Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fourier Series
Hochgeladen von
Bunga TulipOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fourier Series
Hochgeladen von
Bunga TulipCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
FOURIER SERIES
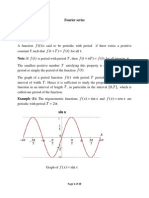
A periodic function f(t) can be represented by an infinite sum of sine and/or cosine
functions that are harmonically related. That is, the frequency of any trigonometric term
in the infinite series is an integral multiple, or harmonic, of the fundamental frequency of
the periodic function. Thus, given f(t) is periodic (e.g. square wave, triangular wave, half
rectified wave, etc.), then f(t) can be represented as follows:
----- (Eq. 1.1)
where n is the integer sequence 1,2,3, ... ,
a0, an, and bn are called the Fourier coefficients, and are calculated from f(t),
0 = 2 is the fundamental frequency of the periodic function f(t) with period T,
T
and
n 0 is known as the n-th harmonic of f(t).
Periodic Functions .
In terms of Eq. (1.1), f(t) can be extended to t ; it becomes a periodic function,
with a period 2, i.e., f(t) = f(t + 2). For instance, instead of [0, 2], we can use [, ]
for limits in Eq. (I.2).
1
a0
T
T
2
T
2
f (t )dt
-------
a0
1
2
an
1
T
T
2
T
2
f (t ) cosntdt ---- a n
1
2
bn
1
T
T
2
T
2
f (t ) sin ntdt ---- bn
1
2
a0
1
2
f (t ) cos ntdt ---- an
1
2
f (t )dt
------
f (t ) sin ntdt ---- bn
1
2
2
0
2
0
2
0
f (t )dt
f (t ) cosntdt
f (t ) sin ntdt
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
Example 1:
Show that f(x) = 5 sin 3x is a periodic function of period 2.
Solution :
f (x + 2 ) = 5 [
)]
=5[
]
where cos 2 = 1 ; sin 2 = 0
= 5 sin 5x
= f (x)
f (x + 2 ) = f(x)
[
(
)
Shown
]
The effect of symmetry on the Fourier coefficients
Even-function symmetry
A function is defined as even if f(t) = f(-t). The equations for the Fourier coefficients
reduce to:
Example :
f (t ) cost
f(t)
-t
f(t)
f (t ' ) f (t ' )
t
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
i.
ii.
iii.
for all n
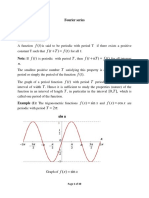
Odd-function symmetry
A function is defined as odd if f(t) = -f(-t); then the Fourier coefficients are given by:
Example ;
f (t ) sin t
f(t)
f(t)
f(t)
i.
ii.
iii.
for all n,
;
for all n,
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
EXAMPLE 2 :
If f(x) =
is defined in the interval < x < and
f(x) = f (x + 2);
a)
state whether the function is odd or even.
b)
determine which components of the Fourier Series are
present in the function.
EXAMPLE 3:
Sketch the waveform and label the axis, period and the amplitude of the periodic
function defined as :
0 , 5 t 0
T = 10
f (t ) ,
0t 5
3
f(x)
3
T
-10
-5
T=10
ao
1 5
f ( x) dx
T 5
1 0
0 dx 0 3 dx
3x 0
10
1
15
10
3
10
15
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
an
2 T
f ( x) cos nwo x dx
T 0
( wo
2 2
)
T 10 5
5
2 0
5 0 . cos nwo x dx 0 3 . cos nwo x dx
10
1
3 . cos n x dx
0
5
5
sin n x
5
3
3 5
5
sin n x
5
5 n
5 0
n
5 0
3
nx
sin
n
5 0
0 untuk semua nilai n
5
bn
2 T
f ( x) sin nwo x dx
T 0
( wo
2 2
)
T 10 5
5
2 0
5 0 . sin nwo x dx 0 3. sin nwo x dx
10
1 5
3. sin n x dx
5 0
5
cos n x
5
3
3 5
5
cos n x
5
5 n
5 0
n
0
3
nx
cos
n
5 0
3
n (5)
n (0)
cos
cos
n
5
5
3
cos n 1
n
5
bila n ganjil (odd), bn =
6
n
bila n genap (even), bn = 0
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
f (t ) a 0 a n cos nwo t bn sin nwo t
n 1
f (t )
3 6 x 1
3x 1
5x
sin sin
sin
.....
2
5 3
5
5
5
EXAMPLE 4 :
f(t)
1
0
-1
T
f (t ) a1Cos 0 t a3Cos3 0 t a5 Cos5 0 t .... a n Cosn 0 t
Untuk 1 kitar (T) ---- merujuk kepada gelombang
i)
f (t ) 1
f (t ) 1
f (t ) 1
a0
1
T
T
T
t
2
4
T
T
t
4
4
T
T
t
4
2
T
0
f (t )dt
4
2
1 4
a0 T (1)dt T (1)dt T (1)dt
T 2
4
4
1
a0 t
T
T
4
T
2
T
4
T
2
1
T
4
T
2
a0
1
T T
T T
T T
( ) ( ) ( )
T
4 2
4 4
2 4
a0
1 T
T
4 2
T 4
2
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
a0
1
T T
T
a0 0
ii)
an
an
2
T
T
2
T
2
f (t ) cos ntdt ;
an
4 2
0 f (t ) cos ntdt
T
T
T
4 4
2
(
1
)
cos
n
t
dt
0
T ( 1) cosnt dt
T
4
T
T
4 sinnt 4 sinnt 2
an
T n 0 n T
4
T
T
4
2
4
an
sinnt 0 sinnt T
nT
4
an
4
nT
T
T
T
sin n ( 4 ) 0 sin n ( 2 ) sin n ( 4 )
an
4
nT
T
T
2
sin
n
(
)
sin
n
(
)
4
2
an
4
2
n
T
an
2
n
2 sin 2 sin n
an
4
n
n
sin 2
2
T
2 T
2 T
2 sin n T ( 4 ) sin n T ( 2 )
Bila n genap (n = 2, 4, 6, .)
an
4
n
4
2(180 )
sin 2 n (0) 0
sin n = 0
; rad 180
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
Bila n ganjil (n = 1, 5, 9, .)
an
4
n
4
4
4
1(180 )
sin 2 (1) (1) @ (5) (1) @ (9) (1)
Bila n ganjil (n = 3, 7, 11, .)
an
f (t )
4
n
4
4
4
3(180 )
sin 2 (3) (1) @ (7) (1) @ (11) (1)
4
1
1
1
Cos t Cos3 t Cos5 t Cos7 t ....
3
5
7
EXAMPLE 5 :
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
bn
2 T
f (t ) sin nwo t dt
T 0
bila n ganjil, bn =
2
n
bila n genap, bn = 0
Siri Fourier ialah
1
2
0
sin nt
2 n 1
n
1 2
2
2
sin t sin 3t
sin 5t .......... ....
2
3
5
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
EXAMPLE 6 :
a)
For the waveform of Figure 1(a),
i.
Find the analitic equation and state the function f(t) whether odd or
even symmetry.
ii.
Calculate the coefficient a 0 , a n and bn .
iii.
Refer to the value of bn , write the Fourier coefficient for
n = 1, 3, 5 and 7.
f(t)
-4
Figure 1(a)
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
Solution :
i.
1
1 0
1
f t dt
4dt
0 4dt
2
2
2
4t 0
4t
0
2
2
4 4
0
2
2
a0
an
f t cos ntdt
0 4 cos ntdt
0 4 cos ntdt
4 sin nt 0
4 sin nt
0
n
n
sin n0 4 sin n 4 sin n 4 sin n0
1
4
n
n
n
n
1 4 sin n 4 sin n
0
n
n
bn
f t sin ntdt
0 4 sin ntdt
0 4 sin ntdt
4 cosnt 0
4 cosnt
0
n
n
1 cosn0 4 cosn 4 cosn 4 cosn0
4
n
n
n
n
4
cos0 cos n cosn cos0
n
4
2 2 cosn 8 1 cosn
n
n
2
1 cosn 0
Oleh itu pekali Fourier adalah a 0 = 0, a n = 0, bn =
8
1 cos n
n
; n = 1, 3, 5,7
Disediakan oleh : Pn Misida Binti Senon
n=1
b1=
n=3
b3=
8
3
n=5
b5=
8
5
n=7
b7=
8
7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Firearm Laws in PennsylvaniaDokument2 SeitenFirearm Laws in PennsylvaniaJesse WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Want To Buy & Sell Expired Domain Names-Follow These 3 StepsDokument6 SeitenWant To Buy & Sell Expired Domain Names-Follow These 3 StepsEmiemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaps, Pro Versus NoviceDokument2 SeitenGaps, Pro Versus Novicertkiyous2947Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series Problems and SolutionDokument78 SeitenFourier Series Problems and SolutionJed Efraim Espanillo100% (1)
- Guillang Vs Bedania and SilvaDokument2 SeitenGuillang Vs Bedania and Silvajdg jdgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Euroleague Basketball: Change Pays Off ForDokument36 SeitenEuroleague Basketball: Change Pays Off ForNikos TagalnikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier PDFDokument31 SeitenFourier PDFGerson Santos100% (1)
- Functional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)Von EverandFunctional Operators (AM-22), Volume 2: The Geometry of Orthogonal Spaces. (AM-22)Noch keine Bewertungen
- HTML5 3D VisualizacionesDokument31 SeitenHTML5 3D VisualizacionesHENRY ISAAC GONZALEZ CRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USDokument656 SeitenTIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USskyttt135Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDokument110 SeitenEe602 Fourier SeriesSyaa MalyqaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week13-14 - Fourier SeriesDokument17 SeitenWeek13-14 - Fourier SeriesFiq Den100% (1)
- Special Power of AttorneyDokument1 SeiteSpecial Power of Attorneywecans izza100% (1)
- ABSTRACT (CG To Epichlorohydrin)Dokument5 SeitenABSTRACT (CG To Epichlorohydrin)Amiel DionisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series and TransformDokument46 SeitenFourier Series and TransformVaibhav Patil100% (1)
- Cbi LNG Storage US Rev8 LoresDokument4 SeitenCbi LNG Storage US Rev8 LoresVilas AndhaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucionario Parte 4 Matemáticas Avanzadas para Ingeniería - 2da Edición - Glyn JamesDokument76 SeitenSolucionario Parte 4 Matemáticas Avanzadas para Ingeniería - 2da Edición - Glyn JamesKimberly Clark86% (7)
- Fourier Series NotesDokument39 SeitenFourier Series NotestanmayeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series Notes Corrected PDFDokument39 SeitenFourier Series Notes Corrected PDFProma ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series NOTESDokument67 SeitenFourier Series NOTESAzue RamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fourier Series EditedDokument46 SeitenThe Fourier Series EditedSarah HillmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier SeriesDokument29 SeitenFourier SeriesMuhammad Izzat ShafawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uraian FourierDokument91 SeitenUraian FourierAgus Dian PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01b-Fourier Series RevisionDokument37 Seiten01b-Fourier Series RevisionGeorges YoussefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourth Exam Fourier - NotesDokument5 SeitenFourth Exam Fourier - NotesGil Kenneth San MiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series, Generalized Functions, Laplace TransformDokument6 SeitenFourier Series, Generalized Functions, Laplace TransformAntonio HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee602 Fourier SeriesDokument110 SeitenEe602 Fourier SeriesArryshah DahmiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Functions: Computing CoefficientsDokument5 SeitenPeriodic Functions: Computing CoefficientsRicky EmeottNoch keine Bewertungen
- F (X) Is C (A, B) Let X, X (A, B) Then F (X) P (X) + R (X) WhereDokument9 SeitenF (X) Is C (A, B) Let X, X (A, B) Then F (X) P (X) + R (X) WhereAlbert WillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18.03 Practice Problems On Fourier Series - SolutionsDokument3 Seiten18.03 Practice Problems On Fourier Series - SolutionsahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1/ Class Test 1: 5. (MCQ Online) (Online Upload)Dokument8 SeitenAssignment 1/ Class Test 1: 5. (MCQ Online) (Online Upload)Kgotso KgengweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Solutions 2013Dokument12 SeitenMidterm Solutions 2013Nonitus OctingentiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ω + ω + =) t n sin (b) t n cos (a a) t (fDokument8 Seitenω + ω + =) t n sin (b) t n cos (a a) t (fVijitha VenkatramananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4-Fourier SeriesDokument42 SeitenChapter 4-Fourier SeriesSarah WahidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Fourier Series - GATE Study Material in PDFDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Fourier Series - GATE Study Material in PDFTestbook BlogNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLC - Fourier Series and Integral FourierDokument24 SeitenCLC - Fourier Series and Integral FourierNam GiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- B Splines PDFDokument7 SeitenB Splines PDFhello worldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Analysis: Lucas Illing 2008Dokument21 SeitenFourier Analysis: Lucas Illing 2008alnemangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier SeriesDokument74 SeitenFourier SeriesBurhan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filtros Adaptados PDFDokument3 SeitenFiltros Adaptados PDFJimeNucha CarbajalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series: Even and Odd Functions & Half Range ExpansionDokument10 SeitenFourier Series: Even and Odd Functions & Half Range ExpansionAli QpskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series M302Dokument21 SeitenFourier Series M302ranscrib300Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series PresentationDokument81 SeitenFourier Series PresentationRajithNimali100% (1)
- The Complex Form: 1. by Utilising The Euler Formula: eDokument15 SeitenThe Complex Form: 1. by Utilising The Euler Formula: eTim TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- S&S L5Dokument77 SeitenS&S L5Aalaa Hussein HamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- D Com FinalsolDokument6 SeitenD Com FinalsolnidulsinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JN 8 T 9 o 5 Ezcxxos 0/bh/9 S 0 Texaioq 71 Vbfrix 1 Z 4 JW 4Dokument9 SeitenJN 8 T 9 o 5 Ezcxxos 0/bh/9 S 0 Texaioq 71 Vbfrix 1 Z 4 JW 4Priyanka CholletiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SR 3 ExercisesDokument138 SeitenSR 3 ExercisesissamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEC Fourier Özgür ÜstünDokument17 SeitenPEC Fourier Özgür ÜstünBatuhan IzmırlıNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 4 SolutionsDokument5 SeitenAssignment 4 SolutionsHIGH DARBHANGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Freq DomainDokument55 SeitenFreq DomainDilara ÇınarelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computing Fourier Series and Power Spectrum With MATLAB - Brian D. Storey PDFDokument15 SeitenComputing Fourier Series and Power Spectrum With MATLAB - Brian D. Storey PDFmikelotingaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier Series A Periodic Function F (T) F (T + T) Can Be Expressed in Terms of Its Fourier Series AsDokument8 SeitenFourier Series A Periodic Function F (T) F (T + T) Can Be Expressed in Terms of Its Fourier Series Ashamza abdo mohamoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Processing: Mike Doggett Staffordshire UniversityDokument43 SeitenSignal Processing: Mike Doggett Staffordshire UniversityTrolldaddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 102 Homework Set 4 SolutionsDokument10 SeitenEE 102 Homework Set 4 SolutionsEunchan KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesDokument27 SeitenTE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesIbra NazlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A10 Soln PDFDokument7 SeitenA10 Soln PDFdoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier SeriesDokument3 SeitenFourier SeriesRaj Economist100% (1)
- Semester A, 2015-16 MA2177 Engineering Mathematics and StatisticsDokument42 SeitenSemester A, 2015-16 MA2177 Engineering Mathematics and Statisticslee ronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laplace TransformationDokument48 SeitenLaplace TransformationGail Nathalie LiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ma Kai-Kuang (Tutorial+Lectures)Dokument157 SeitenMa Kai-Kuang (Tutorial+Lectures)Ang KhengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier SeriesDokument29 SeitenFourier SeriesAngelo Toledo TamboongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTables of Generalized Airy Functions for the Asymptotic Solution of the Differential Equation: Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentVon EverandMathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex ArgumentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Von EverandIntroductory Differential Equations: with Boundary Value Problems, Student Solutions Manual (e-only)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 FT Batch Recipe Editor User GuideDokument211 Seiten2 FT Batch Recipe Editor User GuideleandrovaffonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryDokument30 SeitenCHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryLeo Archival ImperialNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTA Case Digests - 07.23.2021Dokument5 SeitenCTA Case Digests - 07.23.2021Emrico CabahugNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Filtration Lecture NotesDokument16 Seiten3 Filtration Lecture NotesRuben SIbayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2. WHAT IS AGROTECHNOPRENEURSHIPDokument23 SeitenLesson 2. WHAT IS AGROTECHNOPRENEURSHIPRhea Jane DugadugaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACLU Letter of ConcernDokument5 SeitenACLU Letter of ConcernRyan FinnertyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RFP For Corporate Engagement Platform PDFDokument28 SeitenRFP For Corporate Engagement Platform PDFAnupriya Roy ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 C AdminstrationDokument2 Seiten12 C AdminstrationMuditNoch keine Bewertungen
- Violence Against NursesDokument22 SeitenViolence Against NursesQuality Assurance Officer Total Quality ManagementNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible, Dynamic VR Simulation of A Future River Lock Facilitates Prevention Through Design in Occupational Safety and HealthDokument2 SeitenFlexible, Dynamic VR Simulation of A Future River Lock Facilitates Prevention Through Design in Occupational Safety and HealthEdgar Alexander Hurtado MolochoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C&DS Lab Manual UpdatedDokument182 SeitenC&DS Lab Manual UpdatedJesmin MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annexure - IV (SLD)Dokument6 SeitenAnnexure - IV (SLD)Gaurav SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Website Banners With Photoshop PDFDokument18 SeitenCreating Website Banners With Photoshop PDFLiza ZakhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job Schedule Sheet: 'Lead Time Monitoring GraphDokument48 SeitenJob Schedule Sheet: 'Lead Time Monitoring GraphEndraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MyFlixer - Watch Movies and Series Online Free in Full HD On MyFlixerDokument1 SeiteMyFlixer - Watch Movies and Series Online Free in Full HD On MyFlixerGeanina OlteanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal PAS-UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 11 SMADokument10 SeitenSoal PAS-UAS Bahasa Inggris Kelas 11 SMAAlexander TristanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forging 2Dokument17 SeitenForging 2Amin ShafanezhadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q PDokument2 SeitenWarman Slurry Correction Factors HR and ER Pump Power: MPC H S S L Q Pyoel cueva arquinigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Flash Storage System CLI ReferenceDokument454 SeitenOracle Flash Storage System CLI Referencebsduser07Noch keine Bewertungen
- March 2023 Complete Month Dawn Opinion With Urdu TranslationDokument361 SeitenMarch 2023 Complete Month Dawn Opinion With Urdu Translationsidra shabbirNoch keine Bewertungen






























































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)