Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Subject Code: ME-Subject: Experiment No. Title of Experiment
Hochgeladen von
patelmukesh8200 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
91 Ansichten10 SeitenImpulse Turine is a prime mo#er in which fluid under pressure enters a stationary no66le where its pressure 7potential8 energy is con#erted to #elocity 7kinetic8 energy.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
thermo_lab.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenImpulse Turine is a prime mo#er in which fluid under pressure enters a stationary no66le where its pressure 7potential8 energy is con#erted to #elocity 7kinetic8 energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
91 Ansichten10 SeitenSubject Code: ME-Subject: Experiment No. Title of Experiment
Hochgeladen von
patelmukesh820Impulse Turine is a prime mo#er in which fluid under pressure enters a stationary no66le where its pressure 7potential8 energy is con#erted to #elocity 7kinetic8 energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 10
Subject code: ME-304 Subject: Thermodynamics Experiment No.
Title of Experiment: To study the working
principle and working construction of the Impulse
and Reaction steam turines
Page: !-!0
AIM: To study the working principle and working construction of the Impulse and
Reaction steam turines.
APPRATUS:
Model of Impulses turine.
Model of Reaction turine.
O!E"TI#E:
"uantify the con#ersion of mechanical energy to heat energy y
Identifying and $uantifying any possile energy losses in the e%periment.
!
T$EOR%:
1. Introduction
STEAM TURINE: A steam turbine is a mechanical device that extracts thermal energy
from pressurized steam, and con#erts it into rotary motion.
&'())I*I&(TI+, +* )TE(M T-R.I,E)/
!. (ccording to the mode of steam action
Impulse turine
Reaction turine
0. (ccording to the direction of steam flow.
(%ial flows turine
Radial flows turine
3. (ccording to the e%haust condition of steam
.
&ondensing turine
,on-condensing turine
4. (ccording to the of pressure stages.
)ingle stage turines
Multistage impulse and reaction turines
1. (ccording to the numer of cylinders.
)ingle cylinder turines
2oule cylinder turines
Three cylinder turines
*our cylinder turines
0
3. (ccording to pressure of steam
'ow pressure turines4
using steam at a pressure of !.0 to 0 atm
Medium pressure turines4
using steam at pressu
res of upto 40 atm
5igh pressure turines4
utilising pressures ao#e 40 atm
IMPU&SE TURINE/
( Impulse Turine is a prime mo#er in which fluid under pressure enters a stationary
no66le where its pressure 7potential8 energy is con#erted to #elocity 7kin etic8 energy and
asored y the rotor.
3
4
'E(&E#E& IMPU&SE TURINE/
( 2e-'e#el turine is the simplest type of impulse steam turine4 and is commonly used in
which steam impinges upon re#ol#ing lades from a flared no66le.
The flare of the no66le causes e%pansion of the steam4 and hence changes its pressure
energy into kinetic energy. It has the following main components/
1
!. ,o66le/ - It is a circular guide mechanism4 which guides the steam to flow at the
designed direction and #elocity. It also regulates the flow of the steam. The no66le is kept
#ery close to the lades4 in order to minimi6e the losses due to wind age.
0. Runner and lades. / - The runner of the 2e -'a#al impulse turine essentially consists of
a circular disc fi%ed to a hori6ontal shaft. +n the periphery of the runner4 a numer of
lades are fi%ed uniformaly. The steam 9et impinges on the uckets4 which mo#es in the
direction of the 9et. The mo#ement of the lades makes the runner to rotate. The surface of
the lade s is made #ery smooth to minimi6e the frictional losses. The lades are generally
made of special steel alloys.
3. &asing. It is an air tight metallic case4 which contains the turine runner and lades. It
controls the mo#ement of steam from the lades to the condenser4 and does not permit it to
mo#e into the space. Moreo#er4 it is essential to safeguard the runner against any accident.
3
REA"TION TURINE/
( Reaction Turines are those turines in which the energy of the fluid is partly
transformed into kinetic energy efore it enters the runner of the turine.
:
;(R)+,<) RE(&TI+, T-R.I,E/ ( ;arson<s turine is the simplest type of reaction
steam turine4 and is commonly used in which power is otained mainly y an imp ulse
force of the incoming steam and small reacti#e force of the outgoing steam. It has the
following main components/
=
!. &asting/- It is an air - tight metallic case4 in which the steam from the oiler turine4
under a high pressure and temperature4 is distriuted around the fi%ed lades 7guide
mechanism8 in the casting. The casting is designed in such a way that the steam
enters the fi%ed lades with a uniform #elocity.
0. >uide mechanism/- It is a mechanism4 made up with the help of guide lades4 in
the form of a wheel. This wheel is4 generally4 fi%ed to the casting? that is why these
guide lades are also called fi%ed lades. The guide lades are properly designed in
order to/
a8 (llow the steam to enter the runner without shock. This is done y keeping the
relati#e #elocity at inlet of the runner tangential to the lade angle.
8 (llow the re$uired $uantity of steam to enter the turine. This is done y ad9usting
the openings of the lades.
The guide lades may e opened or closed y rotating the regulating shaft4 thus allowing
the steam to flow according to the need. The regulating shaft is operated y means of a
go#ernor whose function is to go#ern the turine 7 i.e. to keep speed constant at #arying
loads8
3. Turine runner/- The turine runner of a ;arson<s reaction turine essentially
consists of runner lades fi%ed to a shaft or rings4 depending upon the type of the
turine. The lades4 fi%ed to the runner4 are propely designed in order to allow the
steam to enter and lea#e the runner without shock. The surf ace of the turine is
made #ery smooth to minimi6e the frictional losses.
4. 2rafting tue/- The steam4 after passing through the runner4 flow into the condenser
through a tue called draft tue. It may e noted that if this tue is not pro#ided in
the turine4 then the steam will mo#e freely and will cause steamed
@
SAMP&E )UATION:
!. E%plain the principle of Impulse A Reaction turineB
0. Chat is working of Impulse A Reaction turineB
3. Chat is staging4 why it is done in reaction turineB
4. Chat is steam trappingB
1. 2eference etween Impulse A Reaction turineB
RE*ERAN"E +I* AN%,:
!0
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Steam TurbineDokument42 SeitenSteam TurbineSreejith VaneryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam TurbineDokument3 SeitenSteam TurbineRohan lallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Iv Atd-Ii Lec Notes PDFDokument5 SeitenUnit Iv Atd-Ii Lec Notes PDFBharani100% (1)
- SteamDokument24 SeitenSteamsanju_17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Steam Turbines and CondensersDokument21 SeitenChapter 5 - Steam Turbines and Condensersvivekfegade81100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering Lab ManualDokument52 SeitenThermal Engineering Lab ManualBharath ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TurbinesDokument34 SeitenTurbinesDipesh Patle100% (2)
- Steam TurbineDokument17 SeitenSteam TurbineDicky Nicky NovemberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam TurbineDokument14 SeitenSteam TurbineJoe Je LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Positive Displacement Pumps Parts List & Function: Sub ObjectiveDokument14 SeitenLesson Positive Displacement Pumps Parts List & Function: Sub Objectivemister pogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine ReportDokument32 SeitenSteam Turbine ReportAbdulBasit50% (2)
- Valve Timing Diagram 1.1 AIMDokument11 SeitenValve Timing Diagram 1.1 AIMswiserd_cars1199Noch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training ReportDokument27 SeitenSummer Training ReportAnkit BishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working of Steam Turbines and Its AuxillariesDokument48 SeitenWorking of Steam Turbines and Its AuxillariesbalajigandhirajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsDokument18 SeitenThermal Energy Steam Sir Charles ParsonsgauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine - WikipediaDokument6 SeitenTurbine - Wikipediarpraj3135Noch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Dokument48 SeitenAutomotive Turbocharged Gas Turbine.Santanu ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine: HistoryDokument9 SeitenSteam Turbine: HistoryrikumohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam TurbineDokument24 SeitenSteam TurbinePujara ManishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Engine Components and ClassificationDokument42 SeitenChapter 1 - Engine Components and ClassificationAdib MaharunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam TurbineDokument16 SeitenSteam TurbineUtkarsh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine 1Dokument73 SeitenSteam Turbine 1Balaji Kalai0% (1)
- Report On Steam TurbineDokument18 SeitenReport On Steam TurbineAmit PareekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 8 Engine Cycles - OttoDokument42 SeitenLecture 8 Engine Cycles - OttoMuhammad AbubakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week No. 9 Transformer and MaintenanceDokument11 SeitenWeek No. 9 Transformer and MaintenanceHaeisy SimsuangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 (2021)Dokument22 SeitenChapter 5 (2021)Tesfay TeklayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam TurbineDokument12 SeitenSteam TurbineMandeep Singh PannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine Fresh01Dokument18 SeitenSteam Turbine Fresh01Sachin Kumar100% (1)
- Boiler Report LalPirDokument45 SeitenBoiler Report LalPirAleem UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine - WikipediaDokument7 SeitenTurbine - WikipediaKiran KotinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Steam TurbineDokument11 Seiten05 Steam TurbineJohn Paulo ArchinueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine 2Dokument5 SeitenSteam Turbine 2Pratibha PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layout of Power Plant LabDokument8 SeitenLayout of Power Plant Labirsalan_shahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine: Chapter # 1Dokument31 SeitenTurbine: Chapter # 1Rohit MahajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine: Soran Universty Faculty of Enginnring Chimecal Engineering Department Third Stage Second Semester 18/5/2022Dokument22 SeitenTurbine: Soran Universty Faculty of Enginnring Chimecal Engineering Department Third Stage Second Semester 18/5/2022Dilgash BahriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Turbine: Navigation SearchDokument42 SeitenSteam Turbine: Navigation Searchh_imdad23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Presentation SlidesDokument188 SeitenLecture Presentation SlidesSamuel DASAOLUNoch keine Bewertungen
- pptPPE (15&17)Dokument22 SeitenpptPPE (15&17)HarshitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine PrincipleDokument57 SeitenTurbine PrincipleSheikh Zakir100% (1)
- Marine Diesel Engine Introduction and TheoryDokument84 SeitenMarine Diesel Engine Introduction and TheoryVamshikrishna Kuruva100% (7)
- IC Engine Seminar ReportDokument25 SeitenIC Engine Seminar Reportrupam_chanda75% (4)
- Steam TurbineDokument46 SeitenSteam TurbinePOWERBOOKONE100% (2)
- Question and Answer On Steam TurbinesDokument33 SeitenQuestion and Answer On Steam TurbineschunkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Training Module On Turbine, Lub Oil, Gland Steam SystemDokument228 SeitenTraining Module On Turbine, Lub Oil, Gland Steam Systemdinesh7136100% (2)
- PEP Session On Steam TurbinesDokument35 SeitenPEP Session On Steam Turbinesdanish moinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Steam PipingDokument14 SeitenChapter 8 Steam PipingChen WsNoch keine Bewertungen
- BHEL Bhopal STM Training ReportDokument20 SeitenBHEL Bhopal STM Training ReportMohit Assudani50% (2)
- Chapter 7Dokument62 SeitenChapter 7birlieNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 TurbochargerDokument14 Seiten12 TurbochargerAisha Zaheer100% (5)
- Turbine & Its Governing and Turbo Generator AlokDokument143 SeitenTurbine & Its Governing and Turbo Generator AlokSHAMSIK2002100% (3)
- TurbineDokument63 SeitenTurbineDiyan Juniarto0% (1)
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiVon EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific American Supplement, No. 633, February 18, 1888Von EverandScientific American Supplement, No. 633, February 18, 1888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Watch Repairing, Cleaning and Adjusting - A Practical HandbookVon EverandWatch Repairing, Cleaning and Adjusting - A Practical HandbookNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Power Primer - An Introduction to the Internal Combustion EngineVon EverandA Power Primer - An Introduction to the Internal Combustion EngineNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Opérate An Amine PlantDokument4 SeitenHow To Opérate An Amine PlantAry HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion in One DimensionDokument1 SeiteMotion in One DimensionAmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Process For Mild SteelDokument9 SeitenOptimization of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Process For Mild Steelzaki amNoch keine Bewertungen
- DL-T 5358-2006 Technical Code For Anticorrosion of Metal Structures in Hydroelectric and Hydraulic EngineeringDokument43 SeitenDL-T 5358-2006 Technical Code For Anticorrosion of Metal Structures in Hydroelectric and Hydraulic Engineeringsaliyarumesh2292Noch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Notes On Mass, Weight and DensityDokument8 SeitenO Level Notes On Mass, Weight and DensityRavi MothoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liner EncoderDokument48 SeitenLiner EncoderShahzad AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alarm Code OverzichtDokument36 SeitenAlarm Code OverzichtMihuța NarcisaNoch keine Bewertungen
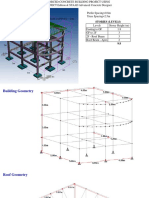
- 2 Storeys BuildingDokument30 Seiten2 Storeys BuildinglavyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erdemir 1 - Tribological and Solid Lubrificant Coatings PDFDokument9 SeitenErdemir 1 - Tribological and Solid Lubrificant Coatings PDFMÔNICA SUEDE S. SILVANoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 MOdern Physics FinalDokument10 SeitenModule 1 MOdern Physics FinalMary Joy BernasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base ChemistryDokument23 SeitenAcid Base ChemistryJunegreg CualNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stefan-Boltzmann Law: 2 H C Exp 1Dokument16 SeitenStefan-Boltzmann Law: 2 H C Exp 1RonyVargasNoch keine Bewertungen
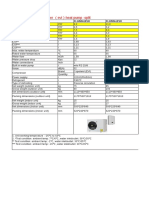
- Low Temperature Air/water Evi Heat Pump - Split: Model Zluaw-10Sh Zluaw-12ShDokument1 SeiteLow Temperature Air/water Evi Heat Pump - Split: Model Zluaw-10Sh Zluaw-12ShHumberto GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME255-mod 2Dokument30 SeitenME255-mod 2Owusu Gyamera Justice DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pressure Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings: Standard Specification ForDokument18 SeitenPolyethylene (PE) Gas Pressure Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings: Standard Specification ForPatricio G. ArrienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Flow Postlab ReportDokument14 SeitenFluid Flow Postlab Reportgracebrewster123Noch keine Bewertungen
- COMPRESOR - Kobelco-Knw-Series-Instruction-Manual-54Dokument54 SeitenCOMPRESOR - Kobelco-Knw-Series-Instruction-Manual-54YERSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- 278 Renu BajajDokument2 Seiten278 Renu BajajAbhinav ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC Syllabus Kerala University (2003 Scheme)Dokument57 SeitenEC Syllabus Kerala University (2003 Scheme)joyasams75% (4)
- Calibration of Temperature Measuring DevicesDokument7 SeitenCalibration of Temperature Measuring DevicesGrace N MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB PHYSICS HL - Chapter 4 Waves PDFDokument10 SeitenIB PHYSICS HL - Chapter 4 Waves PDFAna MariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tmp1a33 TMPDokument12 SeitenTmp1a33 TMPFrontiersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particulate Processing of Metals and CeramicsDokument98 SeitenParticulate Processing of Metals and CeramicsDamy Manesi0% (2)
- Pouring & SolidificationDokument19 SeitenPouring & SolidificationTanmay KothiwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meteorology and Oceanography ReviewerDokument19 SeitenMeteorology and Oceanography ReviewerElevado Elegene L.67% (3)
- Gradient Echo Imaging: Review: MR Physics For CliniciansDokument16 SeitenGradient Echo Imaging: Review: MR Physics For CliniciansFelipe Gustavo Tercero Vega AbantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceiling PHR PHS Suspension IsolatorsDokument14 SeitenCeiling PHR PHS Suspension IsolatorsKunal GujarathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallurgy SyllabusDokument1 SeiteMetallurgy SyllabusSathrudhan ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BNWQ 3 Ak TZ3 RNG Z4 QGW WaDokument14 SeitenBNWQ 3 Ak TZ3 RNG Z4 QGW Wathealtamash21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surfactants For Use As CodispersantsDokument10 SeitenSurfactants For Use As Codispersantsramitkatyal21881Noch keine Bewertungen