Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
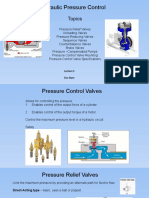
Operating Pressure: The Gauge Pressure During Normal
Hochgeladen von
jokish0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten3 SeitenRelief systems with high pressure trips and pressure safety valves or rupture discs are installed to safely handle hydrocarbons. Pressure safety valves are installed at all potentially hazardous points to prevent pressure from exceeding maximum allowable working pressure. High pressure can develop from overheating, high head pressure, overfilling, regulator failure, external fires, runaway reactions, combustion, freezing, or thermal expansion. Key terms include operating pressure, set pressure, maximum allowable working pressure, accumulation, overpressure, blow-down, and back pressure.
Originalbeschreibung:
Relief Systems Intro
Originaltitel
Relief Systems Intro
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenRelief systems with high pressure trips and pressure safety valves or rupture discs are installed to safely handle hydrocarbons. Pressure safety valves are installed at all potentially hazardous points to prevent pressure from exceeding maximum allowable working pressure. High pressure can develop from overheating, high head pressure, overfilling, regulator failure, external fires, runaway reactions, combustion, freezing, or thermal expansion. Key terms include operating pressure, set pressure, maximum allowable working pressure, accumulation, overpressure, blow-down, and back pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten3 SeitenOperating Pressure: The Gauge Pressure During Normal
Hochgeladen von
jokishRelief systems with high pressure trips and pressure safety valves or rupture discs are installed to safely handle hydrocarbons. Pressure safety valves are installed at all potentially hazardous points to prevent pressure from exceeding maximum allowable working pressure. High pressure can develop from overheating, high head pressure, overfilling, regulator failure, external fires, runaway reactions, combustion, freezing, or thermal expansion. Key terms include operating pressure, set pressure, maximum allowable working pressure, accumulation, overpressure, blow-down, and back pressure.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
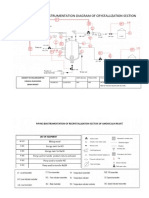
Relief systems are provided on a platform in order to ensure
the safe operation of the facilities.
In accordance with API RP 14C, all hydrocarbons handling
equipment and pressure vessels will be provided with two
levels of over protection, high pressure trip (PSHH) with
shutdown action, and protection by mechanical devices,
Pressure Safety Valve (PSV) or Rupture Disc.
PSVs are installed at every point identified as potentially
hazardous, that is, at points where upset conditions create
pressure which may exceed the maximum
allowable
working pressure.
How High Pressure Develop
Over heating
High head ( from pumping or compression)
Over Filling
Failure of Regulator / Control valve.
External Fire
Runaway Reaction
Combustion of gas/dust
Freezing
Thermal Expansion
Loss of Mixing
Others
Definitions
Operating pressure : The gauge pressure during normal
service.
Set Pressure : The pressure at which the relief device begins
to activate or open.
Maximum Allowable Working Pressure (MAWP) : The
maximum guage pressure permissible at the top of a vessel
for a designated temperature.
Vessel fails at 4 to 5 times of MAWP!!!! . But only hydrostatically
tested to 1.5 times.
Accumulation : The pressure increase over the maximum
allowable working pressure of a vessel during the relief
process. Expressed as % of MAWP.
Over Pressure : The pressure increase in vessel over the set
pressure during the relieving process. Overpressure is equivalent
to the accumulation when the set pressure is at the MAWP.
Expressed as % of set pressure. Must be specified prior relief
design. Typically 10 % ( or for fire 21%) will be used.
Blow-down : The pressure difference between the relief set
pressure and the relief reseating pressure.
Maximum Allowable Accumulated Pressure : The sum of the
maximum allowable working pressure plus the allowable
accumulation.
Back Pressure : The pressure at the outlet of the relief
device during the relief process due to pressure in the
discharge system.
1. Superimposed Back Pressure.
2. Built-up Back Pressure.
Total Back Pressure = Superimposed Back Pressure + Built-up
Back Pressure
1. Superimposed Back Pressure is the back pressure which may
exist at the outlet of a particular relief valve when connected
to a closed system. The pressure can be constant or
variable. The Superimposed back pressure always exists
even when the reliefvalve is closed.
2. Built-up Back Pressure is the pressure at the discharge of a
relief device which develops due to the relief flow through
the device when the relief valve opens. The built-up back
pressuredepends on the valve itself but also on the design of
the relief piping. It can reach excessive values in the case of
vary high set pressures and/or poorly designed piping with
too much pressure Loss. The built-up back pressure is
variable.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Employee Handbook 2013Dokument50 SeitenEmployee Handbook 2013Sergio Artinano100% (1)
- CARPROG Toyota Immo Manual PDFDokument13 SeitenCARPROG Toyota Immo Manual PDFTiberiu Si Alina TimocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Typical Overall Heat-Transfer CoefficientsDokument2 SeitenTypical Overall Heat-Transfer CoefficientsjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure ReliefDokument207 SeitenPressure ReliefAH100% (1)
- Battery Storage Systems EnergyDokument9 SeitenBattery Storage Systems EnergyGunturNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Relief SystemsDokument30 SeitenPressure Relief SystemsBibek MerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogo Kunkle ValveDokument32 SeitenCatalogo Kunkle ValveKelvyn RochaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Safety Valve FundamentalsDokument21 SeitenPressure Safety Valve Fundamentalsaop10468100% (2)
- Lecture 5 Hydraulic PressureDokument47 SeitenLecture 5 Hydraulic PressureSAMUEL MAKATANENoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Design Guideline Separator Vessel Rev01Dokument45 SeitenEngineering Design Guideline Separator Vessel Rev01gad480Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of The LFL and UFL of MixturesDokument1 SeiteCalculation of The LFL and UFL of MixturesjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines On DP, Op, Mop, Maop, Mawp, PSV SetpointsDokument3 SeitenGuidelines On DP, Op, Mop, Maop, Mawp, PSV Setpointsankur2061100% (1)
- API 576 Study NotesDokument5 SeitenAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesDokument27 SeitenProcedure For Inspection Recalibration and Testing of Pressure Safety ValvesNwokedi Okezie86% (7)
- Reciprocating Compressors:: Operation and MaintenanceVon EverandReciprocating Compressors:: Operation and MaintenanceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (7)
- Relief ValvesDokument59 SeitenRelief ValvesAli Naveed Farooki100% (2)
- Relief ValveDokument56 SeitenRelief ValveVYSAKH R NAIRNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGVon EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringVon EverandBatch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relief Valves and Relief SystemsDokument10 SeitenRelief Valves and Relief Systemsmatteo2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spence - 6 - Safety Relief Valve Sizing - 2nd Edition PDFDokument24 SeitenSpence - 6 - Safety Relief Valve Sizing - 2nd Edition PDFJorge DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- API-520 (Key Notes)Dokument5 SeitenAPI-520 (Key Notes)nns_12100% (1)
- Preliminary Heat Exchanger Design ExampleDokument4 SeitenPreliminary Heat Exchanger Design ExamplejokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7022H 400 MS 0000 828 RCDokument18 Seiten7022H 400 MS 0000 828 RCA.A100% (1)
- PSV Data BookDokument16 SeitenPSV Data Bookkenoly123Noch keine Bewertungen
- PSVDokument38 SeitenPSVSajid Raza100% (1)
- Types of Pressure Relief ValvesDokument22 SeitenTypes of Pressure Relief ValvesFaraz MichNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSV Sizing ManualDokument10 SeitenPSV Sizing ManualAkshay bhuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationsDokument104 SeitenPlant Safety and Pressure Relieving OperationskglorstadNoch keine Bewertungen
- P&IDDokument7 SeitenP&IDTagabo AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSV by MSAG-Teguh PDFDokument50 SeitenPSV by MSAG-Teguh PDFAlfian AdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryVon EverandPrevention of Actuator Emissions in the Oil and Gas IndustryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study and Testing of PRVDokument4 SeitenStudy and Testing of PRVBhargava S PadmashaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 576 Study NotesDokument5 SeitenAPI 576 Study NotesabdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSVDokument101 SeitenPSVEngr Adeel Ahmed AbbasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831Dokument32 SeitenPressure Safety Design Practices For Refinery and Chemical Operations 831JO100% (1)
- Security in IoT - Syllabus (FINAL)Dokument1 SeiteSecurity in IoT - Syllabus (FINAL)Jay Mehta100% (1)
- ANEP-26 (Ergonomic Data For Surface Ships)Dokument63 SeitenANEP-26 (Ergonomic Data For Surface Ships)Bahadır Harmancı100% (1)
- An Overview of Pressure Relief DevicesDokument36 SeitenAn Overview of Pressure Relief DevicesAkash Palkar100% (1)
- Pressure Safety ValvesDokument15 SeitenPressure Safety Valvesh_abdullah100% (2)
- PSVDokument13 SeitenPSVUMESH GORE100% (1)
- Contemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsVon EverandContemporary Anaesthetic Equipments.: An Aid for Healthcare ProfessionalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Valves and Relief Valves.Dokument17 SeitenSafety Valves and Relief Valves.Shikhar SwaroopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Take Home From Our Facility PSV SizingDokument18 SeitenTake Home From Our Facility PSV SizingConnor SailorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relief ConceptsDokument9 SeitenRelief ConceptsDeepak ThapliyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9-1Dokument33 SeitenChapter 9-1Priyam PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - PSV by MukharjeeDokument3 SeitenNotes - PSV by MukharjeeWade ColemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas CarriersDokument17 SeitenGuidelines On The Maintenance of Pressure Relief Valves On Board Gas Carriers123habib123fikriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure VesselsDokument19 SeitenPressure Vesselseng20072007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relief Design SizingDokument9 SeitenRelief Design SizingDark KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- W22 Ch09 ReliefIntro ChE6570Dokument95 SeitenW22 Ch09 ReliefIntro ChE6570iamayesha725Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pages From Selection and Sizing of Pressure Relief ValvesDokument1 SeitePages From Selection and Sizing of Pressure Relief Valveszohaib_farooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- HighBeam Research Article APR 13 2016Dokument14 SeitenHighBeam Research Article APR 13 2016Sílvio MonteiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of PSV and Incident When A PSV Could Not OpenDokument3 SeitenTypes of PSV and Incident When A PSV Could Not Opennafees ahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backup of TbankstartupDokument5 SeitenBackup of TbankstartupHoàngViệtAnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parsing Pressure and Temperature RatingsDokument6 SeitenParsing Pressure and Temperature RatingsAhmed AbdullaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTTP WWW Red Bag Com Engineering Guides 582 BN Eg k4 Standard Method For Safety Relief Valve Calculations HTMLDokument9 SeitenHTTP WWW Red Bag Com Engineering Guides 582 BN Eg k4 Standard Method For Safety Relief Valve Calculations HTMLmashudi_fikriNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHP2 Operating Manual PDF299201645659Dokument9 SeitenAHP2 Operating Manual PDF299201645659MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Category: Process Control Question: How Does A Pressure Regulator Work? AnswerDokument1 SeiteCategory: Process Control Question: How Does A Pressure Regulator Work? AnswerAnonymous VWlCr439Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-IDokument16 SeitenPressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3-Isabi_shiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bypass Control Valve: Special Features and ControlsDokument13 SeitenBypass Control Valve: Special Features and ControlsBrain J PérezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch9 ReliefsDokument41 SeitenCh9 ReliefsMohammed JanahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrevitestingDokument23 SeitenTrevitestingworkedoutagainNoch keine Bewertungen
- API STD 521-Control Valve FailureDokument1 SeiteAPI STD 521-Control Valve Failuremuhammad_asim_10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualDokument0 SeitenTechnical Seminar Manual: Anderson Greenwood Crosby - Technicalseminar ManualgshdavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3Dokument16 SeitenPressure Safety Relief Valves Pressure Safety Relief Valves: Technical Bulletin 3 Technical Bulletin 3PravinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacity Correction Factors: Back PressureDokument2 SeitenCapacity Correction Factors: Back PressureSusheel WankhedeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitVon EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SVon EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bound Moisture. This Is Water Retained So That It Exerts A Vapour Pressure Less Than ThatDokument1 SeiteBound Moisture. This Is Water Retained So That It Exerts A Vapour Pressure Less Than ThatjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bound Moisture. This Is Water Retained So That It Exerts A Vapour Pressure Less Than ThatDokument1 SeiteBound Moisture. This Is Water Retained So That It Exerts A Vapour Pressure Less Than ThatjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- How A Steam Jet EjectorDokument1 SeiteHow A Steam Jet EjectorjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Plant Layout Part 1Dokument1 SeiteNotes On Plant Layout Part 1jokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is CommissioningDokument1 SeiteWhat Is CommissioningjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConductanceDokument1 SeiteConductancejokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Do Sundarkand Path & BenifitsDokument1 SeiteHow To Do Sundarkand Path & BenifitsjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impeller TypesDokument1 SeiteImpeller TypesjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineering ReferenceDokument2 SeitenChemical Engineering Referencejokish0% (1)
- Humid PDFDokument4 SeitenHumid PDFFrank MtetwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems and ProcessesDokument2 SeitenSystems and ProcessesjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow and Capacity CalculationsDokument1 SeiteFlow and Capacity CalculationsjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems Review: Systems Are Defined As A Set of Interacting or Interdependent Equipment and ProcessDokument2 SeitenSystems Review: Systems Are Defined As A Set of Interacting or Interdependent Equipment and ProcessjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Use of Simulated Process ModelDokument2 SeitenUse of Simulated Process ModeljokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEPARATOR Design ConsiderationsDokument1 SeiteSEPARATOR Design ConsiderationsjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Mechanical Draft CoolersDokument1 SeiteIntro To Mechanical Draft CoolersjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Modelling and SimulationDokument2 SeitenDefinition of Modelling and Simulationjokish100% (1)
- NPSHADokument5 SeitenNPSHAjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separators: Introduction: 2-Phase Separators 3-Phase SeparatorsDokument1 SeiteSeparators: Introduction: 2-Phase Separators 3-Phase SeparatorsjokishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Image Steganography in LSB: Presented By: Ritu Agarwal 9910103516Dokument17 SeitenImage Steganography in LSB: Presented By: Ritu Agarwal 9910103516MoniNoch keine Bewertungen
- LNT CallDokument1 SeiteLNT CallPraveen MalineniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Norges Sildesalgslag - MackerelDokument2 SeitenNorges Sildesalgslag - MackerelGiuseppe G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yoshi - Level 50 - BoshiDokument6 SeitenYoshi - Level 50 - Boshisomethin9Noch keine Bewertungen
- Medallion Signature Guarantee Considerations and AlternativesDokument16 SeitenMedallion Signature Guarantee Considerations and AlternativesKevin WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projects & Operations: IN: NE Power Systm ImprvmDokument4 SeitenProjects & Operations: IN: NE Power Systm ImprvmGaurang PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Farzana DomicileDokument1 SeiteFarzana DomicileNil OnlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- F5 Steganographic Algorithm-KarthikDokument22 SeitenF5 Steganographic Algorithm-KarthikAhmedShehzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIS AssignmentDokument3 SeitenCIS AssignmentDaniela OrdonezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab #6: Assessment Worksheet Develop A Risk Mitigation Plan Outline For An IT InfrastructureDokument3 SeitenLab #6: Assessment Worksheet Develop A Risk Mitigation Plan Outline For An IT InfrastructureCông ĐạiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CLRP User Account Registration From LraDokument1 SeiteCLRP User Account Registration From LraAngela I.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Create A Mysql Database Using Mysqli and PdoDokument19 SeitenCreate A Mysql Database Using Mysqli and PdoNaveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of IotDokument11 SeitenFoundations of IotSahul Kumar ParidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smarter London Together v1.66 - Published PDFDokument60 SeitenSmarter London Together v1.66 - Published PDFHuynh Bao Minh LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 New Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Vectors (100 in Total)Dokument5 Seiten50 New Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Vectors (100 in Total)Watasow11Noch keine Bewertungen
- ISA-WWID Newsletter 2019spring-SummerDokument14 SeitenISA-WWID Newsletter 2019spring-SummerBo Cu BinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crypto Currency Short PresentationDokument15 SeitenCrypto Currency Short PresentationShekhar VaidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1a - Mediant 1000 MSBG DatasheetDokument2 Seiten1a - Mediant 1000 MSBG DatasheetJuanpa ReinhardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybris Create Components Via IMPEX FilesDokument11 SeitenHybris Create Components Via IMPEX FilesAlex100% (1)
- MTL Product OverviewDokument56 SeitenMTL Product OverviewAries dNoch keine Bewertungen
- Policy 824 Body Worn Camera Pilot FINALDokument8 SeitenPolicy 824 Body Worn Camera Pilot FINALFOX45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management Roles and ResponsibilitiesDokument2 SeitenRisk Management Roles and ResponsibilitiesOmnia HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CookiesDokument59 SeitenCookiesapl_gajera1977Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 1 ITT593Dokument56 SeitenCH 1 ITT593Ain AnuarNoch keine Bewertungen