Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Notes 3
Hochgeladen von
Jeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Notes 3
Hochgeladen von
Jeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Slide 9
What is Quality Circle? [History]
Originates from the concept of Edward Deming
Responsible in the transformation of Japan
from cheap product seller to being a leader in
quality
Spearheaded by JUSE (union of Japanese
Scientists and Engineers)
First introduced to line operators which
voluntarily submit when defects of production
has lowered down
Kaoru Ishikawa become the leader of Quality
Control Movement
What is Quality Circle? [Spread of QC Circle Philosophy
to Other Countries]
Management recognized that people are
intelligent; gave opportunities to use their
brain/mind
Spread first to Korea and Taiwan
Then to many parts of Asia through Asian
Productivity Organization (APO) intergovernmental org based on Tokyo, Japan
Each countries is represented by an National
Productivity Organization (NPO)
NPO have significant role in the promotion of
the QC Circle philosophy
It reached in the United States in 1974
By the late 1970s the QC Circle movement had
spread to Great Britain, Sweden, Denmark,
Australia, and France
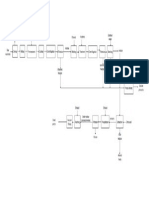
The QC Circle Concept
(QC Circle Activity Flowchart)
Why do we need QC Circle activities?
Customers are very difficult to please
nowadays; demands for better products and
better service is never ending
Management must mobilize the whole
organization towards providing products and
services that satisfy the customers
Processes have to be improved; standards have
to be defined; defective equipment has to be
replaced; people have to be trained; policies
have to be revised
Managements political will is need for all these
things to happen
QC Circle activities are carried out as part of
Total Quality Management (TQM)
The QC Circle provides an opportunity for
members to develop their creative thinking
As the members study and learn together, their
full potential is realized
The productivity will be enhanced,
managements ability to improve will be
developed, and teamwork will be improved
Results in higher morale in the frontline
operations
QC Circle is a small group of frontline operators who
continually control and improve the quality of their
work, products and services; they operate
autonomously and utilize quality control concepts, tools
and techniques.
Characteristics of a QC Circle
Small group
Continual control & improvement in the quality
of work, products & service
Autonomous operation
Utilization of quality control concepts, tools &
techniques
Part of TQM or company-wide QCC
Self-development
Objectives of QC Circle Activities
Establishment of a pleasant workplace
Establishment of a state of control
Enhancement of morale
Establishment of sound human relations
Better income
Improvement in Quality Assurance
Two Patterns of Adoption of the QC Circle Concept
(1) introducing it as a part of company-wide
quality management activity
(2) introducing it prior to the deployment of a
company-wide quality control program
(The management should first learn the basic
aspects of quality control, seven QC tools, problem
solving procedures, and kaizen improvement activities.
Management take the lead in directing its employees in
the line with the companys mission and vision
utilizing all human resources)
Getting Started on QC Circle Activities
Stages Of QC Implementation
1. Preparation
2. Installation
3. Implementation
4. Sustaining QCC
Stages of QC Circle Development
1. Preparation
Preparation of Management
Observation of QC Circle Competitions and
Study of QCC/TQM
2. Installation
Management Declaration of Commitment
Establishment and Appointment of
QC Circle organization
Steering Committee
QCC Office
Facilitator
QC Circle installation plan
In-house training
Volunteers for a Pilot Circle
3. Implementation
Launch of Pilot Circle
Tackling of first problem by following
the 7 steps of the
QC Story
1. Theme selection
2. Current status grasping and
goal setting
3. Establishment of activity plan
4. Cause analysis
5. Countermeasure examination
and implementation
6. Assessment of effectiveness
7. Standardization and
permanent fix
Case presentation for management
Evaluation of Pilot Circle
4. Sustaining QCC
Implementation of the QCC concept companywide
Conduct meetings
Evaluation by Steering Committee and
QC Circle Office
The QCC Organization
QC Circle Steering Committee Composition
Roles of the QC Circle Steering Committee
1) Define the ultimate goal of the QC Circle program in
the company.
2) Formulate a master plan for the installation of the
program.
3) Formulate a plan on how to recognize the exemplary
performance of Circles, members, leaders and
facilitators.
4) Formulate a plan on how to monitor and evaluate the
components of the QC Circle program.
5) Formulate a budget for the program and identify
sources of funds.
6) Define qualifications and functions of facilitators.
7) Act on concerns that may be raised by the QC Circle
Office, the facilitators, or the QC Circles themselves.
8) Evaluate the overall status of the QC Circle program,
including training, rewards and recognition,
promotional activities, and procedures for evaluation of
QC Circle case studies and activities.
9) Formulate corrective and preventive actions based
on findings in the evaluation.
Basic Functions of a QC Circle Office
1. Training facilitators
2. Coordinating training courses, working closely
w/ the dept heads
3. Assisting leaders in their QC Circle acts
4. Motivating QC Cirlce leaders & members
5. Conducting QC Circle case presentations
6. Coordinating QC Circle acts
7. Approving QC Circle actions referred to them,
such as those that have been found not to
violate public law or regulation or company
regulations
Responsibility of a QC Circle Office
1. Implements the policies & plans formulated by
the QC Circle Steering Committee
2. Handles all paperwork & maintains records like
QC Circle registry, min. of meetings, & QC Circle
cases
3. Provides support to the QC Circle Steering
Committee & the leaders
4. Organizes promotional acts like competitions &
visits to other companies w/ QC Circles
Basic Functions of a Facilitator
1. Training leaders
2. Coordinating training courses, working closely
w/ the dept heads
3. Assist leaders in their QC Circle acts
4. Motivating QC Circle leaders & members
5. Arranging QC Circle case presentations
6. Coordinating QC Circle acts
7. Approving QC Cirlce actions referred to them
like those that have been found not to violate
public law or regulation or company regulation
Appointment of QCC Leaders
Participation in a QCC is voluntary
Supervisors often play the role of a leader in a
new Circle; Why?
Some Circles have their members turned into
leaders; others elect their leaders
In the long run, leaders are elected depending
on the themes to tackle, especially when QCC
methods are learnt and disseminated
Basic Functions of a Cirlce Leader
1. Conducting QC Circle meetings
2. Deciding roles of indi & proceeding QC Cirlce act
3. Learning QCC tools & techniques
4. Disseminating what is learned in (3) above
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Trying to improve members abilities
Establishing annual act plan
Encouraging members
Doing administrative work for QC Cirlce Office
Participating in industry-wide conventions
Studying abt QC Circle acts & disseminating the
knowledge
11. Seeking advise & support from the QCC Office
on behalf of its members
The QC Circle should explain, with the assistance of a
facilitator the following topics:
QC Circle Registration
QC Circle Name
QC Circle Logo
QC Circle Leader
Members (with simple bio-data)
Facilitator
Meeting Schedule
Elements of Successful QC Circle meetings
QC Circle meetings kept lively
Facilitator support provided, when needed
Logistical support provided
Ingredients for Effective QC Circle Meetings
1. Members actively participate in discussions
2. Members are committed to the tasks assigned to
them
3. Members listen to each other at all times
4. Discussions are thorough, open, and to the point
5. Disagreements are accepted
6. Members are comfortable in examining the causes
of disagreement and work toward a resolution
7. Members are eager to perform well and continually
seek to improve
8. The leader provides necessary direction and
encourages members to share in the leadership
Implementation of Company-wide QC Circle Program
QC Circle Newsletter
Communications is key to understanding
Publicizing the progress of the Circle is
important
Motivates those who are involved
Includes QC Circle cases presented to
management; pictures + news
The QC Circle Story
Introduction and implementation of the PlanDo-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle
Effective and efficient way of problem-solving
and decision-making process analysis
Each Story shows how QCC members solve a
problem in a systematic PDCA manner
This process is a very effective method for
addressing not only chronic problems in the
workplace but also unforeseen problems and
issues for which the causes have not been
identified
1.Theme Selection
members select a theme from among the
problems in the workplace
theme concerning problems for which they
think solutions would be most beneficial
provide clear vision on the objectives for the
activity
QC Circle cannot study all of the activities of its
work section simultaneously, so it has to focus
on the most critical part of the process
2.Grasping Status & Goal Setting
The main objective of these steps is to gather
information and grasp the status of the problem
so that members can establish a detailed set of
goals
List all possible problems related to the process
Brainstorming can be used to get each members
ideas as to what problems exist in the workshop
A business process has both inputs and outputs
Anything negative about the input is a cause of a
problem; and anything negative about the
output is a problem
3.Establishment of Activity Plan
Based on the data acquired in the second stage,
the members establish an activity plan,
according to the 5W1H concept
The need to speak with facts rather than
opinions has to be stressed because we all have
opinions and very often they are all different
Checksheets and other forms are used for easy
collection, summarization, and analysis of data
How to establish an activity plan?
1. Confirm the problems (use Brainstorming)
2. Select a high priority problem (use a Matrix
Diagram)
3. Define the extent of the problem (must be
defined in quantifiable terms)
4. Establish a goal (SMART goal)
4.Cause Analysis
The main objective of this stage is to confirm
which measures can be taken for what kinds of
problems
results are examined in line with causes
Members consider all possible causes of the
problem
Then they use data to verify the causes, narrow
these down to root causes, and finally select the
most critical root cause
Select the best solution, and establish a detailed
plan on how to implement it
How to proceed cause analysis?
1. List all possible causes of the problem (use
Brainstorming and 5Ys)
2. Show relation among the causes (use 4M1E in an
Ishikawa Diagram)
3. Identify the causes
4. Select root causes
5. Select most critical root cause ( use voting)
6. List all possible ways to eliminate the most critical
root cause
7. Select a best solution
8. Establish a detailed plan (use Gantt Chart)
5.Examination of Countermeasures & Their
Implementation
This stage aims both to correct the root causes
and to establish the most effective measures to
prevent the reoccurrence of the problems
All the people concerned on the issue are
gathered to discuss it, considering factors such
as effectiveness, cost, condition of restrictions,
and impacts on the other factors
Members then implement countermeasures in
daily operations, according to the plan, and
monitor the results (Teamwork is important!)
6.Assessment of Effectiveness
It is carried out together with evaluation for
further improvement of the work
The Circle identifies the tangible and intangible
results, verifies them using data, and compares
them with the initial goal
Tangible results are results targeted
through changes in processes, whereas
intangible results are those in areas such as
improvement in employee learning skills and
education
If the results do not meet the goal, then the
Circle needs to return to previous stages and reexamine the processes
7.Standardization & Permanent Fix
Effective methods are identified, they are
standardized and made a permanent part of
daily operations
Members train the people concerned
Training manuals are created and disseminated
among the people concerned
Evaluation is carried out from time to time,
aimed at ensuring that the process is
maintained appropriately
The last step in this stage is for the Circle to
determine the next problem to tackle, which
may be chosen from the list generated in the
beginning of the first QC Story
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- ItineraryDokument6 SeitenItineraryJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Food Case StudyDokument7 SeitenFunctional Food Case StudyJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- D Rest Chem EngDokument56 SeitenD Rest Chem EngJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics ReviewerDokument4 SeitenMechanics Reviewerrmgc1003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalized Cost P50,000 1.5Dokument7 SeitenCapitalized Cost P50,000 1.5Jeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Functional FoodsDokument6 SeitenReport On Functional FoodsJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- TutorialDokument6 SeitenTutorialJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case-Bart Case StudyDokument4 SeitenCase-Bart Case StudyJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Water and Wastewater Treatment in The Alcoholic BeverageDokument33 SeitenWater and Wastewater Treatment in The Alcoholic BeverageJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise No.5 BiotechDokument6 SeitenExercise No.5 BiotechJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazards in Water Treatment and Distribution SystemDokument4 SeitenHazards in Water Treatment and Distribution SystemJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument7 SeitenReportJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block Scheme DiagramDokument1 SeiteBlock Scheme DiagramJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capitalized Cost P50,000 1.5Dokument7 SeitenCapitalized Cost P50,000 1.5Jeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Sand FilterDokument5 SeitenDesign of Sand FilterJeanne Kamille Evangelista Pinili100% (1)
- Jess Anthony B. Dicdiquin Bs Che IvDokument2 SeitenJess Anthony B. Dicdiquin Bs Che IvJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.3 Environmental Management System (EMS)Dokument1 Seite5.3 Environmental Management System (EMS)Jeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- EditedDokument3 SeitenEditedJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArticleDokument1 SeiteArticleJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waste Management InitiativesDokument1 SeiteWaste Management InitiativesJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banana LiteratureDokument3 SeitenBanana LiteratureJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil Eating BacteriaDokument1 SeiteOil Eating BacteriaJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Type of Fermentation Description (+) Advantages/ (-) DisadvantagesDokument2 SeitenType of Fermentation Description (+) Advantages/ (-) DisadvantagesJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorkDokument1 SeiteWorkJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block Scheme DiagramDokument1 SeiteBlock Scheme DiagramJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banana LiteratureDokument3 SeitenBanana LiteratureJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Cone Blender - ChallengerDokument14 SeitenDouble Cone Blender - ChallengerJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Song For GraduationDokument12 SeitenSong For GraduationJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hazards in Water Treatment and Distribution SystemDokument4 SeitenHazards in Water Treatment and Distribution SystemJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- To ReadDokument4 SeitenTo ReadJeanne Kamille Evangelista PiniliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- TOEFL - Longman TOEFL-534-540Dokument7 SeitenTOEFL - Longman TOEFL-534-540Diah Agustina RatuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Centennial Tower Promotion 1Dokument10 SeitenCentennial Tower Promotion 1madeNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Is The Window To The World. MimieDokument2 SeitenEnglish Is The Window To The World. MimieFARAH NADIANoch keine Bewertungen
- NA BR 1177 EN Dematic AutoStore SubsystemDokument8 SeitenNA BR 1177 EN Dematic AutoStore SubsystemDaniel Garnando KristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belbin's Team ModelDokument2 SeitenBelbin's Team Modelsonu_saisNoch keine Bewertungen
- L 1 Introduction To MorphologyDokument31 SeitenL 1 Introduction To MorphologyIftkhar GorsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AirBossPSS100andEvoplusseriesscba Donning ProcedureDokument1 SeiteAirBossPSS100andEvoplusseriesscba Donning ProcedureMarco LondonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hotel Organizational StructureDokument3 SeitenHotel Organizational StructureChi LinhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qüestionari KPSI.: ActivitiesDokument2 SeitenQüestionari KPSI.: ActivitiesfrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix-Design CalculationsDokument3 SeitenAppendix-Design CalculationsVanessa M. MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet: Soda AshDokument4 SeitenSafety Data Sheet: Soda AshBaher SaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo 5th Chap17 P096Dokument19 SeitenThermo 5th Chap17 P096UTA - Std - Elvin ChantreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title of The Training Program Regional Training of Grades 4-8 Reading Teachers On Care For Non-Readers (CNR) Program Module No., Day & Session NoDokument18 SeitenTitle of The Training Program Regional Training of Grades 4-8 Reading Teachers On Care For Non-Readers (CNR) Program Module No., Day & Session Nomarvin susminaNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLIGHT Punta Arenas - SantiagoDokument3 SeitenFLIGHT Punta Arenas - SantiagoАртем ПичугинNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNSB Bypass Separator Commissioning and Maintenance Guide: Conder® Tanks Covered by This GuideDokument4 SeitenCNSB Bypass Separator Commissioning and Maintenance Guide: Conder® Tanks Covered by This GuidesterlingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparing Registers: MIPS vs. ARM AssemblyDokument12 SeitenComparing Registers: MIPS vs. ARM Assemblyshruti chouhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complete-Crp SPC Shamli r01-1562323540Dokument291 SeitenComplete-Crp SPC Shamli r01-1562323540p nandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation & Role PlayDokument10 SeitenSimulation & Role Playpreeti sharma100% (2)
- Akruti Marathi MultiFont Engine ReadmeDokument22 SeitenAkruti Marathi MultiFont Engine Readmenmshingote2779% (38)
- Procedure: Pressure Equipment Safety: PurposeDokument9 SeitenProcedure: Pressure Equipment Safety: PurposeChegwe CorneliusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recommendation Letter MhandoDokument2 SeitenRecommendation Letter MhandoAnonymous Xb3zHio0% (1)
- Avenger 220 Cruise Street BS IVDokument79 SeitenAvenger 220 Cruise Street BS IVShubham AatopartsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Balanced Cable Measurement Using The 4-Port ENADokument9 SeitenBalanced Cable Measurement Using The 4-Port ENAA. VillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STRUCTUREDokument26 SeitenSTRUCTUREJulia RatihNoch keine Bewertungen
- JRX118SP SpecsheetDokument2 SeitenJRX118SP SpecsheetLuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 78-SAFETY - QUESTIO in PDFDokument21 Seiten78-SAFETY - QUESTIO in PDFIndermohan MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aitkensmethod 170829115234Dokument17 SeitenAitkensmethod 170829115234Yumi koshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro Ducci OnDokument38 SeitenIntro Ducci OnCARLOS EDUARDO AGUIRRE LEONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Test Chapter 19 Ed17Dokument8 SeitenPre-Test Chapter 19 Ed17Sarah ZeidatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimedia Critique Paper 1Dokument4 SeitenMultimedia Critique Paper 1api-345838334Noch keine Bewertungen