Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Rubble Retaining Wall: Up To 5m High
Hochgeladen von
taz_taz30 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
39 Ansichten3 SeitenRetaining Wall
Originaltitel
RW Options
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenRetaining Wall
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
39 Ansichten3 SeitenRubble Retaining Wall: Up To 5m High
Hochgeladen von
taz_taz3Retaining Wall
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Gravity Retaining Wall
a. Rubble Retaining wall
b. Stone masonry wall
c. Gabion Wall
up to
~5m
high
Up to
~6m
high
W
Rubble Retaining wall
Concrete retaining walls provide a durable solution that is required of a structure in contact with
soil and exposed to constant wetting and drying.
Material locally available.
Not much area required for construction purpose.
Normal practice of construction on present sites.
Not much skilled labor are required.
As height of wall increase simultaneously thickness of wall increase
Draining is required to drain water from behind.
Stone Masonry Wall
Well suited to rapidly varying ground levels.
Provide good support to roads.
Easy to construct
Not skill labor are required
Maintenance can easily be done
Material locally available
Not much area required for construction purpose
Cost increase as the height of wall increase
Draining is required to drain water from behind.
Very prone to damage under differential movements. Need to be founded on competent
soils/rock. If on soils then concrete base slab usually needed. Regular movement joints (say
every 5m) required especially at change in height or foundation level.
Gabion Wall
Gabion walls consist of a wire mesh box filled with rock and wired
together to form a retaining wall
Record of satisfactory performance
Advantages of gabions include their ability to be stacked in various
shapes, accommodate ground movement, dissipate energy of flowing
water, and drain freely.
Good base friction providing placed directly on underlying soil.
Construction materials & skill labor are locally available.
Gabion walls are labor intensive to construction
toe
reinforced co
stem
RCC Cantilever Retaining wall
up to
~5m
high
Weight of soil
on heel gives
stability
Thin section as compared to other gravity retaining wall.
Can be built for large height (upto 9m).
Normal practice of RC construction.
gravity wall
Skilled labor are required
Extra space required for base (Heel) construction.
Draining is required to drain water from behind.
toe
heel
key helps to
stop sliding failure
Reinforced concrete cantilever wall
Facing panels
Reinforced soil walls
(usually
attached
reinforcing strips)
Can be built for large heights.
Metal or
reinforcing
Feasible to construct where large area is available.
Height
unlimited
Precast concrete panel are used reducing site machinery space.
Skilled labor must be required.
More space is required on earth retained side.
More excavation is required for placing the Reinforcement.
Extra excavation and back filling increase the cost.
These type of walls do not resist as much to the scouring problem as they are built from surface
of ground.
Embedded cantilever walls VS Gravity Walls
Advantages of embedded walls:
Embedded walls take up little lateral space.
Can be installed without excavation behind the wall and therefore
reduces temporary works (good in very weak or wet soils).
Can be used to help stabilize slopes if embedded below slip surface.
Stiff therefore good when excavation required beside movement
sensitive structures/infrastructure.
Disadvantages of embedded walls:
Require specialist equipment, and access for piling rigs etc
Require more detailed design calculations
Expensive
Anchors and steel piles corrode and need to be protected or designed with adequate initial steel
section to allow for corrosion.
Some are impermeable so drainage needs to be carefully considered in design and construction.
1. Reinforced Concrete Bored Pile walls
Can be installed up to the site boundary with little or no space required behind the wall for
construction
Guide walls required to provide good verticality and lateral positioning for walls.
Specialized skills and equipment are required for their installation
Reinforced concrete pile cap usually provided.
Not easily driven in rock or granular strata as pilling may not be easy in such soil.
Extra cost for pilling and bore.
2. Sheet-Piling Walls (Steel, Timber etc)
Easily installed in soft soils but not easily driven in granular or rocky strata as presently our site
conditions
Limited height due to flexibility (appropriate upto 3-4m) for higher height anchor roads are
required
Extra safety precaution is required for corrosion.
Vulnerable to corrosion attack.
It cannot resist high pressures
Blocks water flow but not completely water tight
3. Post and Plank
Concrete or wooden planks slid between driven or augured H posts (steel) backfilled with
concrete.
Generally cheaper than other wall types
Planks can be pre-formed and transported to site.
Steel posts corrode.
Pile installation difficult in very hard or boulder ground.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DPT1Dokument70 SeitenDPT1jayawiadnyanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOUNDATIONDokument48 SeitenFOUNDATIONSirisha NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation 131210020404 Phpapp01Dokument49 SeitenFoundation 131210020404 Phpapp01jitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Construction in Hilly RegionsDokument9 SeitenBuilding Construction in Hilly Regionsdikshajangra190Noch keine Bewertungen
- PE 561 Advanced Construction Technology: Dr. Dhanya B. S. Associate Professor in Civil Engineering RIT, KottayamDokument52 SeitenPE 561 Advanced Construction Technology: Dr. Dhanya B. S. Associate Professor in Civil Engineering RIT, KottayamSREYAS K MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shear and Retaining Wall Types and ConstructionDokument24 SeitenShear and Retaining Wall Types and ConstructionDev ThakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raft FoundationDokument12 SeitenRaft Foundationurmiladhameliya9586% (7)
- Retaining Walls: Angle of ReposeDokument34 SeitenRetaining Walls: Angle of ReposeHarsh ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Floors and Wall SystemsDokument45 SeitenFloors and Wall SystemsVITHURSHANA VINAYAGAMOORTHYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining WallDokument4 SeitenRetaining WallSupun KulathungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week4-RetainingWallsDokument46 SeitenWeek4-RetainingWallsAteafac Anastasia NjuafacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of foundations and their construction practicesDokument16 SeitenTypes of foundations and their construction practicesHarshit RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Foundation TypesDokument89 SeitenBuilding Foundation TypesAC Suarez100% (1)
- FoundationsDokument49 SeitenFoundationsManjeet CinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCM301 Advanced Construction Tech: Deep Basements & Earth Retaining WallsDokument42 SeitenTCM301 Advanced Construction Tech: Deep Basements & Earth Retaining Wallsyen keanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precast vs In-situ Concrete Construction GuideDokument45 SeitenPrecast vs In-situ Concrete Construction GuideDarren LaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diaphragm Wall Construction GuideDokument18 SeitenDiaphragm Wall Construction Guide04BHANDIWAD SANJANANoch keine Bewertungen
- EARTHQUAKE DESIGN GUIDELINESDokument57 SeitenEARTHQUAKE DESIGN GUIDELINESci_balaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BQS552 Earth Retaining StructureDokument93 SeitenBQS552 Earth Retaining StructureShakir ZufayriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Substructure DesignDokument65 SeitenSubstructure Designmmae64Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1) Deep FoundationsDokument30 Seiten1) Deep FoundationsmehtabhumikaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Retaining WallsDokument51 SeitenEarth Retaining WallsRae Plaza100% (1)
- Prefabricated Structures Components ConnectionsDokument71 SeitenPrefabricated Structures Components ConnectionsraviciviltNoch keine Bewertungen
- CTM3Dokument6 SeitenCTM3Sajil KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Construction & Materials Sem - V Unit-2 19.07.2021Dokument55 SeitenBuilding Construction & Materials Sem - V Unit-2 19.07.2021hyperloop707 designNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Tech. 5Dokument26 SeitenBuilding Tech. 5Bryan PongaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.lecture n3 - Unit I-Sub Structure ConstructionDokument115 Seiten3.lecture n3 - Unit I-Sub Structure ConstructiontwizerehyacintheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 9 - Construction Methods and Operations (Part II)Dokument49 SeitenTopic 9 - Construction Methods and Operations (Part II)Francine GoilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Materials & Methods Lesson 2Dokument136 SeitenConstruction Materials & Methods Lesson 2MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation 2Dokument34 SeitenFoundation 2aamaniammuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formwork Materials and Construction TechniquesDokument38 SeitenFormwork Materials and Construction TechniquesRajnish AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC Shear Wall Construction and Design DetailsDokument35 SeitenRC Shear Wall Construction and Design Detailsgaurav chaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brick MasonryDokument32 SeitenBrick MasonrygeethaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Retaining WallsDokument58 Seiten06 Retaining WallsGarima Mehta100% (1)
- Earth Retaining Structures-1 PDFDokument27 SeitenEarth Retaining Structures-1 PDFSury100% (1)
- RCC Foundation and FootingDokument35 SeitenRCC Foundation and Footingarchi_shwetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth Retaining StructuresDokument42 SeitenEarth Retaining StructuresAr. Soumya P SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining WallDokument62 SeitenRetaining WallParam SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Lintel & Retaining WallsDokument34 SeitenRCC Lintel & Retaining WallsNaveen Kishore0% (1)
- Masonry WallsDokument21 SeitenMasonry Wallstangudusrikanth513gmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earthquake Resistant Building Design GuideDokument44 SeitenEarthquake Resistant Building Design Guidesameer100% (1)
- 18ENG15 - Module 01Dokument49 Seiten18ENG15 - Module 01Ramya shree kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining Walls and Basement OnstructionDokument18 SeitenRetaining Walls and Basement OnstructionreemadeponNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retaining Wall Types NewDokument33 SeitenRetaining Wall Types NewIsbel100% (1)
- Walls Structure Walls StructureDokument32 SeitenWalls Structure Walls StructureNor Alia Shafia100% (1)
- Civil FoundationDokument20 SeitenCivil Foundationkrishnan cdsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction TechniquesDokument8 SeitenConstruction Techniquesarshi_raushan3427Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 05 - Stair, Roof, BrickDokument60 SeitenLecture 05 - Stair, Roof, BrickMd MohibullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Cast Flat Slab ConstructionDokument14 SeitenSite Cast Flat Slab Constructionsanzio sanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Degree Engineeringgaurav - Tandonshallow Foundations PDFDokument52 SeitenDegree Engineeringgaurav - Tandonshallow Foundations PDFvidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flat Roof:: The Construction Cost For RCC Roof Slab of Area 25 X 20 Is Approx. 20,000 RsDokument4 SeitenFlat Roof:: The Construction Cost For RCC Roof Slab of Area 25 X 20 Is Approx. 20,000 RsSAURABH KUMAR SINGH100% (1)
- Pile Foundations Ii - CHP3-1Dokument37 SeitenPile Foundations Ii - CHP3-1Uveys kavakliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 - BasementDokument28 Seiten03 - BasementTsz ching YipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arch 64Dokument24 SeitenArch 64Kookie BTSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sub-Structure ConstructionDokument56 SeitenSub-Structure ConstructionamokeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group5_Concrete-Research-Assignment_Building-Tech4Dokument14 SeitenGroup5_Concrete-Research-Assignment_Building-Tech4Sam AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUBSTRUCTURE FOUNDATIONSDokument116 SeitenSUBSTRUCTURE FOUNDATIONSscribd1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Construction Slabs GuideDokument12 SeitenTypes of Construction Slabs GuidemikeskiedooNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP2000 v15 Steel P-M Interaction RatiosDokument1 SeiteSAP2000 v15 Steel P-M Interaction Ratiostaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- PB SectionDokument1 SeitePB Sectiontaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- S4 PDFDokument1 SeiteS4 PDFtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
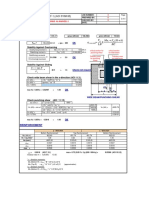
- Design Summary:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)Dokument1 SeiteDesign Summary:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)taz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Design Calc Slide 5Dokument1 SeiteStructural Design Calc Slide 5taz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Input Data:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)Dokument1 SeiteInput Data:: Isolated Foundation (F-1) (ACI 318M-95)taz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isolated Foundation Shear and Reinforcement CheckDokument1 SeiteIsolated Foundation Shear and Reinforcement Checktaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- JZERROOF Plan View DiagramDokument1 SeiteJZERROOF Plan View Diagramtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3d ViewDokument1 Seite3d Viewtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- F3Dokument1 SeiteF3taz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Bracing SketchDokument1 SeiteSteel Bracing Sketchtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Residential Apartment Structural Design BriefDokument5 SeitenResidential Apartment Structural Design Brieftaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- F2 PDFDokument1 SeiteF2 PDFtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- JobDokument1 SeiteJobtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- DL LL W M: Structural Al-Nakheel 6 Two Way SlabDokument1 SeiteDL LL W M: Structural Al-Nakheel 6 Two Way Slabtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Truss Detail - 2 Inch 1-7300Dokument1 SeiteTruss Detail - 2 Inch 1-7300taz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Culvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement DetailsDokument1 SeiteCulvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement Detailstaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Truss Detail - 2 InchDokument1 SeiteTruss Detail - 2 Inchtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Culvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement Details PDFDokument1 SeiteCulvert General Arrangement & Reinforcement Details PDFtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Draw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H DDokument7 SeitenDraw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H Dtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- View Project Schedules with Timescaled Logic DiagramsDokument4 SeitenView Project Schedules with Timescaled Logic Diagramstaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- School Name Remarks Generic/Non GenericDokument1 SeiteSchool Name Remarks Generic/Non Generictaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project Planning & Control-IDokument3 SeitenProject Planning & Control-Itaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Course StudiesDokument16 Seiten3 Course Studiestaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- DWG 03 ModelDokument1 SeiteDWG 03 Modeltaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument17 SeitenAssignmenttaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Draw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H DDokument7 SeitenDraw ADM For The Following Activity Predecessor A - B A, B C A, B D D E G, E F D G D H Dtaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionDokument4 SeitenQuestiontaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- DWG 01 ModelDokument1 SeiteDWG 01 Modeltaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- DWG 02 ModelDokument1 SeiteDWG 02 Modeltaz_taz3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Installation, Operating and Maintenance Instructions For Indeeco Electric Duct HeatersDokument2 SeitenInstallation, Operating and Maintenance Instructions For Indeeco Electric Duct HeatersJed DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONCEPT DESIGN ALUM C.W SCHUCO ANDALUSIA Rev01.10.03.222Dokument118 SeitenCONCEPT DESIGN ALUM C.W SCHUCO ANDALUSIA Rev01.10.03.222MoustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Alsafat BookDokument50 SeitenEnglish Alsafat BookMohammed O. Al-DushyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Progress Report - 12.6.14Dokument13 SeitenDaily Progress Report - 12.6.14bulzae100% (1)
- Aw BillDokument4 SeitenAw BillGunawan AchmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waterproofing, Bitumen, GlazingDokument19 SeitenWaterproofing, Bitumen, GlazingShubhani ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECCS - 2005 - Charles de Gaulle Building in BucharesDokument26 SeitenECCS - 2005 - Charles de Gaulle Building in BucharesmihaidelianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ruukki Sandwich PanelsDokument48 SeitenRuukki Sandwich PanelsPrabu RengarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 San Diego Regional Supplement To GreenbookDokument83 Seiten2012 San Diego Regional Supplement To GreenbookridlasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Housing R&B SOR 21-22Dokument31 SeitenHousing R&B SOR 21-22vikramjeet singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Shed Column Reinforcement Details-ModelDokument1 SeiteIndustrial Shed Column Reinforcement Details-Modelayadi_archiNoch keine Bewertungen
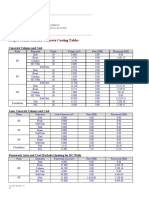
- Project Formwork and Concrete Costing TablesDokument3 SeitenProject Formwork and Concrete Costing TablesAizuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ga 216 07 PDFDokument24 SeitenGa 216 07 PDFabudabeejajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sun Shading Devices Reduce Heat GainsDokument4 SeitenSun Shading Devices Reduce Heat GainsEssa SasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel and Timber Project - Hernandez GroupDokument48 SeitenSteel and Timber Project - Hernandez GroupDean HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08 - Anchor Systems 2011 - Smallest File SizeDokument38 Seiten08 - Anchor Systems 2011 - Smallest File SizefayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material RequirementDokument37 SeitenMaterial RequirementHarish ApNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard For Cold-Formed Steel FramingDokument152 SeitenStandard For Cold-Formed Steel FramingmansocalulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiny House Framing Plans for LucyDokument44 SeitenTiny House Framing Plans for Lucyfaulrafe100% (1)
- Government Engineering College Seminar on Types of PavementsDokument17 SeitenGovernment Engineering College Seminar on Types of PavementsVinod BariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventilation For SchoolsDokument8 SeitenVentilation For SchoolsTatyana SpektorovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concrete Producer Article PDF - Troubleshooting Precast Cracks in Hollow-Core SlabsDokument4 SeitenThe Concrete Producer Article PDF - Troubleshooting Precast Cracks in Hollow-Core SlabsmahmoodgulamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schöck Solutions For PrecastDokument16 SeitenSchöck Solutions For PrecastAbdallah HamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- STULZ CyberAir CWE CWU Brochure 0611 en (ASD Series)Dokument6 SeitenSTULZ CyberAir CWE CWU Brochure 0611 en (ASD Series)sharifmousaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC System - Duct Quantity Take Off (Example Explained)Dokument1 SeiteHVAC System - Duct Quantity Take Off (Example Explained)Rudy Jesus Capa IlizarbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BUDIONG GATE Pow PDFDokument1 SeiteBUDIONG GATE Pow PDFMichael Jorge BernalesNoch keine Bewertungen
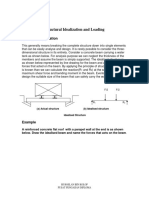
- Topic 2 LoadingsDokument26 SeitenTopic 2 LoadingsnasyahrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example Roof Truss AnalysisDokument6 SeitenExample Roof Truss Analysisravi.lalwani1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CPVC CTS 3 1015 - 1015Dokument24 SeitenCPVC CTS 3 1015 - 1015José María Quintero Q.Noch keine Bewertungen
- All in One Estimating (BY SOCE BD) - FinalDokument21 SeitenAll in One Estimating (BY SOCE BD) - FinalSabbir HossainNoch keine Bewertungen