Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ad-Ii QB-1
Hochgeladen von
Kalpit KauraseOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ad-Ii QB-1
Hochgeladen von
Kalpit KauraseCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Aerodynamics-II QB
AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
AERODYNAMICS II
QUESTION BANK
PART - A
UNIT I ONE DIMENSIONAL COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
1. What is meant by Supersonic flow?
2. What do you understand by the term Gas Dynamics?
3. Differentiate between compressible and incompressible flow
4. Write the Bernoullis equation for incompressible flow.
5. Write the adiabatic relation between temperature, pressure and density.
6. What is meant by Mach angle?
7. Draw the propagation of disturbance waves for subsonic and supersonic
condition.
8. Draw the flow around a wedge for subsonic and supersonic flow.
9. What is meant by Mach cone?
10. Define (i)Zone of action (ii) Zone of silence (iii) Mach Waves (or) Mach lines.
11. Classify the flow regimes interms of Mach number.
12. What is meant by Transonic and supersonic flow?
13. State the First Law of Thermodynamics.
14. Define (i) Adiabatic process (ii) Reversible process (iii) Isentropic process
15. What is meant by System and Surrounding?
16. Differentiate between open system and closed system.
17. State the Second Law of Thermodynamics.
18. Define Thermal and calorical properties.
19. What are the limitations of air consider as perfect gas.
20. What is meant by barotropic fluids?
21. How velocity of the flow varies in convergent and divergent ducts for subsonic
and supersonic condition.
Aerodynamics-II QB
22. What is meant by De Laval Nozzle?
23. Write the Area Mach number relation?
24. Define the following terms:
(i) Static pressure (ii) Dynamic pressure (iii) Total pressure (iv) Pitot pressure (v)
Geometric pressure.
25. Define Pressure Coefficient.
26. Write the Bernoullis equation for compressible flow.
UNIT II NORMAL, OBLIQUE SHOCKS AND EXPANSION WAVES
27. What is meant by Normal Shock?
28. Write the shock relation of the perfect gas?
29. Write the Hugoniot equation and explain each terms involved in it.
30. Define (i) Wave Motion (ii) Wave Speed (iii) Plane waves
31. What is meant by shock tube?
32. What are the applications of shock tube?
33. Define Oblique shock?
34. Differentiate between shock wave and expansion wave.
35. Draw the flow pattern of supersonic flow over corners.
).) and Flow deflection angle (36. Define Shock angle (
).) and Flow deflection angle (37. Write the relation between Shock angle (
38. What is meant by Shock Polar?
39. Define Sonic circle.
40. What is meant by Detached shock?
41. Define Mach Reflection.
42. Write the Prandtl relation of Normal shock wave.
43. Define Hodograph Plane.
44. Draw the shock polar for different Mach numbers.
45. What is meant by Reflection and Intersection of Shocks and Expansion waves?
46. Define Simple and Non-simple regions.
Aerodynamics-II QB
47. Distinguish between Like and Unlike reflection of shock wave.
48. What is meant by Diamond wave pattern in Supersonic nozzle?
49. Define Prandtl Meyer Expansion
50. Define Wave Drag.
UNIT III DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR STEADY COMPRESSIBLE
FLOWS
51. Write the equation of linearised small perturbation potential theory.
52. Write the Prandtl Glauret Rule.
53. Write the Geotherts Rule.
54. Define Mach waves.
55. Define Mach angles.
56. What is perturbation potential function?
57. How is flow over a cone different from flow over a wedge?
58. Write down the critical pressure coefficient from the Prandtl-Glauret rule.
59. What are the assumptions of small perturbation potential theory?
60. What is meant by linearised two-dimensional supersonic theory?
61. What are the assumptions used in linearised two-dimensional supersonic
theory?
62. What are the practical application of Prandtl-Glauert Rule?
63. What is importance of the Geotherts rule?
64. List out the practical application of linearised two-dimensional supersonic
theory.
65. Explain how lift and drag produced in supersonic profiles.
66. Define center of pressure.
67. Draw the pithching moment curve for supersonic profiles.
68. How pithching moment and center of pressure varies with angle of attack for
a supersonic profile?
69. Draw the various supersonic profiles.
70. How lift and drag varies with angle of attack for a supersonic profile?
Aerodynamics-II QB
UNIT IV AIRFOIL IN HIGH SPEED FLOWS
71. State Supersonic area rule.
72. Explain how supersonic airfoil profiles are fundamentally different from
subsonic airfoil profiles
73. Define Critical Mach number.
74. Distinguish between Lower Critical Mach number and Upper Critical Mach
number.
75. What is meant by lift and drag divergence?
76. What is the cause of the Lift and drag divergence over airfoil in high speed
flows?
77. What is meant by shock induced separation?
78. List out the characteristics of swept wings?
79. What is the effect of thickness over the performance of wings?
80. What is the effect of camber over the performance of wings?
81. Define Aspect ratio.
82. What is the effect of aspect ratio over the performance of wings?
83. What is meant by Transonic area rule?
84. What is meant by Sonic barrier?
85. Why drag increases drastically over sonic speed?
86. How the drag coefficient (CD) varies with Mach number (M)?
87. What is meant by tip effects?
88. Name some transonic area ruled aircraft.
UNIT V HIGH SPEED WIND TUNNELS
89. What are the principles of model testing?
90. What are the salient features of Hypersonic wind tunnels?
91. What is a wind tunnel and classify the wind tunnels?
92. What instruments are used to measure the fluctuating pressures on the
models?
93. What are the characteristic features of Hypersonic wind tunnels?
Aerodynamics-II QB
94. What is shock tube and what is its application?
95. What is meant by Blow down tunnel?
96. Distinguish between indraft and induction tunnel?
97. What are the components on the Transonic wind tunnel?
98. List out the calibration carried out in the Transonic wind tunnel.
99. What are the components on the supersonic wind tunnel?
100. List out the calibration carried out in the supersonic wind tunnel.
101. What are the components on the hypersonic wind tunnel?
102. List out the calibration carried out in the hypersonic wind tunnel.
103. What is meant by helium tunnels?
104. What is meant by gun tunnel?
105. What are the application of gun tunnels?
106. What is meant by Shock tube?
107. What are the applications of Shock tube?
108. What is meant by flow visualizations?
109. What are the data we can get from the flow visualization?
110. List out the various flow visualization methods.
111. What are the optical flow visualization methods?
112. Draw the shadowgraph flow visualization setup?
113. Draw the Schlieren flow visualization setup?
PART - B
UNIT I ONE DIMENSIONAL COMPRESSIBLE FLOW
1. Derive the fundamental equation for compressible flow.
2. Explain Quasi-one dimensional flow and area velocity relation.
3. Define De Laval Nozzle and derive the Area Mach number relation.
4. With neat sketch briefly explain the flow in a Convergent-divergent nozzle.
5. Write short notes on
6. Pitot Pressure Probe (ii) Static Pressure Probe (iii) Pitot static probe.
7. Derive the expression for Pressure coefficient with and without compressibility
Aerodynamics-II QB
correction.
8. For an aircraft flying at a speed of 1000kmph, find the variation of speed of
sound a, and Mach number M, with sea level and 11km altitude.
9. During a flight, a fighter aircraft attains its cruise speed of 600 m/s at 10km
altitude after taking off at 150 m/s from sea level. Assuming the speed to have
increased linearly with altitude during the climb, compute the Mach number
variation with altitude.
10. A fighter aircraft attains its maximum speed of 2160 kmph at an altitude of 12
km. The take-off speed at sea level is 270 kmph. If the flight speed increases
linearly with altitude, compute the variation of stagnation temperature with
altitude for a climb up to the maximum speed.
11. Air flows through a duct. The pressure and temperature at station 1 are P1 =
0.7 atm and T1 = 300C, respectively. At a second station, the pressure is 0.5 atm.
Calculate the temperature and density at the second station. Assume the flow to
be isentropic.
12. Air is allowed to expand from an initial state A (where PA = 2.068 x 105 N/m2
and TA = 333K) to state B (where PB = 1.034 x 105 N/m2 and TB = 305 K).
Calculate the change in the specific entropy of the air, and show that the change
in entropy is the same for (a) an isobaric process from A to some intermediate
state C followed by an isovolumetric change from C to B, and (b) an isothermal
change from A to some intermediate state D followed by an isentropic change
from D to B.
13. A storage chamber of a compressor is maintained at 1.8 atmospheres
absolute and 200C. The surrounding ambient pressure is 1 atm. Calculate (a) the
velocity with which airflow will take place from the chamber to the outside
through a unit area hole, (b) the mass flow rate per unit area. Assume air as a
perfect gas.
= 213 K, at exit Pexit = 0.3 atm). = 0.3 atm and T14. A ramjet flies at 11 km
altitude with a flight mach number of 0.9. In the inlet diffuser, the air is brought
to the stagnation condition so that it is stationary just before the combustion
chamber. Combustion takes place at constant pressure and a temperature
increase of 15000C results. The combustion products are then ejected through
the nozzle. (a) Calculate the stagnation pressure and temperature. (b) What will
Aerodynamics-II QB
be the nozzle exit velocity? ( At inlet P
15. A De Laval Nozzle has to be designed for an exit Mach number of 1.5 with exit
diameter of 200mm. Find the ratio of throat area to exit area necessary. The
reservoir conditions are given as P0 = 1 atm; T0 = 200C. Find also the maximum
mass flow rate through the nozzle. What will be the exit pressure and
temperature?
UNIT II NORMAL, OBLIQUE SHOCKS AND EXPANSION WAVES
16. (i) Derive the equation of motion for a Normal shock wave.
(ii) Derive the Prandtl Normal Shock relation for a Perfect gas.
17. Derive the Hugoniot equation and explain the Hugoniot Curve.
18. Briefly explain the Shock tube and its applications.
).) and Flow deflection angle (19. Derive the Relation between Shock angle (
20. Briefly explain the Shock Polar.
21. Briefly explain the functions of Pitot static tube and list out the corrections
needed for subsonic and supersonic flows.
22. How Oblique shock forms? And explain its properties in detail.
23. Briefly explain the characteristic of flow over wedges and concave corners.
24. Briefly explain the features of two dimensional supersonic nozzle contours.
25. Write short notes on:
(i) Weak and detached shocks
(ii) Rayleigh Flow
(iii) Fanno flow
26. Briefly explain the Reflection and Intersection of Shock wave and Expansion
wave.
27. With neat sketches explain the Supersonic shock expansion theory.
28. The flow Mach number, pressure, and temperature ahead of a normal shock
are given as 2.0, 0.5 atm and 300 K respectively. Determine M2, P2 , T2, and V2
behind the wave.
= 1.4 and R = 287 J/kg-K.29. A re-entry vehicle (RV) is at an altitude of 15,000 m
and has a velocity of 1850 m/s. A bow shock wave envelops the RV. Neglecting
Aerodynamics-II QB
dissociation, determine the stagnation pressure and temperature just behind the
shock wave on the RV center line where the shock wave may be treated as
normal shock.. Assume that the air behaves as perfect gas, with
30. A normal shock moves in a constant area tube as shown in figure. In region 1,
V1 = 100 m/s, T1 = 300C and P1 = 0.7 atm. Shock speed CS with respect to a fixed
coordinate system is 600 m/s. Find fluid properties in region 2.
V2 2 1 V1
CS
P2 T2 P1 T1
31. Write short notes on
(i) Supersonic flow over a wedge
(ii) Weak Oblique shocks
(iii) Supersonic Compression
(iv) Supersonic Expansion by Turning
Aerodynamics-II QB
UNIT III DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS OF MOTION FOR STEADY COMPRESSIBLE
FLOWS
32. Derive the linearised small perturbation potential theory.
33. Write short notes on.
(i) Mach waves
(ii) Mach angles
(iii) Solutions for Supersonic flows.
34. Derive the Linearised two-dimensional supersonic flow theory.
35. Derive the Prandtl Glauret affine transformation relations for subsonic flows.
36. Briefly explain the lift, drag, pitching momemt and center of pressure of
supersonic profiles.
37. Write short notes on:
(i) Shock Expansion method
(ii) Small perturbation equation for compressible flows
38. (i) Explain with a neat sketches, swept wing, swing wing and Ogee planform
(8)
(ii) What is a critical Mach number and explain from P-G rule (Prandtl Glauert) (8)
39. (i) What is the main application of small pertubation equation for
compressible flows? Given an example with a neat sketch. (8)
(ii) Explain Prandtl-Glauert compressibility correction for compressible flows.
What are the other methods for compressibility correction? (8)
(iii) What is Area Rule? (8)
UNIT IV AIRFOIL IN HIGH SPEED FLOWS
40. Explain the rules, wing fuselage combinations designs for the Transonic
configurations and supersonic configurations.
41. Briefly explain the characteristics features of the lower critical mach number
Aerodynamics-II QB
and upper critical mach number.
42. Explain in detail about lift and drag divergence.
43. Explain with neat sketch about the shock induced separation.
44. Briefly explain the characteristics features of swept wings.
45. Briefly explain the effects of thickness, camber and aspect ratio over the
performance of wings in high speed flows.
46. Briefly explain the need and characteristic features of Transonic area rule.
47. Explain the following;
(iii) Disadvantages of Swept wings
(iv) Delta wing
UNIT V HIGH SPEED WIND TUNNELS
48. Explain the Hypersonic wind tunnel (Helium) with sketches.
49. (i) Sketch a typical shock tunnel and explain its principle of operation. What
are the advantages and limitations of shock tunnel? (8)
(ii) Explain how measurements of pressure, velocity and Mach number can be
done in a supersonic wind tunnel. (8)
50. Draw a neat sketch of a supersonic wind tunnel circuit and explain the
function of each component.
51. Draw a neat sketch of a transonic wind tunnel circuit and explain the function
of each component.
52. Draw a neat sketch of a hypersonic wind tunnel circuit and explain the
function of each component.
53. Briefly explain the Blow down, indraft and induction tunnel layouts and their
design features.
54. Explain in detail about the various calibration of supersonic wind tunnel.
55. Explain in detail about the various calibration of transonic wind tunnel.
56. Explain in detail about the various calibration of hypersonic wind tunnel.
57. Briefly explain the Helium and gun tunnels and its applications.
58. What is meant by Shock tube? Explain in detail its working principle and
characteristics and list out its application.
59. Briefly explain the various optical methods of flow visualization.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Aero Ae2251 - Aerodynamics - IDokument10 SeitenAero Ae2251 - Aerodynamics - IKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- One-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesVon EverandOne-Dimensional Compressible Flow: Thermodynamics and Fluid Mechanics SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ad IiDokument8 SeitenAd Iisaranstar87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodynamics-II Question BankDokument8 SeitenAerodynamics-II Question Bankhamdanforaero100% (1)
- Aerodynamics - IIDokument10 SeitenAerodynamics - IIVejay RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992Von EverandComputational Wind Engineering 1: Proceedings of the 1st International Symposium on Computational Wind Engineering (CWE 92) Tokyo, Japan, August 21-23, 1992S. MurakamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass - 1 (2021-22)Dokument3 SeitenAss - 1 (2021-22)Nishith KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared and Millimeter Waves V9: Millimeter Components and Techniques, Part IVon EverandInfrared and Millimeter Waves V9: Millimeter Components and Techniques, Part IBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Me 6604 GDJP 2 Marks With AnswersDokument16 SeitenMe 6604 GDJP 2 Marks With AnswersKanagarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smex1015-Gas Dynamics & Jet PropulsionDokument9 SeitenSmex1015-Gas Dynamics & Jet Propulsionsach30131Noch keine Bewertungen
- Me 6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Question BankDokument12 SeitenMe 6604 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Question BanktagoreboopathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Unit-I PART-A (2 Marks)Dokument14 SeitenMe 2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Unit-I PART-A (2 Marks)vsanthanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank GDJPDokument2 SeitenQuestion Bank GDJPsrimuthu_22100% (1)
- 4.gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionDokument8 Seiten4.gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionS ANANTHAKUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank GDJP JOEDokument10 SeitenQuestion Bank GDJP JOEJoe Kamal Raj100% (1)
- ME6336Dokument2 SeitenME6336sumit adityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 9026 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Time: 3 HR Max. Mark: 100Dokument2 SeitenMe 9026 Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion Time: 3 HR Max. Mark: 100Prasanna SekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part-A: Subject: Aerodynamics-IIDokument4 SeitenPart-A: Subject: Aerodynamics-IIManiyarasu OppilamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD2 Coimbatore April 2011 QP PDFDokument3 SeitenAD2 Coimbatore April 2011 QP PDFNIT AERO DEPARTMENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument6 Seiten4robinston jeyasinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodynamics-II Questions BankDokument6 SeitenAerodynamics-II Questions Bankae00505Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignments FinDokument5 SeitenAssignments FinGCVishnuKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Sheet and Assignment IIDokument11 SeitenWork Sheet and Assignment IIAb AnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodynamics II CoachingDokument1 SeiteAerodynamics II CoachingManiyarasu OppilamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodynamics-2 Two Mark QuestionsDokument15 SeitenAerodynamics-2 Two Mark QuestionsArun Raja K KNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE6503 - QP CODE 50028 - Aerodynamics II Key - Nov 2017 PDFDokument25 SeitenAE6503 - QP CODE 50028 - Aerodynamics II Key - Nov 2017 PDFRaahini IzanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 333Dokument2 SeitenMe 333Sandeep Prabakaran100% (1)
- Attachment Gas DynamisDokument2 SeitenAttachment Gas DynamisArif Abdul RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDokument22 SeitenGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDinesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sbu 678Dokument125 SeitenSbu 678prana132Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gojan School of Business and Technology, Chennai-51 Model Examinations-April-2017Dokument4 SeitenGojan School of Business and Technology, Chennai-51 Model Examinations-April-2017Venkatesh MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionDokument12 SeitenME2351-Gas Dynamics and Jet PropulsionmayilsvhecNoch keine Bewertungen
- GDJP QB 24x7 QuestionsDokument4 SeitenGDJP QB 24x7 Questionsleela prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group Assignment IVDokument5 SeitenGroup Assignment IVpickycatyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressible Fluid Flow April 2010 (2006 Ad)Dokument2 SeitenCompressible Fluid Flow April 2010 (2006 Ad)Anil P JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 6: Compressible Flow in Nozzles: Stagnation PropertiesDokument3 SeitenSheet 6: Compressible Flow in Nozzles: Stagnation PropertiesAbdelaziz TamimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 2351Dokument20 SeitenMe 2351Saravanan MathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressible Flow Question BankDokument3 SeitenCompressible Flow Question BankChanduNoch keine Bewertungen
- GDJP Important 2 Marks and 16 Marks With AnswerDokument18 SeitenGDJP Important 2 Marks and 16 Marks With AnswerMechanical Engg DeptNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer All The Questions (10 2 20)Dokument2 SeitenAnswer All The Questions (10 2 20)Andrew CrawfordNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD-II April 2011 QPDokument3 SeitenAD-II April 2011 QPManiarasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME 306-Hw04-2017-2Dokument5 SeitenME 306-Hw04-2017-2Aswad Che RusminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ad Ut Ii Set IDokument2 SeitenAd Ut Ii Set IRaj ManovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ad II (Ae2303) (Univ QP, Nov2010)Dokument3 SeitenAd II (Ae2303) (Univ QP, Nov2010)aeroacademicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Test-I ME-2351-GDJP Part-ADokument1 SeiteInternal Test-I ME-2351-GDJP Part-AVinay MPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFDokument7 SeitenGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFdass143143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manip Al University: IV Sem Aeronautical Engineering, Examinations 2010Dokument2 SeitenManip Al University: IV Sem Aeronautical Engineering, Examinations 2010dreamivory29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aerodynamics II 2 MarksDokument5 SeitenAerodynamics II 2 MarksNithiyakalyani Sabapathi100% (1)
- Question Paper CodeDokument3 SeitenQuestion Paper CodeKeesanth Geetha ChandrasekaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kongu Engineering College: Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument1 SeiteKongu Engineering College: Department of Mechanical EngineeringjuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - NewDokument12 SeitenGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - NewShanmugam SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter No 4Dokument6 SeitenChapter No 4gotu123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sheets (Based On Lecture of The Week) : Department of Aerospace EngineeringDokument5 SeitenTutorial Sheets (Based On Lecture of The Week) : Department of Aerospace EngineeringJASHANPREET SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsDokument22 SeitenGas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion - 2 Marks - All 5 UnitsMohan Prasad.M80% (10)
- Question Bank: AE1254 - PROPULSION IDokument8 SeitenQuestion Bank: AE1254 - PROPULSION ISêlvâkûmâr JayabalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08cmre44 Thermodynamics-Iii Maximum Hours 3 Hours Total Marks 75 Section - A Answer All The Questions (10x2 20)Dokument3 Seiten08cmre44 Thermodynamics-Iii Maximum Hours 3 Hours Total Marks 75 Section - A Answer All The Questions (10x2 20)Senthil AnnaunivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac8401 Aerodynamics QPDokument3 SeitenAc8401 Aerodynamics QPPrasanth SamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echapter Vol2Dokument214 SeitenEchapter Vol2dev shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- SteelsDokument11 SeitenSteelsKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propulsion LabDokument39 SeitenPropulsion LabKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fea QBDokument5 SeitenFea QBKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aircraft Systems Lab ManualDokument28 SeitenAircraft Systems Lab ManualKalpit Kaurase100% (1)
- True Stress-Strain DiagramDokument19 SeitenTrue Stress-Strain DiagramAmruth Babu V T100% (1)
- Thermal Engineering I MANUALDokument35 SeitenThermal Engineering I MANUALKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- AE2305 - Aircraft Structures Repair Lab ManualDokument24 SeitenAE2305 - Aircraft Structures Repair Lab ManualGurunath AeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- F 0463641Dokument6 SeitenF 0463641Kalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3. Flow and Heat Transfer Over A Flat PlateDokument22 SeitenTutorial 3. Flow and Heat Transfer Over A Flat PlatemihailmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- P IiDokument12 SeitenP IiKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 9Dokument13 SeitenExp 9Kalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- B.E & B.Tech. Syllabs For Mechanical Engineering 7 SemesterDokument16 SeitenB.E & B.Tech. Syllabs For Mechanical Engineering 7 SemesterShashi Shekhar SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csvtu 8th Sem Syllabus For Mechanical EngineeringDokument34 SeitenCsvtu 8th Sem Syllabus For Mechanical Engineeringveer_s0% (1)
- Ad ManualDokument30 SeitenAd ManualKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCR Material Testing Price List IndiaDokument4 SeitenTCR Material Testing Price List IndiaanubhavlNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8th Sem SyllabusDokument16 Seiten8th Sem SyllabusKalpit Kaurase0% (1)
- Eat OnDokument32 SeitenEat OnKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design & Drafting Lab ManualDokument49 SeitenDesign & Drafting Lab ManualKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ManualDokument95 SeitenLab ManualKalpit KauraseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas TurbineDokument27 SeitenGas Turbineghgh140100% (1)
- Discharge CoefficientDokument2 SeitenDischarge Coefficientموسى جعفر احمد محمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buckling Force (Euler's Column Formula)Dokument2 SeitenBuckling Force (Euler's Column Formula)iskandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuum Mech Problem Set #3Dokument1 SeiteContinuum Mech Problem Set #3behzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Heat Treatment On The Performance of 30MnB4 Steel For Being Used As Grade 10.9 BoltDokument6 SeitenEffect of Heat Treatment On The Performance of 30MnB4 Steel For Being Used As Grade 10.9 Boltkim983124Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Evaluation of Inflatable Wings For UavsDokument290 SeitenDesign and Evaluation of Inflatable Wings For UavsmegustalazorraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Composite Beam With Deck Slab Design - ISMBDokument94 SeitenSingle Composite Beam With Deck Slab Design - ISMBHAZIRACFS SURAT100% (1)
- Selecting Centrifugal Pumps Data KSB 28Dokument1 SeiteSelecting Centrifugal Pumps Data KSB 28avinashuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starting Methods For Induction MotorsDokument3 SeitenStarting Methods For Induction MotorsKrishnamoorthy Ayyasami100% (1)
- 2011 07 PDFDokument334 Seiten2011 07 PDFmasimaha1379Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Speed Propulsion System Scana PropulsionDokument4 Seiten2 Speed Propulsion System Scana PropulsionMaurizio BernasconiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metric Needle Roller Bearing Interchange GuideDokument18 SeitenMetric Needle Roller Bearing Interchange GuideBang Mat0% (1)
- RDSO TrainingDokument20 SeitenRDSO Trainingmanish kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heisler Graphics PDFDokument3 SeitenHeisler Graphics PDFPedro Augusto Soares100% (1)
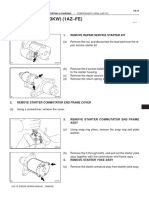
- Starter Assy (1.3Kw) (1Az-Fe) : OverhaulDokument6 SeitenStarter Assy (1.3Kw) (1Az-Fe) : OverhaulHenry SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lycoming Flyer Key ReprintsDokument114 SeitenLycoming Flyer Key Reprintsroux100% (2)
- Servo Gun v2.8 (Eng) ObaraDokument63 SeitenServo Gun v2.8 (Eng) Obaralogaing13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yamaha RX1 Service Manual PDFDokument330 SeitenYamaha RX1 Service Manual PDFJessie O.BechaydaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Doosan TIER 4I Engine (120425)Dokument6 Seiten01 Doosan TIER 4I Engine (120425)Jose Rafael Ramos ChiquilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- VegetaterDokument5 SeitenVegetaterLogeshMechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitation: Arride Learning Online E-Learning AcademyDokument25 SeitenGravitation: Arride Learning Online E-Learning AcademyOm JethwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYS 101 - General Physics I Midterm Exam 2 Solutions: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 14 December 2019 10:00Dokument4 SeitenPHYS 101 - General Physics I Midterm Exam 2 Solutions: Duration: 90 Minutes Saturday, 14 December 2019 10:00Mohammed AL-sharafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collet ChuckDokument4 SeitenCollet ChuckMoco DocoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercury Marine Owner ManualDokument145 SeitenMercury Marine Owner ManualParapendio Club MilazzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Columns - Homework Solutions 2 PDFDokument6 SeitenColumns - Homework Solutions 2 PDFChristopher GeereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylinder 80-300 W INERGEN PDFDokument1 SeiteCylinder 80-300 W INERGEN PDFIskandar HasibuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4Dokument3 SeitenEngineering Mechanics (ME 105) Tutorial Sheet-4baruaoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sec02 1Dokument19 SeitenSec02 1Mahmoud NaDaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actuated ValvesDokument4 SeitenActuated ValvestjendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Von EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksVon EverandArtificial Intelligence: From Medieval Robots to Neural NetworksBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsVon EverandArtificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Von EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- A Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingVon EverandA Welder’s Handbook to Robotic ProgrammingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindVon EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureVon EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Dark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityVon EverandDark Aeon: Transhumanism and the War Against HumanityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Evil Robots, Killer Computers, and Other Myths: The Truth About AI and the Future of HumanityVon EverandEvil Robots, Killer Computers, and Other Myths: The Truth About AI and the Future of HumanityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Atlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceVon EverandAtlas of AI: Power, Politics, and the Planetary Costs of Artificial IntelligenceBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (9)
- Arduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!Von EverandArduino: The ultimate Arduino guide for beginners, including Arduino programming, Arduino cookbook, tips, tricks, and more!Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- The Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityVon EverandThe Fourth Age: Smart Robots, Conscious Computers, and the Future of HumanityBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- In the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkVon EverandIn the Age of AI: How AI and Emerging Technologies Are Disrupting Industries, Lives, and the Future of WorkBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- How to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionVon EverandHow to Survive a Robot Uprising: Tips on Defending Yourself Against the Coming RebellionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (129)
- Artificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindVon EverandArtificial You: AI and the Future of Your MindBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsVon EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessVon EverandComprehensive Guide to Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- What to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationVon EverandWhat to Expect When You're Expecting Robots: The Future of Human-Robot CollaborationBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Create Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceVon EverandCreate Profitable Side Hustles with Artificial IntelligenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationVon EverandChatGPT: The Future of Intelligent ConversationBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (8)
- Mastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesVon EverandMastering Drones - A Beginner's Guide To Start Making Money With DronesBewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Collection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsVon EverandCollection of Raspberry Pi ProjectsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryVon EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (8)