Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Normally Open Normally Close
Hochgeladen von
totoq51Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Normally Open Normally Close
Hochgeladen von
totoq51Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
"Normally Open" or "Normally Closed" are classifications that refer to actuated (not manually
operated) valves. For an actuated valve, the "normal" state refers to its position when the actuator is
not energized.
Therefore a normally open valve is one that is open until the actuator is energized to close it; if power
to the actuator fails, the valve opens or "fails open".
Likewise with a normally closed valve if power to the actuator fails, the valve closes or "fails closed".
The "normal" state of an actuated valve must not be confused with the "usual" position of the valve
during routine operation of the system. A normally closed valve may be open continuously over a long
period of time while a process is running, but it is still a normally closed valve. It just happens that
this normally closed valve is usually open.
For an actuated valve to return to its "normal" position, there must be some force, often a spring, that
moves the valve from its actuated state back to its normal state. If a valve is actuated to open and
then actuated to close, it will "fail" in whichever position it is in when the activator is de-energized.
This type of a valve is not considered "fail safe".
A normally closed valve might be used in an application such as the loading of gasoline transport
trucks where in the event of a power or automation system failure, you would want to stop flow.
A normally open valve might be used in a situation where you want flow to continue in the event of a
power or automation system failure. This might be the case for the cooling water system for a nuclear
reactor or for an actuated valve on the water piping to the fire protection system.
Read
more: http://wiki.answers.com/Q/Is_normally_open_valve_and_fail_open_valve_the_same#ixzz27XN
3kkP3
Fail-Safe Valves
Normally-Closed Valves, Normally-Open Valves, and Valves that can be
Converted between Normally-Open and Normally-Closed
Actuated or automatic valves that revert to a pre-determined position after the
actuating force is removed are referred to as "fail-safe" valves. The most common
type is "fail-safe normally-closed." On the other hand, "fail-safe normally-open"
valves are much less common, but are equally important. These are often found in
cooling systems, or are used where flow is shut off only for periodic maintenance, etc.
Some valves, such as spring-loaded air actuated ball valves, can be converted between
types.
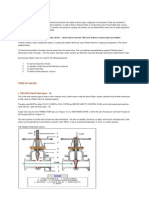
The illustration below shows two air-actuated shut-off valves, identical but for the fact
that one is normally-open and the other is normally-closed. The only real difference
between the valves is the location of the spring in relation to the piston. Because these
valves use compressed air to overcome the spring force, the air acts on the opposite
side of the piston. If you study the valves, you can see where the air is fed in.
Normally-Closed Valves
An example of a normally-closed actuated valve is Plast-O-Matic's Series EASMT
Solenoid Valve. The valve opens when energized, and when that current is turned off,
an isolated spring inside the valve forces it closed. The magnetic force of the solenoid
coil must overcome the force of the spring to open the valve. Unless acted upon, the
spring force keeps the valve closed. In the event of a power failure, the valve will
automatically close.
An example of a normally-closed automatic valve is Plast-O-Matic's Series CKM
Check Valve. The valve opens when pressure is present at the inlet (or upstream) side.
When that pressure ceases, the diaphragm inside the valve automatically forces it
closed. The inlet pressure must overcome the force of the diaphragm to open the
valve. Unless acted upon by inlet pressure, the diaphragm force keeps the valve
closed. In fact, the valve closes before reverse flow can take place. (note that the
above refers exclusively to Series CKM/CKS; most check valves, including ball type,
are not normally-closed valves.)
Normally-Open Valves
An example of a normally-open actuated valve is Plast-O-Matic's Series EASY-NO
Solenoid Valve. The valve closes when energized, and when that current is turned off,
an isolated spring inside the valve forces it open. The magnetic force of the solenoid
coil must overcome the force of the spring to close the valve. Unless acted upon, the
spring force keeps the valve open. In the event of a power failure, the valve will
automatically open.
An example of a normally-open automatic valve is Plast-O-Matic's Series PRE
Pressure Regulator. The valve is set to remain open at a predetermined pressure, and
begins to close automatically when downstream pressure exceeds that predetermined
pressure. When pressure downstream drops back to accepted levels, a spring inside
the valve forces it back open. The downstream pressure must overcome the force of
the spring to close the valve. Unless acted upon by excessive downstream pressure,
the spring keeps the valve open.
Valves that can be Converted between Normally-Open and Normally-Closed
Air-Actuated, Spring-Return Ball Valves -- Plast-O-Matic Series ABVS, ABRS &
ABMS -- are examples of valves that can be normally-open or normally-closed. In
these valves, a rather large spring is used to force the actuator back to its original
position, whether that is open or closed.
One of the advantages of a Plast-O-Matic Air x Spring Actuated Ball Valve is that it
can be converted fairly easily between one type or the other. Because the spring forces
the actuator one way or the other, it is simply a matter of redirecting what the spring
acts upon.
With Series ABVS, this is done by backing off the adjusting cap (so the spring will
not be compressed) then unscrewing the spring housing from one side of the actuator
and moving it to the opposite side. (Likewise, the compressed air is swapped).
Converting Series ABRS & ABMS is a little more complex. The actuator must be
removed from the valve (very easy to do), then a retaining ring on the bottom of the
actuator must be removed (requires retaining ring pliers). The pinion shaft is then
pushed out from the top, rotated 180, then re-inserted. The actuator will then act upon
the valve opposite the way it did before.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingVon EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- GROENEVELDDokument62 SeitenGROENEVELDJuan SantiagoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is Normally Open Valve and Fail Open Valve The SameDokument1 SeiteIs Normally Open Valve and Fail Open Valve The Samecakhokhe100% (2)
- Stormchokes OverviewDokument6 SeitenStormchokes OverviewJumi mikol100% (2)
- Tutorial 4 Heat TransferDokument8 SeitenTutorial 4 Heat Transfertotoq510% (1)
- F-5 Parts Catalog: Serial NoDokument96 SeitenF-5 Parts Catalog: Serial Nokien100% (1)
- Fail-Safe Valves PDFDokument3 SeitenFail-Safe Valves PDFRahul LavandNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM HydraulicsDokument4 SeitenFM HydraulicsOnkar KakadNoch keine Bewertungen
- FC&FO ValveDokument2 SeitenFC&FO ValverdidaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 4Dokument26 SeitenSection 4Fernanda Medeiros CarvalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- H D S: C 3 D S C V: OW TO O Tuff Hapter Istribution Ystem Ontrol AlvesDokument18 SeitenH D S: C 3 D S C V: OW TO O Tuff Hapter Istribution Ystem Ontrol AlvesRodelas JanineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Solenoid ValvesDokument2 SeitenDifferent Types of Solenoid ValvesJe MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference between relief and safety valvesDokument3 SeitenDifference between relief and safety valvesSurya Kiran KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bleed ValveDokument8 SeitenBleed Valvejanju81Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8 - PressurevalvesDokument68 Seiten8 - PressurevalvesMohamed ZahranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Rapping SystemDokument8 SeitenAutomatic Rapping SystemAnonymous j0aO95fgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mustang Series M116-52 or M6116-52 (Globe), M1116-52 or M61116-52 (Angle) Installation InstructionsDokument2 SeitenMustang Series M116-52 or M6116-52 (Globe), M1116-52 or M61116-52 (Angle) Installation InstructionsWattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling Reference - Surge ValvesDokument5 SeitenModeling Reference - Surge Valvespca97Noch keine Bewertungen
- ValvesDokument194 SeitenValvesvikrantsingh2908100% (2)
- Stainless Series S116-52 or S6116-52 (Globe), S1116-52 or S61116-52 (Angle) Installation InstructionsDokument2 SeitenStainless Series S116-52 or S6116-52 (Globe), S1116-52 or S61116-52 (Angle) Installation InstructionsWattsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromechanical Valve Liquid Gas Electric Current SolenoidDokument3 SeitenElectromechanical Valve Liquid Gas Electric Current SolenoidAjay KaundalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Fittings, ValvesDokument10 SeitenPipe Fittings, Valvesaasatti100% (1)
- Plug Valves: Pumps and Water Distribution 183Dokument2 SeitenPlug Valves: Pumps and Water Distribution 183Rohit ShresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M2.7 ValvesDokument27 SeitenM2.7 ValvesUJWAL UMESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid valve guideDokument4 SeitenSolenoid valve guideVivekanandhan Porselvan100% (1)
- Control ValveDokument37 SeitenControl Valvevipin12krishnan100% (2)
- THE GATE VALVE (See Figure: 13)Dokument7 SeitenTHE GATE VALVE (See Figure: 13)vikrantsingh2908Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenFluid Mechanics Lab Reportayesha noorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective: Apparatus:: Solenoid ValveDokument4 SeitenObjective: Apparatus:: Solenoid ValveAbid HameedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equipment Used During VentingDokument9 SeitenEquipment Used During VentingRahulChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wellhead & X mas TreeDokument24 SeitenWellhead & X mas Treejagop91351Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Liquid Gas Compressor: Booster PumpDokument6 SeitenPressure Liquid Gas Compressor: Booster PumpAlvynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ValvesDokument23 SeitenControl ValvesAndriy IshchenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ValvesDokument15 SeitenValveskinskunja100% (1)
- Types of Valves and Their Uses in Hydraulic SystemsDokument76 SeitenTypes of Valves and Their Uses in Hydraulic SystemsN NandiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve Type Used in Power PlantDokument14 SeitenValve Type Used in Power PlantGourav Choudhuri0% (1)
- Solenoid ValveDokument5 SeitenSolenoid ValvetkaneeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIS Exp No 6Dokument3 SeitenAIS Exp No 6Abhijit SomnatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relieve Valve Types and OperationDokument11 SeitenRelieve Valve Types and OperationBryan K. Aylas ParedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Valve PDFDokument39 SeitenControl Valve PDFRush SfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ValveDokument39 SeitenControl Valveryukyu100% (1)
- Solenoid Valve: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument3 SeitenSolenoid Valve: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNatrajj SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ValvesDokument11 SeitenValvesJigar BariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure-Control Valves PDFDokument15 SeitenPressure-Control Valves PDFRagab Abulmagd100% (1)
- Fail Open (FO) - Air To Close&Fail Closed (FC) - Air To OpenDokument3 SeitenFail Open (FO) - Air To Close&Fail Closed (FC) - Air To OpenAmmar InstrumentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech ManualDokument44 SeitenTech ManualJonathan Negrete OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solenoid Valve Working PrincipleDokument1 SeiteSolenoid Valve Working Principlejayesh_1686Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Control Valves - Sg. STANCU CosminDokument36 SeitenHydraulic Control Valves - Sg. STANCU Cosminstancu cosminNoch keine Bewertungen
- So, You Think You Know Shuttle Valves?Dokument6 SeitenSo, You Think You Know Shuttle Valves?AkileshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shuttle Valve PDFDokument6 SeitenShuttle Valve PDFDEBASISH SARKARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ValveDokument39 SeitenControl ValvewirawansatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve Selection & MaintenanceDokument120 SeitenValve Selection & MaintenanceOmar Khaled100% (1)
- A Solenoid Valve Is An Electromechanical Valve For Use With Liquid or GasDokument3 SeitenA Solenoid Valve Is An Electromechanical Valve For Use With Liquid or GasNaresh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM 90 01Dokument29 SeitenTM 90 01juliancardona77Noch keine Bewertungen
- VALVE TYPES AssignmentDokument10 SeitenVALVE TYPES Assignmentbabe100% (2)
- What Is Solenoid Valve and Its Types With PDFDokument8 SeitenWhat Is Solenoid Valve and Its Types With PDFpntnhan21thNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choosing the Right Pressure Relief ValveDokument17 SeitenChoosing the Right Pressure Relief ValveJoseph JoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.5 Valve CharacteristicsDokument8 Seiten8.5 Valve CharacteristicsKogulan SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Control ValvesDokument2 SeitenHydraulic Control Valvesandrija_ganzbergerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Control ValvesDokument55 SeitenPressure Control ValvesShriram AvasarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryVon EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGVon EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- IACS Common Structural Rules Knowledge Centre Q&AsDokument10 SeitenIACS Common Structural Rules Knowledge Centre Q&Astotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prayer Katalog2Dokument2 SeitenPrayer Katalog2ahmed_mahdy_jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of Simple Pressure DropDokument1 SeiteCalculation of Simple Pressure DropqalambatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finite Difference HeatDokument6 SeitenFinite Difference HeatGilberto Roman0% (1)
- Calculation of Simple Pressure DropDokument1 SeiteCalculation of Simple Pressure DropqalambatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Craw Fish Origami EasyDokument1 SeiteCraw Fish Origami Easytotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief Journey Through Arabic GrammarDokument28 SeitenA Brief Journey Through Arabic GrammarMourad Diouri100% (5)
- Heat Transfer Excel Calculations 1Dokument39 SeitenHeat Transfer Excel Calculations 1Sharon LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- The International System of Units (SI) Converter PDFDokument27 SeitenThe International System of Units (SI) Converter PDFMaey AkimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ice Controllable Pitch PropellerDokument9 SeitenIce Controllable Pitch Propellertotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fabrication and Material Selection Case Study 1Dokument3 SeitenFabrication and Material Selection Case Study 1totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Naval Architechture TermsDokument5 SeitenNaval Architechture Termstotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teoría Básica de Transformada de Laplace PDFDokument127 SeitenTeoría Básica de Transformada de Laplace PDFDoris Giovanna MitreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis: Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachDokument38 SeitenEnergy, Energy Transfer, and General Energy Analysis: Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachmohamadfaizalrosliNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE A4 FormatDokument4 SeitenIEEE A4 Formatprem035Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Velocity Coupling Methods SIMPLE and SIMPLER AlgorithmsDokument29 SeitenPressure Velocity Coupling Methods SIMPLE and SIMPLER Algorithmstotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Incropera Heat 7th Edition Solution Ch3-1Dokument6 SeitenIncropera Heat 7th Edition Solution Ch3-1totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- List of SymbolsDokument4 SeitenList of Symbolstotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Conversion: LengthDokument35 SeitenUnit Conversion: LengthBhupesh MulikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Kaedah NabawiDokument5 Seiten10 Kaedah Nabawitotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cooling Brass Plate with Air Jet ImpingementDokument1 SeiteCooling Brass Plate with Air Jet Impingementtotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cylindrical Nuclear Fuel Rod Temperature CalculationDokument1 SeiteCylindrical Nuclear Fuel Rod Temperature Calculationtotoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4 Heat Transfer - Question2Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 4 Heat Transfer - Question2totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q6Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q6totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3 Heat Transfer Question 3Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 3 Heat Transfer Question 3totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4 Heat Transfer - Question 1Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 4 Heat Transfer - Question 1totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q5Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q5totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q3Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q3totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q1 Q2Dokument1 SeiteTutorial 2 Heat Transfer Q1 Q2totoq51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Manual EVOPICVDokument20 SeitenTechnical Manual EVOPICVzoltanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stationary Air Compressors Compresseur D'air Stationnaire Compresores de Aire EstacionariosDokument8 SeitenStationary Air Compressors Compresseur D'air Stationnaire Compresores de Aire EstacionariosA delca-Noch keine Bewertungen
- Page 1 of 11: ECS 10-19-1 Packaged EquipmentDokument11 SeitenPage 1 of 11: ECS 10-19-1 Packaged EquipmentFlorin Daniel AnghelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam and Steam Condensate PDokument14 SeitenSteam and Steam Condensate PDanny BoysieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindle 4.2.2 Torque Characteristics PDFDokument6 SeitenHindle 4.2.2 Torque Characteristics PDFpandit1010Noch keine Bewertungen
- FPT Nef 67 M28Dokument210 SeitenFPT Nef 67 M28Salvatore DesariNoch keine Bewertungen
- NUMECO 3001B Project Proposal: Group MembersDokument3 SeitenNUMECO 3001B Project Proposal: Group MembersJoker DerozanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pacific Pride F-19 Finished Plan For Flutek-Kawasaki Type Steering Gear Hull No - s059Dokument215 SeitenPacific Pride F-19 Finished Plan For Flutek-Kawasaki Type Steering Gear Hull No - s059htetmyaung5331Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manual Motobomba Shark Carvin InglesDokument12 SeitenManual Motobomba Shark Carvin Inglesgilbertot938Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISH ExhibitorsDokument18 SeitenISH ExhibitorssahirprojectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 - FL - Catalog Fusible Link Ball Valve Ss BodyDokument16 Seiten2016 - FL - Catalog Fusible Link Ball Valve Ss BodySujith Sekar GnanasekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- LFL PDFDokument13 SeitenLFL PDFmangal deo pathak100% (1)
- 7123AF Aquatherm Fusiotherm Hot & Cold Water System 2010Dokument9 Seiten7123AF Aquatherm Fusiotherm Hot & Cold Water System 2010starykltNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - FM200 - SinorixDokument68 Seiten2 - FM200 - SinorixBelal SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Davis-FET CatalogDokument19 SeitenDavis-FET CatalogfarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL17 Chlorine - AnalyzerDokument56 SeitenCL17 Chlorine - Analyzerbalzac191Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Sealing Gate Valve PN40Dokument4 SeitenMetal Sealing Gate Valve PN40Emran HaniniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Cooled Fcu Piping DetailsDokument14 SeitenWater Cooled Fcu Piping Detailsfernandoreyes893Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rules-56-Under-Sec-31-Full-Factories ActDokument6 SeitenRules-56-Under-Sec-31-Full-Factories ActGopal RamalingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneutrol 5/2-directional valve Series 740 technical specificationsDokument4 SeitenPneutrol 5/2-directional valve Series 740 technical specificationsNadeem naderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Operation Manual Semi-Auto Capsule Filling Machine Two HeadsDokument11 Seiten1 - Operation Manual Semi-Auto Capsule Filling Machine Two HeadsLuisPlayer45100% (1)
- 312781E Manifold Promix 2KSDokument22 Seiten312781E Manifold Promix 2KSJose Padilla gaytanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PN427604Dokument152 SeitenPN427604Cesar MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Reverse Braking System For AutomobileDokument48 SeitenAutomatic Reverse Braking System For AutomobileSaravanan Viswakarma100% (1)
- LG - LBUM7280BL Exploded ViewDokument55 SeitenLG - LBUM7280BL Exploded ViewGuillermo HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Trailer Braking System GuideDokument36 SeitenAir Trailer Braking System Guidelungu mihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Saver Series Single Cartridge Air DryersDokument52 SeitenSystem Saver Series Single Cartridge Air DryersModestasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire N GasDokument20 SeitenFire N GasRachid MenserNoch keine Bewertungen