Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Radiation
Hochgeladen von
gkawsar22Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Radiation
Hochgeladen von
gkawsar22Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
s behaviour is not always down to its electrons!
For example: carbon has three isotopes:
Isotopes are atoms with the same proton number but different number of neutrons.
The three isotopes of carbon as illustrated above are named as follows:
Carbon-12: C12- just less than 99% of carbon atoms
Carbon-13: C13 - just greater than 1% of carbon atoms
Carbon-14: C14 - very small percentage.
The Carbon-14 atom is the most interesting! It has an unstable nucleus because of the extra neutrons.
As a simple rule, atoms prefer having the same number of neutrons as protons. Otherwise the imbalance can cause
the nucleus to be unstable. The result of this unstable nucleus is that the atom 'throws' out particles, in order, to
become more stable. In the case of the carbon-14 atom it throws out a particle to become a nitrogen atom. This
process of losing particles is called decay.
Carbon-14 is said to be radioactive. It is called a radioisotope or radionuclide. When it decays it gives out
radiation.
It is not only carbon that has radioactive isotopes. Atoms belonging to elements at the bottom of the Periodic Table
tend to have several radioisotopes because they have lots of neutrons as compared to protons.
All radioisotopes eventually turn into stable atoms by giving out radiation.
Decay is a Random Process
You can't control the decay of a nucleus because it is a nuclear reaction not a chemical one. Hence, heat or catalysts
have no effect. This lack of control is why decay is random.
Take the example above, it could take seconds or hundreds of years to turn an atom of polonium-216 into an atom
of lead-208!
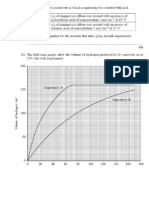
Even though, decay is random, scientists have come up with a way of estimating the time taken for decay to occur for
a specific radioisotope. This is called the Half-Life.
The half-life is the time taken for half the radioisotope in a sample to decay.
Types of radiation
Radiation consists of three types of particle:
1. Alpha: An alpha particle is made up of 2 protons and 2 neutrons, so it has a proton number of 2, and a mass of 4
units. This is identical to the nucleus of a helium atom.
In equations or diagrams like the one below, the nucleus of a helium atom is often used to show the emission (giving
out) of alpha radiation. An alpha particle moves quickly out of the radioisotope but soon slows down in air. Its
penetrating power is poor as even paper and skin can stop it in its tracks!
Advantages and Disadvantages of Radioactivity
Share|
Email | Print
The harmful effects of radiation
If radiation collides with molecules in the air or in your body, it throws out of them electrons. By throwing
out electrons you produce charged particles called ions. This means it is the radiation responsible for
ionising molecules.
If this happens in our body, the cells may die or they may undergo a change called a mutation. The result
is called radiation sickness. A large dose of radiation will cause death!
Small doses of radiation over a long period of time can cause the cells to multiply. However, these cells are
mutated. Some time later cancer may occur.
Background Radiation
We are surrounded by background radiation all of the time! Background radiation comes from the soil,
rocks, the air, water, plants, building materials and food. Some radiation is due to cosmic rays from outer
space. However, fortunately, our body can withstand low level radiation without ill effects because it is able
to repair any damage.
Radiation can be useful
As we've seen from the above narrative, radiation can be harmful, even cause death. However, it can also
be most helpful.
Cancer Treatment:
Gamma rays are capable of passing deep inside the body and damage cells on their travels. But as well as
causing cancer, they can be used to kill off cancer cells and even cure people from this illness. This
treatment is called radiotherapy. Cobalt-60 is commonly used to kill cancer cells. The idea is to aim
accurately at these cells with the correct strength.
Killing Microbes:
Gamma rays successfully kill microbes that cause food to decay. So food treated with this radiation have a
longer shelf life. Surgical instruments and syringes are also treated with gamma rays, in order, to prevent
infections been transferred from patient to patient.
Tracers:
A Geiger Counter is an instrument that measures radiation. If radioisotopes are added to oil or gas,
engineers can follow the radioisotope, and trace any leaks in oil or gas pipes.
Carbon Dating:
When an animal or plant dies it stops taking in carbon. But its carbon-14 content continues to decay. If we
compare the carbon-14 with that from a living thing, and knowing the half-life of carbon-14, the age of
animal and plant remains can be calculated. This is known as carbon dating.
Dating Rocks:
Twelve out of every 1000 potassium atoms is the radioistope potassium-40. Its half life is a staggering
twelve thousand years and decays to eventually form the stable argon atom. By measuring the argon
content of many rocks that contain potassium, scientists can calculate the age of the rock.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Types of ExtractionDokument5 SeitenTypes of ExtractionMohammad NafaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- HeinemannIGCSE Chemistry Chapter1Dokument3 SeitenHeinemannIGCSE Chemistry Chapter1gkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Qualifying Test Result (2014-15) Subject: Chemistry: Bangladesh School MuscatDokument2 SeitenQualifying Test Result (2014-15) Subject: Chemistry: Bangladesh School Muscatgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Report of Preparatory Mockigcse SCDokument55 SeitenReport of Preparatory Mockigcse SCgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The Aqueous Chemistry of CationsDokument11 SeitenThe Aqueous Chemistry of Cationsgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- BondingDokument5 SeitenBondinggkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Relative Atomic MassDokument8 SeitenRelative Atomic Massgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Acid & BaseDokument3 SeitenAcid & Basegkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Periodic TableDokument3 SeitenPeriodic Tablegkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- AtomsDokument4 SeitenAtomsgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- ElectrolysisDokument7 SeitenElectrolysisgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 13.3: How Does Concentration Affect Reaction Rate?Dokument2 SeitenActivity 13.3: How Does Concentration Affect Reaction Rate?gkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Energy From ChemicalsDokument4 SeitenEnergy From Chemicalsgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Crude OilDokument4 SeitenCrude Oilgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Acid & BaseDokument3 SeitenAcid & Basegkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Test Nichrome Wire Wire Wire ColourDokument2 SeitenTest Nichrome Wire Wire Wire Colourgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Seperatting and AnalysisDokument3 SeitenSeperatting and Analysisgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- GCSE CHEMISTRY ACIDS, BASES & SALTS HIGH DEMAND QUESTIONSDokument21 SeitenGCSE CHEMISTRY ACIDS, BASES & SALTS HIGH DEMAND QUESTIONSeeenusNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide To Practical QuestionsDokument10 SeitenA Guide To Practical Questionsgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of ReactionDokument3 SeitenRate of Reactiongkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classifying Materials Activity 5.1 - Physical Properties TestDokument1 SeiteClassifying Materials Activity 5.1 - Physical Properties Testgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- 0906 O Level Grade BoundariesDokument2 Seiten0906 O Level Grade Boundariesryuzaki589Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q 2Dokument25 SeitenQ 2gkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Q 1Dokument36 SeitenQ 1gkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygen and OxidesDokument5 SeitenOxygen and Oxidesgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Making SaltsDokument1 SeiteMaking Saltsgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Theory of DiffusionDokument1 SeiteKinetic Theory of Diffusiongkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Energy Changes in ReactionsDokument2 SeitenIntroducing Energy Changes in Reactionsgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing Reversible ReactionsDokument3 SeitenIntroducing Reversible Reactionsgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rishte ki baat SMS messages collectionDokument108 SeitenRishte ki baat SMS messages collectionTushar AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEG Newsletter 65 2006 AprilDokument48 SeitenSEG Newsletter 65 2006 AprilMilton Agustin GonzagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- 5511Dokument29 Seiten5511Ckaal74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaDokument35 SeitenMarketing Plan for Monuro Clothing Store Expansion into CroatiaMuamer ĆimićNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL - The Firm and Its EnvironmentDokument5 SeitenDLL - The Firm and Its Environmentfrances_peña_7100% (2)
- Log File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsDokument334 SeitenLog File Records Startup Sequence and Rendering CallsKossay BelkhammarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Maths 1 AlgorithmsDokument7 SeitenDecision Maths 1 AlgorithmsNurul HafiqahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leaked David Fry II Conversation Regarding Loopholes and Embezzlement at AFK Gamer LoungeDokument6 SeitenLeaked David Fry II Conversation Regarding Loopholes and Embezzlement at AFK Gamer LoungeAnonymous iTNFz0a0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms For Image Processing and Computer Vision: J.R. ParkerDokument8 SeitenAlgorithms For Image Processing and Computer Vision: J.R. ParkerJiaqian NingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Entries & Ledgers ExplainedDokument14 SeitenJournal Entries & Ledgers ExplainedColleen GuimbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- John Hay People's Alternative Coalition Vs Lim - 119775 - October 24, 2003 - JDokument12 SeitenJohn Hay People's Alternative Coalition Vs Lim - 119775 - October 24, 2003 - JFrances Ann TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Table of Specification for Pig Farming SkillsDokument7 SeitenTable of Specification for Pig Farming SkillsYeng YengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Briana SmithDokument3 SeitenBriana SmithAbdul Rafay Ali KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Towards A Human Resource Development Ontology Combining Competence Management and Technology-Enhanced Workplace LearningDokument21 SeitenTowards A Human Resource Development Ontology Combining Competence Management and Technology-Enhanced Workplace LearningTommy SiddiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- GLF550 Normal ChecklistDokument5 SeitenGLF550 Normal ChecklistPetar RadovićNoch keine Bewertungen
- 621F Ap4405ccgbDokument8 Seiten621F Ap4405ccgbAlwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1Dokument12 SeitenQuickTransit SSLI Release Notes 1.1subhrajitm47Noch keine Bewertungen
- Obstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaDokument82 SeitenObstetrical Hemorrhage: Reynold John D. ValenciaReynold John ValenciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NewspaperDokument11 SeitenNewspaperКристина ОрёлNoch keine Bewertungen
- Good Ethics Is Good BusinessDokument9 SeitenGood Ethics Is Good BusinesssumeetpatnaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Instructions To Examiners:: Calculate The Number of Address Lines Required To Access 16 KB ROMDokument17 SeitenImportant Instructions To Examiners:: Calculate The Number of Address Lines Required To Access 16 KB ROMC052 Diksha PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os PPT-1Dokument12 SeitenOs PPT-1Dhanush MudigereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accomplishment Report 2021-2022Dokument45 SeitenAccomplishment Report 2021-2022Emmanuel Ivan GarganeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventory Control Review of LiteratureDokument8 SeitenInventory Control Review of Literatureaehupavkg100% (1)
- Electronics Ecommerce Website: 1) Background/ Problem StatementDokument7 SeitenElectronics Ecommerce Website: 1) Background/ Problem StatementdesalegnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polytechnic University Management Services ExamDokument16 SeitenPolytechnic University Management Services ExamBeverlene BatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRODUCTDokument82 SeitenPRODUCTSrishti AggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIS Multi-Criteria Analysis by Ordered Weighted Averaging (OWA) : Toward An Integrated Citrus Management StrategyDokument17 SeitenGIS Multi-Criteria Analysis by Ordered Weighted Averaging (OWA) : Toward An Integrated Citrus Management StrategyJames DeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pom Final On Rice MillDokument21 SeitenPom Final On Rice MillKashif AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 - Impact of Open Spaces On Health & WellbeingDokument24 Seiten2010 - Impact of Open Spaces On Health & WellbeingmonsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowVon EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessVon EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishVon EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldVon EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingVon EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismVon EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (500)