Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hochgeladen von
Kevinsinaga0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten4 SeitenIn Hodgkin's lymphoma, cells in the lymphatic system grow abnormally. The disease compromises your body's ability to fight infection. The prognosis continues to improve for people with this diagnosis.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
HODGKIN’S LYMPHOMA.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenIn Hodgkin's lymphoma, cells in the lymphatic system grow abnormally. The disease compromises your body's ability to fight infection. The prognosis continues to improve for people with this diagnosis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
98 Ansichten4 SeitenHodgkin's Lymphoma
Hochgeladen von
KevinsinagaIn Hodgkin's lymphoma, cells in the lymphatic system grow abnormally. The disease compromises your body's ability to fight infection. The prognosis continues to improve for people with this diagnosis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
HODGKINS LYMPHOMA
Hodgkin's lymphoma formerly known as Hodgkin's disease is a
cancer of the lymphatic system, which is part of your immune system.
In Hodgkin's lymphoma, cells in the lymphatic system grow abnormally
and may spread beyond the lymphatic system. As Hodgkin's lymphoma
progresses, it compromises your body's ability to fight infection. Hodgkin's
lymphoma is one of two common types of cancers of the lymphatic system. The
other type, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is far more common. Advances in diagnosis
and treatment of Hodgkin's lymphoma have helped give people with this
diagnosis the chance for a full recovery. The prognosis continues to improve for
people with Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Hodgkin's lymphoma signs and symptoms may include:
Painless swelling of lymph nodes in your neck, armpits or groin
Persistent fatigue
Fever and chills
Night sweats
Unexplained weight loss as much as 10 percent or more of your body
weight
Loss of appetite
Itching
Increased sensitivity to the effects of alcohol or pain in your lymph nodes
after drinking alcohol
It's not clear what causes Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Doctors know that most Hodgkin's lymphoma occurs when an infection-
fighting cell called a B cell develops a mutation in its DNA. The mutation tells the
cells to divide rapidly and to continue living when a healthy cell would die. The
mutation causes a large number of oversized, abnormal B cells to accumulate in
the lymphatic system, where they crowd out healthy cells and cause the signs and
symptoms of Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Various types of Hodgkin's lymphoma exist. The type is based on the
types of cells involved in your disease and their behavior. Your type determines
your treatment options.
Nama : Kevin S. Jeremia
Nama Medis : Neisseria Menigntidis
Nama Korona : Bacteriology
No. Absen : 05
01
Classical Hodgkin's lymphoma is the more common type of this disease. It
can be broken down further into subtypes. People diagnosed with classical
Hodgkin's lymphoma have large, abnormal cells called Reed-Sternberg cells in
their lymph nodes.
Subtypes of classical Hodgkin's lymphoma include:
Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin's lymphoma
Mixed cellularity Hodgkin's lymphoma
Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin's lymphoma
Lymphocyte-rich classical Hodgkin's lymphoma
This much rarer type of Hodgkin's lymphoma involves large, abnormal cells
that are sometimes called popcorn cells because of their appearance. Treatment
may be different from the classical type. People with this type of Hodgkin's
lymphoma may have a better chance of a cure when the disease is diagnosed at an
early stage.
Factors that increase the risk of Hodgkin's lymphoma include:
Your age. Hodgkin's lymphoma is most often diagnosed in people
between the ages of 15 and 30, as well as those older than 55.
A family history of lymphoma. Having a close family member who has
Hodgkin's lymphoma or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma increases your risk of
developing Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Your sex. Males are slightly more likely to develop Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Past Epstein-Barr infection. People who have had illnesses caused by the
Epstein-Barr virus, such as infectious mononucleosis, are more likely to
develop Hodgkin's lymphoma than are people who haven't had Epstein-
Barr infections.
A weakened immune system. Having a compromised immune system,
such as from HIV/AIDS or from having an organ transplant requiring
medications to suppress the immune response, increases the risk of
Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Which treatment options are appropriate for your Hodgkin's lymphoma
depends on your type and stage of disease, your overall health, and your
preferences. The goal of treatment is to destroy as many cancer cells as possible
and bring the disease into remission.
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses chemicals to kill lymphoma
cells. Chemotherapy drugs travel through your bloodstream and can reach nearly
all areas of your body. Chemotherapy is often combined with radiation therapy in
people with early-stage classical type Hodgkin's lymphoma. Radiation therapy is
typically done after chemotherapy. In advanced Hodgkin's lymphoma,
chemotherapy may be used alone or combined with radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy drugs can be taken in pill form, through a vein in your arm or
sometimes both methods of administration are used. Several combinations of
chemotherapy drugs are used to treat Hodgkin's lymphoma. Side effects of
chemotherapy depend on the specific drugs you're given. Common side effects
include nausea and hair loss. Serious long-term complications can occur, such as
heart damage, lung damage, fertility problems and other cancers, such as
leukemia.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays, to kill cancer
cells. For classical Hodgkin's lymphoma, radiation therapy can be used alone, but
it is often used after chemotherapy. People with early-stage lymphocyte-
predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma typically undergo radiation therapy alone.
During radiation therapy, you lie on a table and a large machine moves
around you, directing the energy beams to specific points on your body. Radiation
can be aimed at affected lymph nodes and the nearby area of nodes where the
disease might progress. The length of radiation treatment varies, depending on the
stage of the disease.
Radiation therapy can cause skin redness and hair loss at the site where the
radiation is aimed. Many people experience fatigue during radiation therapy.
More-serious risks include heart disease, stroke, thyroid problems, infertility and
other forms of cancer, such as breast or lung cancer.
A stem cell transplant is a treatment to replace your diseased bone marrow
with healthy stem cells that help you grow new bone marrow. A stem cell
transplant may be an option if Hodgkin's lymphoma returns despite treatment.
During a stem cell transplant, your own blood stem cells are removed,
frozen and stored for later use. Next you receive high-dose chemotherapy and
radiation therapy to destroy cancerous cells in your body. Finally your stem cells
are thawed and injected into your body through your veins. The stem cells help
build healthy bone marrow.
No alternative medicines have been found to treat Hodgkin's lymphoma. But
alternative medicine may help you cope with the stress of a cancer diagnosis and
the side effects of cancer treatment. Talk to your doctor about your options, such
as:
Acupuncture
Aromatherapy
Massage
Meditation
Relaxation techniques
REFERENCES
1. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hodgkins-
lymphoma/basics/con-20030667
2. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/201886-overview#showall
3. http://www.leukaemia.org.au/blood-cancers/lymphomas/hodgkin-
lymphoma
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Surviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsVon EverandSurviving Leukemia and Hodgkin's Lymphoma: An Overview Of Effective Treatment MethodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Hodgkin LymphomaDokument16 SeitenNon Hodgkin LymphomaadnajaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin's Dise A Se: CompanyDokument10 SeitenHodgkin's Dise A Se: CompanyMahmood SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- History: Robert J. LukeDokument17 SeitenHistory: Robert J. LukeFlorilette Bautista CabatbatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin's DiseaseDokument4 SeitenHodgkin's DiseaseLillabinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoma SignsDokument7 SeitenLymphoma SignsDr Keerti MadhukarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To LymphomaDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Lymphomalyrad11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology 2 Case Analysis: College of Allied Medical ProfessionsDokument9 SeitenHematology 2 Case Analysis: College of Allied Medical ProfessionsJoshua De lunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoma 1Dokument15 SeitenLymphoma 1AHMEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non-Hodgkin's LymphomaDokument19 SeitenNon-Hodgkin's LymphomaryeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoma TestDokument15 SeitenLymphoma TestSaqlain MughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin Lymphoma CellsDokument20 SeitenHodgkin Lymphoma CellsAnonymous lKO78aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts: Sézary Syndrome: What Is Lymphoma?Dokument6 SeitenFast Facts: Sézary Syndrome: What Is Lymphoma?Pramita SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Grade Non Hodgkin Lymphoma BookletDokument116 SeitenHigh Grade Non Hodgkin Lymphoma BookletDwinita ViviantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) - A Quick GuideDokument6 SeitenAbout Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) - A Quick GuideDwinita ViviantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treating Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) - A Quick GuideDokument11 SeitenTreating Non Hodgkin's Lymphoma (NHL) - A Quick GuidelaclinicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin's DiseaseDokument41 SeitenHodgkin's DiseaseDanilyn_Jumamo_1564100% (2)
- Hodgkins LymphomaDokument26 SeitenHodgkins LymphomaHealth Education Library for PeopleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin'S Disease: By: Myla Mutoc Monic Navarro Leah PahamutangDokument8 SeitenHodgkin'S Disease: By: Myla Mutoc Monic Navarro Leah PahamutangNica Gaborne NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis On Hodgkin LymphomaDokument5 SeitenThesis On Hodgkin Lymphomafjm38xf3100% (2)
- Hodgkin'sDokument35 SeitenHodgkin'sDorothy Pearl Loyola PalabricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LYMPHOMADokument12 SeitenLYMPHOMAश्रीकृष्ण हेङ्गजूNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Cancer 101: What You Need to Know About Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention"Von Everand"Cancer 101: What You Need to Know About Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention"Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. A Guide for Patients, Survivors, and Loved Ones. April 2021Von EverandUnderstanding Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. A Guide for Patients, Survivors, and Loved Ones. April 2021Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. A Guide for Patients, Survivors, and Loved Ones. September 2015Von EverandUnderstanding Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. A Guide for Patients, Survivors, and Loved Ones. September 2015Noch keine Bewertungen
- LymphomaDokument5 SeitenLymphomaBlossom Wawa IINoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Hodgkin's Disease?: Lymphoma CancerDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Hodgkin's Disease?: Lymphoma CancerAnusha VergheseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unraveling Cancer: Progress and Future Directions in Cancer ResearchVon EverandUnraveling Cancer: Progress and Future Directions in Cancer ResearchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Hodgkin Lymphoma. A Guide For Patients, Survivors, and Loved Ones. October 2017Von EverandUnderstanding Hodgkin Lymphoma. A Guide For Patients, Survivors, and Loved Ones. October 2017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin LymphomaDokument4 SeitenHodgkin LymphomaMinelle Sanchez InsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkins-Lymphoma Docx PeDokument5 SeitenHodgkins-Lymphoma Docx PeTra NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Day of The Prevention of The Cardiovascular Risk by SlidesgoDokument76 SeitenEuropean Day of The Prevention of The Cardiovascular Risk by Slidesgobinojdaniel17Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Final Lymphoma and MyelomaDokument16 Seiten3 Final Lymphoma and MyelomaRumela Chakraborty100% (1)
- Treatment of Hodgkin Lymphoma - Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment in India: Omegahospitals, HyderabadDokument2 SeitenTreatment of Hodgkin Lymphoma - Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment in India: Omegahospitals, HyderabadRyan ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer PathologiesDokument5 SeitenCancer PathologiesInnocent GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoma Group 1Dokument40 SeitenLymphoma Group 1queengorgeoushannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaDokument6 SeitenChronic Lymphocytic LeukemiaJhannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin'S LymphomaDokument7 SeitenHodgkin'S LymphomaHarish Kumar KumawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Hodgkin's LymphomaDokument27 SeitenNon Hodgkin's LymphomaAnsu MaliyakalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alterations in Hematologic System HealthDokument12 SeitenAlterations in Hematologic System HealthKelly HollenbeakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Hodgkin LymphomaDokument53 SeitenNon Hodgkin LymphomaMeilina Elin WardhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoma by AbrarDokument11 SeitenLymphoma by AbrarZain HadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Previously Known As Hodgkin's Disease, Is A Type ofDokument9 SeitenHodgkin's Lymphoma, Previously Known As Hodgkin's Disease, Is A Type ofMarilou PadillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeukemiaDokument23 SeitenLeukemiaAli Ismail86% (7)
- Cancer Treatment TypesDokument43 SeitenCancer Treatment TypesM Sai Pradhyumna100% (2)
- Hodgkin's DiseaseDokument28 SeitenHodgkin's DiseasebikeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LeukemiaDokument23 SeitenLeukemiaMrnj MelorinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoma PDFDokument3 SeitenLymphoma PDFkapczukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Cancer (Osteosarcoma) : Carolea Casas & Brittany HogueDokument222 SeitenBone Cancer (Osteosarcoma) : Carolea Casas & Brittany Hoguegiggs_libraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Hodgkin Lymphoma PresentationDokument17 SeitenNon Hodgkin Lymphoma PresentationClayton Green100% (1)
- Childhood Malignancies - Hodgkin's LymphomaDokument6 SeitenChildhood Malignancies - Hodgkin's Lymphomavictortayor_26105009Noch keine Bewertungen
- NHL Arshad KhanDokument30 SeitenNHL Arshad KhanArshad khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LymphomaDokument46 SeitenLymphomashapan biswaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HodgkinDokument2 SeitenHodgkinMRla CiriloNoch keine Bewertungen
- L-3 Introduction To LeukemiaDokument26 SeitenL-3 Introduction To LeukemiaAbood dot netNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Lymphoma?Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is Lymphoma?lee jennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- LymphomaDokument69 SeitenLymphomaDawit g/kidanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1 Apolonio, Leizel, R. Corpuz Rolyn Mañalac Joelle Anne Señeres Loui AnneDokument33 SeitenGroup 1 Apolonio, Leizel, R. Corpuz Rolyn Mañalac Joelle Anne Señeres Loui AnneLeizel ApolonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Promotion-Mix (: Tools For IMC)Dokument11 SeitenPromotion-Mix (: Tools For IMC)Mehul RasadiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hướng Dẫn Chấm: Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019 Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề) HDC gồm có 4 trangDokument4 SeitenHướng Dẫn Chấm: Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019 Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề) HDC gồm có 4 trangHưng Quân VõNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation About GyroscopesDokument24 SeitenPresentation About GyroscopesgeenjunkmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM2576/LM2576HV Series Simple Switcher 3A Step-Down Voltage RegulatorDokument21 SeitenLM2576/LM2576HV Series Simple Switcher 3A Step-Down Voltage RegulatorcgmannerheimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Arts in Theology: Christian Apologetics/ Seventh-Day Adventist Contemporary IssuesDokument13 SeitenBachelor of Arts in Theology: Christian Apologetics/ Seventh-Day Adventist Contemporary IssuesRamel LigueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evs ProjectDokument19 SeitenEvs ProjectSaloni KariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peer PressureDokument13 SeitenPeer PressuremightymarcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand Strategy - in B2BDokument6 SeitenBrand Strategy - in B2BKrishan SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1Dokument84 SeitenAnatomy of the pulp cavity กย 2562-1IlincaVasilescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis PaperDokument53 SeitenThesis PaperAnonymous AOOrehGZAS100% (1)
- Friction: Ultiple Hoice UestionsDokument5 SeitenFriction: Ultiple Hoice Uestionspk2varmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JIS G 3141: Cold-Reduced Carbon Steel Sheet and StripDokument6 SeitenJIS G 3141: Cold-Reduced Carbon Steel Sheet and StripHari0% (2)
- Hidrl1 PDFDokument7 SeitenHidrl1 PDFRajesh Kumar100% (1)
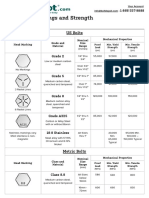
- Bolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartDokument2 SeitenBolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartGregory GaschteffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Lab Midterm Study GuideDokument15 SeitenMicro Lab Midterm Study GuideYvette Salomé NievesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementation of E-Governance To Improve The Civil Administration Service Quality in Public SectorDokument11 SeitenImplementation of E-Governance To Improve The Civil Administration Service Quality in Public SectorChristie YohanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Closing The Gap ReportDokument64 Seiten2016 Closing The Gap ReportAllan ClarkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- India TeenagersDokument3 SeitenIndia TeenagersPaul Babu ThundathilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disassembly Procedures: 1 DELL U2422HB - U2422HXBDokument6 SeitenDisassembly Procedures: 1 DELL U2422HB - U2422HXBIonela CristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delusion in SocietyDokument2 SeitenDelusion in SocietyGasimovskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MultiLoadII Mobile Quick Start PDFDokument10 SeitenMultiLoadII Mobile Quick Start PDFAndrés ColmenaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rom 2 - 0-11 (En)Dokument132 SeitenRom 2 - 0-11 (En)Mara HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Production Engineer Samphhhhhle ResumeDokument2 SeitenMechanical Production Engineer Samphhhhhle ResumeAnirban MazumdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ყვავილები ელჯერნონისთვისDokument348 Seitenყვავილები ელჯერნონისთვისNia NorakidzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sociology As A Form of Consciousness - 20231206 - 013840 - 0000Dokument4 SeitenSociology As A Form of Consciousness - 20231206 - 013840 - 0000Gargi sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 Khan S.Dokument7 Seiten22 Khan S.scholarlyreseachjNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Covenant Taken From The Sons of Adam Is The FitrahDokument10 SeitenThe Covenant Taken From The Sons of Adam Is The FitrahTyler FranklinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDokument8 SeitenCummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDaniel KrismantoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 23Dokument9 SeitenChapter 23Javier Chuchullo TitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Government College of Nursing Jodhpur: Practice Teaching On-Probability Sampling TechniqueDokument11 SeitenGovernment College of Nursing Jodhpur: Practice Teaching On-Probability Sampling TechniquepriyankaNoch keine Bewertungen