Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Open Channel Flow
Hochgeladen von
murad_ceCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Open Channel Flow
Hochgeladen von
murad_ceCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Open Channel Flow
Open Channel flow
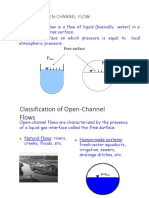
Open channel flow may be defined as the flow of water in a conduit with a free surface. It is subjected
to atmospheric pressure. So, Open channel flow is known as free surface flow.
Open Channel Flow
Kinds of open channel flow
Natural and Artificial channels
Natural open channels include all channels that exist naturally on the earth, i.e. rivers and
tidal estuaries.
Prismatic and Non-prismatic channels
A channel unvarying cross section and constant bottom slope is called prismatic channel;
otherwise, it is non-prismatic. The artificial channels are usually prismatic and the natural
channels are generally non-prismatic.
Rigid and Mobile Boundary Channels
A channel with immovable bed and sides is knows as rigid boundary channel, i.e. lined canal,
sewer and non-erodible unlined canals. If the channel boundary is composed of loose
sedimentary particles moving under the action of lowing water, the channel is called a mobile
boundary channel. An alluvial channel is a mobile boundary channel transporting the same
type of material as that comparing the channel perimeter.
Small and Large Slope Channels
An open channel having a bottom slope greeter than 1 in 10 is called a channel of large slope;
otherwise, it is a channel of small slope. The slope of ordinary channels, natural or artificial is
far less than 1 in 10. Some artificial channels like drops and chutes have slopes far more than 1
in 10.
Channels Geometry
The most common section of prismatic or regular or uniform channels are
Rectangular
Trapezoidal
Triangular
Parabola
Circular
Depth of flow: The vertical distance between the lowest points to the water surface. The depth
of flow section is the depth of flow normal to the direction of flow. The relation between and
is
Stage: The elevation of the water surface relative to a horizontal datum and may be positive or
negative.
Flow area (A) : The flow area is the cross-sectional area of the flow normal to the direction of
flow.
Wetted Perimeter: The length of the interface between water and channel boundary.
Hydraulic radius (R): The ratio of the flow area to the wetted perimeter.
Hydraulic depth (D): The ratio of the flow area to the top width.
Calculation of Geometric elements of Open Channel Flow
1. Rectangle
2. Trapezoidal
3. Triangle
b
h
h
b
S
1
S
1 h
z = cy h
Z
d
0
h
Rectangle Trapezoid Rectangle
Parabola Circle
4. Parabola (Perimeter equation
)+
5. Circle
[(
)]
)
Wide Channel
When the width of a rectangular channel is very large compare to the depth i.e. b>>h, (generally if
b10h), the sides of the channel have practically no influence on the velocity distribution in the
central region. Such a channel is known as a wide channel.
For a wide channel
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Lecture - 1.pdf Version 1Dokument23 SeitenLecture - 1.pdf Version 1kaafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsVon EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow in Open ChannelsDokument15 SeitenFlow in Open ChannelsAnil Nani100% (1)
- Note Hydrualics and HydrologyDokument4 SeitenNote Hydrualics and HydrologyAkinwamideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lacture OneDokument30 SeitenLacture OnekaafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 421 Open Channel Flow Part-1 (2322)Dokument37 SeitenCE 421 Open Channel Flow Part-1 (2322)Afrahim Chowdhury Fashol 201-47-393Noch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel Module1Dokument24 SeitenOpen Channel Module1pankaj_mbmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Project (Open Flow)Dokument7 SeitenHydraulic Project (Open Flow)RhuBenThiRaan0% (1)
- Open Channel Flow Hydraulics: Lecture - 1Dokument16 SeitenOpen Channel Flow Hydraulics: Lecture - 1Charan DeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel Flow: Athira Suresh I.C.E.TDokument49 SeitenOpen Channel Flow: Athira Suresh I.C.E.TAthira SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Flow in Open ChannelsDokument83 SeitenWater Flow in Open ChannelsShashank ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Flow in Open ChannelDokument30 SeitenChapter 1 Flow in Open ChannelLiew Sam TatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow of Open ChannelDokument61 SeitenFlow of Open Channelmr_sam91100% (1)
- Open Channel FlowDokument5 SeitenOpen Channel FlowShahid RøckzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 01Dokument51 SeitenChapter 01Koushik DaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Resource Engineering II CE-421Dokument23 SeitenWater Resource Engineering II CE-421Md. Murshedul Islam 173-47-091Noch keine Bewertungen
- CE308 - Ch3 - Open Channel Flow v2Dokument169 SeitenCE308 - Ch3 - Open Channel Flow v2Tefvizname AntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Modelling of Various Open Channel Flow ParametersDokument13 SeitenMatlab Modelling of Various Open Channel Flow ParametersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLW Opench-Nb ExamplesDokument61 SeitenFLW Opench-Nb ExamplesEng Bagaragaza RomualdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel FlowDokument52 SeitenOpen Channel Flowعبادي العائب100% (1)
- Open Channels (1) - 1Dokument160 SeitenOpen Channels (1) - 12020-100230Noch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel Flow MetersDokument2 SeitenOpen Channel Flow MetersPisic_FluffyNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM CPDokument14 SeitenFM CPVaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences Between Pipe Flow and Open Channel FlowDokument3 SeitenDifferences Between Pipe Flow and Open Channel FlowAmritpal Singh0% (1)
- Open Channel HydraulicsDokument81 SeitenOpen Channel HydraulicsAbdulbasit Aba BiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Open Channel FlowDokument34 SeitenChapter 1 Open Channel FlowGODDEY ABAHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slides 1 Flow in Open ChannelDokument30 SeitenSlides 1 Flow in Open ChannelTing Wee KietNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2... Extra Work - HYDRAULICS Flow in PipesDokument55 Seiten2... Extra Work - HYDRAULICS Flow in PipesMuhirirwe Cecilia SandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 000 My PPT - Mod 3 Open ChannelDokument31 Seiten000 My PPT - Mod 3 Open ChannelChinnu NinanNoch keine Bewertungen
- D4C Notes On Open Channel FlowDokument87 SeitenD4C Notes On Open Channel FlowSTOCK MSOWOYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 3Dokument32 SeitenChapter1 3researchditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Properties of Channel SectionDokument25 SeitenGeometric Properties of Channel SectionShishirRijalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel FlowDokument34 SeitenOpen Channel Flowjss_devNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes 1 Flow in Open ChannelDokument8 SeitenNotes 1 Flow in Open ChannelTing Wee KietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lect oDokument22 SeitenLect oShishirRijalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drainage Basin - MorphologicalDokument34 SeitenDrainage Basin - MorphologicalArul SankaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open ChannelsDokument21 SeitenOpen ChannelsShlomo GoldbergsteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel FlowDokument5 SeitenOpen Channel FlowMohammad Bin AdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Outline Report in HydrologyDokument15 SeitenOutline Report in HydrologyMary Joy DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecturenote - 603449035open Channel Hydraulics Chapter OneDokument10 SeitenLecturenote - 603449035open Channel Hydraulics Chapter OneAlfatah muhumedNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFC 21103 Hydraulics: Learning OutcomesDokument13 SeitenBFC 21103 Hydraulics: Learning Outcomeshibby_tomeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erosion Sedimentation and The River BasinDokument59 SeitenErosion Sedimentation and The River BasinBen Fraizal UkailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel FlowDokument62 SeitenOpen Channel Flowhammadi100% (1)
- Hydraulic Geometry River or Channel Bed Confirmation River or Channel Pattern Channel Types Channel Fluid DynamicsDokument3 SeitenHydraulic Geometry River or Channel Bed Confirmation River or Channel Pattern Channel Types Channel Fluid DynamicsAbhishek GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel Flow Calculations With The Manning Equation 12 11 14 FinalDokument25 SeitenOpen Channel Flow Calculations With The Manning Equation 12 11 14 FinalrcalaforraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel Flow Chapter1Dokument40 SeitenOpen Channel Flow Chapter1rashikawrk25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uniform Open Channel Flow-R1Dokument25 SeitenUniform Open Channel Flow-R1Kenn Wahh100% (1)
- Chapter 1Dokument29 SeitenChapter 1Fong Pei TyngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: ER Lapong: MSU-General SantosDokument59 SeitenPrepared By: ER Lapong: MSU-General SantosJireh Loquinario100% (1)
- Lecture Notes Part 1 (Exit)Dokument19 SeitenLecture Notes Part 1 (Exit)girmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel Flow Meters ArticleDokument2 SeitenOpen Channel Flow Meters Articlekrimchand1825100% (1)
- Hydraulics II CE 2602 LECTURE NOTESDokument42 SeitenHydraulics II CE 2602 LECTURE NOTESAmanuel BezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1Dokument90 SeitenChapter 1Payal ChakoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- HE - M6 - L1 - Open Channel FlowDokument19 SeitenHE - M6 - L1 - Open Channel FlowSahil WadhwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Assignment: Dibrugarh UniversityDokument12 SeitenHome Assignment: Dibrugarh UniversityUdayan MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manning Equation - Open Channel Flow Using Excel: Course ContentDokument40 SeitenManning Equation - Open Channel Flow Using Excel: Course Contentmushava nyokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aengr410 2015 - IntroDokument85 SeitenAengr410 2015 - IntroIseas Dela PenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Channel FlowDokument22 SeitenOpen Channel FlowNjuguna WaweruNoch keine Bewertungen
- HHM Unit 1Dokument31 SeitenHHM Unit 1Swati ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Materials: Mr. O'Rourke ConstructionDokument12 SeitenConstruction Materials: Mr. O'Rourke Constructionmurad_ceNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUST Civil SyllabusDokument33 SeitenAUST Civil Syllabusmurad_ceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Rule 2009Dokument22 SeitenWater Rule 2009murad_ceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bangladesh Is The Largest Deltaic Floodplain in The World With A Total Area of 147570 KM of Which 88892 KM Is Occupied by Major Rivers and EstuariesDokument1 SeiteBangladesh Is The Largest Deltaic Floodplain in The World With A Total Area of 147570 KM of Which 88892 KM Is Occupied by Major Rivers and Estuariesmurad_ceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto CAD Command ListDokument2 SeitenAuto CAD Command Listmurad_ce100% (1)
- Page101 Mehedi PapDokument13 SeitenPage101 Mehedi Papmurad_ceNoch keine Bewertungen