Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question Papers
Hochgeladen von
Buddhisagar BastolaOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question Papers
Hochgeladen von
Buddhisagar BastolaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
APPLIED MECHANICS CIVIL I/II...
@UTEC
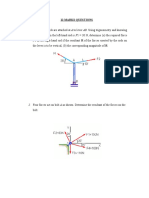
1. A 70-kg cylinder is supported by two cables AC and BC, which are attached to the top of vertical posts. A horizontal
force P, perpendicular to the plane containing the posts, holds the cylinder in the position shown. Draw the free-body
diagram needed to determine the magnitude of P and the force in each cable.
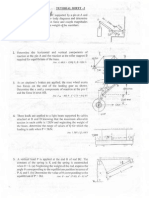
2. A rectangular plate is supported by three cables as shown. Knowing that the tension in cable AC is 60 N, determine the
weight of the plate.
3. Four forces act on a 700 3 375-mm plate as shown. ( a ) Find the resultant of these forces. ( b ) Locate the two points
where the line of action of the resultant intersects the edge of the plate.
4. A 10-ft boom is acted upon by the 840-lb force shown. Determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at the balland-socket joint at A.
5. The 6-m pole ABC is acted upon by a 455-N force as shown. The pole is held by a ball-and-socket joint at A and by two
cables BD and BE. For a = 3 m, determine the tension in each cable and the reaction at A.
6. Neglecting friction and the radius of the pulley, determine (a) the tension in cable ADB, (b) the reaction at C.
7. Determine by direct integration the centroid of the area shown. Express your answer in terms of a and b.
8. Determine the moment of inertia and the radius of gyration of the shaded area with respect to the x axis.
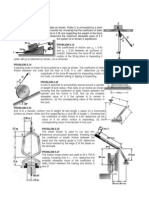
9. The coefficients of friction are s =0.40 and k =0.30 between all surfaces of contact. Determine the smallest force P
required to start the 30-kg block moving if cable AB (a) is attached as shown, (b) is removed.
10. Two slender rods of negligible weight are pin-connected at C and attached to blocks A and B, each of weight W.
Knowing that =80 and that the coefficient of static friction between the blocks and the horizontal surface is 0.30,
determine the largest value of P for which equilibrium is maintained.
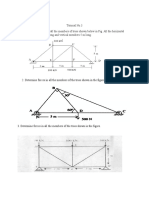
11. Determine the force in each member of the Pratt roof truss shown. State whether each member is in tension or
compression.
12. Determine the force in each member of the truss shown.
13. The position of a particle which moves along a straight line is defined by the relation x = t - 6t -15t +40, where x is
expressed in feet and t in seconds. Determine (a) the time at which the velocity will be zero, (b) the position and distance
traveled by the particle at that time, (c) the acceleration of the particle at that time, (d) the distance traveled by the particle
from t = 4 s to t = 6 s.
14. The motion of a particle is defined by the relation x = 6t - 8 + 40cos t, where x and t are expressed in inches and
seconds, respectively. Determine the position, the velocity, and the acceleration when t = 6 s.
15. A basketball player shoots when she is 16 ft from the backboard. Knowing that the ball has an initial velocity v0 at an
angle of 30 with the horizontal, determine the value of v0 when d is equal to 9 in.
16. Determine the required velocity of the belt B if the relative velocity with which the sand hits belt B is to be (a) vertical,
(b) as small as possible.
17. The two blocks shown are originally at rest. Neglecting the masses of the pulleys and the effect of friction in the
pulleys and assuming that the coefficients of friction between block A and the horizontal surface are s = 0.25 and k
=0.20, determine (a) the acceleration of each block, (b) the tension in the cable.
18. The two blocks shown start from rest. The horizontal plane and the pulley are frictionless, and the pulley is assumed to
be of negligible mass. Determine the acceleration of each block and the tension in each cord.
19. A 30-kg block is dropped from a height of 2 m onto the 10-kg pan of a spring scale. Assuming the impact to be
perfectly plastic, determine the maximum deflection of the pan. The constant of the spring is k = 20 kN/m.
20. The coefficient of restitution between the two collars is known to be 0.80. Determine (a) their velocities after impact,
(b) the energy loss during impact.
21. The thin plate ABCD of mass 8 kg is held in the position shown by the wire BH and two links AE and DF. Neglecting
the mass of the links, determine immediately after wire BH has been cut (a) the acceleration of the plate, (b) the force in
each link.
22. A pulley weighing 12 lb and having a radius of gyration of 8 in. is connected to two blocks as shown. Assuming no
axle friction, determine the angular acceleration of the pulley and the acceleration of each block.
25. A package is projected 10 m up a 15 incline so that it just reaches the top of the incline with zero velocity. Knowing
that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the package and the incline is 0.12, determine (a) the initial velocity of the
package at A, (b) the velocity of the package as it returns to its original position.
23. Draw SFD and BMD. Point out the salient features on the diagrams.
60KN/m
10 KN/m
20KN
30KN
2m
2m
6m
2m
24. Draw SFD and BMD. Point out the salient features on the diagrams.
20KN/m
50KNm
10 KN/m
15KN
2m
1m
3m
2m
0.5 m
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 12 MarksDokument23 Seiten12 Markslakshmigsr6610Noch keine Bewertungen
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Dokument8 SeitenE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Sheet2 PDFDokument15 SeitenQuestion Sheet2 PDFSaumyak RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 7 10Dokument9 SeitenHomework 7 10Engr Ghulam MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorials 1 5Dokument7 SeitenTutorials 1 5faizankhan260690Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 MOSDokument47 SeitenAssignment 1 MOSGaurav RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 3Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 3piyush kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrussDokument5 SeitenTrussChaubey AjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenAssignment 1mohityaav0% (1)
- Question Bank & Bit BankDokument20 SeitenQuestion Bank & Bit BankKomma HemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics LongDokument5 SeitenMechanics Longsivaraju8Noch keine Bewertungen
- System of CoPlanar Forces Notes Engineering MechanicsDokument7 SeitenSystem of CoPlanar Forces Notes Engineering MechanicsKiran BeldarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Errata Pages For StaticsDokument10 SeitenErrata Pages For StaticsRenrenBassigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics (17CA03302) : Lecture NotesDokument74 SeitenEngineering Mechanics (17CA03302) : Lecture NotesBADINEHALSANDEEPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedDokument20 SeitenApplied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedYoukesh GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Problems Worked Out in ClassDokument5 SeitenEquilibrium of Rigid Bodies: Problems Worked Out in ClassAman GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics SPDokument67 SeitenStatics SPDianne VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-16 Planar Kinematics of A Rigid BodyDokument26 SeitenChapter-16 Planar Kinematics of A Rigid BodyhamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE201 Statics Chap5Dokument26 SeitenCE201 Statics Chap5zeromeansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 19Dokument36 SeitenLecture 19castles15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering MechanicsDokument37 SeitenEngineering Mechanicser_paramjeetgillNoch keine Bewertungen
- SRB DRBDokument44 SeitenSRB DRBAcads AccountNoch keine Bewertungen
- FrictionDokument20 SeitenFrictiondearsaswatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid MechanicsDokument19 SeitenSolid MechanicsManoj ManoharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particle Dynamics (QB)Dokument38 SeitenParticle Dynamics (QB)dymeowkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm1 B - SolutionsDokument4 SeitenMidterm1 B - SolutionsDamirAljosevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7: Velocity in Mechanisms: Toggle PressDokument10 SeitenChapter 7: Velocity in Mechanisms: Toggle PressGopal BhuniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument14 SeitenUntitledAlok KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resolution of ForceDokument5 SeitenResolution of ForcegyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mukavemet 9Dokument18 SeitenMukavemet 9Uğur DorukNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9P Equilibrium of RigidBodies 2D 2018Dokument25 Seiten9P Equilibrium of RigidBodies 2D 2018Ömer faruk SilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems FluidmechanicsDokument5 SeitenProblems Fluidmechanicsanon_182348362Noch keine Bewertungen
- Me 2560 Practice Problems Test I I I RecitationDokument3 SeitenMe 2560 Practice Problems Test I I I RecitationJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lame and Particle 2D 3D 1Dokument2 SeitenLame and Particle 2D 3D 1Syed ShaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 SolutionDokument9 SeitenAssignment 3 SolutionMurat BayrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of A ForceDokument5 SeitenMoment of A ForceA BarrettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Type of Forces, Newton's Third Law, Free Body DiagramDokument27 SeitenPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Type of Forces, Newton's Third Law, Free Body DiagramPriyanshu sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework No2Dokument3 SeitenHomework No2vitorctbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eg 231 Tutorial Sheet 1Q - 230118 - 105359Dokument19 SeitenEg 231 Tutorial Sheet 1Q - 230118 - 105359NINEBO MWEWANoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1. ProblemsDokument20 Seiten3.1. Problemssaumya irugalbandaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bedford Statics Practice ProblemsDokument6 SeitenBedford Statics Practice Problemsstats12Noch keine Bewertungen
- S1S1516 AssignmentDokument5 SeitenS1S1516 AssignmentHafizHumbleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFDokument7 SeitenTutorial 1 Rigid Bodies and FBD PDFBharat SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics TutorialDokument4 SeitenStatics TutorialAshley ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECH1230 Exam Paper v4 2013 2014 SolutionsDokument18 SeitenMECH1230 Exam Paper v4 2013 2014 SolutionssebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bs Experiment 1Dokument5 SeitenBs Experiment 1Hui Zhi100% (2)
- ASSIGNMENT 1 Essentials of Mechanical EngineeringDokument2 SeitenASSIGNMENT 1 Essentials of Mechanical EngineeringHari OmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seatwork No. 2Dokument3 SeitenSeatwork No. 2Glenford Rene Pabularcon0% (1)
- TR 334 Tutorial-1Dokument5 SeitenTR 334 Tutorial-1Adaminovic MrishoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank HTDokument12 SeitenQuestion Bank HTgreatrijuvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 0910 Spring Set2Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 0910 Spring Set2Sarp Yiğit ŞirinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil Iii Year 2017-2018Dokument109 SeitenCivil Iii Year 2017-2018Frank JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statics SheetDokument6 SeitenStatics SheetAhmad Ash SharkawiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction (MEC 107)Dokument2 SeitenFriction (MEC 107)Piyush JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics Tutorials 08 09Dokument14 SeitenMechanics Tutorials 08 09Yun RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 4Dokument4 SeitenTutorial 4Rajkamal NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Dokument9 SeitenAssignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Parth PawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Dokument4 SeitenInfant Jesus College of Engineering: PART A (10 X 2 20 Marks)Robinston Jeyasingh KNoch keine Bewertungen
- GNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Dokument3 SeitenGNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Stefano MazzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Dokument19 SeitenNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body - Yagyanath PoudelDokument39 SeitenBody - Yagyanath PoudelBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Pat Checklist 111Dokument6 SeitenSolar Pat Checklist 111Buddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportBody AKASHDokument33 SeitenReportBody AKASHBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.2.1 License # 16797TXAP7B5CCKDokument2 SeitenETABS 2016 Concrete Frame Design: ETABS 2016 16.2.1 License # 16797TXAP7B5CCKBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Statement: 2. ScopeDokument32 SeitenProblem Statement: 2. ScopeBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MahendraKumariBhusal@BodyDokument33 SeitenMahendraKumariBhusal@BodyBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shailaja Shrestha@BodyDokument32 SeitenShailaja Shrestha@BodyBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full Project ProposalDokument23 SeitenFull Project ProposalBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- My SlidesDokument41 SeitenMy SlidesBuddhisagar BastolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Three: Tools For Exploring The World: Physical, Perceptual, and Motor DevelopmentDokument43 SeitenChapter Three: Tools For Exploring The World: Physical, Perceptual, and Motor DevelopmentHsieh Yun JuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Will Smith BiographyDokument11 SeitenWill Smith Biographyjhonatan100% (1)
- Answer Key To World English 3 Workbook Reading and Crossword Puzzle ExercisesDokument3 SeitenAnswer Key To World English 3 Workbook Reading and Crossword Puzzle Exercisesjuanma2014375% (12)
- Tachycardia Algorithm 2021Dokument1 SeiteTachycardia Algorithm 2021Ravin DebieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes 3A - Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure 2019Dokument19 SeitenLecture Notes 3A - Basic Concepts of Crystal Structure 2019Lena BacaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 and 2Dokument4 SeitenUnit 1 and 2Aim Rubia100% (1)
- MECANISMOS de Metais de TransicaoDokument36 SeitenMECANISMOS de Metais de TransicaoJoão BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Freshers Jobs 26 Aug 2022Dokument15 SeitenFreshers Jobs 26 Aug 2022Manoj DhageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education: Income Generating ProjectDokument5 SeitenDepartment of Education: Income Generating ProjectMary Ann CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThaneDokument2 SeitenThaneAkansha KhaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitsubishi FanDokument2 SeitenMitsubishi FanKyaw ZawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teks Drama Malin KundangDokument8 SeitenTeks Drama Malin KundangUhuy ManiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revit 2023 Architecture FudamentalDokument52 SeitenRevit 2023 Architecture FudamentalTrung Kiên TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Technology Project Management: by Jack T. MarchewkaDokument44 SeitenInformation Technology Project Management: by Jack T. Marchewkadeeps0705Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Can Literary Spaces Support Neurodivergent Readers and WritersDokument2 SeitenHow Can Literary Spaces Support Neurodivergent Readers and WritersRenato Jr Bernadas Nasilo-anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ymrtc LogDokument26 SeitenYmrtc LogVinicius Silveira0% (1)
- A Junk Project - An Income Generating ProjectDokument2 SeitenA Junk Project - An Income Generating ProjectHercules Verdeflor ValenzuelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research On Export Trade in BangladeshDokument7 SeitenResearch On Export Trade in BangladeshFarjana AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hindi ShivpuranDokument40 SeitenHindi ShivpuranAbrar MojeebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Control 3G CDMADokument18 SeitenPower Control 3G CDMAmanproxNoch keine Bewertungen
- College of Computer Science Software DepartmentDokument4 SeitenCollege of Computer Science Software DepartmentRommel L. DorinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL RouterAndSwitches AE Kn1of3 AnswerDokument19 SeitenCL RouterAndSwitches AE Kn1of3 Answereugene ngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Prmy Gr4 Math Ph1 HWSHDokument55 SeitenFinal Prmy Gr4 Math Ph1 HWSHKarthik KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jayesh PresentationDokument22 SeitenJayesh PresentationanakinpowersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Formal Letter LPDokument2 SeitenFormal Letter LPLow Eng Han100% (1)
- Packet Unit 3 - Atomic Structure-Answers ChemistryDokument11 SeitenPacket Unit 3 - Atomic Structure-Answers ChemistryMario J. KafatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebops PDFDokument2 SeitenEbops PDFtuan nguyen duyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The Marshall AttackDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding The Marshall Attacks.for.saad8176Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade9 January Periodical ExamsDokument3 SeitenGrade9 January Periodical ExamsJose JeramieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building For The Environment 1Dokument3 SeitenBuilding For The Environment 1api-133774200Noch keine Bewertungen