Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
PragyanPhukanCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
PragyanPhukanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Syllabus - Physics (PH)
Mathematical Methods:
Calculus of single and multiple variables, partial derivatives, Jacobian, imperfect and perfect differentials, Taylor
expansion, Fourier series.
Vector algebra, Vector Calculus, Multiple integrals, Divergence theorem, Greens theorem, Stokes theorem.
First order equations and linear second order differential equations with constant coefficients.
Matrices and determinants, Algebra of complex numbers.
Mechanics and General Properties of Matter:
Newtons laws of motion and applications, Velocity and acceleration in Cartesian, polar and cylindrical coordinate
systems, uniformly rotating frame, centrifugal and Coriolis forces,
Motion under a central force, Keplers laws, Gravitational Law and field, Conservative and non-conservative
forces.
System of particles, Center of mass, equation of motion of the CM, conservation of linear and angular momentum,
conservation of energy, variable mass systems.
Elastic and inelastic collisions.
Rigid body motion, fixed axis rotations, rotation and translation, moments of Inertia and products of Inertia,
parallel and perpendicular axes theorem.
Principal moments and axes.
Kinematics of moving fluids, equation of continuity, Eulers equation, Bernoullis theorem.
Electricity and Magnetism:
Coulombs law, Gausss law. Electric field and potential.
Electrostatic boundary conditions, Solution of Laplaces equation for simple cases.
Conductors, capacitors, dielectrics, dielectric polarization, volume and surface charges, electrostatic energy.
Biot-Savart law, Amperes law, Faradays law of electromagnetic induction, Self and mutual inductance.
Alternating currents.
Simple DC and AC circuits with R, L and C components.
Displacement current, Maxwells equations and plane electromagnetic waves, Poyntings theorem, reflection and
refraction at a dielectric interface, transmission and reflection coefficients (normal incidence only).
Lorentz Force and motion of charged particles in electric and magnetic fields.
Kinetic theory, Thermodynamics:
Elements of Kinetic theory of gases.
Velocity distribution and Equipartition of energy.
Specific heat of Mono-, di- and tri-atomic gases.
Ideal gas, van-der-Waals gas and equation of state.
Mean free path.
Laws of thermodynamics. Zeroth law and concept of thermal equilibrium. First law and its consequences.
Isothermal and adiabatic processes. Reversible, irreversible and quasi-static processes. Second law and entropy.
Carnot cycle.
AMaxwells thermodynamic relations and simple applications. Thermodynamic potentials and their applications.
Phase transitions and Clausius-Clapeyron equation. Ideas of ensembles, Maxwell-Boltzmann, Fermi-Dirac and
Bose-Einstein distributions.
Modern Physics:
Inertial frames and Galilean invariance. Postulates of special relativity. Lorentz transformations. Length
contraction, time dilation. Relativistic velocity addition theorem, mass energy equivalence.
Blackbody radiation, photoelectric effect, Compton effect, Bohrs atomic model, X-rays. Wave-particle duality,
Uncertainty principle, the superposition principle, calculation of expectation values, Schrdinger equation and its
solution for one, two and three dimensional boxes.
Solution of Schrdinger equation for the one dimensional harmonic oscillator. Reflection and transmission at a step
potential, Pauli exclusion principle.
Structure of atomic nucleus, mass and binding energy. Radioactivity and its applications. Laws of radioactive
decay.
Solid State Physics, Devices and Electronics:
Crystal structure, Bravais lattices and basis. Miller indices. X-ray diffraction and Bragg's law;
Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, variation of resistivity with temperature. Fermi level. p-n junction diode, IV characteristics, Zener diode and its applications,
BJT: characteristics in CB, CE, CC modes.
Single stage amplifier, two stage R-C coupled amplifiers. Simple Oscillators: Barkhausen condition, sinusoidal
oscillators.
OPAMP and applications: Inverting and non-inverting amplifier.
Boolean algebra: Binary number systems; conversion from one system to another system; binary addition and
subtraction. Logic Gates AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR exclusive OR; Truth tables; combination of gates; de
Morgans theorem.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Physical Quantities and Units (1) - HomeworkDokument14 SeitenPhysical Quantities and Units (1) - HomeworkWuileapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preliminary Exam Preliminary Exam: EE111 EE111Dokument2 SeitenPreliminary Exam Preliminary Exam: EE111 EE111Abdul Halil AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power-Cast II: Cast Transformers 112.5-13,000 kVA 2.5V Through 46 KV Primary Voltage 120V Through 15 KV Secondary VoltageDokument4 SeitenPower-Cast II: Cast Transformers 112.5-13,000 kVA 2.5V Through 46 KV Primary Voltage 120V Through 15 KV Secondary Voltageingreyes7Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gamma Match: 1 Equal Size ElementsDokument7 SeitenThe Gamma Match: 1 Equal Size ElementsOreolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Types of CircuitsDokument8 SeitenBasic Types of CircuitsJoan BalendrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy Viva Unit 12017-11-11 204059Dokument6 SeitenPhy Viva Unit 12017-11-11 204059Harsh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid or Effective Grounding and Resistance GroundingDokument8 SeitenSolid or Effective Grounding and Resistance GroundingDishant DhokeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 7: Magnetic SurveyingDokument2 SeitenLab 7: Magnetic SurveyingAshrafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic and Gyro Compass and Steering Systems - B.J. WaDokument71 SeitenMagnetic and Gyro Compass and Steering Systems - B.J. Wamaneesh100% (1)
- Electricity Class Notes Latest 21.10. 2019Dokument3 SeitenElectricity Class Notes Latest 21.10. 2019bittuchintuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aperture AntennasDokument69 SeitenAperture AntennasLockonStratosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio Communication Assignment 01Dokument79 SeitenRadio Communication Assignment 01Amila Srimaal GamageNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.EEE304 Power System Protection TechniquesDokument2 Seiten1.EEE304 Power System Protection TechniquesVijay VenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 2-Orbital-Motion-PPQDokument8 SeitenTask 2-Orbital-Motion-PPQᴛᴀsɴᴇᴇᴍNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compression CompactionDokument46 SeitenCompression CompactionNoonaNuzha Lestary NuzhaAyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Singh B 1960 PHD ThesisDokument285 SeitenSingh B 1960 PHD ThesisMarcoTacoNoch keine Bewertungen
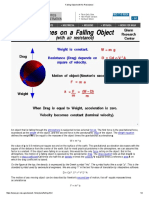
- Air ResistanceDokument2 SeitenAir ResistanceJMathiJaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN 647 - Distributed Generation and MicrogridsDokument53 SeitenEN 647 - Distributed Generation and MicrogridsSumeet MehardaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE Report - Computer Representation of Excitation Systems, 1968Dokument5 SeitenIEEE Report - Computer Representation of Excitation Systems, 1968samuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction - 02 - Chapter2 - NaganoDokument42 SeitenDynamic Soil Structure Interaction - 02 - Chapter2 - Naganonevam21100% (1)
- Positioners: Sizing & SelectionDokument4 SeitenPositioners: Sizing & SelectionsnamprogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid MechanicDokument4 SeitenFluid MechanicteknokolikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Center of MassDokument2 SeitenCenter of MassAnn Margarette MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holiday Homework - Ix PDFDokument11 SeitenHoliday Homework - Ix PDFaditya kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19Dokument24 Seiten19physicsdocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Mathematical Modelling Ideas, Methods, ExamplesDokument360 SeitenPrinciples of Mathematical Modelling Ideas, Methods, Examplesmarmaduke32100% (1)
- FUTA POst UTME Physics QuestionsDokument17 SeitenFUTA POst UTME Physics QuestionsRejoiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws & Weight 1 QPDokument11 SeitenNewton's Laws & Weight 1 QPRabia RafiqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- History Perawatan Generator Rev.01Dokument28 SeitenHistory Perawatan Generator Rev.01Nur Ali SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water Height Field GDC2008Dokument24 SeitenWater Height Field GDC2008Denny TNoch keine Bewertungen