Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Stages of Care - Postoperative Management of The Lower Extremity Amputation - American Academy of Orthotists & Prosthetists
Hochgeladen von
JuanitoCabatañaLimIIIOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Stages of Care - Postoperative Management of The Lower Extremity Amputation - American Academy of Orthotists & Prosthetists
Hochgeladen von
JuanitoCabatañaLimIIICopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
Stages of Care Postoperative Management of the Lower
Extremity Amputation
StagesofCare
Understandingthetimeframeofrecoveryfromlowerlimbamputationisessentialtothe
designandimplementationofanypostoperativemanagementstrategy.Althoughtoday's
healthcaresystemhasplacedanemphasisonspeed,theconsensuscommitteeparticipants
agreedthatplacinganemphasisonshorteningthetimeofhealingandrecoveryfollowing
limblossisnotnecessarilythewisestpath.
Regardlessoftheetiology,thepostoperativerecoveryperiodaftertheamputationofalower
extremitytypicallyis12to18monthsandsimplycannotberushed.1This'recoveryperiod'
includesactivityrecovery,reintegration,prostheticmanagement,andtraining.Some
membersoftheexpertpaneloftheconsensuscommitteefeltthatsettingfastpacedand
oftenunrealisticgoalscanleadtoasenseoffailureinanindividualwhoisactually
progressingnormally.
Thepostoperativeyearlongcontinuumdoesnotseparateeasilyinto"stages".However,an
attempttodefinethestagesofrecoveryhasbeenmadetofacilitatediscussionofhowthe
goalsevolvethroughouttherehabilitativeprocess.
A.PreoperativeStage
Thepreoperativestagetypicallystartswiththeverydifficultdecisionofwhethertoamputate.
Thisstagealsoincludesanassessmentofthevascularstatusanddecisionsonattemptsto
improvecirculation.Thedifficultprocessoflevelselection,preoperativeeducation,emotional
support,physicaltherapyandconditioning,nutritionalsupport,andpainmanagementalsoall
occurinthisstageofcare.
B.AcuteHospitalPostoperativeStage
Theacutehospitalpostoperativestageisthetimeinthehospitalaftertheamputationsurgery.
Thishospitaltimetypicallyrangesfrom5to14days.
C.ImmediatePostacuteHospitalStage
Ingeneral,thisstagebeginswithhospitaldischargeandextends4,6,oreven8weeksafter
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
1/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
surgery.Thisisthetimeofrecoveryfromsurgery,atimeofwoundhealing,andatimeofearly
rehabilitation.Frequently,endpointsofthisstagearecharacterizedasthepointofwound
healingandthepointofbeingreadyforprostheticfitting.However,itshouldbenotedthat
healingofaresiduallimbisacontinuousprocess,andthelimbdoesnothaveaclearand
decisivepointof"beinghealed."Furthermore,prostheticreadinessisatransitionpointthatis
difficulttostandardizeandmeasure.Muchofthecurrentresearchcomparingdifferent
postoperativemanagementstrategiesattemptstousethesetwoelusiveendpointswith
varyingresults.
D.IntermediateRecoveryStage
Thisisthetimeoftransitionfromapostoperativestrategytothefirstformalprostheticdevice.
Historically,thisdevicewascalledthe"preparatory"prosthesis,butwiththeuseofhigher
technologyearlierintheprocess,itissometimessimplycalledthe"firstprosthesis."Theterm
"preparatory"hastraditionallybeenlinkedtoverybasicprostheticstylesandcomponents.
Theconsensuscommitteeparticipantsfeltthatthehistoricalinterpretationof"preparatory
prosthesis"isnolongeradequate.
Itisduringthisstagethatthemostrapidchangesinlimbvolumeoccur,duetothebeginning
ofambulationandprostheticuse.Theimmediaterecoveryperiodbeginswiththehealingof
thewoundandusuallyextends4to6monthsfromthehealingdate.Althoughdifficultto
define,thisstageendswiththerelativestabilizationoftheresiduallimbsize,asdefinedby
consistencyofprostheticfitforseveralmonths.
E.TransitiontoStableStage
Thisperiodisdefinedasaperiodofrelativelimbstabilizationafterthefourthstagewhen
rapidlimbvolumechangesoccurred.Althoughlimbvolumechangesarenotasdrasticasin
thisstage,thelimbwillcontinuetochangetosomedegree,foraperiodof12to18months
afterinitialhealing.Historically,thisstagewasmarkedasatransitionfromthe"preparatory"
tothedefinitiveprosthesis.Currently,withtheuseofhighertechnologyandmodularsystems
inthepreviousstage(IntermediateRecoveryStage),thistransitionisnolongerdefinedbya
changeintheprosthesis,butratherachangefromarapidlychanginglimbtoaslower
maturationofthelimb.Theprosthesiswillstillrequireoccasionaladjustments,andvisitsto
theprosthetistwillremainrelativelyfrequentuntilafterthefirstyearofprostheticuse.Modular
systemsareappropriateandencouragedtoenhanceeaseofsocketreplacementinthis
stage.
Inthisphasethepatientshouldmovetowardsocialreintegrationandhigherfunctional
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
2/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
traininganddevelopmentaswellasbecomingmoreempoweredandindependentfromhisor
herhealthpractitioner.
Thefittingofthedefinitiveprosthesismaycertainlyoccurwithinthistimeperiodhowever,
limbstabilizationmustoccurbeforedefinitivefitting.Residuallimbvolumemustbestableso
thedevicecanbeusedforanextendedperiodoftime.Thisextendedperiodoftimeis
typically25yearsinadultsandaslongas1yearingrowingchildren.
Defininglimbstabilityisverydifficult.Formostpatients,theperiodoflimbstabilization
requiresatleast6monthsofprostheticuse.
ClinicalConcerns
Theexpertpanelforthisconsensuscommitteeidentifiedfourteenclinicalconcernsinthe
stagesofrecovery.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
DeterminationofAmputationLevel
Minimizesystemiccomplications
Preventcontractures
Bedmobilityandtransfers
Painmanagement
Protectamputatedlimbfromtrauma
Fallprevention
Emotionalcare/education
Manageandteachaboutwoundhealing
Promoteresiduallimbmuscleactivity
Earlyambulation
Advancedambulation
Controllimbvolumechanges
Trunkandbodymotorcontrolandstability
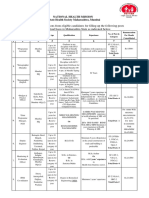
Eachconcernwilltakeonadifferentlevelofimportanceatdifferentstagesofthehealing
process.Sincethegoalsofcarechangeateachstageofrehabilitation,atableofclinical
concernsandtreatmentgoalswasestablishedbytheconsensuscommitteeforeachstage.
(Table1)Theremaybeoverlapbetweenstageswhichmayvarywithindividualdifferences.
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
3/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
Table1.Changingclinicalconcernsduringthestagesofrecoveryafteralowerlimb
amputation
Theseclinicalconcernsandtreatmentgoalsmaybeusedbycliniciansfordevelopmentof
treatmentprotocolsandguidelineswithintheircommunities.Eachgoalofthetableisranked
inrelativeimportancewithregardtothelevelofclinicalconcernateachstageof
rehabilitation.Forexample,thedeterminationofamputationlevelisofconcernatthe
preoperativestagehowever,itisusuallyoflittleconcernafterthesurgery.Conversely,
emotionalcareisofhighclinicalconcernthroughmostoftherehabilitationprocess,witha
slightdropoffintheintermediaterecoverystageandwitharenewedconcernataround1
yearaftertheamputation.
Althoughprogressionthroughthesephasesislargelyindividual,thetimeneededtoprogress
isreportedconsistentlybetween12and18months.Itisduringthisextendedtimethatmany
individualsstillhavesignificantchangesinlimbvolumethatmustbeconsideredand
managed.Duringthis12to18monthperiod,socialreintegration,lifeplanning,andgoal
settingallprogressaswell.Forpediatricamputees,thestagesofrecoveryandtheclinical
concernsaremodifiedtotakeintoaccountthedevelopmentalmilestonesofthegrowingchild.
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
4/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
Finally,inthelaterportionsoftheprocesscomethemasteryofprostheticuseandadesired
rangeofactivities.
PhysicalTherapyandProstheticManagement
Althoughtheroleofallteammembersistoassess,educate,andmotivatethepatient,the
roleoftwoparticularmembersoftheteam,thephysicaltherapistandtheprosthetist,during
thislongperiodisoftenunderestimated.
Physicaltherapytreatmentcontinuesthroughoutthisentireperiodwithspecific
rehabilitationprotocolsdesignedtomeetthespecificneedsofeachamputee.Continual
reevaluationandupdatingoftheamputee'sprogramisessentialtoensurethateach
patientreacheshisorhermaximalactivitylevelwithaprosthesis.
Althoughthepatientmustbeanactiveparticipantinhisorherrehabilitativecare,
thetreatmentguidelinesandspecificexercisesarethetherapist'sresponsibility
andanintegralcomponentofthecontinuumofcareforthefirst12to18months.
Initialprostheticmanagementafteramputationrequiresstrategiesdifferentfromthose
usedduringtheperiodafterresiduallimbstabilization.
Duringtheinitialtimeframe,theprosthetistis"chasingamovingtarget,"asthe
residuallimbchangesdramaticallyinvolumeandshape.Therefore,thedefinitive
prosthesisshouldnotbeprescribedorfituntilthelimbhasbeguntostabilizeand
the"movingtarget"hasslowedconsiderably.
Stabilizationisdifficulttodefineandneedstobefurtherresearched.However,
whenapatienthasusedaprosthesisfulltimeforaperiodofatleast6monthsand
whenthelimbvolumehasstabilizedtoapointthatsocketfitremainsrelatively
consistentforatleast2to3weeks,adefinitiveprosthesismaybeindicated.
Intermediateprostheticmanagementconcentratesonedemareductionandtodefine
limbstabilization.
Additionalstudiesneedtobedonetodeterminethemostappropriatetechniqueto
achievethisstabilization.
Littleliteratureisavailablethatattemptstodefinewhenadjustmentofthecurrent
socketmaymeettheneedsofthepatientversuswhensocketreplacementis
required.Clearly,researchisneededinthisarea.
Finally,itshouldbenotedthatapatientmayreturntoworkduringthisrehabilitativeperiod,
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
5/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
notjustattheendoftheprocess.
CloseWindow[1]
PostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation
TableofContents[2]
WoundHealing
ImagecourtesyofRobertBrown,CPO,FAAOP
Manylowerlimbamputationsdonothealideallyinaprimaryfashion,anditiscommonthat
smallareasofthewoundrequiresecondaryhealingandaperiodofminoropenwoundcare.
Revisionsurgeryisalsofrequentlyrequired.1
Woundhealingproblemsaremostcommonlyrelatedtotheinjury,disease,vascularity,
tobaccouse,andthenatureofamputationsthemselves.Skinandwoundproblemsarerarely
"caused"byasinglefactorandformanyindividualsarenotpreventable.Itisuncommonfor
lowerlimbamputationstohealprimarilywithnowoundissues.
Itshouldbenotedthathealingofanamputatedlimbisacontinuousprocess,andthereisnot
aclearanddecisivepointof'completedhealing'.Therefore,'timetoheal'isnotaprecise
measure.However,documentinghealingcontinuestobeimportantforpatientcareandfor
research.
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
6/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
Determininghealingtimeispronetosubjectiveinterpretationofcompletionof:
epithelialization[3],
interpretationofthesmallopenareas,
individualbias,
timingofthereturntoclinicvisits,and
researchsavvyorknowledgeoftheprostheticandrehabilitationteam.
Thisisanareaofsignificantcontroversy.Oftenthedefinitionof"healed"and"healing"varies
fromstudytostudy.Thus,itisimportantthatfuturestudiesclearlydefinehowthe"timeto
heal"hasbeendeterminedforeachparticularstudy.
'Timetoheal'mayalwaysbedifficulttostandardizeandtomeasure,andinrealitycannotbe
determinedaccuratelyfromsimpleretrospectivereviewofaclinicalchart.TheConsensus
Committeedefinedcategoriesofwoundhealingtoaidtheclinicianandtheresearcherin
standardizingthisoftensubjectivearea.Inaddition,theconsensuscommitteemade
recommendationsonwoundhealingandweighbearingactivity.
Thecategoriesare:
A.CategoriesofWoundHealing
CategoryI.
PrimaryHealing:healswithoutopenareas,infection,orwound
complications.(Figures1&2)
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
7/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
Figure1.CategoryI.Theincisionsiteis
healingwithsomesmallopenareasthat
shouldhealintime.Noinfectionpresent.
ImagecourtesyofJohnRheinstein,CO,
FAAOP&LewSchon,MD.
Figure2.CategoryI.Thesuturesare
removedfromtheincisionsite.Healing
appearstobeproceedingwithsomesmall
openareasthatshouldhealintime.No
infectionpresent.
ImagecourtesyofJohnRheinstein,CP,
FAAOP&LewSchon,MD
Figure3.CategoryII.Ahealingamputationwithfluidandgranulatedtissueinareaswhere
thedrainagetubeswereremoved.
ImagecourtesyofJohnRheinstein,CP,FAAOP&LewSchon,MD
CategoryII.
SecondaryHealing:smallopenareasthatcanbemanagedand
ultimatelyhealwithdressingstrategiesandwoundcare.Additional
surgeryisnotrequired.(Figure3)Thiscanoccasionallybethe
originalplanwithsomeportionoftheamputationintentionallyleft
open.(Figure4)
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
8/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
Figure4.Openamputation.A,severelyabscessedrightfootofa43yearoldinsulin
dependentdiabeticpriortosupramalleolaramputationandwidedebridementofascending
infectionofallcruralcompartments.B,theanteriorcompartmentwoundat17days
demonstratesgranulationattimeofpartialclosure.C,lateralviewofdistalpartialclosure.
Onlyenoughbonetoeffectmyodesisclosurewasremoved.D,thesameresiduallimb3
monthsfollowinginitialopenamputationthelimbisreadyforprostheticfitting.
Imagecourtesyof:18ATranstibialAmputation:SurgicalProceduresandImmediate
PostsurgicalManagement.In:BowkerJH,MichaelJW,eds.AtlasofLimbProsthetics:
Surgical,Prosthetic,andRehabilitationPrinciples,2ndedition,Rosemont,IL:AAOS,2002.
ImagedownloadedfromtheO&PVirtualLibrary,www.oandplibrary.org[4]AccessedJune
2008.
CategoryIII.
Requiresminorsurgicalrevisionofskinand/orsubcutaneous
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
9/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
tissuebutnomuscleorbone.(Figure5)
Figure5.CategoryIII.Anexampleofawoundwithareasofnecroticskin.Thislimbwill
requireminorrevisionsurgerytothewoundsiteandmoreaggressivetreatmentprotocolsto
preventamajorrevision.
ImagecourtesyofNUPOC
CategoryIV.
Requiresmajorsurgicalrevisioninvolvingmuscleand/orbone
however,thewoundhealsatinitialamputation'level'.Forexample,a
midlengthtranstibialamputationthatisrevisedandeventuallyheals
atashortertranstibiallevel.(Figure6)
CategoryV.
Requiresrevisiontoahigheramputationlevel.Forexample,a
Symesamputationthatmustberevisedtoeitheraknee
disarticulationoratransfemoralamputation.(Figure7)
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
10/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
Figure7CategoryIVpossibleCategoryV.Ifinfectionhasreachedtheboneand
oseteomyelitishassetinthenrevisionoftheskin,muscleandbonewillberequiredtoa
moreproximalamputationlevel.
ImagedownloadedfromtheO&PVirtualLibrary,www.oandplibrary.org[5]AccessedJune
2008.
Formoreinformationregardingwoundhealing[6],visitthefollowinglinks:
B.WoundsandWeightBearingActivity
ImagecourtesyofJohnRheinstein,CP,FAAOP&LewSchon,MD
Presenceofanopenwoundorthepresenceofsuturesdoesnotnecessarilyprecludeweight
bearing.Theinstitutionofactivity,orevencontinuationof,canbehelpfulincontrollingedema
andfacilitatinghealing.Thishasbeendemonstratedintheliteraturesincetheearly1920s.2
Althoughinitialinstinctsaretoavoidprostheticuseandweightbearingwheneverthereisa
woundorskinproblem,thismaynotbeappropriateinsomecases.Whileatreatingphysician
mustexaminethewoundandtheprosthetistmustexaminethedeviceforevidenceofdevice
specificpressurepoints,theliteratureactuallysupportsweightbearingandcontinuedactivity
incertainsituationstoenhancewoundhealing.3,4However,moreresearchneedstobe
conductedtoelucidatethemostappropriatedurationandamountofweightbearingto
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
11/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
enhancewoundhealing.
Gooddirectcommunicationabouthealingissuesandwoundsamongprovidersandeducation
ofthepatientarevital.Repeatedwoundassessmentandmodificationofthetreatmentplan
asneededareimportant.Decisionsregardingweightbearingactivityshouldbemadebased
on:
1. theprogressionoftheparticularwound,
2. thelackofprogression,or
3. theworseningwoundappearance.
CloseWindow[7]
PostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation
TableofContents[8]
References
1. ^CloseWindow(www.oandp.org)
2. ^TableofContents(www.oandp.org)
3. ^ViewExpandedContent(www.oandp.org)
4. ^www.oandplibrary.org(www.oandplibrary.org)
5. ^www.oandplibrary.org(www.oandplibrary.org)
6. ^ViewExpandedContent(www.oandp.org)
7. ^CloseWindow(www.oandp.org)
8. ^TableofContents(www.oandp.org)
ExcerptedfromStagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists
&Prosthetists
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08
C221FA8ABD71
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
12/13
12/16/2014
StagesofCarePostoperativeManagementoftheLowerExtremityAmputation|AmericanAcademyofOrthotists&Prosthetists
READABILITYAnArc90LaboratoryExperimenthttp://lab.arc90.com/experiments/readability
http://www.oandp.org/olc/lessons/html/SSC_02/07stages.asp?frmCourseSectionId=514F43738EDF434ABA08C221FA8ABD71
13/13
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Which of The Following Statements Are True About The Impact of Cultural Awareness, Cultural Safety, and Cultural Competence On Different Work RolesDokument36 SeitenWhich of The Following Statements Are True About The Impact of Cultural Awareness, Cultural Safety, and Cultural Competence On Different Work RolesOke Adasen100% (8)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Management of Angle Class I Malocclusion With Severe Crowding and Bimaxillary Protrusion by Extraction of Four Premolars A Case ReportDokument6 SeitenManagement of Angle Class I Malocclusion With Severe Crowding and Bimaxillary Protrusion by Extraction of Four Premolars A Case Reportfitri fauziahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Therapy For Children With Down SyndromeDokument6 SeitenPhysical Therapy For Children With Down SyndromeJuanitoCabatañaLimIII100% (1)
- Down Syndrome: Presentation By: Katherine MateosDokument18 SeitenDown Syndrome: Presentation By: Katherine MateosJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Medications and CAM in ASDDokument54 SeitenMedications and CAM in ASDJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 AmputationDokument23 Seiten02 AmputationJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- AmputationDokument14 SeitenAmputationJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- 2-Physiotherapy For FracturesDokument17 Seiten2-Physiotherapy For FracturesJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Levels of AmputationsDokument6 SeitenLevels of AmputationsJuanitoCabatañaLimIII100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Diseases of The Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue Guideline DifferencesDokument4 SeitenChapter 13 Diseases of The Musculoskeletal System and Connective Tissue Guideline DifferencesJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractures, Dislocations & Other Injuries: TraumaDokument43 SeitenFractures, Dislocations & Other Injuries: TraumaJuanitoCabatañaLimIIINoch keine Bewertungen
- 396 1 MHSS Namibia MC Costing ReportDokument74 Seiten396 1 MHSS Namibia MC Costing Reportckgeorge1303Noch keine Bewertungen
- 6450a6d07795498d Derma360reportDokument12 Seiten6450a6d07795498d Derma360reportNeelam PahujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacy OrientationDokument23 SeitenPharmacy OrientationMohan AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal 2 Terapi Bedah - HDokument4 SeitenJurnal 2 Terapi Bedah - HYusuf DiansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD 12 Science Group B Ready Recknor VDokument36 SeitenSTD 12 Science Group B Ready Recknor Vfree accag100% (2)
- This Content Downloaded From 103.229.203.198 On Wed, 13 Apr 2022 07:01:02 UTCDokument7 SeitenThis Content Downloaded From 103.229.203.198 On Wed, 13 Apr 2022 07:01:02 UTCDewi Utami IrianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ��تجميعات الفارما�Dokument4 Seiten��تجميعات الفارما�Turky TurkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ella - (Effective Reporting and Record-Keeping in Health and Social Care Services)Dokument8 SeitenElla - (Effective Reporting and Record-Keeping in Health and Social Care Services)Rajesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Priorities of Nursing ResearchDokument37 SeitenPriorities of Nursing ResearchJisna AlbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Records Disposition Schedule-Doh (Blank)Dokument2 SeitenRecords Disposition Schedule-Doh (Blank)Karenina Victoria67% (3)
- Barriers To Work-Life Balance For Hospital Nurses: Workplace Health & Safety March 2015Dokument5 SeitenBarriers To Work-Life Balance For Hospital Nurses: Workplace Health & Safety March 2015mustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytotoxic Drugs Related Waste Risk Management Guide 5633 PDFDokument132 SeitenCytotoxic Drugs Related Waste Risk Management Guide 5633 PDFFabrício CamargoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 622 2267 1 PBDokument10 Seiten622 2267 1 PBNanda FallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Development of Nursing Profession (Autosaved)Dokument33 SeitenHistory of Development of Nursing Profession (Autosaved)renu100% (1)
- Disposition: Dr. William Blake Bowler (Cpso# 50188)Dokument3 SeitenDisposition: Dr. William Blake Bowler (Cpso# 50188)noNoch keine Bewertungen
- 39 Patient Autonomy Informed ConsentDokument3 Seiten39 Patient Autonomy Informed ConsentMARICRIS NEBIARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal ClubDokument26 SeitenJournal Clubysindhura23gmailcom100% (1)
- NHM Recruitment Advt.Dokument6 SeitenNHM Recruitment Advt.DiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (DOWNLOAD) PDF AHFS Drug Information 2017: Book DetailsDokument1 Seite(DOWNLOAD) PDF AHFS Drug Information 2017: Book DetailsMuh Bagus Sumarsono100% (2)
- Hope 2 ParqDokument1 SeiteHope 2 ParqJohn Michael PanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assesment of Knowledge of Analgesic Drugs in Pregnant WomenDokument6 SeitenAssesment of Knowledge of Analgesic Drugs in Pregnant WomenMahrukh AmeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHMY701: Pharmacology For Professional Practice Timetable: Semester One, 2021 - North CampusDokument1 SeitePHMY701: Pharmacology For Professional Practice Timetable: Semester One, 2021 - North Campusmeg biscaldiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lawsuit Filed On Behalf of A 4-Year-Old Girl Seeks To Force UNLV To Reopen A HIV ProgramDokument44 SeitenLawsuit Filed On Behalf of A 4-Year-Old Girl Seeks To Force UNLV To Reopen A HIV ProgramLas Vegas Review-JournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Being A DoctorDokument2 SeitenThe Advantages and Disadvantages of Being A DoctorKarinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PALLIATIVE RadiationDokument13 SeitenPALLIATIVE RadiationFeras OskanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dentistry and Community IUST 010-011Dokument72 SeitenDentistry and Community IUST 010-011sharif100% (1)
- B.P.P.K - Course OutcomesDokument3 SeitenB.P.P.K - Course OutcomesDr. B. Sree Giri PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tracheostomy ManagementDokument25 SeitenTracheostomy ManagementlogoioanninaNoch keine Bewertungen