Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Autonomic Nervous System Cheat Sheet - Key Terms & Divisions
Hochgeladen von
Chris_Barber090 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
345 Ansichten1 SeiteAutonomic Nervous System
Originaltitel
Autonomic Nervous System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenAutonomic Nervous System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
345 Ansichten1 SeiteAutonomic Nervous System Cheat Sheet - Key Terms & Divisions
Hochgeladen von
Chris_Barber09Autonomic Nervous System
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
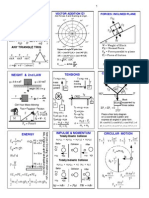
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
15: The Autonomic Nervous System
Key Terms
Autonomic Nervous System: The autonomic nervous
system is made up of afferent and efferent neurons that
connect the autonomic nervous system to visceral effector
organs.
Parasympathetic Division: The parasympathetic division
of the autonomic nervous system is active during periods of
rest and digestion. The parasympathetic division
innervation involves the cranial nerves, such as the facial
nerve.
Sympathetic Division: The sympathetic division of the
autonomic nervous system is active during times of physical
or mental stress on the body. As the system`s activity
increases, skeletal muscles and heart rate are prepared for
a fight-or-flight response.
Sensory Information: The autonomic nervous system
generates a response, based on the information received
from the sensory branch.
Vagus Nerve: The vagus nerve synapses with the
intramural ganglion. There are many targets, including: the
visceral organs of the neck, thoracic cavity and most of the
abdominal cavity. This leads to stimulation of secretion and
an increase in motility in the stomach and intestine.
Nicotinic and Muscarinic Receptors: The nicotinic
receptor subtype is located on all the ganglionic neurons.
Muscarinic receptors are located at cholinergic
neuroeffector junctions (small narrow synaptic clefts).
Alpha and Beta Receptors: Alpha receptors are located
primarily on the surface of smooth muscle cells in blood
vessels. Beta receptors are located in the heart, liver and
skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Plexuses: Within the abdominopelvic cavities,
both the parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers mix in
special plexuses.
Autonomic Control: The control of the autonomic nervous
system can be divided as follows: (1) sympathetic division
is controlled from the posterior and lateral hypothalamus,
and (2) the parasympathetic division is controlled from
portions of the anterior and medial hypothalamus.
Sympathetic Division
Levels of Autonomic Control
Parasympathetic Division
Autonomic Plexuses
The parasympathetic division of the autonomic
nervous system is active during periods of rest and
digestion. The parasympathetic division innervation
involves the cranial nerves, such as the facial nerve.
Within the abdominopelvic cavities, both the
parasympathetic and sympathetic fibers mix in
special plexuses: cardiac, pulmonary, esophagus,
celiac, inferior mesenteric and the hypogastric plexus.
RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Physics Rules 5Dokument10 SeitenPhysics Rules 5Chris_Barber09100% (6)
- MCAT Hormones and EnzymesDokument2 SeitenMCAT Hormones and EnzymesDevie Saha100% (3)
- Mnemonics for MCAT Biology/BiochemistryDokument57 SeitenMnemonics for MCAT Biology/BiochemistryBlinka199100% (2)
- Brain Anatomy Function Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenBrain Anatomy Function Cheat SheetCiprian C.83% (6)
- MCAT Review OChem Notes (Full)Dokument74 SeitenMCAT Review OChem Notes (Full)Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyDelixae Phoinix80% (5)
- Hormone regulation and the hypothalamus-pituitary axisDokument16 SeitenHormone regulation and the hypothalamus-pituitary axisCal GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideVon EverandNervous System: A Tutorial Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Gly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDDokument20 SeitenGly, Ala, Val, Leu, Iso, Phe, Tryp, Met, Pro: ND RDfmd8421Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acid NotesDokument15 SeitenAmino Acid NotesChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry MnemonicsDokument20 SeitenBiochemistry MnemonicsAnnapurna Dangeti100% (1)
- Biology Lecture 5 Hormone ChartDokument2 SeitenBiology Lecture 5 Hormone Chartmark_pedersen_6Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Chemistry MCAT - 1Dokument63 SeitenGeneral Chemistry MCAT - 1pparik10100% (2)
- VirusesDokument1 SeiteVirusesChris_Barber09100% (2)
- Molecular Cell Biology MasterDokument6 SeitenMolecular Cell Biology Masterdealt100% (5)
- MCAT Crash CourseDokument15 SeitenMCAT Crash CourseDe ShepNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImmunologyDokument1 SeiteImmunologyChris_Barber0986% (7)
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDokument3 SeitenProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protein Synthesis Notes PDFDokument3 SeitenProtein Synthesis Notes PDFChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT ChemistryDokument3 SeitenMCAT ChemistryDurvPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFDokument16 SeitenMCAT Biology Notes 3 PDFChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- ProteinsDokument1 SeiteProteinsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology OutlinesDokument21 SeitenBiology OutlinesKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- Chemical Basis of LifeDokument1 SeiteChemical Basis of LifeChris_Barber09100% (2)
- MCAT Physics Reference NotesDokument16 SeitenMCAT Physics Reference NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- MCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesDokument4 SeitenMCAT Biochem Amino Acids Review: Protein Structure & EnzymesNicole Ann LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain MnemonicsDokument1 SeiteBrain Mnemonicsphileo182Noch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology - DNA and Protein SynthesisDokument23 SeitenMolecular Biology - DNA and Protein SynthesisChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Selective Attention and Problem Solving TechniquesDokument28 SeitenSelective Attention and Problem Solving TechniquesMahdeeHaqueSyed100% (2)
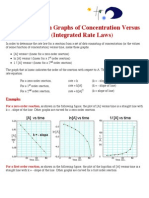
- Rate Law GraphsDokument2 SeitenRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rate Law GraphsDokument2 SeitenRate Law GraphsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology IntroductionDokument1 SeiteCell Biology IntroductionChris_Barber09100% (1)
- MCAT Gen Chem NotesDokument8 SeitenMCAT Gen Chem NotesViviana PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Physiology IntroductionDokument1 SeiteHuman Physiology IntroductionChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- McatDokument11 SeitenMcatE12H12100% (1)
- MCAT Mnemonic SDokument17 SeitenMCAT Mnemonic STasneem MahmoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes CarbohydratesDokument21 SeitenNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Physics Rules 4Dokument6 SeitenPhysics Rules 4Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDokument1 SeitePeripheral Nervous SystemChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Muscular SystemDokument1 SeiteMuscular SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Urinary SystemDokument1 SeiteUrinary SystemChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Biotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentDokument40 SeitenBiotechnoloy Introduction and Application: Table of ContentnescafeforeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Structure and Replication Lecture QuestionsDokument3 SeitenDNA Structure and Replication Lecture QuestionsAyodejiES1Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT Hormones SummaryDokument1 SeiteMCAT Hormones Summaryrvar839Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio MCAT NotesDokument2 SeitenBio MCAT NotesJuan DeSantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsDokument30 SeitenMaster AAMC MCAT-2015 Topics List: Reorganized and Duplicates Removed 1. Amino AcidsSukhvir AujlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Cells To Systems Test Bank Chapter 1Dokument15 SeitenFrom Cells To Systems Test Bank Chapter 1lucas pone67% (3)
- AP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesDokument7 SeitenAP Psychology Mnomonic DevicesBellony SandersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examkrackers General Chemistry NotesDokument16 SeitenExamkrackers General Chemistry NotesddNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology: Anterior Pituitary HormonesDokument12 SeitenBiology: Anterior Pituitary Hormoneserika12767% (3)
- Physiology Exam (Dr. Ramadan) : Complete The Following StatementsDokument4 SeitenPhysiology Exam (Dr. Ramadan) : Complete The Following StatementsramadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Lecture 1 - Atoms, Molecules, and Quantum MechanicsDokument3 SeitenChemistry Lecture 1 - Atoms, Molecules, and Quantum MechanicsChethranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Hindbrain FeaturesDokument26 SeitenNervous System Hindbrain FeaturesShere Almansuori100% (1)
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Dokument5 SeitenBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT Physics ReviewDokument57 SeitenMCAT Physics ReviewrinieroxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Perception and Cognitive ProcessesDokument158 SeitenSensory Perception and Cognitive ProcessesmedmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Midterm 1 QuestionsDokument2 SeitenBiochemistry Midterm 1 Questionselfin_treeNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY MCQS TESTDokument12 SeitenBIOLOGY MCQS TESTKamran ParvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body System ChecklistDokument6 SeitenBody System Checklistapi-422967453Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Notes PDFDokument2 SeitenHeart Notes PDFChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System Gizmos LabDokument5 SeitenCirculatory System Gizmos LabLast FazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ANP PHYSIOLOGYDokument8 SeitenANP PHYSIOLOGYElijah KamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Book 2Dokument63 SeitenPharmacology Book 2Ahmed AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 3 NotesDokument50 SeitenExam 3 NotesAnonymous C6g8uUmWGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam 3 NotesDokument50 SeitenExam 3 NotesAnonymous C6g8uUmWGNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Lec PharmaDokument30 Seiten3rd Lec Pharmanightfury200313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive System NotesDokument3 SeitenReproductive System NotesChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Dokument5 SeitenBacteria: Type of Food Depends On Organism)Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Dokument4 SeitenNucleic Acids and Their Structure: Information?Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT O-Chem NotesDokument1 SeiteMCAT O-Chem NotesChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System PDFDokument3 SeitenDigestive System PDFChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- BSC 2010: Explore Macromolecules and Their FunctionsDokument11 SeitenBSC 2010: Explore Macromolecules and Their FunctionsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Notes PDFDokument2 SeitenHeart Notes PDFChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovasculary System PDFDokument5 SeitenCardiovasculary System PDFChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes RNA and DNADokument23 SeitenNotes RNA and DNAChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leaving GroupsDokument1 SeiteLeaving GroupsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Notes CarbohydratesDokument3 SeitenNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aromatic Notes 2 PDFDokument6 SeitenAromatic Notes 2 PDFChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Carbs: Nature's Most Abundant MoleculesDokument24 SeitenCarbs: Nature's Most Abundant MoleculesGulus CfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionDokument2 SeitenChapter 16:substituent Effects in Aromatic SubstitutionChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Extra Chirality ProblemsDokument21 SeitenExtra Chirality ProblemsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Rules 1Dokument2 SeitenPhysics Rules 1Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- MCAT Physics Equation SheetDokument6 SeitenMCAT Physics Equation SheetChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Regents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsDokument3 SeitenRegents Physics Exam Prep: 101 Facts You Should Know: MechanicsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Equation SheetDokument2 SeitenPhysics Equation SheetChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- AAMC 11 Essay 1Dokument6 SeitenAAMC 11 Essay 1Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Rules 2Dokument4 SeitenPhysics Rules 2Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics 1 Review: Essential Equations and ConceptsDokument9 SeitenAP Physics 1 Review: Essential Equations and ConceptsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- 107 Rules in PhysicsDokument2 Seiten107 Rules in PhysicsChris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen
- AAMC 11 Essay 2Dokument5 SeitenAAMC 11 Essay 2Chris_Barber09Noch keine Bewertungen