Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
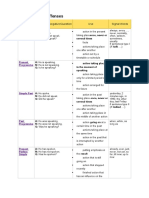
Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Present
Hochgeladen von
Mariana PasatOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Present
Hochgeladen von
Mariana PasatCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
tense
Simple
Present
Affirmative/Negative/Question
A: He speaks.
N: He does not speak.
Q: Does he speak?
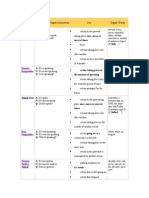
Present
A: He is speaking.
Progressive N: He is not speaking.
Q: Is he speaking?
Simple Past A: He spoke.
N: He did not speak.
Q: Did he speak?
Past
A: He was speaking.
Progressive N: He was not speaking.
Q: Was he speaking?
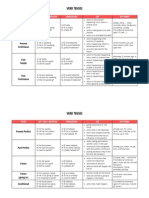
Present
Perfect
Simple
A: He has spoken.
N: He has not spoken.
Q: Has he spoken?
Use
action in the present taking place once, never or several
times
facts
actions taking place one after another
action set by a timetable or schedule
action taking place in the moment of speaking
action taking place only for a limited period of time
action arranged for the future
action in the past taking place once, never or several
times
actions taking place one after another
action taking place in the middle of another action
action going on at a certain time in the past
actions taking place at the same time
action in the past that is interrupted by another action
putting emphasis on the result
action that is still going on
action that stopped recently
finished action that has an influence on the present
Signal Words
always, every , never, normally, often,
seldom, sometimes, usually
if sentences type I (If I talk, )
at the moment, just, just now, Listen!, Look!,
now, right now
yesterday, 2 minutes ago, in 1990, the other
day, last Friday
if sentence type II (If I talked, )
when, while, as long as
already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till
now, up to now
action that has taken place once, never or several times
before the moment of speaking
Present
A: He has been speaking.
Perfect
N: He has not been speaking.
Progressive Q: Has he been speaking?
Past Perfect A: He had spoken.
putting emphasis on the course or duration (not the result) all day, for 4 years, since 1993, how long?,
the whole week
action that recently stopped or is still going on
finished action that influenced the present
action taking place before a certain time in the past
already, just, never, not yet, once, until that
Simple
N: He had not spoken.
Q: Had he spoken?
day
if sentence type III (If I had talked, )
sometimes interchangeable with past perfect progressive
putting emphasis only on the fact (not the duration)
action taking place before a certain time in the past
sometimes interchangeable with past perfect simple
putting emphasis on the duration or course of an action
action in the future that cannot be influenced
spontaneous decision
assumption with regard to the future
decision made for the future
conclusion with regard to the future
action that is going on at a certain time in the future
action that is sure to happen in the near future
action that will be finished at a certain time in the future
by Monday, in a week
Future II
A: He will have been speaking.
Progressive N: He will not have been speaking.
Q: Will he have been speaking?
action taking place before a certain time in the future
for , the last couple of hours, all day long
Conditional A: He would speak.
I Simple
N: He would not speak.
Q: Would he speak?
action that might take place
action that might take place
putting emphasis on the course / duration of the action
action that might have taken place in the past
Past Perfect A: He had been speaking.
Progressive N: He had not been speaking.
Q: Had he been speaking?
Future I
Simple
Future I
Simple
A: He will speak.
N: He will not speak.
Q: Will he speak?
A: He is going to speak.
N: He is not going to speak.
Q: Is he going to speak?
for, since, the whole day, all day
in a year, next , tomorrow
If-Satz Typ I (If you ask her, shewill
help you.)
assumption: I think, probably, perhaps
in one year, next week, tomorrow
(going to)
Future I
A: He will be speaking.
Progressive N: He will not be speaking.
Q: Will he be speaking?
Future II
Simple
A: He will have spoken.
N: He will not have spoken.
Q: Will he have spoken?
Conditional A: He would be speaking.
I
N: He would not be speaking.
Progressive Q: Would he be speaking?
Conditional A: He would have spoken.
II Simple
N: He would not have spoken.
in one year, next week, tomorrow
putting emphasis on the course of an action
if sentences type II
(If I were you, I would go home.)
if sentences type III
(If I had seen that, I would have helped.)
Q: Would he have spoken?
Conditional A: He would have been speaking.
II
N: He would not have been
Progressive speaking.
Q: Would he have been speaking?
action that might have taken place in the past
puts emphasis on the course / duration of the action
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3Von EverandTiempos verbales pasivos en inglés: Aprende tiempos verbales en inglés, #3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple Tense GuideDokument3 SeitenPresent Simple Tense GuidePavlina HaralampievaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple Presentgulzar72Noch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Dokument3 SeitenSimple Present: I Talk, )Krupesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present tense verbs guideDokument4 SeitenPresent tense verbs guideZandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Chart ExplainedDokument3 SeitenTense Chart ExplainedKiki MulqiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentSorin Mihai VassNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument4 SeitenTable of English TensesKashif WakeelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDenis SăndicăNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses ChartDokument3 SeitenEnglish Tenses ChartAndreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English TensesGonzalo AstorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument2 SeitenTable of English TensesMariana Crăciun100% (1)
- Table TensesDokument4 SeitenTable TensesmariminniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordshpeter195798Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVeronica BurdujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsAbdulaziz2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Present SimpleRobertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses Table and ChartDokument6 SeitenEnglish Tenses Table and ChartRatmi 'Bundanya Rena'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentXorianopoulou SofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English TensesCristina-Raluca RuşeţNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsTaris TallasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentHazel-mae LabradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentJavier J SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses in 40 CharactersDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tenses in 40 CharactersAndrea Paredes GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Tense Verbs and Their UsesDokument3 SeitenPresent Tense Verbs and Their UsesLyana LorenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentAdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TenseDokument3 SeitenTenseMădălina RădulescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Questi On Use Signal Words: Simple PresentRuxanda RusuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentRaj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument5 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Questio N Use Signal Words: Simple PresentFitrie RnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTense Positive/negative/question Usage Signal WordsMyriam GGoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Presentdddiana21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Use Signal WordsAdriana MuresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English TensesShoba DevarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tense ChartDokument4 SeitenEnglish Tense Chartdieba105Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument5 SeitenTable of English TensesMaria CristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsthirtysecondsmarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument4 SeitenEnglish TensesAgung ArdyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument4 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsanon1000Noch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument2 SeitenEnglish TensesGustavo SteffenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Present: TalkedDokument4 SeitenSimple Present: TalkedDangVanTamNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument18 SeitenTensesNora Mestiri100% (1)
- Simple Present: I Talk, )Dokument2 SeitenSimple Present: I Talk, )romina5_13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tense Overview With ExamplesDokument5 SeitenVerb Tense Overview With ExamplesSaulo ZunigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument3 SeitenTenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Wordsyingying1102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument1 SeiteTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentVlasta LoncaricNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument5 SeitenTensesGanesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Timpuri LeDokument3 SeitenTimpuri LemadybyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument1 SeiteSummary Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsCTMundialNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tenses Summary ChartDokument2 SeitenEnglish Tenses Summary ChartRedi BylekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chart of English TensesDokument2 SeitenChart of English TensesNorafiqah Rifhan RamlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Tense TableDokument5 SeitenEnglish Tense TablekaterynavelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English TensesDokument3 SeitenTable of English Tensesiuliana13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Table of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDokument2 SeitenTable of English Tenses: Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal WordsDebyPuspitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi TalkDokument4 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/ Use Signal Words: Ifi Talkshel087Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentDokument3 SeitenTense Affirmative/Negative/Question Use Signal Words: Simple PresentLecherooMendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1BACH - Verb TensesDokument3 Seiten1BACH - Verb TensesEnrique FerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument1 SeiteTensesNucă EvelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Chart With Examples, Use and Signal WordsDokument2 SeitenTenses Chart With Examples, Use and Signal WordssfiedlercNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Cambridge Series in Statistical and Probabilistic Mathematics) Gerhard Tutz, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munchen - Regression For Categorical Data-Cambridge University Press (2012)Dokument574 Seiten(Cambridge Series in Statistical and Probabilistic Mathematics) Gerhard Tutz, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität Munchen - Regression For Categorical Data-Cambridge University Press (2012)shu100% (2)
- Viennas Cafe Louvre in The 1920s and 1930Dokument18 SeitenViennas Cafe Louvre in The 1920s and 1930Friso HoeneveldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krashen's 5 Hypotheses of Second Language AcquisitionDokument69 SeitenKrashen's 5 Hypotheses of Second Language Acquisitionabdo mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 NDDokument52 Seiten2 NDgal02lautNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIGNMENTDokument5 SeitenASSIGNMENTPanchdev KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numl Lahore Campus Break Up of Fee (From 1St To 8Th Semester) Spring-Fall 2016Dokument1 SeiteNuml Lahore Campus Break Up of Fee (From 1St To 8Th Semester) Spring-Fall 2016sajeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intermediate Reading Comprehension Test 03Dokument5 SeitenIntermediate Reading Comprehension Test 03MZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Puzzles Freebie: Includes Instructions!Dokument12 SeitenLogic Puzzles Freebie: Includes Instructions!api-507836868Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsDokument31 SeitenComparative Ethnographies: State and Its MarginsJuan ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance AppraisalsDokument73 SeitenPerformance AppraisalsSaif HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bible Study RisksDokument6 SeitenBible Study RisksVincentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplier Development at Honda, Nissan and ToyotaDokument28 SeitenSupplier Development at Honda, Nissan and Toyotapresidonsi100% (1)
- Animal Quiz: SuperlativesDokument2 SeitenAnimal Quiz: SuperlativesLuis LemusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distance Learning 2016 Telecom AcademyDokument17 SeitenDistance Learning 2016 Telecom AcademyDyego FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined RubricsDokument3 SeitenCombined Rubricsapi-446053878Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Research TeamDokument4 SeitenThe Research Teamapi-272078177Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report-Picic & NibDokument18 SeitenReport-Picic & NibPrincely TravelNoch keine Bewertungen
- WORKSHOP ON ACCOUNTING OF IJARAHDokument12 SeitenWORKSHOP ON ACCOUNTING OF IJARAHAkif ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Merry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)Dokument6 SeitenMerry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)gmit92Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2200SRM0724 (04 2005) Us en PDFDokument98 Seiten2200SRM0724 (04 2005) Us en PDFMayerson AlmaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What's The Line Between Middle Class, Upper Middle Class, and Upper Class in Britain - QuoraDokument11 SeitenWhat's The Line Between Middle Class, Upper Middle Class, and Upper Class in Britain - QuoraFaizan ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrinsic Resistance and Unusual Phenotypes Tables v3.2 20200225Dokument12 SeitenIntrinsic Resistance and Unusual Phenotypes Tables v3.2 20200225Roy MontoyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark SchemeDokument6 SeitenWjec Gcse English Literature Coursework Mark Schemef6a5mww8100% (2)
- FunambolDokument48 SeitenFunambolAmeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyDokument4 SeitenEpithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyrenee belle isturisNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Ledger Journal Import ProcessDokument13 SeitenGeneral Ledger Journal Import ProcessMadhavi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science & Technology: Wireless Sensor Network and Internet of Things (Iot) Solution in AgricultureDokument10 SeitenScience & Technology: Wireless Sensor Network and Internet of Things (Iot) Solution in AgricultureSivajith SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perkin Elmer Singapore Distribution CaseDokument3 SeitenPerkin Elmer Singapore Distribution CaseJackie Canlas100% (1)
- The City - Populus' As A Self-Governing CorporationDokument24 SeitenThe City - Populus' As A Self-Governing Corporation马寅秋Noch keine Bewertungen
- Christian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Dokument78 SeitenChristian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Nwaozuru JOHNMAJOR ChinecheremNoch keine Bewertungen