Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dec2012 Milk Adulteration
Hochgeladen von
rakesh53390 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten1 SeiteMethods for detection of common adulterants in milk and milk products.
These are very simple tests which can be done at home.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMethods for detection of common adulterants in milk and milk products.
These are very simple tests which can be done at home.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
23 Ansichten1 SeiteDec2012 Milk Adulteration
Hochgeladen von
rakesh5339Methods for detection of common adulterants in milk and milk products.
These are very simple tests which can be done at home.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
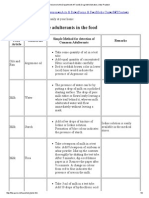
S no.
Product Adulterant Method of detection Remarks
1 Milk Water The presence of water can be detected by putting a drop of milk on a
polished slanting surface. The drop of pure milk flows leaving a white
trail behind, whereas milk adulterated with water will flow immediately
without leaving mark
2 Milk Starch Add a few drops of tincture of iodine or iodine solution. Formation of Iodine solution is easily available
blue colour indicates the presence of starch in medical stores
3 Milk Urea Take a teaspoon of milk in a test tube. Add teaspoon of soybean or
arhar powder. Mix up the contents thoroughly by shaking the test tube.
After five minutes, dip a red litmus paper in it. Remove the paper after
half a minute. A change in colour from red to blue indicates the
presence of urea in the milk.
4 Milk Vanaspati Take 3 ml of milk in a test tube. Add 10 drops of hydrochloric acid.
Mix up one teaspoonful of sugar. After 5 minutes, examine the mixture.
The red colouration indicates the presence of Vanaspati in milk.
5 Milk Formalin Take 10 ml of milk in a test tube and add 5 ml of conc. Sulphuric acid Formalin enhances the life of
from the sides of the wall without shaking. If a violet or blue ring milk and thus is added for
appears at the intersection of the two layers then it shows presence preservation purpose.
of formalin.
6 Milk Detergent Shake 5-10 ml of sample with an equal amount of water, lather indicates
the presence of a detergent.
7 Milk Synthetic Milk Synthetic milk has a bitter after taste, gives a soapy feeling on rubbing
between the fingers and turns yellowish on heating.
8 Milk Synthetic milk- The milk can easily be tested by urease strips because synthetic milk is
test for protein devoid of protein.
9 Milk Glucose/ Milk does not contain glucose/inverted sugar, if test for glucose with If it is made synthetically by
Inverted sugar urease strip is found positive. It means milk is adulterated. adding colour, water, paint, oils,
alkali, detergent etc.Glucose/
inverted sugar syrup is added to
milk to increase consistency and
test.
10 Ghee, cottage Coal tar dyes Add 5 ml of dilute sulphuric acid or conc. Hydrochloric acid to one teaspoon
cheese, full of melted sample in a test tube. Shake well. Pink colour (in case of
condensed sulphuric acid) or crimson colour ( in case of hydrochloric acid) indicates coal
milk, khoa, tar dyes. If hydrochloric acid does not give colour, dilute it with water to get
milk powder colour.
etc.
S. no Food article adulterant Method for detection Remarks
1 Sweet Curd Vanaspati Take 1 teaspoon full of curd in a test tube. Add 10 drops of hydrochloric acid.
Mix up the contents shaking the test tube gently. After 5 minutes, examine
the mixture. Red colouration indicates the presence of Vanaspati.
2 Rabdi Blotting paper Take a teaspoon of rabri in a test tube. Add 3 ml of hydrochloric acid and 3 ml
of distilled acid. Stir the contents with a glass rod. Remove the rod and
examine. Presence of fine fibres to the glass rod will indicate the presence of
blotting paper.
3 Khoa and Starch Boil a small quantity of sample with some water, cool and add a few drops of
its products iodine solution. Formation of blur colour indicates the presence of starch.
4 Chhana or Starch Boil a small quantity of sample with some water, cool and add a few drops of
Paneer iodine solution. Formation of blue colour indicates the presence of starch.
S. no Food article adulterant Method for detection Remarks
1 Ghee Vanaspati or Take about on teaspoon full of melted ghee with equal quantity of conc. The test is specific for sesame oil
Margarine Hydrochloric acid in a stoppered test tube and add to it a pinch of sugar. which is compulsorily added to
Shake for 1 minute and leave for 5 minutes. Appearance of crimson colour Vanaspati and Margarine. Some coal
in lower (acid) indicates presence of Vanaspati or margarine. tar colours also give a positive test.
If the test is positive i.e. red colour
develops only by adding strong
hydrochloric acid (without adding
crystals of sugar) then the sample is
adulterated with coal tar dye. If the
crimson or red colour develops after
adding and shaking with sugar, then
alone Vanaspati or margarine is
present.
2 Ghee Mashed The presence of mashed potatoes or sweet potatoes in a sample of ghee can
potatoes, be easily detected by adding a few drops of iodine, which is brownish in
sweet colour turns to blue if mashed potatoes/sweet potatoes/other starches
potatoes are present.
and other
starches
3 Butter Vanaspati Take about one teaspoon full of melted sample of butter with equal quantity The test is specific for sesame oil
or margarine of conc. Hydrochloric acid in a stoppered test tube and add to it a pinch of which is compulsorily added to
sugar. Shake for i minute and let it for 5 minutes. Appearance of crimson Vanaspati and Margarine. Some coal
colour in lower (acid) of Vanaspati or margarine. tar colours also give a positive test.
If the test is positive i.e. red colour
develops only by adding strong
hydrochloric acid (without adding
crystals of sugar) then the sample is
adulterated with coal tar dye. If the
crimson or red colour develops after
adding and shaking with sugar, then
alone Vanaspati or margarine is
present.
4 Butter Mashed The presence of mashed potatoes or sweet potatoes in a sample of butter
potatoes can easily be detected by adding a few drops of iodine (which is brownish
and other in colour), turns to blue.
starches
5 Edible oil Prohibited Take 5 ml of sample in a test tube and add 5ml of conc. Hydrochloric acid.
colour Shake gently; let it stand for 5 minutes. Colour will separate in the upper
layer of the solution.
6 Coconut oil Ant other oil Place a small bottle of oil in refrigerator. Coconut oil solidifies leaving the
adulterant as a separate layer.
Methods for detection of common adulterants in milk and milk products
MILK
MILK PRODUCTS
OILS AND FATS
Source: Food Safety and Standard Authority of India
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Milk Water The Presence of Water Can Be by Putting A Drop of Milk On A Polished Slanting SurfaceDokument1 SeiteMilk Water The Presence of Water Can Be by Putting A Drop of Milk On A Polished Slanting SurfaceNithish KannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Adulteration and Its Quick TestDokument17 SeitenFood Adulteration and Its Quick TestZubair AbidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detection of Food AdulterationDokument10 SeitenDetection of Food AdulterationDavara Paresh R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Food Adultration: Types of Food AdulterationDokument6 SeitenFood Adultration: Types of Food AdulterationshiviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adulto-Meter: Use of Technology To Test Adulteration of Edible ProduceDokument4 SeitenAdulto-Meter: Use of Technology To Test Adulteration of Edible ProduceSreejithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food AdulterationDokument15 SeitenFood AdulterationSelvasundar Kumar100% (1)
- Analysis of MilkDokument6 SeitenAnalysis of MilkSwati RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project-24: Study of Common Food Adulterants in Fat, Oil, Butter, Sugar, Turmeric Powder, Chilli Powder and PepperDokument4 SeitenProject-24: Study of Common Food Adulterants in Fat, Oil, Butter, Sugar, Turmeric Powder, Chilli Powder and PepperMayank KatiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milk and Milk ProductsDokument16 SeitenMilk and Milk ProductsSubhabrata MabhaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milk AdulterationDokument6 SeitenMilk AdulterationAlex1315Noch keine Bewertungen
- Product TestingDokument8 SeitenProduct TestingmanishrastogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detect Formalin in MilkDokument3 SeitenDetect Formalin in MilkboonsomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tests To Detect Adulteration in MilkDokument3 SeitenTests To Detect Adulteration in Milksng1607Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tests To Detect Adulteration in MilkDokument5 SeitenTests To Detect Adulteration in MilkezhilnarasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food AdulterationsDokument6 SeitenFood AdulterationsKamaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adulteration ManualDokument4 SeitenAdulteration ManualAshish GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry ProjectDokument20 SeitenChemistry Projectsanjeev sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To The Department of Food & Drug Administration, Uttar PradeshDokument9 SeitenWelcome To The Department of Food & Drug Administration, Uttar PradeshUtk AgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Neutralizers, Adulterants and Preservatives in Milk and Milk ProductsDokument17 SeitenEstimation of Neutralizers, Adulterants and Preservatives in Milk and Milk ProductsRishi DadhichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atharva Yogesh Pawar Class: V TH B Sanjivani AcademyDokument23 SeitenAtharva Yogesh Pawar Class: V TH B Sanjivani AcademyPriyanka PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- S - N - T Page No. C: L O OpicDokument15 SeitenS - N - T Page No. C: L O OpicAbhishek RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adult Rants and PreservativesDokument7 SeitenAdult Rants and PreservativesAjitKumarJhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Tests For Various Adulterations in FoodDokument5 SeitenChemical Tests For Various Adulterations in FoodSinivas ParthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing Methodology Preparation of Milk Sample For Analysis: ReferenceDokument1 SeiteTesting Methodology Preparation of Milk Sample For Analysis: ReferenceJoselynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sunday, November 2, 2008Dokument4 SeitenSunday, November 2, 2008shruti_10garg9349Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tests To Detect Adulteration of MilkDokument3 SeitenTests To Detect Adulteration of MilkvipulrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Food AdulterationDokument17 SeitenCommon Food AdulterationAbhaySharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harsh Food AdultrationDokument13 SeitenHarsh Food AdultrationHarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bakery - FOOD ADULTERATIONDokument22 SeitenBakery - FOOD ADULTERATIONPamilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Biosciences: Report of Microbial and Chemical Analysis of Milk and Milk Products at SUMUL Dairy, SuratDokument37 SeitenDepartment of Biosciences: Report of Microbial and Chemical Analysis of Milk and Milk Products at SUMUL Dairy, SuratTaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platform TestDokument5 SeitenPlatform Testmohityahoo100% (1)
- Idoc - Pub Common Food AdulterationDokument17 SeitenIdoc - Pub Common Food AdulterationSudarshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adulterants in Foods and Its Detection MethodsDokument13 SeitenAdulterants in Foods and Its Detection MethodsprinceejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food AdulterationDokument14 SeitenFood AdulterationAnmol YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baraka WordDokument19 SeitenBaraka WordBosire keNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report - Adulteration of Foods r1Dokument13 SeitenProject Report - Adulteration of Foods r1S Balagopal SivaprakasamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adulteration Lab ReportDokument8 SeitenAdulteration Lab ReportchromeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milk Analysis in Verka 1307073649 Phpapp02 110602230930 Phpapp02Dokument62 SeitenMilk Analysis in Verka 1307073649 Phpapp02 110602230930 Phpapp02Jeganathan RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adultrants by Veena MamDokument50 SeitenAdultrants by Veena MamAayushi BalyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Adulteration Chemistry Class 12 ProjectDokument11 SeitenFood Adulteration Chemistry Class 12 ProjectagargfawgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Project Class 12Dokument13 SeitenChemistry Project Class 12chemistry projectNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Adulteration Chemistry Class 12 ProjectDokument10 SeitenFood Adulteration Chemistry Class 12 ProjectRockstas ArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milk Adulteration TestsDokument5 SeitenMilk Adulteration TestsMudassar IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adulteration in Food StuffDokument19 SeitenAdulteration in Food StuffPranav ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Food AdulterationDokument18 SeitenCommon Food AdulterationShyam JalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-5 Simple Tests For Common Adulterants in Food: AddedDokument3 SeitenA-5 Simple Tests For Common Adulterants in Food: AddedTanmay JagetiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food AdulterationDokument17 SeitenFood Adulterationatarushi9383% (18)
- FC. Lab Manual Second YearDokument15 SeitenFC. Lab Manual Second YearMengistu FisehaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Chemistry Testing SUGAR, STARCH ETCDokument5 SeitenFood Chemistry Testing SUGAR, STARCH ETCrangerblue75% (12)
- Common Food Adulteration ProjectDokument20 SeitenCommon Food Adulteration Projectn611704Noch keine Bewertungen
- Food Chemistry Testing SUGAR STARCH ETCDokument5 SeitenFood Chemistry Testing SUGAR STARCH ETCStephanie Ngooi Ming MingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vegan Bath and Beauty Recipes: 50 Recipes for Soaps, Bath Salts, Bubble Baths, Shower Gels and Bath Fizzies, Bath Bombs, and Body Wash: Skin Care Series, #1Von EverandVegan Bath and Beauty Recipes: 50 Recipes for Soaps, Bath Salts, Bubble Baths, Shower Gels and Bath Fizzies, Bath Bombs, and Body Wash: Skin Care Series, #1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Food AdulterationDokument27 SeitenFood AdulterationKesavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology ExperimentsDokument5 SeitenBiology Experimentsrchataika863Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bhartiya Vidya BhavanDokument9 SeitenBhartiya Vidya BhavanArpan JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Barak 22Dokument22 SeitenBarak 22Bosire keNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPERIMENTDokument11 SeitenEXPERIMENTDeepansh VyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise No. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids, Carbohydrates and Proteins IDokument6 SeitenExercise No. 7 Analysis of Milk For The Lipids, Carbohydrates and Proteins IMaureen VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EfectosDokument25 SeitenEfectosCristiam Manuel Pablo LuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bengali-Style Lamb in Coconut: 81 Christie Street ST Leonards NSWDokument1 SeiteBengali-Style Lamb in Coconut: 81 Christie Street ST Leonards NSWssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medieval RecipesDokument156 SeitenMedieval RecipesCharmaineTanti100% (2)
- Andalusian CookbookDokument235 SeitenAndalusian CookbookVincent Coleman100% (1)
- Zoom G1on Operation ManualDokument34 SeitenZoom G1on Operation ManualHoàng Ngọc-Tuấn100% (1)
- Bengali Fish StewDokument1 SeiteBengali Fish StewssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Humbucker To Single CoilDokument7 SeitenHumbucker To Single CoilssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCD MonitorDokument1 SeiteLCD MonitorssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- G2Nu G21NuDokument56 SeitenG2Nu G21Nucdfgh100% (1)
- House Curve - OdsDokument1 SeiteHouse Curve - OdsssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICC ChannelsDokument7 SeitenICC ChannelsssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yeh07 Dafx Distortion PDFDokument8 SeitenYeh07 Dafx Distortion PDFssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secrets of Roman ConcreteDokument3 SeitenSecrets of Roman ConcreteNorcathNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Curve - OdsDokument1 SeiteHouse Curve - OdsssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shiller PE Index SSRN-id2088140 PDFDokument41 SeitenShiller PE Index SSRN-id2088140 PDFssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- MindstreetDokument4 SeitenMindstreetssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- LadyDokument2 SeitenLadyssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure CookerDokument2 SeitenPressure CookerssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProteinsDokument6 SeitenProteinsssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equal Loudness LevelDokument16 SeitenEqual Loudness LevelssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCD MonitorDokument1 SeiteLCD MonitorssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Secrets of Roman ConcreteDokument3 SeitenSecrets of Roman ConcreteNorcathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yeh07 Dafx Distortion PDFDokument8 SeitenYeh07 Dafx Distortion PDFssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoom G1on Operation ManualDokument34 SeitenZoom G1on Operation ManualHoàng Ngọc-Tuấn100% (1)
- Andalusian CookbookDokument235 SeitenAndalusian CookbookVincent Coleman100% (1)
- LicenseDokument9 SeitenLicenseashishanupamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tikona DetailsDokument1 SeiteTikona DetailsssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- DreamerDokument3 SeitenDreamerssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrueCrypt User Guide PDFDokument150 SeitenTrueCrypt User Guide PDFThedudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bogner SharpFSchDokument1 SeiteBogner SharpFSchssslayerNoch keine Bewertungen