Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Demographics
Hochgeladen von
cbellsnlOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Demographics
Hochgeladen von
cbellsnlCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bolivia
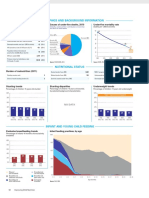
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 9,354 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Latin America, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 1,243 (2006) undernutrition
Unmet need for family planning (%) 23 (2003) Sepsis/Infections, Anaemia
Births (000) 264 (2006) Injuries Malaria Measles Causes of neonatal
including AIDS 0% Contraceptive
150 5% 1% 0% deaths 58 Pre-pregnancy
82 (2006) HIV/AIDS Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) 58 (2003) 8% prevalence rate
Birth registration (%) 125 Diarrhoea Diarrhoea 2%
14% 0% Tetanus 2% Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 61 (2006) 120 Other 8% Hypertensive (1 or more) 79 Pregnancy
Congenital 9% Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) --- Abortion disorders
Pneumonia 12% Skilled attendant
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 50 (2006) 26% 67 Birth
90 17% Infection 23% C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) at birth
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 27 (2000) 61 Neonatal (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) 15,21,6 (2003)
38% *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 16 (2006) 60 Obstructed labor
42 Asphyxia 26% Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) 61 (2003) 13% Exclusive
54 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 290 (2005) 30 breastfeeding
MDG Target Haemorrhage
89 (2005) Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) --- Measles
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) Preterm 31% 21% 81
0 Other Other causes
Total maternal deaths 760 (2005) 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 25% 21%
Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN
0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 for CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 33 (2003) Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 74 (2003) 100 100 100
83 79
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 2 (2003) Low birthweight incidence (%) 7 (2003) 80 80 80 71
69 69 65 67
59
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 53 60
47
60
Percent
Percent
Percent
46 43
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses
40 40 40
At least one dose Two doses
100 100 100 20 20 20
85
80 80 80 73 0 0
1989 1994 1998 2000 2003 1989 1994 1998 2000 2002 2003 1987 1992 1997 2002 2006
60 60 50 54 60 50 DHS DHS DHS MICS DHS DHS DHS DHS MICS Other NS DHS
Percent
Percent
Percent
43 68 42
Source: WHO/UNICEF
39 38 39
31
40 40 40
42 39
20 20 20
35 31 33
38
WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
6 6
0 0 0
1998 2003 1994 1998 2000 2003 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
DHS DHS DHS DHS MICS DHS
Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 95 100 100
91
CHILD HEALTH 85
80 72 80 80
68
60
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60 60
49
60
49
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles 46
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs* transmission of HIV
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 40 33 40
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib 22
20 20 14 20
100
81 0 0 0
80 81 1990 2004 1990 2004 Poorest 2nd 3rd 4th Wealthiest
81 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
60 1994 1998 2000 2003
Percent
No data No data DHS DHS MICS DHS
40 POLICIES SYSTEMS
20
Coverage gap (%) 48 44 33 33
International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 Substitutes Partial Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 186 (2007) poorest/wealthiest --- 2.5 2.4 2.8
Source: WHO/UNICEF
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
*Sub-national risk of malaria transmission General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea --- poorest-wealthiest (%) --- 38 30 30
% of total government expenditure (%) 13 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials* Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics Yes Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 32 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age Yes
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 3.3 (2001)
100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available Partial Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 per child (US$) 6 (2005)
Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
60
59 54
60 54 52
life saving interventions --- Official Development Assistance to maternal and
Bolivia
Percent
Percent
43 neonatal health per live birth (US$) 11 (2005)
No data 40
40 34 40 Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
30 National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
Convention 183 Partial
20 20 services (% of recommended minimum) 48 (2003)
Specific notification of maternal deaths ---
0 0
1994
DHS
1998
DHS
2000
MICS
2003
DHS
1994
DHS
1998
DHS
2000
MICS
2003
DHS
Countdown to 2015
*Sub-national risk of malaria transmission 2008 Report
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben inDokument1 SeiteBen incbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guinea BissauDokument1 SeiteGuinea BissaucbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Go LaDokument1 SeiteAn Go LacbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burkina FasoDokument1 SeiteBurkina FasocbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ye MenDokument1 SeiteYe MencbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition LCADokument2 SeitenNutrition LCAShernia EliboxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liberia: Country ProfileDokument4 SeitenLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12Noch keine Bewertungen
- CAH Causes Death U5 Neonates 2008Dokument1 SeiteCAH Causes Death U5 Neonates 2008raissa leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition PHL PDFDokument2 SeitenNutrition PHL PDFJaiy HingcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Country Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child SurvivalDokument4 SeitenCountry Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survivalpaperpin27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition IDN PDFDokument2 SeitenNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1malnutrition As Health ProblemDokument37 Seiten1malnutrition As Health ProblemIntan Sahara BachsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal CZEDokument4 SeitenMaternal CZEYajie LuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Health. Women and Child HealthDokument45 SeitenGlobal Health. Women and Child HealthjulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jamaica: Country ProfileDokument4 SeitenJamaica: Country ProfileZineil BlackwoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoDokument44 SeitenA Practical Approach To Preventing Child Deaths: What The Pediatrician Can DoSophia Loraine Dorone JesuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- K11 Gizi BurukDokument66 SeitenK11 Gizi BurukBudi UtamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapDokument84 SeitenEssential Newborn Care: From Evidence To Practice: Maria Asuncion Silvestre, MD, FPSNBM, FaapShane Lim GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Dokument63 SeitenKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essential Newborn CareDokument54 SeitenEssential Newborn CareBrigitte CovarrubiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manajemen Terpadu Balita SakitDokument16 SeitenManajemen Terpadu Balita SakitwarnadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hasil Pencapaian Indikator Mdgs Puskesmas Mamajang TAHUN 2016Dokument11 SeitenHasil Pencapaian Indikator Mdgs Puskesmas Mamajang TAHUN 2016MuMu GuevaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.3.3 Diarrhea-4 Januari-3 JanDokument56 Seiten1.3.3 Diarrhea-4 Januari-3 JanmaryamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philippines: No Data Available No Data AvailableDokument1 SeitePhilippines: No Data Available No Data Availablemed wardNoch keine Bewertungen
- PROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisDokument2 SeitenPROBLEM ANALYSIS TREE or Maternal Newborn and Child Mortality in Areas Most Hit by The Anglophone CrisisEpie marcNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDokument30 SeitenOn Epidemological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthBisma Maqbool67% (3)
- Reporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)Dokument35 SeitenReporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)National Press FoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherDokument16 SeitenMaternal Health: Family Revolves Around MotherFatima IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 The High Risk MotherDokument161 Seiten1 The High Risk MotherRaquel M. MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Serbia: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 8 820 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 107 000Dokument1 SeiteSerbia: 2016 TOTAL POPULATION: 8 820 000 2016 TOTAL DEATHS: 107 000Dejan ŽujovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sign - Symptom AND Management of Severe MalnutritionDokument62 SeitenSign - Symptom AND Management of Severe MalnutritionTiara KhairinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOR Health System Profiles 2018Dokument2 SeitenMOR Health System Profiles 2018Chaymae SahraouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indicative Target TemplateDokument11 SeitenIndicative Target TemplateMulugeta DagneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Status of Pakistan Jan 2014Dokument18 SeitenHealth Status of Pakistan Jan 2014Dr.Abuzar ShiraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mal2009 Indonesia 0024Dokument3 SeitenMal2009 Indonesia 0024Tristiani YogastutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dma en PDFDokument1 SeiteDma en PDFElijah DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria in IndiaDokument5 SeitenMalaria in IndiaRanveer Raj BhatnagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AKI Provinsi Bali 2018 3Dokument29 SeitenAKI Provinsi Bali 2018 3witaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pakistan 2015Dokument2 SeitenPakistan 2015shujahkianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthDokument30 SeitenEpidemiological Aspects of Maternal and Child HealthNitin Sharma100% (1)
- Codigo RojoDokument32 SeitenCodigo RojoradiolafiesteraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ye MenDokument1 SeiteYe MencbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guinea BissauDokument1 SeiteGuinea BissaucbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cabizares Handle CaseDokument8 SeitenCabizares Handle CaseMae AbabonNoch keine Bewertungen
- CATAINA, Maria Elizabeth D. - Case-scenario-DRDokument3 SeitenCATAINA, Maria Elizabeth D. - Case-scenario-DRMarielle CatainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUESTIONS DUTY OB BSN2 6B CARAGANandVELORIADokument3 SeitenQUESTIONS DUTY OB BSN2 6B CARAGANandVELORIAMikko McDonie VeloriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Follow Through Case StudyDokument13 SeitenFollow Through Case Studyily tuivanualevuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 26a. Post Partum HemorrhageDokument35 Seiten26a. Post Partum HemorrhageAubrey100% (1)
- Abnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXDokument53 SeitenAbnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXHamss Ahmed100% (2)
- Baby Budget ProjectDokument6 SeitenBaby Budget ProjectDarian RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incompetent CervixDokument29 SeitenIncompetent CervixCyrelle Jen TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NFDN 2004 Assignment 2Dokument2 SeitenNFDN 2004 Assignment 2api-318245320Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brgy Health Plan As of December 26, 2019Dokument23 SeitenBrgy Health Plan As of December 26, 2019Napieh Bulalaque PolisticoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perry: Maternal Child Nursing Care, 6th Edition: Chapter 08: Nursing Care of The Family During Pregnancy Key PointsDokument2 SeitenPerry: Maternal Child Nursing Care, 6th Edition: Chapter 08: Nursing Care of The Family During Pregnancy Key PointsNicole HumesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal Corticosteroid Therapy For Fetal Maturation - ACOGDokument21 SeitenAntenatal Corticosteroid Therapy For Fetal Maturation - ACOGherryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Raed Falah Khalifa - Medics Index Member ProfileDokument5 SeitenDr. Raed Falah Khalifa - Medics Index Member ProfileMedicsindex Telepin SlidecaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherDokument15 SeitenRevised OB Handout Part 1 MAY 2023 PNLE RefresherMatelyn OargaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SASOG Launches Initiative To Improve Women's Health in South AfricaDokument2 SeitenSASOG Launches Initiative To Improve Women's Health in South AfricaBhekisisa HealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fr. Caroselli Street, Poblacion, Valencia City, BukidnonDokument1 SeiteFr. Caroselli Street, Poblacion, Valencia City, BukidnonEduardo AnerdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruDokument21 SeitenAspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruPusparasmi Mas Ayu SuprabhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pregnancy Brain: A Mind-Body Approach To Stress Management During A High-Risk Pregnancy - GeneralDokument5 SeitenPregnancy Brain: A Mind-Body Approach To Stress Management During A High-Risk Pregnancy - GeneralcolomehuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Building Through Gestational SurrogacyDokument7 SeitenFamily Building Through Gestational Surrogacyნათია დემეტრაძეNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study: ScenarioDokument4 SeitenCase Study: ScenarioCheska PalomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prenatal AssessmentDokument2 SeitenPrenatal AssessmentPrincess Pilove GawongnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Case Iufd+covid-19 Fuad SaddamDokument57 SeitenEnglish Case Iufd+covid-19 Fuad SaddamanggatrifiandaprimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20hr Maternity Staff Course - Ses 5Dokument35 Seiten20hr Maternity Staff Course - Ses 5Norhanie Dida-agun AlimodenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 133 Ritgen - JMFNM - AquinoDokument9 Seiten133 Ritgen - JMFNM - AquinoDavid A Tovar ONoch keine Bewertungen
- Abortus Spontaneous Incomplete With Previous Curettage InfectionDokument4 SeitenAbortus Spontaneous Incomplete With Previous Curettage InfectionNofita AizzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NBE Guidelines High-Risk-Pregnancy-PerinatologyDokument23 SeitenNBE Guidelines High-Risk-Pregnancy-PerinatologyATUL178Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Relationship Between Maternal Health Literacy and Pregnancy OutcomeDokument11 SeitenThe Relationship Between Maternal Health Literacy and Pregnancy Outcome1854 Joshua LallawmsangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Client Survey On Breastfeeding: HindiDokument3 SeitenClient Survey On Breastfeeding: HindiShang DimolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chief Report 16.08.2019Dokument78 SeitenChief Report 16.08.2019Inez WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- July 10-11Dokument6 SeitenJuly 10-11Rendy PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healing PCOS: A 21-Day Plan for Reclaiming Your Health and Life with Polycystic Ovary SyndromeVon EverandHealing PCOS: A 21-Day Plan for Reclaiming Your Health and Life with Polycystic Ovary SyndromeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementVon EverandADHD Women: A Holistic Approach To ADHD ManagementBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- The Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouVon EverandThe Autoimmune Cure: Healing the Trauma and Other Triggers That Have Turned Your Body Against YouNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeVon EverandThe Longevity Book: The Science of Aging, the Biology of Strength, and the Privilege of TimeBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (13)
- What to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Von EverandWhat to Expect When You’re Expecting (5th Edition)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Skinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!Von EverandSkinny Bitch: A No-Nonsense, Tough-Love Guide for Savvy Girls Who Want to Stop Eating Crap and Start Looking Fabulous!Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (489)
- Summary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Fast Like a Girl: A Woman’s Guide to Using the Healing Power of Fasting to Burn Fat, Boost Energy, and Balance Hormones: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- All in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayVon EverandAll in Her Head: The Truth and Lies Early Medicine Taught Us About Women’s Bodies and Why It Matters TodayBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Reclaiming Childbirth as a Rite of Passage: Weaving ancient wisdom with modern knowledgeVon EverandReclaiming Childbirth as a Rite of Passage: Weaving ancient wisdom with modern knowledgeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (16)
- Pregnancy Hacks: 350+ Easy Hacks for a Happy and Healthy Pregnancy!Von EverandPregnancy Hacks: 350+ Easy Hacks for a Happy and Healthy Pregnancy!Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Awakening Fertility: The Essential Art of Preparing for PregnancyVon EverandAwakening Fertility: The Essential Art of Preparing for PregnancyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (36)
- Essential Labor: Mothering as Social ChangeVon EverandEssential Labor: Mothering as Social ChangeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (25)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Von EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (124)
- Breaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodVon EverandBreaking Free from Body Shame: Dare to Reclaim What God Has Named GoodBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (33)
- The Hormone Secret: Discover Effortless Weight Loss and Renewed Energy in Just 30 DaysVon EverandThe Hormone Secret: Discover Effortless Weight Loss and Renewed Energy in Just 30 DaysBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Period Power: Harness Your Hormones and Get Your Cycle Working For YouVon EverandPeriod Power: Harness Your Hormones and Get Your Cycle Working For YouBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (25)
- The Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenVon EverandThe Pain Gap: How Sexism and Racism in Healthcare Kill WomenBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (154)
- A Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersVon EverandA Radical Guide for Women with ADHD: Embrace Neurodiversity, Live Boldly, and Break Through BarriersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (72)
- I'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionVon EverandI'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (27)
- WomanCode: Perfect Your Cycle, Amplify Your Fertility, Supercharge Your Sex Drive, and Become a Power SourceVon EverandWomanCode: Perfect Your Cycle, Amplify Your Fertility, Supercharge Your Sex Drive, and Become a Power SourceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (91)
- Younger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondVon EverandYounger Next Year, 2nd Edition: Live Strong, Fit, Sexy, and Smart-Until You're 80 and BeyondBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (111)
- The Fifth Vital Sign: Master Your Cycles & Optimize Your FertilityVon EverandThe Fifth Vital Sign: Master Your Cycles & Optimize Your FertilityBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (12)
- The Mama Natural Week-by-Week Guide to Pregnancy and ChildbirthVon EverandThe Mama Natural Week-by-Week Guide to Pregnancy and ChildbirthBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (21)
- I'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionVon EverandI'll Start Again Monday: Break the Cycle of Unhealthy Eating Habits with Lasting Spiritual SatisfactionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (125)
- Women's Brains: The Female Brain Explained through Neural AnalysesVon EverandWomen's Brains: The Female Brain Explained through Neural AnalysesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (22)
- Nurture: A Modern Guide to Pregnancy, Birth, Early Motherhood—and Trusting Yourself and Your BodyVon EverandNurture: A Modern Guide to Pregnancy, Birth, Early Motherhood—and Trusting Yourself and Your BodyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (14)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Von EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (7)
- Natural Hospital Birth: The Best of Both WorldsVon EverandNatural Hospital Birth: The Best of Both WorldsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (33)