Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
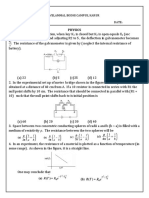
Physics I Problems PDF
Hochgeladen von
BOSS BOSSOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Physics I Problems PDF
Hochgeladen von
BOSS BOSSCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Problems
weight when completely immersed in water? (c) Repeat part (b) if
the crown is solid lead with a very thin gold plating, but still has a
weight in air of 12.9 N.
12.78 .. A piece of steel has a weight w, an apparent weight (see
Problem 12.77) wwater when completely immersed in water, and
an apparent weight wfluid when completely immersed in an
unknown uid. (a) Prove that the uids density relative to water
(specic gravity) is 1w - wfluid2>1w - wwater2. (b) Is this result
reasonable for the three cases of wfluid greater than, equal to, or
less than wwater ? (c) The apparent weight of the piece of steel in
water of density 1000 kg>m3 is 87.2% of its weight. What
percentage of its weight will its apparent weight be in formic acid
1density 1220 kg>m32?
12.79 ... You cast some metal of density rm in a mold, but you
are worried that there might be cavities within the casting. You
measure the weight of the casting to be w, and the buoyant force
when it is completely surrounded by water to be B. (a) Show that
V0 = B>1rwater g2 - w>1rm g2 is the total volume of any enclosed
cavities. (b) If your metal is copper, the castings weight is 156 N,
and the buoyant force is 20 N, what is the total volume of any
enclosed cavities in your casting? What fraction is this of the total
volume of the casting?
12.80 . A cubical block of wood 0.100 m on a side and with a
density of 550 kg>m3 oats in a jar of water. Oil with a density of
750 kg>m3 is poured on the water until the top of the oil layer is
0.035 m below the top of the block. (a) How deep is the oil layer?
(b) What is the gauge pressure at the blocks lower face?
12.81 .. Dropping Anchor. An iron anchor with mass 35.0 kg
and density 7860 kg>m3 lies on the deck of a small barge that has
vertical sides and oats in a freshwater river. The area of the bottom of the barge is 8.00 m2. The anchor is thrown overboard but is
suspended above the bottom of the river by a rope; the mass and
volume of the rope are small enough to ignore. After the anchor is
overboard and the barge has nally stopped bobbing up and down,
has the barge risen or sunk down in the water? By what vertical
distance?
12.82 .. Assume that crude oil from a supertanker has density
750 kg>m3. The tanker runs aground on a sandbar. To reoat the
tanker, its oil cargo is pumped out into steel barrels, each of which
has a mass of 15.0 kg when empty and holds 0.120 m3 of oil. You
can ignore the volume occupied by the steel from which the barrel
is made. (a) If a salvage worker accidentally drops a lled, sealed
barrel overboard, will it oat or sink in the seawater? (b) If the barrel oats, what fraction of its volume will be above the water surface? If it sinks, what minimum tension would have to be exerted
by a rope to haul the barrel up from the ocean oor? (c) Repeat
parts (a) and (b) if the density of the oil is 910 kg>m3 and the mass
of each empty barrel is 32.0 kg.
12.83 ... A cubical block of density rB and with sides of length L
oats in a liquid of greater density rL. (a) What fraction of the
blocks volume is above the surface of the liquid? (b) The liquid is
denser than water 1density rW2 and does not mix with it. If water
is poured on the surface of the liquid, how deep must the water
layer be so that the water surface just rises to the top of the block?
Express your answer in terms of L, rB, rL, and rW. (c) Find the
depth of the water layer in part (b) if the liquid is mercury, the
block is made of iron, and the side length is 10.0 cm.
12.84 .. A barge is in a rectangular lock on a freshwater river. The
lock is 60.0 m long and 20.0 m wide, and the steel doors on each
end are closed. With the barge oating in the lock, a 2.50 * 10 6 N
load of scrap metal is put onto the barge. The metal has density
9000 kg>m3. (a) When the load of scrap metal, initially on the
399
bank, is placed onto the barge, what vertical distance does the water
in the lock rise? (b) The scrap metal is now pushed overboard into
the water. Does the water level in the lock rise, fall, or remain the
same? If it rises or falls, by what vertical distance does it change?
12.85 . CP CALC A U-shaped
tube with a horizontal portion of Figure P12.85
length l (Fig. P12.85) contains
a liquid. What is the difference
in height between the liquid
columns in the vertical arms (a)
if the tube has an acceleration a
toward the right and (b) if the
l
tube is mounted on a horizontal
turntable rotating with an angular speed v with one of the vertical
arms on the axis of rotation? (c) Explain why the difference in
height does not depend on the density of the liquid or on the crosssectional area of the tube. Would it be the same if the vertical tubes
did not have equal cross-sectional areas? Would it be the same if the
horizontal portion were tapered from one end to the other? Explain.
12.86 . CP CALC A cylindrical container of an incompressible liquid Figure P12.86
with density r rotates with constant
y
angular speed v about its axis of
symmetry, which we take to be the
y-axis (Fig. P12.86). (a) Show that
v
the pressure at a given height within
r
the uid increases in the radial direch
tion (outward from the axis of rotation) according to 0 p>0r = rv2r.
(b) Integrate this partial differential
equation to nd the pressure as a
function of distance from the axis of rotation along a horizontal
line at y = 0. (c) Combine the result of part (b) with Eq. (12.5) to
show that the surface of the rotating liquid has a parabolic shape;
that is, the height of the liquid is given by h1r2 = v2r 2>2g. (This
technique is used for making parabolic telescope mirrors; liquid
glass is rotated and allowed to solidify while rotating.)
12.87 .. CP CALC An incompressible uid with density r is in a
horizontal test tube of inner cross-sectional area A. The test tube
spins in a horizontal circle in an ultracentrifuge at an angular speed
v. Gravitational forces are negligible. Consider a volume element
of the uid of area A and thickness dr a distance r from the rotation axis. The pressure on its inner surface is p and on its outer surface is p + dp. (a) Apply Newtons second law to the volume
element to show that dp = rv2rdr. (b) If the surface of the uid
is at a radius r0 where the pressure is p0, show that the pressure p at
a distance r r0 is p = p0 + rv21r 2 - r 022>2. (c) An object of
volume V and density rob has its center of mass at a distance Rcmob
from the axis. Show that the net horizontal force on the object is
rVv2Rcm, where Rcm is the distance from the axis to the center of
mass of the displaced uid. (d) Explain why the object will move
inward if rRcm 7 robRcmob and outward if rRcm 6 robRcmob.
(e) For small objects of uniform density, Rcm = Rcmob.What happens to a mixture of small objects of this kind with different densities in an ultracentrifuge?
12.88 ... CALC Untethered helium balloons, oating in a car that
has all the windows rolled up and outside air vents closed, move in
the direction of the cars acceleration, but loose balloons filled
with air move in the opposite direction. To show why, consider
only the horizontal forces acting on the balloons. Let a be the
magnitude of the cars forward acceleration. Consider a horizontal tube of air with a cross-sectional area A that extends from the
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fluid ND ElasticityDokument54 SeitenFluid ND ElasticityChhaya Sharma ce18b028Noch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet-1 (Fluid Mechanics) : Concept Coaching ClassesDokument6 SeitenWorksheet-1 (Fluid Mechanics) : Concept Coaching ClassesSachin GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Solids & FluidsDokument8 SeitenMechanical Properties of Solids & FluidsShardaVermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NSEP Topper Batch (2023) : Mechanical Properties of FluidDokument4 SeitenNSEP Topper Batch (2023) : Mechanical Properties of Fluidssmeenakshi85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics (Supplement) 12th (An) WADokument6 SeitenFluid Mechanics (Supplement) 12th (An) WAPrashantcool1999Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsDokument8 Seiten8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsUpeka WeerasinghaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08.12.2022 OpenDokument15 Seiten08.12.2022 OpenNaveen Raj VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0003.Dokument54 SeitenWa0003.subhrojyoti balaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic-Wise GATE1Dokument32 SeitenTopic-Wise GATE1CHHAVI AGARWAL0% (1)
- Physics I Problems PDFDokument1 SeitePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2024 Mock2 Liquid StateDokument5 Seiten2024 Mock2 Liquid StateRahul NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbbotDokument2 SeitenAbbotMasiyat DishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDokument20 SeitenMechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment ME401 For GATE PreparationDokument26 SeitenAssignment ME401 For GATE Preparationhameem mohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics (QB) 13thDokument16 SeitenFluid Mechanics (QB) 13thRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions - Mechanical Engineering Principle Lecture and Tutorial - Covering Basics On Distance, Velocity, Time, Pendulum, Hydrostatic Pressure, Fluids, Solids, EtcDokument8 SeitenQuestions - Mechanical Engineering Principle Lecture and Tutorial - Covering Basics On Distance, Velocity, Time, Pendulum, Hydrostatic Pressure, Fluids, Solids, EtcshanecarlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic Fluids - FinalDokument2 SeitenTopic Fluids - FinalMoni KakatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11th Test-5 - 020241Dokument9 SeitenClass 11th Test-5 - 020241Pushkar KirangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDokument5 SeitenMechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDebroop MajumderNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIT2 06S13 ps1 PDFDokument4 SeitenMIT2 06S13 ps1 PDFNatasha StamlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - Viscosity and Surface TensionDokument4 SeitenAssignment - Viscosity and Surface TensionMayur Kumar GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- CP S HW CH 9 DetailedDokument6 SeitenCP S HW CH 9 DetailedVei AdoptanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 Science Unit 15 Eng.Dokument5 SeitenGrade 10 Science Unit 15 Eng.Liza MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics I Problems PDFDokument1 SeitePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSS0% (1)
- Assignment 2 - ViscosityDokument7 SeitenAssignment 2 - ViscosityluluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Equations ProblemsDokument6 SeitenDifferential Equations ProblemsNygen Keith Louise TurlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument11 SeitenFluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsHey Zac100% (1)
- IX - Science - Physics - Ch-9 Gravitation - Assignment-6Dokument1 SeiteIX - Science - Physics - Ch-9 Gravitation - Assignment-6Shweta DuhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hge Set 1-09-02Dokument4 SeitenHge Set 1-09-02Ice DelevingneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics dpp2Dokument3 SeitenPhysics dpp2Vivek GusainNoch keine Bewertungen
- FluidsDokument1 SeiteFluidsMary Joy Delgado33% (3)
- Settling 5Dokument6 SeitenSettling 5Aduchelab AdamsonuniversityNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP - Solids & FluidsDokument6 SeitenDPP - Solids & FluidsMohammed Aftab AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sat-4 (Authentic) ViscosityDokument7 SeitenSat-4 (Authentic) ViscosityLAKSHMI SUNEETANoch keine Bewertungen
- MORSEL 20 (Fluid Statics)Dokument4 SeitenMORSEL 20 (Fluid Statics)Lalitha RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid-ST+vis-JP - QDokument5 SeitenFluid-ST+vis-JP - QAnkit Jaipuria100% (1)
- 03 - Hydrostatics Ex. Module-2Dokument7 Seiten03 - Hydrostatics Ex. Module-2Raju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch13 SSMDokument18 SeitenCh13 SSMJuanca AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 3 FloatationDokument7 SeitenWorksheet 3 FloatationABHISHEK PANDANoch keine Bewertungen
- F. M. 1Dokument3 SeitenF. M. 1Aashish PardeshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shinken ME AE - 2021 Model AnswersDokument13 SeitenShinken ME AE - 2021 Model AnswersresearchditNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParticulateDokument6 SeitenParticulateAduchelab AdamsonuniversityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Dokument51 SeitenFluid Mechanics Exercises FINAL 1676700516410Shahroz NomaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineers Academy: Uestion ANKDokument12 SeitenEngineers Academy: Uestion ANKNishant GauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics-Part Test-3 SolutionDokument5 SeitenPhysics-Part Test-3 SolutionRaju SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code No: 43035/43036Dokument8 SeitenCode No: 43035/43036SRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- 43403125mech 2102Dokument5 Seiten43403125mech 2102080Zaid MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- (D) None of The Above: Answer BDokument6 Seiten(D) None of The Above: Answer BAduchelab AdamsonuniversityNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 NSEP-TEST-6 Fluidsoundwave PCDokument11 Seiten6 NSEP-TEST-6 Fluidsoundwave PCShohom DeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SettlingDokument5 SeitenSettlingAduchelab AdamsonuniversityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Savitsky Brown 76Dokument20 SeitenSavitsky Brown 76yauret123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phy G12 P1 2019 MarchDokument17 SeitenPhy G12 P1 2019 MarchSUNILNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisVon EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsVon EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Case Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesVon EverandCase Studies in Fluid Mechanics with Sensitivities to Governing VariablesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheet PDFDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English Worksheet PDFManoj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheet PDFDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English Worksheet PDFManoj GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDokument1 SeiteTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English WorksheetsBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abraham LincolnDokument2 SeitenAbraham LincolnBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (17) - After A BathDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (17) - After A BathBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (16) - A Happy ChildDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (16) - A Happy ChildBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Assignments (1) - My Friends and GrammerDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class 1 English Assignments (1) - My Friends and GrammerBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets 2 PDFDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets 2 PDFnagsraviNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (19) - Bubble, Straw and ShoeDokument2 SeitenCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (19) - Bubble, Straw and ShoeBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhagwad GitaDokument6 SeitenBhagwad GitaBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdul Kal AmDokument3 SeitenAbdul Kal AmBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Albert EinsteinDokument2 SeitenAlbert EinsteinBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (18) - After A BathDokument1 SeiteCBSE Class 1 English Worksheets (18) - After A BathBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- BuddhaDokument5 SeitenBuddhaBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDokument1 SeiteTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDokument1 SeiteTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDokument1 SeiteTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDokument1 SeiteTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- TN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksDokument1 SeiteTN HSC Physics Bookback One MarksBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 150ah C20Dokument2 Seiten150ah C20movick.25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromDokument9 SeitenAntimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Essential Oil FromTrần Thuý QuỳnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- F1055 15708Dokument15 SeitenF1055 15708Alejandro ValdesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sumitomo PDFDokument20 SeitenSumitomo PDF何家銘Noch keine Bewertungen
- Juba Form Two ExamDokument8 SeitenJuba Form Two ExamHossam Abdalla SalehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm 578Dokument5 SeitenAstm 578ASWANTH T S100% (1)
- QuietR Rotary Duct Liner Product Data SheetDokument2 SeitenQuietR Rotary Duct Liner Product Data SheetJorge SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composites enDokument20 SeitenComposites enpolymer_foam100% (1)
- Laser Cooling and Trapping of Neutral AtomsDokument21 SeitenLaser Cooling and Trapping of Neutral Atomsdevendratiwari0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mal 4Dokument5 SeitenMal 4Heri HidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gantry CraneDokument20 SeitenGantry Cranekushaljp8989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scale Up ArticleDokument8 SeitenScale Up ArticleAndrek QueckNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1. Fossils: Picture 3.1 Cast and Mold FossilDokument6 Seiten1.1. Fossils: Picture 3.1 Cast and Mold Fossilsushan19Noch keine Bewertungen
- KPCL - Steam Blowing ProcedureDokument7 SeitenKPCL - Steam Blowing ProcedureAtiqur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AccuDry Indoor Outdoor 113 WebDokument4 SeitenAccuDry Indoor Outdoor 113 WebCesar NietoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTSE Question Bank & Solutions (Complete Syllabus) PDFDokument7 SeitenNTSE Question Bank & Solutions (Complete Syllabus) PDFSaksham50% (2)
- A-Level-Chemistry Edexcel FACER Sample-Chapter PDFDokument36 SeitenA-Level-Chemistry Edexcel FACER Sample-Chapter PDFahamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture26 PDFDokument4 SeitenLecture26 PDFgautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zinc Chloride Sol Msds PDFDokument6 SeitenZinc Chloride Sol Msds PDFJunia Alfa NessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DK7740A Wire CutDokument45 SeitenDK7740A Wire Cutdprdouglas100% (2)
- 1st Preliminary Exam (Science 6) 2021-2022 - Google FormsDokument4 Seiten1st Preliminary Exam (Science 6) 2021-2022 - Google FormsEl CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Specifications For Road Works SERIES 4000-Bituminous Layers and SealsDokument51 SeitenStandard Specifications For Road Works SERIES 4000-Bituminous Layers and SealsKisali SarakikyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JAP169 Chapter Summary 5Dokument6 SeitenJAP169 Chapter Summary 5Ovelia KayuzakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGSCE Reviewer Multiple Choice PDFDokument52 SeitenIGSCE Reviewer Multiple Choice PDFAlan Peter50% (2)
- Aiats Aieee 2012 Test-1 SolutionDokument10 SeitenAiats Aieee 2012 Test-1 Solutionblue_l1Noch keine Bewertungen
- PTQ (Petroleum Technology Quarterly) Vol 20 No 4 Q3 (Jul, Aug, Sep) 2015Dokument148 SeitenPTQ (Petroleum Technology Quarterly) Vol 20 No 4 Q3 (Jul, Aug, Sep) 2015Roo FaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synergism in Solvent ExtractionDokument26 SeitenSynergism in Solvent ExtractionabrahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incorporation of Waste Plastic in Asphalt Binders To Improve TheirDokument9 SeitenIncorporation of Waste Plastic in Asphalt Binders To Improve TheirSandor ManesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Au in C - HutchingsDokument8 SeitenAu in C - HutchingsLuis TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problemas Geotecniafree1Dokument46 SeitenProblemas Geotecniafree1Dickey Design100% (3)