Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
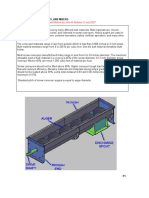
Conveyor Tension and Trajectory Calculation
Hochgeladen von
Gregory Nick Toledo VelizOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Conveyor Tension and Trajectory Calculation
Hochgeladen von
Gregory Nick Toledo VelizCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
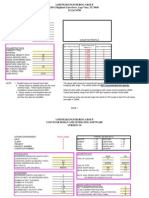
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.
03
Specifier Sheet and Recommendation Summary
01/07/15
Date
Telephone
Telefax
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
Project Name
Conveyor Reference
Standard Loading Conditions:
Conveyor Length (ft)
Tonnage Rate (tons/hour)
Belt Speed (fpm)
Material Lift Height (ft)
Ambient temperature (F) Min
Ambient temperature (F) Max
Initial Velocity of Material (fpm)
Number of Belt Cleaners
Number of Return Belt Scrapers
Length of Skirt Zone (ft)
Depth of Mat'l in skirt zone (in)
Number of Non-driven Pulleys
Elev. Above Sea Level (ft)
Mat'l, friction coeff
1000
800
300
-10
100
1
12
3
4
3300 ft
Coal, bitum. mined,
Bulk Density (pcf)
Size Consist
0.075
Coal, lignite, 45 pcf
REQUIRED POWER:
BELT PULL SUMMARY:
Standard Loading Belt Pull
Extra pull for Hopper (if any)
Extra pull for Slider Bed (if any)
Extra pull for Diverter or Tripper (if any)
TOTAL Required Belt Pull (Te):
44.9 HP
Force (lbs)
4,714
4,714
RECOMMENDED OPTIONS:
SPECIAL NOTES:
Minimum allowable belt width for lump size is 12 in
Minimum Acceptable Diameter is 14 in. *
Avg is 50% Max Lump Size
Max. Lump Size (in)
*A smaller pulley diameter may cause belt carcass or fastener damage.
RECOMMENDED "SINGLE DRIVE" MOTORIZED PULLEY:
Material Surcharge Angle
Belt Width
25 deg.
Models Available:
Fabric
Power:
Belt Speed:
50HP
Belt Carcass Type
300 FPM
630
Idler Roll diameter
5 in
Face Width:
43.31 in.
42 in
CEMA Type
Troughing Idler Spacing
Angle of Wrap**
4 ft
180 degrees
Type of Take-up
Type of Belt
Drive Location
RECOMMENDED "DUAL DRIVE" MOTORIZED PULLEY:
Partial (2/3)
Automatic
Power:
Belt Speed:
25 HP/each
300 FPM
2 ply, 225 piw
Head
Face Width:
43.31 in.
Type of Lagging
Elevating or Horizontal
Material Flow
well maintained
Condition of Idlers & Pulleys
Type of Dual Drive, if any
none
** This parameter is for either single or dual drive arrangement.
Models Available:
500
Power savings - 1 shift and 3 shift per day:
(Motorized Pulley compared to exposed motor, gearbox, V-belt conveyor drives)
Save: 9135 Kw-Hrs/Yr, 1 shift/day or 27404 Kw-Hrs/Yr, 3 shifts/day
Save: $731 /Yr, 1 shift/day or $2192 /Yr, 3 shifts/day @ $0.08/Kw-Hr
Special Loading Conditions:
1. For hopper feeder specify opening dimensions below.
2. For slider bed, specify bed length & type of bed mat'l below.
3. If belt is driven on return run, specify drive pulley location.
4. If belt has cleats and/or sidewalls show dimensions below.
5. If conveyor has a tripper, define tripper below.
6. If conveyor has diverter(s), define below.
1. Hopper Feeder Design Parameters
Hopper opening width (in)
Hopper opening length (in)
5. Tripper Design Parameters
Tripper length (ft)
Material lift height on tripper (ft)
No. of belt cleaners on tripper
Length of tripper skirt zone (ft)
2. Slider Bed Design Parameters
Slider Bed Length (ft)
Type of Slider Bed Material
Slider Bed Frictional Coefficient
4. Sidewall & Cleated Belt Parameters:
Sidewall & cleat height (in)
Thickness of sidewall (in)
Distance between cleats (in)
Thickness of cleats (in)
Extra Sidewall & Cleat Wt (incl above)
None
3. Drive Pulley Location ("return run" drive only)
Conveyor Length, tail to drive snub (ft)
Height, top of tail to bottom of drive (ft)
\\vboxsrv\conversion_tmp\scratch_2\256611390.xls.ms_office, Specifier, Page 1 of 8
Depth of material in skirt zone (in)
No. of non-driven pulleys on tripper
Estimated belt tension, Te (lbs)
Estimated factor, Ky
0.03
6. Material Diverter (Belt Plow)
No. of diverters that work simultaneously
1/7/2015 12:42 PM
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.03
Model Selector
01/07/15
Date
Telephone
Telefax
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Project Name
Conveyor Reference
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
REQUIRED POWER:
BELT PULL SUMMARY:
Standard Loading Belt Pull
Extra pull for Hopper (if any)
Extra pull for Slider Bed (if any)
Extra pull for Diverter or Tripper (if any)
TOTAL Required Belt Pull (Te):
44.9 HP
Force (lbs)
4,714
4,714
Select Model
320H
Check Radial Load (to prevent
internal damage to pulley)
Maximum Allowable Radial Load
Estimated Maximum Radial Load**
Error: Selected model is incorrect.
Force (lbs)
7,868
10,466
Choose stronger or larger model to handle estimated radial load.
RECOMMENDED OPTIONS (if any):
SPECIAL NOTES (if any):
Minimum allowable belt width for lump size is 12 in
Minimum Acceptable Diameter is 14 in. *
*A smaller pulley diameter may cause belt carcass or fastener damage.
Check Pulley Diameter
(to prevent belt damage.)
Minimum Acceptable Diameter is 14 in.
Selected Diameter is 12.64 in
Error: selected diameter is incorrect.
Choose larger diameter to prevent belt or fastener damage.
Check Maximum Belt Tension
prevent belt damage)
Maximum Belt Tension (T1)
Allowable Fabric Belt Tension
(to
Force (lbs)
7,590
9,450
RECOMMENDED "SINGLE DRIVE" MOTORIZED PULLEY:
Power:
Belt Speed:
Face Width:
Models Available:
50HP
300 FPM
43.31 in.
630
Belt Tension Calculation Summary
Te, effective belt tension
T2, to prevent belt/pulley slippage
T2, to limit belt sag to 2 %
T1, maximum belt tension
Force (lbs)
4,714
2,876
2,808
7,590
**Measured at Drive A in Dual Drive, if applicable.
Calculation for "Dual Drive on Carry Side" is under construction.
RECOMMENDED "DUAL DRIVE" MOTORIZED PULLEY:
Power:
Belt Speed:
Face Width:
Models Available:
25 HP/each
300 FPM
43.31 in.
500
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.03
Bulk Handling Trajectory Calculator and Plotter
(based on CEMA 5th Edition)
1/7/15
Date
Phone
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Fax
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
Project Name
Conveyor Ref.
System Design Parameters:
Belt Width
Material Trajectory:
42 in
Small Pulley (scale: inches)
Troughing Idler Angle
35
Diameter Pulley (in)
13.26 in
Lagging Thickness (in)
0.31 in
Belt Speed
300 fpm
Surcharge Angle
25 deg.
Tonnage Rate (TPH)
Material Density (pcf)
Belt Thickness (in)
Distance to Chute Plate (in)
800
45
0.75
24
Angle of Conv. Inclination (deg)
350
39
36
33
30
27
24
21
18
15
12
9
6
3
0
-3
-6
-9
-12
-15
-18
-21
-24
-27
Alternate Belt Speed (fpm)
18
15
12
9
6
3
0
-3
-6
-9
-12
-15
-18
-21
-24
Design Trajectory - red line; Alternate speed - blue.
WARNING: Material cross section exceeds CEMA allowable maximum.
Calculated Results:
Calc'd mat'l height at centerline
9 in
Calc'd actual height of C.O.G.*
4 in
Calc'd actual mat'l cross section
CEMA Max Allow. height at center
CEMA Max Height of C.O.G.*
CEMA Max Allow. cross section
271.1 sq ft
Mat'l Cross Section at Pulley Face:
Small Pulley (scale: inches)
9
8 in
3 in
211.8 sq ft
3
0
Note:
18
15
12
-3
-6
-9
-12
-15
top of belt (based on actual cross section) to plot
-3
-18
This program uses actual C.O.G.* height above
trajectory. Height of C.O.G. for CEMA
max. allow. cross section is given for ref. only.
Design Cross Section - red line; CEMA max allow. - black line.
*C.O.G. = center of gravity of material, shown as and
\\vboxsrv\conversion_tmp\scratch_2\256611390.xls.ms_office, trajectory, Page 3 of 8
1/7/2015 12:42 PM
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.03
Material Cross Section Plotter
1/7/15
Date
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Fax
Phone
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
Reference Name
Conveyor Number
Cross Section at Troughing Idler:
Narrow Belt (scale: inches)
System Design Parameters:
Tonnage Rate (tph)
Belt Speed (fpm)
Bulk Density (lbs/cu ft)
Material Surcharge Angle
800
300
45
15
25 degrees
Belt Width
42 in.
Idler Angle
35 degrees
12
9
6
3
Material Geometry in Troughing Idler:
CEMA Max. Allow. Cross Section
Calculated Cross Section
-3
15
12
-3
-6
Legend: Solid Line is CEMA Max. Allowable; Red Line is Calculated.
Warning: Specified Material Cross Section Exceeds CEMA Max. Allowable.
Material Geometry at Pulley Discharge:
Calculated Cross Section
Material Height at Centerline
Height of Center of Gravity (A1)
Assumed Edge Distance
Calculated Surcharge Angle
CEMA Max. Allow height at center
CEMA Max Height of C.O.G.
CEMA Standard Edge Distance
-9
-12
131%
3.2 in
0.8 in
11 in
-15
Calc'd Xsec/CEMA Xsec
CEMA Standard Edge Distance
Calculated Edge Distance
Calc'd Material Height at Centerline
1.5 sq ft
1.9 sq ft
2 sq ft
#DIV/0!
#DIV/0!
0.41 in
0 deg
7.8 in.
3.1 in.
1.61 in
9
6
SSX
3.1
3
0.00
0
-3
18
15
12
-3
-6
-9
-12
-15
-18
Note:
This program calculates height of actual C.O.G.*
by assuming that actual edge distance at pulley
face equals 1/2 of actual edge distance in troughed
section. Height of C.O.G.* for CEMA maximum
allowable cross section pulley face is given for
reference only.
Cross Section at Pulley Face:
Narrow Belt (scale: inches)
Legend: Solid Line is CEMA Max. Allowable; Red Line is Calculated.
* C.O.G. = center of gravity of material
\\vboxsrv\conversion_tmp\scratch_2\256611390.xls.ms_office, Page 4 of 8
1/7/2015 12:42 PM
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.03
Material Cross Section Plotter
1/7/15
Date
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Fax
Phone
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
Reference Name
Conveyor Number
System Design Parameters:
Tonnage Rate (tph)
Belt Speed (fpm)
Bulk Density (lbs/cu ft)
Material Surcharge Angle
800
300
45
25 degrees
Belt Width
42 in.
Idler Angle
35 degrees
Cross Section at Troughing Idler:
Wide Belt (scale: inches)
42
36
30
24
18
12
Material Geometry in Troughing Idler:
CEMA Max. Allow. Cross Section
Calculated Cross Section
-6
42
36
30
24
18
12
Cross Section at Pulley Face:
Wide Belt (scale: inches)
18
12
6
3.1
0.00
-6
48
42
36
30
24
18
12
-6
-12
-18
-24
-30
-36
-42
-48
Note:
This program calculates height of actual C.O.G.*
by assuming that actual edge distance at pulley
face equals 1/2 of actual edge distance in troughed
section. Height of C.O.G.* for CEMA maximum
allowable cross section pulley face is given for
reference only.
-6
2 sq ft
#DIV/0!
#DIV/0!
0.41 in
0 deg
7.8 in.
3.1 in.
1.61 in
-12
Legend: Solid Line is CEMA Max. Allowable; Red Line is Calculated.
Warning: Specified Material Cross Section Exceeds CEMA Max. Allowable.
Material Geometry at Pulley Discharge:
Calculated Cross Section
Material Height at Centerline
Height of Center of Gravity (A1)
Assumed Edge Distance
Calculated Surcharge Angle
CEMA Max. Allow height at center
CEMA Max Height of C.O.G.
CEMA Standard Edge Distance
-18
-24
-30
131%
3.2 in
0.8 in
11 in
-36
-42
Calc'd Xsec/CEMA Xsec
CEMA Standard Edge Distance
Calculated Edge Distance
Calc'd Material Height at Centerline
1.5 sq ft
1.9 sq ft
Legend: Solid Line is CEMA Max. Allowable; Red Line is Calculated.
* C.O.G. = center of gravity of material
\\vboxsrv\conversion_tmp\scratch_2\256611390.xls.ms_office, Page 5 of 8
1/7/2015 12:42 PM
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.03
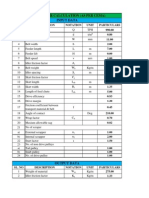
Design Parameter Summary
01/07/15
Date
Telephone
Telefax
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
Project Name
Conveyor Reference
Power Calculation Summary
Calculated power to drive conveyor belt:
Drive pulley bearing friction:
Power at motor:
Gear loss in motorized pulley:
Calculated power
Derate for high elevation
Derate for high temperature
Required Power for motorized pulley:
Symbol
Value
Te
ang
Cw
T2
4714 lbs
180 degrees
0.61
2876 lbs.
T1
T1 + T2
T_L
Tatype
Beltype
w
str
pstr
btr
Ai
Cs
H
Kt
Kx
7590 lbs
10466 lbs
Partial (2/3)
Automatic
2 ply, 225 piw
42 in.
9450 lbs.
80 %
3/16 to 7/16 in.
1.8 lbs
0.0754
0 ft
1.59
0.52 lbs/ft
Ky
L
Q
Si
Tac
Tam
Tb
Tbc
Te
Tm
Tp
0.03
1000 ft
800 tph
4 ft
290 lbs
69 lbs
0 lbs
210 lbs
4714 lbs
0 lbs
160 lbs
Tpl
Tsb
Ttr
Tx
Tyb
Tyc
Tym
Tyr
V
Wb
Wm
Sag
Ls
Hd
0 lbs
80 lbs
0 lbs
824 lbs
831 lbs
545 lbs
2541 lbs
286 lbs
300 fpm
12 lbs/ft
89 lbs/ft
2.0%
42.9
0.6
43.5
1.4
44.9
HP
HP
HP
HP
HP
HP
HP
44.9 HP
Definition of Terms
Te = effective belt tension at drive.
ang = angle of belt wrap around drive pulley(s).
Cw = "wrap factor", to determine slack side tension to prevent belt slippage on drive pulley.
T2 = estimated slack-side tension required to either keep belt from slipping on pulley surface
or maintain trough at allowable sag percentage, whichever is greater.
T1 = Te + T2
T1 + T2 = Sum of belt forces on drive pulley. NOTE: This is not a vector sum.
T_L = type of lagging specified for drive pulley(s).
Tatype = type of take-up specified to apply "slack-side tension".
Beltype = type of belt carsass specified.
w = belt width
str = tensile strength of specified belt.
pstr = percentage of available belt tensile strength used.
btr = thickness range of specified belt
Ai = belt tension required to overcome frictional resistance and rotate idlers.
Cs = skirtboard friction factor.
H = vertical distance that material is lifted or lowered.
Kt = ambient temperature correction factor.
Kx = factor to calculate frictional resistance of the idlers and the sliding resistance between
belt and idler rolls.
Ky = factor to calculate resistance of belt and resistance of load to flexure as they move over idlers.
L = length of conveyor.
Q = tons per hour conveyed.
Si = troughing idler spacing.
Tac = total of the tensions from conveyor accessories.
Tam = tension required to accelerate the material continuously as it is fed onto belt.
Tb = tension required to lift or lower the belt.
Tbc = tension required to overcome belt cleaner drag.
Te = effective belt tension at drive.
Tm = tension required to lift or lower conveyed material.
Tp = tension required to overcome resistance of belt to flexure around pulleys and resistance
of pulleys to rotate on their bearings.
Tpl = tension required to overcome belt plow drag.
Tsb = tension required to overcome skirtboard drag.
Ttr = tension required to overcome special loading condition(s.)
Tx = tension required to overcome carrying and return idler friction.
Tyb = total of tensions due to resistance of belt to flexure as it rides over carrying and return idlers.
Tyc = tension due to resistance of belt to flexure as it rides over carrying idlers.
Tym = tension due to resistance of material to flexure as it rides over carrying idlers.
Tyr = tension due to resistance of belt to flexure as it rides over return idlers.
V = design belt speed.
Wb = weight of belt per unit of length of conveyor.
Wm = weight of material per unit of length of conveyor.
Sag = recommended maximum sag percentage to avoid spillage in troughed section of belt.
Ls = Length of conveyor from tail pulley to Drive snub (for return run drive only)
Hd = Height of conveyor from top of tail pulley to bottom of drive pulley (for return run drive only)
\\vboxsrv\conversion_tmp\scratch_2\256611390.xls.ms_office, Design Parameters, Page 6 of 8
1/7/2015 12:42 PM
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.03
Bulk Handling Belt Conveyor Terminology
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
Conveyor Profile
Initial Velocity of Material
Conveyor Cross Section in Skirt Zone
Belt Conveyor with Tripper
Hopper Feeder Conveyor
Cleated Belt with Sidewalls
Belt Conveyor with Two Diverter(s)
"CEMA" Idler Type Definitions
(Based on Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association Manual)
Belt Width
Idler Type >
Idler (deg) >
18
24
30
36
42
48
54
60
72
84
96
20
300
300
300
275
-
A
35
300
300
280
256
-
45
300
289
270
248
-
20
410
410
410
410
390
380
-
B
35
410
410
410
410
363
353
-
Idler Load Ratings* (lbs)
C
45
20
35
45
20
410 900 900 900
410 900 900 900 1200
410 900 900 900 1200
396 900 837 810 1200
351 850 791 765 1200
342 800 744 720 1200
750 698 675 1200
700 650 630 1150
1050
-
D
35
1200
1200
1200
1200
1200
1116
1070
977
-
45
1200
1200
1200
1200
1200
1080
1035
945
-
20
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1750
E
35
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1674
1628
45
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1800
1620
1575
*These ratings are for three-equal-roll idlers and are based on a 30,000 hour minimum
BU bearing life at 500 RPM. BU bearing life represents the statistical point in hours where
a minimum of 90% of the bearings will still be functional with no increase in torque or noise.
Material Surcharge Angle Guide
(Based on Conveyor Equipment Manufacurters Association Manual)
Surcharge
Angle
Angle of
Repose
Description of Material
0 to 19
Uniform size, very small rounded particles, either very wet or very dry; such as dry
silica sand, cement, and wet concrete.
10
20 to 29
Rounded, dry polished particles, of medium weight, such as whole grain and beans.
20
30 to 34
Irregular, granular or lumpy materials of medium weight, such as anthracite coal,
cottonseed meal, and clay.
25
35 to 39
Typical common materials such as bituminous coal, stone, and most ores.
40+
Irregular, stringy, fibrous, interlocking material, such as wood chips, bagasse, and
tempered foundry sand.
30
\\vboxsrv\conversion_tmp\scratch_2\256611390.xls.ms_office, Terminology, Page 7 of 8
1/7/2015 12:42 PM
Rulmeca Motorized Pulley Power Calculation Program - Standard Version 6.03
Conveyor Height Calculator
Inclined conveyor length (ft)
Angle of inclination (degrees)
Material lift height (ft)
6508-B Windmill Way
Wilmington, NC 28405
Ph 910-794-9294
Fax 910-794-9296
www.rulmecacorp.com
Copyright - Rulmeca Corp.
\\vboxsrv\conversion_tmp\scratch_2\256611390.xls.ms_office, Lift Height, Page 8 of 8
1/7/2015 12:42 PM
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Apron Weigh FeederDokument4 SeitenApron Weigh FeederRaji SuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of ConveyorsDokument15 SeitenDesign of ConveyorsRamachandran VenkateshNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEMA8 5pgDokument5 SeitenCEMA8 5pgkmats100% (2)
- Gr5.Science Teachers Guide JPDokument108 SeitenGr5.Science Teachers Guide JPCyril jay BedrijoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor CalcsDokument3 SeitenBelt Conveyor Calcspandu_chemengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor Design DraftDokument47 SeitenConveyor Design DraftSandi Apriandi100% (1)
- Apron FeederDokument2 SeitenApron FeederRaji Suri100% (1)
- DAT Belt ConveyorDokument8 SeitenDAT Belt ConveyorEDUARDONoch keine Bewertungen
- Chain Pull and Power Calculation - WC 2125 KGMDokument2 SeitenChain Pull and Power Calculation - WC 2125 KGMdeddy ariyanto100% (1)
- Belt Conveyors With Shaft SizingDokument5 SeitenBelt Conveyors With Shaft SizingRakhi Mor100% (2)
- Chain Conveyor ExampleDokument4 SeitenChain Conveyor ExampledeeptidhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw ConveyorDokument5 SeitenScrew ConveyorEDUARDO100% (3)
- Belt Conveyor CalculationDokument8 SeitenBelt Conveyor CalculationFarrahxviiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design (Imperial) 7.23Dokument9 SeitenDesign (Imperial) 7.23Salih HasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Feeder Calculation CEMADokument7 SeitenBelt Feeder Calculation CEMANAITIK100% (4)
- Hoist DesignDokument16 SeitenHoist DesignluisparedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bucket Elevator Calculation: Yellow Cell To Be FilledDokument2 SeitenBucket Elevator Calculation: Yellow Cell To Be Filledm_verma21100% (2)
- Screw ConveyorDokument4 SeitenScrew ConveyorRaji SuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor: Designer's ChoiceDokument4 SeitenBelt Conveyor: Designer's ChoiceAmeu CostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Selection CalculationDokument29 SeitenBelt Selection CalculationElwathig BakhietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor CalculationDokument56 SeitenConveyor CalculationsigisyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor Take Up DesignDokument4 SeitenBelt Conveyor Take Up DesignKroya HunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor Chains TsubakiDokument184 SeitenConveyor Chains Tsubakitepu msosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- M 275 ContentDokument40 SeitenM 275 ContentAnonymous DQ4wYUmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chute Calculation ExampleDokument1 SeiteChute Calculation ExampleBimal DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Feeder Calc. Pns Line 1Dokument4 SeitenBelt Feeder Calc. Pns Line 1Waris La Joi Wakatobi67% (3)
- SCC500EDokument32 SeitenSCC500Eardane100% (1)
- Huang 2014 Slope Stability Analysis by The Limit Equilibrium MethodDokument378 SeitenHuang 2014 Slope Stability Analysis by The Limit Equilibrium MethodpamelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Conveyor CalculationDokument2 SeitenScrew Conveyor CalculationJK71% (7)
- Screw Conveyor Calculation SheetDokument36 SeitenScrew Conveyor Calculation SheetMugurelVasilescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feeder Breaker Chain (Renold Chain) Double Pitch Sprocket DesignDokument1 SeiteFeeder Breaker Chain (Renold Chain) Double Pitch Sprocket DesignWaris La Joi Wakatobi0% (1)
- Design (Metric) 6.25Dokument8 SeitenDesign (Metric) 6.25Salih Has100% (2)
- Analisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIDokument10 SeitenAnalisis Drag Scrapper Chain Feeder (FB01 & FB02) EPIWaris La Joi WakatobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyor CalcsDokument3 SeitenBelt Conveyor Calcsjnmanivannan100% (4)
- Conveyor Design Summary ReportDokument53 SeitenConveyor Design Summary ReportTotok ChemScoutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Conveyor CalculationDokument1 SeiteScrew Conveyor CalculationRavindra RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor CalculationDokument46 SeitenConveyor CalculationBuditama Chandranegara100% (1)
- Travelling Tripper CalculationDokument5 SeitenTravelling Tripper CalculationHarshGupta100% (2)
- Conveyor Design-DraftDokument42 SeitenConveyor Design-Draftmkchy1295% (21)
- Screw Conveyor Calculation - Rev. 1Dokument19 SeitenScrew Conveyor Calculation - Rev. 1octatheweelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mod 4 Perform Mensuration & CalculationDokument41 SeitenMod 4 Perform Mensuration & CalculationDaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibrating ScreensDokument3 SeitenVibrating ScreensvinodsnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor CalculationsDokument3 SeitenConveyor Calculationsmishra_1982Noch keine Bewertungen
- Screw ConveyorsDokument4 SeitenScrew ConveyorsAshish SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BELT FEEDER Preliminary Dimension IngDokument29 SeitenBELT FEEDER Preliminary Dimension Ingshani5573100% (1)
- CONVEYOR CALCULATION SHEET DraftDokument24 SeitenCONVEYOR CALCULATION SHEET DraftRaghava0% (1)
- Mechanical Conveyors: 29 Materials HandlingDokument2 SeitenMechanical Conveyors: 29 Materials HandlingSMNCI Cadet EngineersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project: Vijayawada Thermal Power Station, Stage-IV Unit#7 (500 MW) Subject: Conveyor Design Calculation As Per 5th Edition of CEMADokument7 SeitenProject: Vijayawada Thermal Power Station, Stage-IV Unit#7 (500 MW) Subject: Conveyor Design Calculation As Per 5th Edition of CEMASara Lopez100% (8)
- Konveyör Hesabı 7.24Dokument9 SeitenKonveyör Hesabı 7.24Salih HasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Conveyor DesignDokument9 SeitenScrew Conveyor DesignAJAY1381Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conveyor Design CalcDokument6 SeitenConveyor Design CalcGregory Nick Toledo VelizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belt Conveyors With Shaft SizingDokument5 SeitenBelt Conveyors With Shaft SizingArun Chopra100% (1)
- Conveyor CalculationDokument32 SeitenConveyor CalculationsutanuprojectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screw Conveyor DesignDokument8 SeitenScrew Conveyor DesignPavan Kumar100% (1)
- Design Aspects of A Motorised Travelling TripperDokument5 SeitenDesign Aspects of A Motorised Travelling Trippercar5lyle100% (1)
- Bucket ElevatorDokument2 SeitenBucket ElevatorAndrés Lagos Méndez100% (5)
- Belt Conveyor Capacity - CalculatorDokument6 SeitenBelt Conveyor Capacity - CalculatorRolando Daclan67% (3)
- Screw Conveyor CalculationDokument14 SeitenScrew Conveyor Calculationvvijaybhan100% (2)
- BELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectoryDokument3 SeitenBELT CONVEYOR - Discharge TrajectorySergio Diaz DuarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- TS of Travelling TripperDokument10 SeitenTS of Travelling TripperShashank HegdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Slide Data SheetDokument2 SeitenAir Slide Data SheetTECHCONS Consulting and Engineering Pvt LtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design (Imperial) 7.23Dokument9 SeitenDesign (Imperial) 7.23ozgurturunc4Noch keine Bewertungen
- RCS3-CT8C/CTZ5C: ROBO Cylinder High-Speed TypeDokument8 SeitenRCS3-CT8C/CTZ5C: ROBO Cylinder High-Speed TypeElectromateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Mechanics, Haldane, and Leibniz PDFDokument5 SeitenQuantum Mechanics, Haldane, and Leibniz PDFDren HotiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 A) PDS - E - JER - v4.1Dokument4 Seiten3 A) PDS - E - JER - v4.1Anish KarthikeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0010.Dokument6 SeitenWa0010.Ali SalmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS 1041 - 7-Temperature MeasureDokument19 SeitenBS 1041 - 7-Temperature MeasuregadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 - Truss AnalysisDokument44 SeitenLab 1 - Truss AnalysisPULLNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Few Basics of ElectrochemistryDokument7 SeitenA Few Basics of ElectrochemistryAbdulbar kelilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Advance 1 Paper 2Dokument11 SeitenJee Advance 1 Paper 2iLearn MathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Localize (Phase Ambiguity)Dokument54 SeitenLocalize (Phase Ambiguity)Mirko ZambelliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolted Flanged Joint Creep/Relaxation Results at High TemperaturesDokument7 SeitenBolted Flanged Joint Creep/Relaxation Results at High TemperaturesjlbarretoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHS General Physics 1 1Dokument37 SeitenSHS General Physics 1 1nicole b100% (3)
- Ec8701 Antennas and Microwaveengineering 548086392 Antenna NotesDokument608 SeitenEc8701 Antennas and Microwaveengineering 548086392 Antenna NotesGeetha SupriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sa Node Action PotentialDokument2 SeitenSa Node Action PotentialAljon AniesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Memoria de Calculo SismicoDokument2 SeitenMemoria de Calculo SismicoRodrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Laplace Transform-Part1Dokument12 SeitenLecture 3 - Laplace Transform-Part1John AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubular Heat Exchanger in Phosphoric AcidDokument18 SeitenTubular Heat Exchanger in Phosphoric Acidleo nineNoch keine Bewertungen
- GGN DD 013Dokument143 SeitenGGN DD 013Akshit KhuranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bma63/Uma63 - Complex Analysis - Ii: Gßó Öuõh SS J (Suø ÷/õvupDokument6 SeitenBma63/Uma63 - Complex Analysis - Ii: Gßó Öuõh SS J (Suø ÷/õvupJohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Format Usulan SSH, ASB Dan SBUDokument2 SeitenFormat Usulan SSH, ASB Dan SBUAndini AnugrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- F 414 - 96 Rjqxnc1sruqDokument5 SeitenF 414 - 96 Rjqxnc1sruqmonica andrea suarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactivity and Half LifeDokument5 SeitenRadioactivity and Half LifeMaria Sol LambertNoch keine Bewertungen
- History and Philosophy of Science and TechnologyDokument6 SeitenHistory and Philosophy of Science and TechnologyPhilip LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC331-Chapter-03 - Rivets & BearingsDokument52 SeitenMEC331-Chapter-03 - Rivets & BearingsMuhammad Muadz Amirul AzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Properties of Toluene: 1. Common DataDokument11 SeitenPhysical Properties of Toluene: 1. Common DataPhượng NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Circular GearsDokument10 SeitenNon Circular GearsihaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotor Particulars D275R14 Generator: Drawn Rev Ecn/Description Approved 00 KMC Original Issue CLDokument1 SeiteRotor Particulars D275R14 Generator: Drawn Rev Ecn/Description Approved 00 KMC Original Issue CLpwmvsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CWI-Module 4 - Weld Joint Geometry & Welding Symbols (Compatibility Mode)Dokument80 SeitenCWI-Module 4 - Weld Joint Geometry & Welding Symbols (Compatibility Mode)thanhtung156Noch keine Bewertungen
- Murmurs From The Vascular Members: A Generalized Theoretical OutlookDokument13 SeitenMurmurs From The Vascular Members: A Generalized Theoretical OutlookAsian Journal of Basic Science & ResearchNoch keine Bewertungen