminetsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bim 2019Dokument4 SeitenBim 2019jasminetso100% (1)
- IM On ACCO 20043 Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 2 - FINALDokument106 SeitenIM On ACCO 20043 Financial Accounting and Reporting Part 2 - FINALlorah jane SilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief Description On The CompanyDokument4 SeitenBrief Description On The CompanyDuong Trinh MinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- U 1 - Financial StatementsDokument20 SeitenU 1 - Financial Statementsbashaer abubakrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting For Business Combination - Practice MaterialDokument2 SeitenAccounting For Business Combination - Practice MaterialZYRENE HERNANDEZNoch keine Bewertungen
- United Paragon Mining Corporation SEC 17 Q June302020Dokument51 SeitenUnited Paragon Mining Corporation SEC 17 Q June302020Jon DonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barclays SQ U.S. Payments, Processors & IT Services A Look at The WDokument22 SeitenBarclays SQ U.S. Payments, Processors & IT Services A Look at The Woldman lokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balance Sheet As at 31st December, 2015 Liabilities Rs. Assets RsDokument3 SeitenBalance Sheet As at 31st December, 2015 Liabilities Rs. Assets RsTrendingNoch keine Bewertungen
- A AU UD DI IT TI IN NG G P PR RO OB BL LE EM MS S: Quiz No. 6 Quiz No. 6Dokument13 SeitenA AU UD DI IT TI IN NG G P PR RO OB BL LE EM MS S: Quiz No. 6 Quiz No. 6Shane CabinganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Finance LectureDokument124 SeitenCorporate Finance LectureMuhammad Kashif ZafarNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIMA 30013 FS Analysis Premium FSDokument4 SeitenFIMA 30013 FS Analysis Premium FSdcdeguzman.pup.pulilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit .2 The Accounting CycleDokument29 SeitenUnit .2 The Accounting CycleYonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Ledger Default AccountsDokument4 SeitenGeneral Ledger Default AccountsAhmed ElghannamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Office ExampleDokument5 SeitenHome Office ExampleGwenn VillamorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Posting and Preparation of Trial Balance 1Dokument33 SeitenPosting and Preparation of Trial Balance 1iTs jEnInONoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ConsolidationDokument33 SeitenBasic ConsolidationSrabon BaruaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ias 12 Income TaxesDokument5 SeitenIas 12 Income TaxessomicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting Libby 7th Edition Solutions ManualDokument5 SeitenFinancial Accounting Libby 7th Edition Solutions Manualstephaniehornxsoiceygfp100% (46)
- Acctg7 - CH 8Dokument22 SeitenAcctg7 - CH 8Jao FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8811 Chartof Accounts 6 TheditionelectronicversionDokument127 Seiten8811 Chartof Accounts 6 TheditionelectronicversionNyasha MakoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dry RunDokument5 SeitenDry RunMarc MagbalonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conso FS SubsequentDokument1 SeiteConso FS SubsequentreiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projected Cash Flow Statement in ExcelDokument19 SeitenProjected Cash Flow Statement in ExcelfarshidianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reen LawnsDokument8 SeitenReen LawnsAshish BhallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepare Adjusting Entries For DeferralsDokument15 SeitenPrepare Adjusting Entries For DeferralsKirammin Bararrah100% (1)
- 8919 - Consolidation Subsequent To The Date of AcquisitionDokument4 Seiten8919 - Consolidation Subsequent To The Date of AcquisitionFayehAmantilloBingcangNoch keine Bewertungen
- F7 Workbook Q PDFDokument129 SeitenF7 Workbook Q PDFDipak GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDokument13 SeitenSdebate ddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gesco Kabab: Worksheet For The Month Ended in December 31, 2021Dokument20 SeitenGesco Kabab: Worksheet For The Month Ended in December 31, 2021TanjinNoch keine Bewertungen
- (ASC) Accounting For Business CombinationDokument13 Seiten(ASC) Accounting For Business CombinationRENZ ALFRED ASTRERONoch keine Bewertungen
- Enero - ACC 222 Exercise - FS AnalysisDokument4 SeitenEnero - ACC 222 Exercise - FS AnalysisregineNoch keine Bewertungen