Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Autocad 2D: Lesson 2 - Editing
Hochgeladen von
JaydipPatelOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Autocad 2D: Lesson 2 - Editing
Hochgeladen von
JaydipPatelCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
AutoCAD 2D
Lesson 2 Editing
Pre-reqs/Technical Skills
Basic computer use
Completion of AutoCAD Lesson 1
Expectations
Read lesson material
Implement steps in software while reading through lesson material
Complete quiz on Blackboard
Submit completed assignment on Blackboard
Attend help sessions as necessary
Post comments on lesson web page
Objectives/Measurables
Learn to edit drawing elements in AutoCAD, measured via assignment score
Learn various features in AutoCAD, measured via Blackboard quiz score
Lecture Topics
Editing drawing objects
Table of Contents
AutoCAD 2D ...................................................................................................................................... 1
Lesson 2 Editing ................................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Pre-reqs/Technical Skills ........................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Expectations ..................................................................................................................................................................................................... 1
Objectives/Measurables ............................................................................................................................................................................. 1
Lecture Topics ................................................................................................................................................................................................. 1
Introduction AutoCAD 2010/2011............................................................................................................................................... 1
Editing .......................................................................................................................................................................................................... 2
Moving ................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 2
Rotating ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 3
Offsetting ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Mirroring ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Copying ............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Arraying ............................................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Chamfer/Fillet.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Assignment............................................................................................................................................................................................... 16
Introduction AutoCAD 2010/2011
AutoCAD is a 2D and 3D computer aided drafting (CAD) program. It is used primarily for mechanical and
architectural drafting. Essentially, it provides a computer-based method for producing engineering drawings.
The 2010+ versions integrates the Windows Ribbon interface which may be unfamiliar to those who have used
earlier versions. This module uses the default Ribbon interface and is designed for those new to AutoCAD or
those who wish to use the new Ribbon interface.
1
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Editing
AutoCAD includes several features for editing previously drawn objects. These features include moving,
rotating, offsetting, mirroring, copying and arraying. Each of these features and their uses will be covered in this
tutorial.
Moving
To move an object, or group of objects, use the Move feature. Move can be found in the Modify pane of the
Home tab (Figure 1).
Figure 1 - Move
To use the Move feature, click the Move button (shown in Figure 1). Now select the objects to move. You can
left-click each object in turn to select them (Ctrl or Shift clicking is not necessary) or use the click-drag
techniques covered in Lesson 1. Hit the Enter key to move to the next step. AutoCAD will prompt for a base
point (Figure 2), this point is used as a reference point for the Move feature. You can click to select a point or
enter the point manually by typing in the x-coordinate, a comma and then the y-coordinate. Press Enter to move
to the next step.
Figure 2 - Move: Select Base Point
2
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
AutoCAD will prompt for a second point (Figure 3). Once selected, AutoCAD will move the objects along a vector
from the first point to the second point based on the distance between these points. The second point can be
selected with a click or entered manually. Press the Enter key to complete the move.
Figure 3 - Move: Select Second Point
Rotating
Rotating objects works similarly to moving objects. To rotate, select the Rotate button in the Modify pane of the
Home tab (Figure 4).
Figure 4 - Rotate
After clicking the Rotate button, you must select the objects to be rotated. Use the same techniques as for
moving objects. Once selected, hit the Enter key to move to the next step. Like moving, you must select a base
point (Figure 5). This can be clicked or entered manually. The object(s) will be rotated about the base point.
3
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Figure 5 - Rotate: Specify Base Point
The next step is to set the rotation angle (Figure 6). This can be set by moving the cursor until the object is at
the desired angle or by entering an angle manually by typing it in (in degrees) and then hitting the Enter key.
Unless rotating an object for aesthetic reasons, it is generally a good idea to enter rotation angles manually to
ensure that they are correct.
Figure 6 - Rotate: Specify Rotation Angle
Once the angle is selected, the object(s) will be rotated (Figure 7).
Figure 7 - A Rotated Object
4
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Offsetting
When you need to create an object similar to an existing object, but translated a fixed distance away, the Offset
command can be used. To offset an object, select Offset in the Modify pane of the Home tab (Figure 8).
Figure 8 - Offset
Unlike moving and copying, selecting objects is not the first step in offsetting. AutoCAD will first prompt for an
offset distance (Figure 9). This is the distance the object will be moved when copied. Enter the distance using
the number keys and press Enter when done.
Figure 9 - Offset: Setting the Distance
Now AutoCAD will prompt to select the objects to offset. Only one object at a time can be selected (Figure 10).
Figure 10 - Offset: Selecting Objects
5
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Once selected, AutoCAD will prompt for a point on the side to offset to (Figure 11). This does not need to be a
precise point, just click on the side you want the new object to appear (this distance set during the first step will
be used, AutoCAD just needs to know which way to offset).
Figure 11 - Offset: Picking a Side
The object will be offset (Figure 12), and AutoCAD will prompt for another object to offset. The original distance
will be used for any additional offsets. To cancel the Offset command, press the Esc key.
Figure 12 - An Offset Line
Mirroring
To copy or move objects by mirroring them about a line, use the Mirror command. The Mirror feature is started
by clicking the Mirror button in the Modify pane of the Home tab (Figure 13).
Figure 13 - Mirror
6
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Like moving objects, the first step to mirroring objects is to select them. Once selected, AutoCAD will prompt for
the first point of the mirror line (Figure 14). This is the line the objects will be mirrored across (it defines the
plane of the mirror). This point can be entered manually or selected with a click.
Figure 14 - Mirror: First Mirror Line Point
AutoCAD will then prompt for the second point of the mirror line (Figure 15). Once again, this can be entered
manually or simply clicked.
Figure 15 - Mirror: Second Mirror Line Point
Now AutoCAD will prompt on whether or not to erase the source object. If you type Y, the originally selected
objects will be deleted. If you type N, the original objects will be kept and new objects created that mirror the
original ones (Figure 16).
Figure 16 - A Mirrored Object
7
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Copying
Copying works similarly to moving but leaves the original object(s) intact. To activate the Copy feature, click the
Copy button in the Modify pane of the Home tab (Figure 17).
Figure 17 - Copy
Like with moving objects, the first step is to select the object(s) to copy. Once objects are selected, a base point
must be selected (Figure 18).
Figure 18 - Copy: Specifying the Base Point
Once a base point is selected, a second point must be selected. This second point will be used like in the Move
feature (Figure 19). However, unlike Move, AutoCAD will prompt for more points after copying the object. This
allows you to quickly make several copies of the originally selected objects (Figure 20).
8
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Figure 19 - Copy: Specifying the Second Point
Figure 20 - Multiple Copies
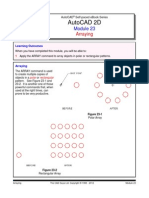
Arraying
If you need to make several copies of an object that are translated or rotated at fixed increments, you can use
the Array feature. Start the Array feature by clicking the Array button in the Modify pane of the Home tab
(Figure 21).
Figure 21 - Array
9
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Clicking the Array button will open the Array dialog (Figure 22). This dialog lets you specify the kind of array to
be made (rectangular or polar) along with the specific properties of the array. Experiment with the row and
column options and watch how the sample window changes. To change the distance rows and columns are
offset, enter numbers in the Row offset and Column offset text boxes. You can also select the Pick Row Offset
and Pick Column Offset buttons to change these distances. If used, the Pick buttons will let you select two
points, an origin and a destination, based on objects currently drawn. Change the dialog to Polar array if you
need to array objects circularly about a point (Figure 23).
Figure 22 - Array Dialog (Rectangular)
Figure 23 - Array Dialog (Polar)
10
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Before you can complete the Array, you must select the objects to be arrayed. To do this, click the Select
objects button. This will let you select the objects to be arrayed in a similar manner to the Move and Copy
features. Once selected, the Array dialog will reappear. Once the parameters are entered as necessary, click OK
to complete the Array (Figure 24).
Figure 24 - A Polar Array
Chamfer/Fillet
Chamfers and Fillets are used to break sharp corners. A chamfer breaks the corner with a straight line segment.
A fillet breaks the corner with a circular arc (Figure 25).
Figure 25 - Chamfer and Fillet
To chamfer a corner, select the Chamfer button in the Modify pane of the Home tab (Figure 26).
11
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Figure 26 - Chamfer
AutoCAD will immediately prompt for the objects to chamfer. Unless you have previously set chamfer distances,
you must set them now. To set the chamfer distances, type distance and press the Enter key (Figure 27).
Figure 27 - Chamfer: Setting the Distance
AutoCAD will now prompt for the first chamfer distance (look towards the bottom of the screen in the big text
box). Type this distance in and press the Enter key. AutoCAD will them prompt for the second distance, type
this in as well and press Enter. For a visual representation of what these distances mean, see Figure 26. Once
the distances are entered, you will need to select the two objects to chamfer in order (Figure 28 and Figure 29).
12
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Figure 28 - Chamfer: Picking the First Line
Figure 29 - Chamfer: Picking the Second Line
Once the two items are selected, the chamfer will be applied (Figure 30).
Figure 30 - Finished Chamfer
To create a fillet, click the Fillet button in the Modify pane of the Home tab (Figure 31).
13
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Figure 31 - Fillet
Like with Chamfer, Fillet requires you enter the operation parameters (in this case the fillet radius) before you
select the objects. To enter the radius, type radius then press Enter (Figure 32).
Figure 32 - Fillet: Setting the Radius
AutoCAD will then prompt for a radius for the chamfer. Type this number then press Enter (Figure 33).
Figure 33 Fillet: Entering the Radius
Like chamfer, two objects will need to be selected for the fillet. Once selected, the filet will be applied (Figure
34).
14
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Figure 34 - A Finished Fillet
Wrapping Up
You now have seen several of AutoCADs object editing features. These features can be used in conjunction
with the basic drawing features to create complex objects. Experiment with these features and complete the
following assignment.
15
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
IDE20 Software, AutoCAD 2D Lesson 2 Editing
Document URL: http://ide20.com/upload/ModuleAC/Lesson02.pdf
Developer: rhutch@mst.edu
Assignment
Create a drawing in AutoCAD that includes the following features (points are in parentheses):
A square rotated 30 degrees clockwise (1)
A triangle mirrored about a vertical line (1)
A square with all four sides offset to the outside (2)
A circle arrayed rectangularly with 2 columns and 4 rows (2)
A square polar arrayed around 360 degrees with 5 total copies (including the original) (2)
A square with a fillet and a chamfer (2)
An example is shown in Figure 35. Submit a .dwg file to the appropriate link under Assignments in Blackboard.
Figure 35 - Assignment Example
16
Copyright 2010, Missouri S&T
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- AutoCAD BasicsDokument66 SeitenAutoCAD BasicsketipakketipungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad PDFDokument35 SeitenAutocad PDFHarsh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compelling 3D Features in AutoCAD HandoutDokument44 SeitenCompelling 3D Features in AutoCAD Handoutincaurco0% (1)
- CAD Modeling Lab AssignmentsDokument19 SeitenCAD Modeling Lab AssignmentsSaibabu SoloNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUTOCADDokument30 SeitenAUTOCADajay1119867% (3)
- SynthesisDokument51 SeitenSynthesissudhir100% (1)
- Autocad 2d Module 23 PDFDokument0 SeitenAutocad 2d Module 23 PDFRam LamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D AutoCADDokument264 Seiten3D AutoCADMario Rodriguez LujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tools For 2d Digital ModellingDokument45 SeitenTools For 2d Digital ModellingNaGamani KanDanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutoCAD in 3DDokument6 SeitenAutoCAD in 3DMustafa AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutoCAD 2D Advanced Sample Modules - The CAD GuysDokument56 SeitenAutoCAD 2D Advanced Sample Modules - The CAD Guysmrb88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Triconex DocumentDokument51 SeitenTriconex DocumentsendutdutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Fundamentals SolutionsDokument14 SeitenNetworking Fundamentals SolutionsEVAN MARSHALLNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIM For SAP Solutions 20.4 Installation Guide English VIM200400 IGD en 09 PDFDokument266 SeitenVIM For SAP Solutions 20.4 Installation Guide English VIM200400 IGD en 09 PDFyoeesefNoch keine Bewertungen
- XM The ISO 27000 Family of Standards 230516Dokument1 SeiteXM The ISO 27000 Family of Standards 230516kenyrNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICRCheck PrixaDokument3 SeitenMICRCheck PrixaOliver JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Ebook PDF) AutoCAD 2002 2D TutorialDokument25 Seiten(Ebook PDF) AutoCAD 2002 2D TutorialKayemba Ismael0% (1)
- Autocad 2D: Lesson 2 - EditingDokument16 SeitenAutocad 2D: Lesson 2 - EditingCarmen PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad 2D: Lesson 1 - Getting StartedDokument11 SeitenAutocad 2D: Lesson 1 - Getting StartedJaydipPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NX 7.5 TutorialDokument19 SeitenNX 7.5 TutorialSumeet Gawade100% (1)
- Brilliant Computer Education 2D Manual: AutocadDokument38 SeitenBrilliant Computer Education 2D Manual: AutocadGudapati PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutoCAD 3D Interface and ModelingDokument50 SeitenAutoCAD 3D Interface and ModelinghazemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 1: AutocadDokument30 SeitenChapter - 1: AutocadRaghava VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CATIA V5: Jntuh College of Enginering ManthaniDokument43 SeitenIntroduction To CATIA V5: Jntuh College of Enginering ManthaniarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To 3d Drawing UpdatedDokument29 SeitenIntroduction To 3d Drawing UpdatedSidrak MekuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D CADD Module1Dokument17 Seiten3D CADD Module1Domingo Brioso Gamis IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To AutoCADDokument11 SeitenIntroduction To AutoCADJiji MacasoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rohit - My ReportDokument22 SeitenRohit - My ReportNavneet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anurag Group of Institutions Autonomous Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument4 SeitenAnurag Group of Institutions Autonomous Department of Mechanical EngineeringKanukula Raghu ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CadDokument76 SeitenCadHassan XoghayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cad-Cam Lab Manual 2022-23manualDokument63 SeitenCad-Cam Lab Manual 2022-23manualMvk MvkNoch keine Bewertungen
- CADDDokument66 SeitenCADDusiaf007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad 2d NotesDokument33 SeitenAutocad 2d NotesGudapati PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad 2016: Second StageDokument9 SeitenAutocad 2016: Second StageIbrahim DewaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brief Abstract.: Week Two: Auto Cad. Technologist'S Name: MR - KeterDokument6 SeitenBrief Abstract.: Week Two: Auto Cad. Technologist'S Name: MR - Ketervincent rotichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad: Submitted by Subumitted TO Aman Rana 173200023Dokument17 SeitenAutocad: Submitted by Subumitted TO Aman Rana 173200023AMAN SHARMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sakshi Ahire (Inplant Traning)Dokument26 SeitenSakshi Ahire (Inplant Traning)Tejas DeoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- CEE 317 GeoSurveying Homework Contour MapDokument5 SeitenCEE 317 GeoSurveying Homework Contour MapRamiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD-CAM LAB MANUAL 2021-22manualDokument59 SeitenCAD-CAM LAB MANUAL 2021-22manualShashankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CATIA V5: Release 16 (A Hands-On Tutorial Approach)Dokument33 SeitenIntroduction To CATIA V5: Release 16 (A Hands-On Tutorial Approach)Vinoth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation ON: AUTOCAD 2015Dokument23 SeitenPresentation ON: AUTOCAD 2015Sahil Bhati0% (1)
- BSC Information TechnologyDokument9 SeitenBSC Information TechnologyLukasi DeoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD Week 11 17 With 3D ACTIVITIESDokument18 SeitenCAD Week 11 17 With 3D ACTIVITIESDylan AngelesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDD Student ManualDokument15 SeitenMDD Student ManualKaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating and Modifying Points in AutoCAD Civil 3DDokument5 SeitenCreating and Modifying Points in AutoCAD Civil 3Dskbansal1976Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module CAD IDokument39 SeitenModule CAD IKrisandi SaptyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autocad ReportDokument8 SeitenAutocad ReportAmni AishahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer-Aided Draftingwps OfficeDokument5 SeitenComputer-Aided Draftingwps OfficeMarvin Espenocilla EspeñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 5 A B CadmodelfeaturesDokument12 Seiten5 5 A B Cadmodelfeaturesapi-312626334Noch keine Bewertungen
- Secrets Revealed For Construction Simulation in Navisworks ManageDokument40 SeitenSecrets Revealed For Construction Simulation in Navisworks ManageGláuber LucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On AutocadDokument35 SeitenProject Report On AutocadKamaljeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Cad 2 D Fundamentals Tutor I A FFLDokument25 SeitenA Cad 2 D Fundamentals Tutor I A FFLvrrobyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation on Summer Training in AutoCADDokument74 SeitenPresentation on Summer Training in AutoCADAatish kumar0% (1)
- Autocad Project ReportDokument45 SeitenAutocad Project ReportSanjay RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating A Mesh in Autocad and Importing It Into Plate 'N' SheetDokument6 SeitenCreating A Mesh in Autocad and Importing It Into Plate 'N' Sheetnehal vaghelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto CadDokument5 SeitenAuto CadMelusi Ethan KaitanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Panasonic VRF User GuideDokument13 SeitenPanasonic VRF User GuidePriesilia PresleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented By:-Rahul SainiDokument18 SeitenPresented By:-Rahul SainiashishNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01102014Dokument3 Seiten01102014JaydipPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech Gate 2014 Session 4Dokument22 SeitenMech Gate 2014 Session 4Rahul SoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- MITRES 18 001 Strang TableseqDokument4 SeitenMITRES 18 001 Strang TableseqSarandos KlikizosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01102014candidates ListDokument2 Seiten01102014candidates ListJaydipPatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cmat Test PatternDokument1 SeiteCmat Test PatternKiran VadegharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentacion Arturo CalleDokument43 SeitenPresentacion Arturo CalleNavarro JissellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Huawei Command Line CheckDokument2 SeitenFrom Huawei Command Line CheckHussein DhafanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 504C - Microprocessor & Microcontroller: Short Answer Type QuestionsDokument2 SeitenEE 504C - Microprocessor & Microcontroller: Short Answer Type QuestionsSoham JanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S2212017312004604 MainDokument9 Seiten1 s2.0 S2212017312004604 MainTHAPELO PROSPERNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introducing the Vertica Analytic Database - Query Data 214x Faster on 90% Less HardwareDokument10 SeitenIntroducing the Vertica Analytic Database - Query Data 214x Faster on 90% Less HardwareRamprasadh KottapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Text DBMSDokument1 SeiteText DBMSvishnugehlotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5: Information Representation Method-HTML-I SolutionsDokument15 SeitenChapter 5: Information Representation Method-HTML-I SolutionsAman Singh75% (4)
- 2016-Db-Marcin Przepiorowski-Rman - From Beginner To Advanced-PraesentationDokument65 Seiten2016-Db-Marcin Przepiorowski-Rman - From Beginner To Advanced-PraesentationTruong Vu VanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Playlist ObserverDokument43 SeitenPlaylist ObserverJavier Gonzalez100% (1)
- Research Areas and Topics at INSTITUTIONDokument7 SeitenResearch Areas and Topics at INSTITUTIONKaushal PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cvi Upgrade Check ResolveDokument10 SeitenCvi Upgrade Check ResolvesyedshoebhussainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSBI Training in HyderabadDokument18 SeitenMSBI Training in HyderabadKosmikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Create 3d Printing Website To Make MoneyDokument13 SeitenCreate 3d Printing Website To Make MoneyIvan DerežićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Downloads for WebMatrix SitesDokument6 SeitenTop Downloads for WebMatrix SitesAarti OstwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- User's Guide For TV Board V59Dokument23 SeitenUser's Guide For TV Board V59chackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universal Control 3.4.1 Milestone Release Notes: Version InformationDokument2 SeitenUniversal Control 3.4.1 Milestone Release Notes: Version Informationfaleminderit31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Et200s 2ao U ST Manual en-USDokument22 SeitenEt200s 2ao U ST Manual en-USsurendra n patelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructions For Authors of SBC Conferences Papers and AbstractsDokument4 SeitenInstructions For Authors of SBC Conferences Papers and AbstractsWill MakenzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Error Messages Technology Template SiemensDokument50 SeitenError Messages Technology Template SiemensMoumene Djafer BeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 PDFDokument3 Seiten1 PDFAnurag KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manuel S. Enverga University Foundation: Granted Autonomous StatusDokument4 SeitenManuel S. Enverga University Foundation: Granted Autonomous StatusRonaldo MaañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RealLAB2 ManualDokument5 SeitenRealLAB2 ManualDiscord GrindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurowerk EEG23Dokument4 SeitenNeurowerk EEG23hassan MOHACHINoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Software Reverse Engineering With Ghidra Session 1Dokument58 SeitenIntroduction To Software Reverse Engineering With Ghidra Session 1Chancemille RemoNoch keine Bewertungen