Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Notes On Koine Greek, Pt. 38
Hochgeladen von
pisteuomenOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Notes On Koine Greek, Pt. 38
Hochgeladen von
pisteuomenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Notes On Koine Greek: Part 38
www.MichaelHalcomb.com
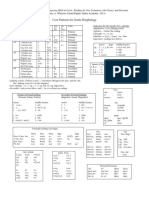
1. Imperfect Active Indicative eimi: Back in portion 6 of these “Notes”, we
encountered the Present Active Indicative of eimi. Here, we compare that
paradigm to its Imperfect Active Indicative counterpart.
2. Conjugation: The 6 conjugations for “eimi” in the present are in the first table
while the 6 for the imperfect are in the second one; these should all be committed
to memory:
Pres. Act. Ind. eimi Table *Take note once more of the
Singular Plural “movable “nu”. Recall the
1 eimi esmen rule concerning these letters
from Pt. 4 of my notes!
2 ei este
3 esti (n) eisi (n)
*Note: One way to remember this table with a little more ease is to note that the first two letters of the first two
terms in each set match the first to letters of the third term in each set. You can see this via the matched colors
above.
Imperf. Act. Ind. eimi Table
Singular Plural
1 h;mhn h-men
2 h-j h-te
3 h-n h-san
*Take note that each of the
conjugations with the exception of the *Take note that each of the
1st person sg. all begin with an eta (h-) corners of the table (1st & 3rd
which has an umlauted rough person singulars and plurals)
breathing mark. all end with a “n”.
3. eimi in the Imperfect: Where in the Present, eimi was translated as “I am”,
“You are”, etc. in the Imperfect, as you might have guessed, it is rendered “I
was”, “You were”, etc. Here are two English tables to compare to one another:
Present Active Indicative (Translated) Imperfect Active Indicative (Translated)
Singular Plural Singular Plural
1 I am We are 1 I was We were
2 You are You are 2 You were You were
3 He/She/It is They are 3 He/She/It was They were
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Greek Primer: For Beginners in New Testament GreekVon EverandA Greek Primer: For Beginners in New Testament GreekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aorist Passive and Future Passive Indicative Personal EndingsDokument4 SeitenAorist Passive and Future Passive Indicative Personal EndingslomeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Simple, Continuous, Perfect: Present TenseDokument8 Seiten(Simple, Continuous, Perfect: Present TenseHoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Koine Greek, Pt. 48Dokument1 SeiteNotes On Koine Greek, Pt. 48pisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1Dokument3 SeitenLesson 1LuisSpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sight-Reading for Piano Made Easy - Quick and Simple Lessons for the Amateur PianistVon EverandSight-Reading for Piano Made Easy - Quick and Simple Lessons for the Amateur PianistNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Conjugation Latin Verb LessonDokument2 Seiten1st Conjugation Latin Verb LessonPylegangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task # 7 Simple PresentDokument1 SeiteTask # 7 Simple PresentSergio Pablo Vargas MenendezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Jet Lang - 03072010Dokument30 SeitenGrammar Jet Lang - 03072010drkameleon2462Noch keine Bewertungen
- Whitacre GRC Core Patterns For Greek MorphologyDokument1 SeiteWhitacre GRC Core Patterns For Greek MorphologycoschaosNoch keine Bewertungen
- mtc quantrongming cs dng toraâmthanhli ộ ơ ệ đượ ử ụ để ạ ờ nói,chnghnnh l i,môihocrng ẳ ạ ư ưỡ ặ ăDokument9 Seitenmtc quantrongming cs dng toraâmthanhli ộ ơ ệ đượ ử ụ để ạ ờ nói,chnghnnh l i,môihocrng ẳ ạ ư ưỡ ặ ăĐỨC PHÚC TRẦNNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 What Is Stress?Dokument12 Seiten1 What Is Stress?yoothong20100% (1)
- Italian VDokument11 SeitenItalian VJerry's CellsNoch keine Bewertungen
- ShakespeareslanguageDokument2 SeitenShakespeareslanguageMIGUEL ALEJANDRO SALMON FRANCONoch keine Bewertungen
- GRAMMAR Present SimpleDokument5 SeitenGRAMMAR Present SimpleeugeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inglês - Esa CompletaDokument151 SeitenInglês - Esa CompletaLuigi EmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Long Vowels LessonsDokument10 SeitenLong Vowels Lessonsaarti.takawane6610Noch keine Bewertungen
- To BeDokument1 SeiteTo BeAlysha RellerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Upgrade Your GrammarDokument23 SeitenTenses Upgrade Your Grammarrup 144fpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn ChineseDokument20 SeitenLearn ChineseSachin SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ar Verbs Present Tense HandoutDokument3 SeitenAr Verbs Present Tense Handoutkalani08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simple present (现在式) - writingDokument8 SeitenSimple present (现在式) - writingONG YIET FONG MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poetry: A. Sound PatternsDokument4 SeitenPoetry: A. Sound Patternspara sa projectNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fill in The Blanks With The Correct Form of Words Given:: 1) Repeated ActionsDokument6 SeitenFill in The Blanks With The Correct Form of Words Given:: 1) Repeated ActionsFran Muñoz MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latin Study Guide 1 Declension Singula R Feminine Nom - A Gen - Ae Dat - Ae Acc - Am Abl - Ā Plural Nom - Ae Gen - Arum Dat - Is Acc - As Abl - IsDokument7 SeitenLatin Study Guide 1 Declension Singula R Feminine Nom - A Gen - Ae Dat - Ae Acc - Am Abl - Ā Plural Nom - Ae Gen - Arum Dat - Is Acc - As Abl - IsChris JagoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MNTG Textbook Ch01 2019Dokument6 SeitenMNTG Textbook Ch01 2019Cris Licsi MantesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Koine Greek, Pt. 3Dokument1 SeiteNotes On Koine Greek, Pt. 3pisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Phonetic Inventory of Iu MienDokument18 SeitenThe Phonetic Inventory of Iu MienAlex GnatushenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Koine Greek, Pt. 40Dokument1 SeiteNotes On Koine Greek, Pt. 40pisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4Dokument4 SeitenUnit 4Theresa KutepovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated Lesson 1Dokument8 SeitenUpdated Lesson 1Rjay MedenillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TurkishDokument5 SeitenTurkishSe RinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gramatica EsperantoDokument214 SeitenGramatica EsperantoAlberto GrazianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Phonetics StudentDokument7 SeitenIntroduction To Phonetics Studentmunazzah91Noch keine Bewertungen
- Class 1: I. Pronunciation in Latin VowelsDokument3 SeitenClass 1: I. Pronunciation in Latin VowelssonyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latin Module 5Dokument14 SeitenLatin Module 5Đinh Văn DuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presente Indicativo (Present Simple) : - As - A - Amos - Emos - Imos - A:is - E:is - Í:s - AnDokument6 SeitenPresente Indicativo (Present Simple) : - As - A - Amos - Emos - Imos - A:is - E:is - Í:s - AnThảo PhươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhonemeDokument19 SeitenPhonemefaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present ContinousDokument2 SeitenPresent Continouscon.liviu2030100% (1)
- Aoe I Uü: PhoneticsDokument9 SeitenAoe I Uü: PhoneticsDANIELA ALMANZA ROMERONoch keine Bewertungen
- Sappho 31 PDFDokument3 SeitenSappho 31 PDFMaff Di MuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- PronounciationDokument35 SeitenPronounciationsheyra 89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Huong Dan g1 TVDokument1.084 SeitenHuong Dan g1 TVLê HồngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Albanian MorphologyDokument6 SeitenAlbanian MorphologyMetaleiro100% (1)
- German QuicklyDokument229 SeitenGerman Quicklyjohnrownby83% (23)
- Whitacre - Basic Hellenistic Greek Morphology PDFDokument36 SeitenWhitacre - Basic Hellenistic Greek Morphology PDFMelissa Baez SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 25 Feb 23Dokument3 SeitenHomework 25 Feb 23Soy Un Minion BomberoNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Species CounterpointDokument2 SeitenFirst Species CounterpointRyanMPetersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb 2Dokument1 SeiteVerb 2Hament KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 PHONICSDokument5 SeitenLesson 3 PHONICS20223327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Verbal Derivation in MicmacDokument13 SeitenVerbal Derivation in Micmacwaymac007Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Stress Syllables in EnglishDokument5 SeitenHow To Stress Syllables in EnglishMir NaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word Stress in EnglishDokument6 SeitenWord Stress in EnglishHafid Tlemcen Rossignol PoèteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Nine: The Imperfect TenseDokument12 SeitenChapter Nine: The Imperfect Tensesteffen hanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Three French Verb Groups and The Present TenseDokument6 SeitenThe Three French Verb Groups and The Present TenseSamira Yağlıca100% (1)
- Nouns: Meet I ng1Dokument9 SeitenNouns: Meet I ng1Naura Kamila TumanggorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Aorist Tense Part IIDokument7 SeitenThe Aorist Tense Part IInaomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Steps To Koine - SampleDokument6 SeitenFirst Steps To Koine - SamplepisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversational Koine Institute - Winter (2013) - Spring (2014) FlyerDokument1 SeiteConversational Koine Institute - Winter (2013) - Spring (2014) FlyerpisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKI - LPTS FlyerDokument1 SeiteCKI - LPTS FlyerpisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 800 Words SampleDokument7 Seiten800 Words SamplepisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- "For Bloggers": A GlossaHouse InitiativeDokument2 Seiten"For Bloggers": A GlossaHouse InitiativepisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversational Koine InstituteDokument1 SeiteConversational Koine InstitutepisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- ΓΡΚ Constitution and GuidelinesDokument6 SeitenΓΡΚ Constitution and GuidelinespisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Getting French - pt4Dokument1 SeiteGetting French - pt4pisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conversational KoineDokument1 SeiteConversational KoinepisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyglot SampleDokument22 SeitenPolyglot SamplepisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Registration FormDokument2 Seiten2010 Registration FormpisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure - Child SponsorshipDokument2 SeitenBrochure - Child SponsorshippisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aramaic Annotations - Part 27Dokument1 SeiteAramaic Annotations - Part 27pisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aramaic Annotations - PT 25Dokument1 SeiteAramaic Annotations - PT 25pisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aramaic Annotations - Part 22Dokument1 SeiteAramaic Annotations - Part 22pisteuomenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Practice Test 1Dokument25 SeitenExam Practice Test 1Patricia BoweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Pronouns GermanDokument7 SeitenPersonal Pronouns Germanvarungupta1988Noch keine Bewertungen
- Common Errors in EnglishDokument18 SeitenCommon Errors in EnglishS.RamarajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Level 1 - Chu00ednh Thu1ee9c - 2 - RepairedDokument73 SeitenWriting Level 1 - Chu00ednh Thu1ee9c - 2 - RepairedTùng NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOFclass 2Dokument8 SeitenSOFclass 2Mallika GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 6 DLP Q3 English Part 4Dokument14 SeitenGrade 6 DLP Q3 English Part 4Riza Toledo MaglenteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use Commas To Separate Independent ClausesDokument4 SeitenUse Commas To Separate Independent ClausesasunnaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson No. 5 - Reflexive PronounsDokument7 SeitenLesson No. 5 - Reflexive PronounsLaurenz De JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Too and Enough: Lintas Minat Bahasa Inggris Kelas X IPS By: Lilis Suryani, M.PDDokument14 SeitenToo and Enough: Lintas Minat Bahasa Inggris Kelas X IPS By: Lilis Suryani, M.PDLilis SuryaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Twenty Questions: Units 4-5-6Dokument45 SeitenTwenty Questions: Units 4-5-6MARIONoch keine Bewertungen
- Beginner Apr 10 PG 76 To 77Dokument2 SeitenBeginner Apr 10 PG 76 To 77Agroservicios UbillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4as DETAILED LESSON PLAN CAINONGLJDokument5 Seiten4as DETAILED LESSON PLAN CAINONGLJLady Jane Cainong89% (62)
- Present Perfect ProgressiveDokument3 SeitenPresent Perfect ProgressivePolyna PolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MABS 68 I Reading in Buddhist Sanskrit Texts I: Grammatical FoundationDokument27 SeitenMABS 68 I Reading in Buddhist Sanskrit Texts I: Grammatical Foundation张晓亮Noch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching 'Asking and Giving Information' Through Task Based LearningDokument29 SeitenTeaching 'Asking and Giving Information' Through Task Based Learningfilosofi kupukupuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 5 First Quarter Week 1 - Day 5 I. ObjectivesDokument3 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan in English 5 First Quarter Week 1 - Day 5 I. ObjectivesElvz C. Diones100% (4)
- Modal Verbs Complete ExerciseDokument11 SeitenModal Verbs Complete ExercisedanielaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verbs of Movement in The Bulgarian Frame PDFDokument1 SeiteVerbs of Movement in The Bulgarian Frame PDFHamzeh MousaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sentence Structures - Harvey Ibe - Lesson PlanDokument14 SeitenSentence Structures - Harvey Ibe - Lesson PlanHarvey Kurt IbeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARTICLES A An The ZeroDokument12 SeitenARTICLES A An The ZeroIvana LalicNoch keine Bewertungen
- (1910) Life of The Black PrinceDokument332 Seiten(1910) Life of The Black PrinceHerbert Hillary Booker 2ndNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spot The Error AdverbsDokument8 SeitenSpot The Error AdverbsDhiman NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdmissionDokument11 SeitenAdmissionTarikul ChadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Written Expression Skill 25Dokument2 SeitenStructure and Written Expression Skill 25Al HaziqNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS Level 2 SyllabusDokument4 SeitenIELTS Level 2 Syllabusfithrah auliya ansarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iol 2005 Indiv Sol - enDokument4 SeitenIol 2005 Indiv Sol - envistianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaDokument2 SeitenPerfect Tenses Cheat Sheet: by ViaAura SkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- If - Conditionals 8th GradeDokument2 SeitenIf - Conditionals 8th GradeYasmeen CoptyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Rules For Writing Straight News LeadsDokument31 SeitenSix Rules For Writing Straight News LeadsJosebelle Satorre Bagulaya100% (1)
- Navigate Upper-Intermediate Wordlist Unit 12 PDFDokument2 SeitenNavigate Upper-Intermediate Wordlist Unit 12 PDFjoel zapanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksVon EverandArizona, Utah & New Mexico: A Guide to the State & National ParksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptVon EverandThe Bahamas a Taste of the Islands ExcerptBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Japanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensVon EverandJapanese Gardens Revealed and Explained: Things To Know About The Worlds Most Beautiful GardensNoch keine Bewertungen
- New York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksVon EverandNew York & New Jersey: A Guide to the State & National ParksNoch keine Bewertungen
- South Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptVon EverandSouth Central Alaska a Guide to the Hiking & Canoeing Trails ExcerptBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Naples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoVon EverandNaples, Sorrento & the Amalfi Coast Adventure Guide: Capri, Ischia, Pompeii & PositanoBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)