Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ye Men
Hochgeladen von
cbellsnlCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ye Men
Hochgeladen von
cbellsnlCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Yemen
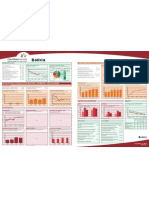
DEMOGRAPHICS MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH
Total population (000) 21,732 (2006) Under-five mortality rate Causes of under-five deaths Causes of maternal deaths Coverage along the continuum of care
Deaths per 1000 live births Globally more than one third of child deaths are attributable to Regional estimates for Asia, 1997-2002
Total under-five population (000) 3,639 (2006) undernutrition
Unmet need for family planning (%) 39 (1997)
Births (000) 839 (2006) Malaria Injuries Measles Causes of neonatal Abortion
Contraceptive
150 139 8% 4% 2% HIV/AIDS deaths
Antenatal visits for woman (4 or more visits, %) 11 (1997) Obstructed labor
6%
prevalence rate 23 Pre-pregnancy
Birth registration (%) --- 0%
Diarrhoea 3%
Other 6% 9% Antenatal visit
Under-five mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 100 (2006) 120 Diarrhoea Tetanus 7% (1 or more) 41 Pregnancy
100 16%
Intermittent preventive treatment for malaria (%) ---
Congenital 8% Hypertensive Haemorrhage
Infant mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 75 (2006) disorders Skilled attendant
90 31% at birth 27 Birth
Asphyxia 21% C-section rate (total, urban, rural; %) 9%
Neonatal mortality rate (per 1000 live births) 37 (2000) Neonatal (Minimum target is 5% and maximum target is 15%) 1, 2, 1 (1997)
46 33% *Postnatal care Neonatal period
Total under-five deaths (000) 84 (2006) 60 Sepsis/Infections,
Infection 25% Early initiation of breastfeeding (within 1 hr of birth, %) 47 (1997) including AIDS Exclusive
12 Infancy
Maternal mortality ratio (per 100,000 live births) 430 (2005) 30 MDG Target 12% breastfeeding
Other
39 (2005) 17% Postnatal visit for baby (within 2 days for home births, %) --- Other causes Measles
Lifetime risk of maternal death (1 in N) Preterm 29% Anaemia 80
0 Pneumonia
21%
Total maternal deaths 3,600 (2005) 13%
1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 20% 0 20 40 60 80 100
Source: Lawn JE, Cousens SN
Source: UNICEF, 2006 Source: WHO, 2006 for CHERG (Nov 2006) Source: Khan, Khalid S., et al, Lancet 2006:367:1066-74 Source: DHS, MICS, Other NS
*See Annex for indicator definition
Antenatal care Skilled attendant at delivery Neonatal tetanus protection
INTERVENTION COVERAGE FOR MOTHERS, NEWBORNS AND CHILDREN Percent women aged 15-49 years attended at least once by a Percent live births attended by skilled health personnel Percent of newborns protected against tetanus
NUTRITION skilled health provider during pregnancy
Stunting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 58 (2003) Complementary feeding rate (6-9 months, %) 76 (2003) 100 100 100
Wasting prevalence (moderate and severe, %) 14 (2003) Low birthweight incidence (%) 32 (1997) 80 80 80
61
Underweight prevalence Exclusive breastfeeding Vitamin A supplementation 60 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent children < 5 years underweight for age* Percent infants < 6 months exclusively breastfed Percent children 6-59 months receiving vitamin A doses 41
40 34 40 40
26 27
At least one dose Two doses 22
16
100 100 100 20 20 20
100 100
95
80 80 80 0 0 0
1991-1992 1997 2003 1991-1992 1997 2003 1985 1990 1995 2000 2006
60 48
60 60 49 DHS DHS Other NS DHS DHS Other NS
Percent
Percent
Percent
Source: WHO/UNICEF
42 36
40 40 40
20
20 20 13
18
12 20
15
WATER AND SANITATION EQUITY
0 0 0 0 0 0 15
0 0 0
1997 2003 1991-1992 1997 2003 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Water Sanitation Coverage gap by wealth quintile
DHS Other NS DHS DHS Other NS
Source: UNICEF
Percent population using improved drinking water sources Percent population using improved sanitation facilities
*Based on 2006 WHO reference population Rural Urban Total Rural Urban Total
100 100 100
CHILD HEALTH 84 82 86
80 71 71 80 80
68 65 67
Immunization Malaria prevention Prevention of mother to child 60 60 60
Percent
Percent
Percent
Percent of children immunised against measles 43
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses DPT
Percent children < 5 years sleeping under ITNs* transmission of HIV
Percent HIV+ pregnant women receiving ARVs for PMTCT
40 40 32 40
Percent of children immunised with 3 doses Hib 28
19
20 20 20
100
85 0 0 0
85
80 1990 2004 1990 2004 Poorest 2nd 3rd 4th Wealthiest
80 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006 Source: WHO/UNICEF JMP, 2006
60 1997
Percent
No data No data DHS
40 POLICIES SYSTEMS
20
Coverage gap (%) 67
International Code of Marketing of Breastmilk Financial Flows and Human Resources
0 Substitutes Yes Ratio
1990 1995 2000 2005 2006 Per capita total expenditure on health (US$) 82 (2007) poorest/wealthiest 1.8
Source: WHO/UNICEF
New ORS formula and zinc for management of Difference
*Sub-national risk of malaria transmission General government expenditure on health as
diarrhoea Partial poorest-wealthiest (%) 36
% of total government expenditure (%) 6 (2007)
Diarrhoeal disease treatment Malaria treatment Pneumonia treatment
Percent children < 5 years with diarrhoea receiving oral rehydration Percent febrile children < 5 years using antimalarials* Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia taken to Community treatment of pneumonia with antibiotics Partial Out-of-pocket expenditure as % of total
therapy or increased fluids, with continued feeding appropriate health provider
Percent children < 5 years with suspected pneumonia receiving expenditure on health (%) 59 (2007)
IMCI adapted to cover newborns 0-1 week of age No
antibiotics
Density of health workers (per 1000 population) 1.0 (2004)
100 100 Costed implementation plan(s) for maternal,
newborn and child health available Yes Official Development Assistance to child health
80 80 per child (US$) 6 (2005)
Midwives be authorised to administer a core set of
60 60 life saving interventions --- Official Development Assistance to maternal and
Yemen
Percent
Percent
47 neonatal health per live birth (US$) 17 (2005)
40 No data
40 Maternity protection in accordance with ILO
32 National availability of Emergency Obstetric Care
23
28 Convention 183 No
18 services (% of recommended minimum) 14 (2004-2005)
20 20
7 Specific notification of maternal deaths ---
0 0
1991-1992
DHS
1997
DHS
1991-1992
DHS
1997
DHS
2003
Other NS
Countdown to 2015
*Sub-national risk of malaria transmission 2008 Report
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guinea BissauDokument1 SeiteGuinea BissaucbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Go LaDokument1 SeiteAn Go LacbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben inDokument1 SeiteBen incbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burkina FasoDokument1 SeiteBurkina FasocbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liberia: Country ProfileDokument4 SeitenLiberia: Country Profilegeorgeloto12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)Dokument35 SeitenReporting On Reproductive Health in Africa (Ayorinde Ajayi)National Press FoundationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal CZEDokument4 SeitenMaternal CZEYajie LuoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Situation Analysis (1) FinalDokument5 SeitenSituation Analysis (1) Finalsitikantha sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Country Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in FijiDokument4 SeitenCountry Health Profile: Maternal, Newborn & Child Survival in Fijipaperpin27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Child-Related Factors Affecting StuntingDokument1 SeiteChild-Related Factors Affecting StuntingJoulesNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPI Scorecard - Sudan - Q1 - 2018Dokument1 SeiteEPI Scorecard - Sudan - Q1 - 2018محمد أبو القاسم عليNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsDokument4 SeitenJamaica Country Profile Highlights Maternal and Child Health StatisticsZineil BlackwoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 Angola Fact SheetsDokument2 Seiten24 Angola Fact SheetsHigidio EduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition IDN PDFDokument2 SeitenNutrition IDN PDFdini mutia KhairunnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Tendency of Stunting Among Children Under Five in The North - 2023 - JornalDokument8 SeitenThe Tendency of Stunting Among Children Under Five in The North - 2023 - JornalJuan ZilkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globo Can Ecuador 2020Dokument2 SeitenGlobo Can Ecuador 2020Park Triple S Kim HyungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Care: Sector ReportDokument16 SeitenHealth Care: Sector Reportmona galalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Mortality in OmanDokument2 SeitenMaternal Mortality in OmanmRta03100% (1)
- 2022 March of Dimes Report Card For LouisianaDokument2 Seiten2022 March of Dimes Report Card For LouisianaCurtisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adolescence and Preg Position PaperDokument2 SeitenAdolescence and Preg Position PaperNichole Trisha MontalbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major causes of death in children under five globally in 2008Dokument1 SeiteMajor causes of death in children under five globally in 2008raissa leeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 March of Dimes Report Card-ArkansasDokument2 Seiten2022 March of Dimes Report Card-ArkansasCurtisNoch keine Bewertungen
- AFRO Profile082020 2 PDFDokument2 SeitenAFRO Profile082020 2 PDFcr89omfNoch keine Bewertungen
- 496 Mongolia Fact SheetsDokument2 Seiten496 Mongolia Fact SheetsShotokan Karate MongoliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOR Health System Profiles 2018Dokument2 SeitenMOR Health System Profiles 2018Chaymae SahraouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Pelatihan KotaDokument7 SeitenModul Pelatihan KotaladyanjaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maharashtra - Disease Burden ProfileDokument4 SeitenMaharashtra - Disease Burden ProfileMeghdoot DeherkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materi Sesi 1 - Pembicara 1 - Dr. Asri C. Adisasmita, MPH, PH.D (Seminar Kesehatan Nasional Universitas Indonesia Tahun 2017 FKM)Dokument33 SeitenMateri Sesi 1 - Pembicara 1 - Dr. Asri C. Adisasmita, MPH, PH.D (Seminar Kesehatan Nasional Universitas Indonesia Tahun 2017 FKM)Niluh Putu DikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Health Statistics 2007Dokument12 SeitenWorld Health Statistics 2007wellunwellNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOMBE MNCH (Jan-June18) Scorecard v2Dokument2 SeitenGOMBE MNCH (Jan-June18) Scorecard v2Omer HussenNoch keine Bewertungen
- KMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016Dokument63 SeitenKMC To Reduce Neonatal Mortality Hadi P Unair 29 Sept 2016mimimomopipiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamil Nadu - Disease Burden ProfileDokument4 SeitenTamil Nadu - Disease Burden ProfileLakshmi PriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Gender Development (GAD) Plan: Client - FocusedDokument16 SeitenAnnual Gender Development (GAD) Plan: Client - FocusedZander YapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing IudDokument52 SeitenStakeholder Meeting - Revitalizing Iudkarun009640Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Algeria Fact SheetsDokument2 Seiten12 Algeria Fact SheetsJohn WayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- 96 Brunei Darussalam Fact SheetsDokument2 Seiten96 Brunei Darussalam Fact SheetsMaria VidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bihar Disease Burden ProfileDokument4 SeitenBihar Disease Burden ProfileHn LkNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD Clinical CliniciansDokument69 SeitenSTD Clinical Cliniciansayush231195Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mal2009 Indonesia 0024Dokument3 SeitenMal2009 Indonesia 0024Tristiani YogastutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECD_Countdown2030_Dominican-RepublicDokument1 SeiteECD_Countdown2030_Dominican-RepublicKarla De WindtNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- The GambiaDokument1 SeiteThe GambiacbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ye MenDokument1 SeiteYe MencbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben inDokument1 SeiteBen incbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Burkina FasoDokument1 SeiteBurkina FasocbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tanzania, United Republic ofDokument1 SeiteTanzania, United Republic ofcbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben inDokument1 SeiteBen incbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben inDokument1 SeiteBen incbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sierra LeoneDokument1 SeiteSierra LeonecbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben inDokument1 SeiteBen incbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ben inDokument1 SeiteBen incbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicscbellsnlNoch keine Bewertungen