Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Steady State Heat Conduction: Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 1
Hochgeladen von
abdullah1sOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Steady State Heat Conduction: Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 1
Hochgeladen von
abdullah1sCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mechanical Engineering Dept.
CEME NUST 1
Ch-3: Steady State Heat Conduction
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 2
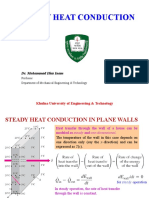
Steady State Heat Conduction
Considerable Temperature Difference between the inner and the outer surfaces
of the wall (significant temperature gradient in the x-direction)
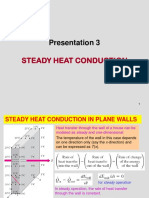
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
The wall surface is nearly isothermal
Steady 1-dimensional modeling approach is justified
Assuming heat transfer is the only energy
interaction and there is no heat generation, the
energy balance is:
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 3
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
rate of heat transfer through the wall must be
constant, Q
cond,wall
= constant
Temperature Distribution
general heat conduction equation in Cartesian
coordinates
no change in temperature of wall with time at any point
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 4
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
Temperature Distribution contd--
temperature distribution across a wall is
linear and is independent of thermal
conductivity
heat through the plane wall using Fouriers Eq.
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 5
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
Temperature Distribution contd--
once the rate of heat conduction is available,
temperature T(x) at any location x can be
determined by replacing T
2
in above Eq. by T,
and L by x
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 6
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
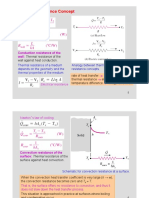
Thermal Resistance Concept
Heat Conduction through a plane wall can be rearranged as:
Where R
wall
is the conduction resistance
Thermal Resistance of a medium depends on the geometry and the
thermal properties of the medium
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 7
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
Analogy to Electrical Current Flow
Above Eq. is analogous to the relation for electric current flow I, expressed as:
Heat Transfer
Rate of heat transfer
Thermal resistance
Temperature difference
Electrical current flow
Electrical resistance
Electric current
Voltage difference
Thermal Resistance Concept contd--
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 8
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
Thermal Resistance Concept contd--
Convection Resistance
Thermal resistance can also be applied to convection processes
Newtons Law of Cooling for convection heat transfer rate (Q
conv
=hA
s
(T
s
-T ))
can be rearranged as:
R
conv
is the convection resistance
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 9
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
Thermal Resistance Concept contd--
Radiation Resistance
Rate of Radiation Heat Transfer between a surface and the surrounding
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 10
Steady State Heat Conduction
Steady Heat Conduction in Plane Walls
Thermal Resistance Concept contd--
Radiation and Convection Resistance
A surface exposed to the surrounding might involves convection and radiation
simultaneously
Convection and Radiation Resistances
are parallel to each other
When T
surr
T
, radiation effect can
properly be accounted for by replacing h in
the convection resistance relation by
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 11
Steady State Heat Conduction
Heat Conduction Through a Composite Wall
Quantity of heat transmitted per unit
time through each slab/layer is same
Assuming a perfect contact between the
layers and no temperature drop occurs
across the interface between the materials
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 12
Steady State Heat Conduction
Heat Conduction Through a Composite Wall
For composite wall
consists of n layers
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 13
Steady State Heat Conduction
Heat Conduction Through a Composite Wall
Parallel Arrangement
total heat transfer is the sum of the heat
transfers through each layer
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 14
Steady State Heat Conduction
Heat Conduction Through a Composite Wall
Combined Parallel-Series Arrangement
Total rate of heat transfer through the
composite system
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 15
Steady State Heat Conduction
The Overall Heat-transfer Coefficient
While dealing with the problems of fluid to fluid heat transfer across a metal
boundary, it is usual to adopt an overall heat transfer coefficient U
Mechanical Engineering Dept. CEME NUST 16
Steady State Heat Conduction
The Overall Heat-transfer Coefficient
If U is Overall Coefficient of Heat Transfer
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Friction and Lubrication in Mechanical DesignDokument569 SeitenFriction and Lubrication in Mechanical DesignFernanda Boulhosa Rodamilans75% (4)
- Heat Transfer & ThermodynamicsDokument194 SeitenHeat Transfer & ThermodynamicsBetty Blue100% (1)
- Lec 7 1Dokument38 SeitenLec 7 1Sara100% (1)
- Resistance ConceptDokument38 SeitenResistance ConceptNihad S ZainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass TransferDokument46 SeitenHeat and Mass Transferabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass TransferDokument46 SeitenHeat and Mass Transferabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steady Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDokument53 SeitenSteady Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsMiguel RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thrust Block DesignDokument12 SeitenThrust Block DesignJorge Castro Cucurella100% (1)
- Length Power Dynamic Viscosity Heat FluxDokument9 SeitenLength Power Dynamic Viscosity Heat FluxAnubhav KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- C9789810694364SM PDFDokument34 SeitenC9789810694364SM PDFJohnrey FlandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction Heat Transfer and Heat SinksDokument62 SeitenConduction Heat Transfer and Heat SinksPATEL PUNIT100% (1)
- Detailed Syllabus - IsRO Technical Assistant (Mech-ECE)Dokument18 SeitenDetailed Syllabus - IsRO Technical Assistant (Mech-ECE)Abhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serie (Conducción en Estado Estable)Dokument6 SeitenSerie (Conducción en Estado Estable)Arturo CoPaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Stresses and Temperature Control of Mass ConcreteVon EverandThermal Stresses and Temperature Control of Mass ConcreteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Fizik F5 2023 (Answers)Dokument25 SeitenModul Fizik F5 2023 (Answers)nyshahidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap03 HT 3e LectureDokument73 SeitenChap03 HT 3e LecturebpulatstudentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 STEADY HEAT CONDUCTION 2021Dokument102 SeitenChapter 3 STEADY HEAT CONDUCTION 2021BT20MEC058AdeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass TransferDokument25 SeitenHeat and Mass Transferabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 LECTURE 2 - One-Dimensional, Steady-State ConductionDokument32 Seiten2.1 LECTURE 2 - One-Dimensional, Steady-State ConductionKingsley CassityNoch keine Bewertungen
- One Dimensional Steady State Conduction: By: Taz 1Dokument52 SeitenOne Dimensional Steady State Conduction: By: Taz 1Adam AndualemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument29 SeitenChapter 2tafariafessamorodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3A Chapter3 Sec.3.1 3.4 ColorDokument49 Seiten3A Chapter3 Sec.3.1 3.4 ColorAdven SimarmataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat 4e Chap03 LectureSpring 2023Dokument72 SeitenHeat 4e Chap03 LectureSpring 2023sarahjheehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat 4e Chap03 LectureDokument51 SeitenHeat 4e Chap03 LectureAbhijit Kushwaha100% (1)
- Heat Transfer: Lecture Notes 3 BDA 3063/30603Dokument34 SeitenHeat Transfer: Lecture Notes 3 BDA 3063/30603Foong Kah LoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 LECTURE 2 - One-Dimensional, Steady-State ConductionDokument32 Seiten2.1 LECTURE 2 - One-Dimensional, Steady-State ConductionKingsley CassityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFDokument62 SeitenChapter 2 - Steady Heat Conduction PDFAroon KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Dimensional Steady-State ConductionDokument31 SeitenOne-Dimensional Steady-State ConductionSajjad KheirandishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steady Heat ConductionDokument47 SeitenSteady Heat ConductionXuânNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap03 Steady Heat ConductionDokument63 SeitenChap03 Steady Heat ConductionDilara ŞimşekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Thermal & Hydraulic EngineeringDokument24 SeitenApplied Thermal & Hydraulic EngineeringRahil Makwana0% (1)
- David - Conduction On Steady StateDokument26 SeitenDavid - Conduction On Steady StateStephen TabiarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferDokument30 Seiten5MA039 - Introduction To Heat TransferNaveen KarunarathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeatDokument75 SeitenHeatVanessaYanjanHarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer - Convection - Thickness of Thermal Boundary Layer PDFDokument16 SeitenHeat Transfer - Convection - Thickness of Thermal Boundary Layer PDF102MERishav Pratap SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steady Heat Conduction: Buyung JunaidinDokument17 SeitenSteady Heat Conduction: Buyung JunaidinAisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat T CH 2-1Dokument67 SeitenHeat T CH 2-1Fira tubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Chapter ThreeDokument62 SeitenHeat Transfer Chapter ThreeteddiyfentawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat TransferDokument11 SeitenHeat TransferzulkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5Dokument22 SeitenLecture 5ssaalleehh340Noch keine Bewertungen
- Null PDFDokument31 SeitenNull PDFDeekshaomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Heat Conduction For Rectangle, CylindersDokument18 SeitenGeneral Heat Conduction For Rectangle, CylindersTamoor TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer: CVS 467 Building Physics and ServicesDokument14 SeitenHeat Transfer: CVS 467 Building Physics and ServicesharryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass Chapter 3Dokument56 SeitenHeat and Mass Chapter 3Mvelo PhungulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minggu 3 KonveksiDokument31 SeitenMinggu 3 KonveksiYudha PradhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 05Dokument9 SeitenClass 05Dia' AfanehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Heat Transfer Coefficient PDFDokument28 Seiten7 Heat Transfer Coefficient PDFNavarre LatchmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3-Steady Heat ConductionDokument49 SeitenChapter 3-Steady Heat Conductionumutalidemirpolat50Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steady Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDokument41 SeitenSteady Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsWan Nur FakhiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3 - ConductionDokument57 SeitenWeek 3 - ConductionYohan ManaligodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vdocuments - MX - Chapter 3 Steady Heat Conduction Unimap Notes Mehmet Kanoglu UniversityDokument53 SeitenVdocuments - MX - Chapter 3 Steady Heat Conduction Unimap Notes Mehmet Kanoglu UniversityMahmoud Al-Ma'aitahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat 4e Chap03 LectureDokument51 SeitenHeat 4e Chap03 LecturePanitan JANTARAMSRINoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 3: Steady Heat ConductionDokument51 SeitenPresentation 3: Steady Heat ConductionhussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steady Heat ConductionDokument95 SeitenSteady Heat ConductionFAKE RAKIBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steady Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & ApplicationsDokument51 SeitenSteady Heat Conduction: Heat and Mass Transfer: Fundamentals & Applicationsmissing wonderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Basics of Heat Transfer (ENSC 14a)Dokument27 Seiten1 Basics of Heat Transfer (ENSC 14a)Aldwin Angelo Culing MontañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction PDFDokument156 SeitenIntroduction PDFIsyana MelzNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMT NotesDokument65 SeitenHMT NotesMadhu SujanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Mengr 3100 - Basic Mechanical EngineeringDokument10 Seiten1 - Mengr 3100 - Basic Mechanical EngineeringronnelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 MODDokument73 SeitenModule 1 MODbbfe89f31eNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMT Lab ManualDokument107 SeitenHMT Lab ManualUzair KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument52 SeitenChapter 2BISRAT YIHUNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Resistance Concept: Conduction Resistance of The WallDokument6 SeitenThermal Resistance Concept: Conduction Resistance of The WallMANoch keine Bewertungen
- 24th August HEAT GENERATION IN A SOLIDDokument11 Seiten24th August HEAT GENERATION IN A SOLIDSaloni.Dhawale Btech2018Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and MeasurementDokument8 SeitenInstrumentation and Measurementabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amphibous Stem Sellular InstrumentationDokument8 SeitenAmphibous Stem Sellular Instrumentationabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture About DepressionDokument11 SeitenLecture About Depressionabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and IntrumentsDokument6 SeitenMeasurement and Intrumentsabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture About DepressionDokument11 SeitenLecture About Depressionabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture About DepressionDokument11 SeitenLecture About Depressionabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Olunteer/non Professional Egistration Orm: Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research CentreDokument3 SeitenOlunteer/non Professional Egistration Orm: Shaukat Khanum Memorial Cancer Hospital & Research Centreabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electronics .. Combinational LogicDokument44 SeitenBasic Electronics .. Combinational Logicabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrumentation Anbd MeasurementDokument11 SeitenIntrumentation Anbd Measurementabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and MeasurementDokument8 SeitenInstrumentation and Measurementabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- (B) Machine Design (4) .Welded SymbolsDokument21 Seiten(B) Machine Design (4) .Welded Symbolsabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Education & FreedomDokument17 SeitenEducation & Freedomabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and MeasurementDokument13 SeitenInstrumentation and Measurementabdullah1s0% (1)
- Air Conditioning SystemsDokument11 SeitenAir Conditioning Systemsabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement and InstrumentationDokument8 SeitenMeasurement and Instrumentationabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and MeasurementDokument7 SeitenInstrumentation and Measurementabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument4 SeitenAssignmentabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supposedly Kurds Are Yazidi, SDokument1 SeiteSupposedly Kurds Are Yazidi, Sabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics: Assignement 1Dokument3 SeitenThermodynamics: Assignement 1abdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumentation and MeasurementDokument7 SeitenInstrumentation and Measurementabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument4 SeitenAssignmentabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welded Joints CompleteDokument28 SeitenWelded Joints Completeabdullah1s100% (1)
- The Seven Types of Non-BelieiversDokument5 SeitenThe Seven Types of Non-Belieiversabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Trinity HeresyDokument23 SeitenThe Trinity Heresyabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jinnah The QuaidDokument4 SeitenJinnah The Quaidabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Right To KnowDokument22 SeitenYour Right To Knowabdullah1sNoch keine Bewertungen
- 36-Unsteady State Heat Conduction Lumped Heat Capacity Analysis - 14-Aug-2019Material - I - 14-Aug-2019 - TRANSIENT - HEAT - CONDUCTION PDFDokument9 Seiten36-Unsteady State Heat Conduction Lumped Heat Capacity Analysis - 14-Aug-2019Material - I - 14-Aug-2019 - TRANSIENT - HEAT - CONDUCTION PDFsiva yandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rpa99 2003Dokument8 SeitenRpa99 2003Atul WanodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion in One Dimension: Chapter OutlineDokument35 SeitenMotion in One Dimension: Chapter OutlineJayjo SegundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 WeirDokument32 Seiten11 WeirGray Fiore FullbusterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vortex Drop ShaftDokument9 SeitenVortex Drop ShaftMarco PazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Influence Lines FOR Statically Determinate Beams: StructureDokument34 SeitenUnit Influence Lines FOR Statically Determinate Beams: StructureRaj BakhtaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13.6 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: W F DX MVDokument3 Seiten13.6 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: W F DX MVsreejitha KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difusión MethodsDokument5 SeitenDifusión MethodsKeily VilcarromeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Models Mems Fluid Structure InteractionDokument16 SeitenModels Mems Fluid Structure InteractionhahaerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Monotonic and Cyclic Properties of Ductile IronsDokument16 SeitenComparison of Monotonic and Cyclic Properties of Ductile IronsDomingos AzevedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- (B) Velocity and Acceleration in Polar CoordinateDokument2 Seiten(B) Velocity and Acceleration in Polar CoordinateAkshay SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AllenDokument40 SeitenAllenDhanpat RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrum Physics - May 2016Dokument100 SeitenSpectrum Physics - May 2016Popovici DraganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appliedmechanics00poorrich PDFDokument264 SeitenAppliedmechanics00poorrich PDFNileshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction Coefficient in PipesDokument16 SeitenFriction Coefficient in PipesVanessa AyalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force and PressureDokument90 SeitenForce and PressureAzra BaigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical No-5 (Curvilinear Motion)Dokument8 SeitenPractical No-5 (Curvilinear Motion)Jay V. GoyelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROBLEM 13.14: SolutionDokument1 SeitePROBLEM 13.14: SolutionNattamon PetchkeawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buckling of Thin-Walled Circular CylindersDokument60 SeitenBuckling of Thin-Walled Circular CylindersLudovic MoutienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From Chapter 18-6Dokument10 SeitenPages From Chapter 18-6taNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress Analysis of Pressure Vessels Based On ANSYSDokument4 SeitenStress Analysis of Pressure Vessels Based On ANSYSsandeeppandey0789Noch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric PropertiesDokument20 SeitenVolumetric Propertiespk9zg2rxkgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Class 11 Vol 1Dokument992 SeitenPhy Class 11 Vol 1praneshjs2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- MEC 412 Experiment 2 Lab ManualDokument5 SeitenMEC 412 Experiment 2 Lab ManualAnas OmarNoch keine Bewertungen