Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Soil
Hochgeladen von
Winard WantogCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Soil
Hochgeladen von
Winard WantogCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Soil is the mixture of minerals, organic matter, gases, liquids, and the myriad of organisms that together support
plant life. It is a natural body that exists as part of
the pedosphere and which performs four important functions: it is a medium for plant growth; it is a means ofwater storage, supply and purification; it is a modifier of
the atmosphere of Earth; and it is a habitat for organisms that take part in decomposition of organic matter and the creation of a habitat for new organisms.
Soil is considered to be the "skin of the earth" with interfaces between the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere of Earth, andbiosphere.[1] Soil consists of a solid phase
(minerals and organic matter) as well as a porous phase that holds gases and water.[2][3][4]Accordingly, soils are often treated as a three-state system.[5]
Soil is the end product of the influence of the climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), biotic activities (organisms), and parent materials (original
minerals) interacting over time.[6] Soil continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which
include weathering with associated erosion.
Most soils have a density between 1 and 2 g/cm3.[7] Little of the soil of planet Earth is older than the Pleistocene and none is older than the Cenozoic,
[8]
although fossilized soils are preserved from as far back as the Archean.[9]
Soil science has two main branches of study: Edaphology and Pedology. Pedology is focused on the formation, description (morphology), and classification of soils in
their natural environment,[10] whereas edaphology is concerned with the influence of soils on organisms. In engineering terms, soil is referred to as regolith, or loose
rock material that lies above the 'solid geology'.[11] Soil is commonly referred to as "earth" or "dirt"; technically, the term "dirt" should be restricted to displaced soil.[12]
As soil resources serve as a basis for food security, the international community advocates for its sustainable and responsible use through different types of Soil
Governance.
water
n a clear colourless tasteless odourless liquid that is essential for plant and animal life and constitutes, in impure form, rain, oceans, rivers, lakes, etc.
It is a neutral substance, an effective solvent for many compounds, and is used as a standard for many physical properties. Formula: H2O
Related adj aqueous
the quality or state of being warm; moderate or gentle heat.
the sensation of moderate heat.
liveliness of feelings, emotions, or sympathies; ardor or fervor;enthusiasm or zeal:
She spoke her mind with great warmth. There was warmth in hisgreeting and in his handshake.
the quality of being intimate and attached:
All children need warmth and affection from their families.
an effect of brightness, cheerfulness, coziness, etc., achieved by theuse of warm colors:
The room has warmth since it was redecorated.
the means or ability to produce a sensation of heat:
a jacket with little warmth
orographic rainfull is precipitation that results when moist air is lifted over a topographic barrier such as a mountain range..
1. Soil Type: Sandy
Sandy soil has the largest particles among the different soil types. Its dry and gritty to the touch, and because the particles have huge spaces between
them, it cant hold on to water.
Water drains rapidly, straight through to places where the roots, particularly those of seedlings, cannot reach. Plants dont have a chance of using the
nutrients in sandy soil more efficiently as theyre swiftly carried away by the runoff.
The upside to sandy soil is that its light to work with and warms much more quickly in the spring.
Testing what type of soil youre working with involves moistening the soil and rolling it into a ball to check the predominating soil particle. When you roll
the slightly wet sandy soil in your palms, no ball should be formed and it crumbles through your fingers easily.
2. Soil Type: Silty
Silty soil has much smaller particles than sandy soil so its smooth to the touch. When moistened, its soapy slick. When you roll it between your fingers,
dirt is left on your skin.
Silty soil retains water longer, but it cant hold on to as much nutrients as youd want it to though its fairly fertile. Due to its moisture-retentive quality,
silty soil is cold and drains poorly.
Silty soil can also easily compact, so avoid trampling on it when working your garden. It can become poorly aerated, too.
3. Soil Type: Clay
Clay soil has the smallest particles among the three so it has good water storage qualities. Its sticky to the touch when wet, but smooth when dry.
Due to the tiny size of its particles and its tendency to settle together, little air passes through its spaces. Because its also slower to drain, it has a tighter
hold on plant nutrients. Clay soil is thus rich in plant food for better growth.
Clay soil is cold and in the spring, takes time to warm since the water within also has to warm up. The downside is that clay soil could be very heavy to
work with when it gets dry. Especially during the summer months, it could turn hard and compact, making it difficult to turn. (When clay soil is worked
while its too wet though, its prone to damage).
If moistened soil feels sticky, rolls up easily, and forms into a ball or sausage-like shape, then youve got yourself clay.
4. Soil Type: Peaty
Peaty soil is dark brown or black in color, soft, easily compressed due to its high water content, and rich in organic matter. Peat soil started forming over
9,000 years ago, with the rapid melting of glaciers. This rapid melt drowned plants quickly and died in the process. Their decay was so slow underwater
that it led to the accumulation of organic area in a concentrated spot.
Although peat soil tends to be heavily saturated with water, once drained, it turns into a good growing medium. In the summer though, peat could be
very dry and become a fire hazard. (I kid you notpeat is the precursor of coal.) The most desirable quality of peat soil, however, is in its ability to hold
water in during the dry months and its capacity to protect the roots from damage during very wet months.
Peat contains acidic water, but growers use it to regulate soil chemistry or pH levels as well as an agent of disease control for the soil.
When wet peat soil is rolled, you wont form a ball. Its spongy to the touch and when squeezed, water could be forced out.
5. Soil Type: Saline Soil
The soil in extremely dry regions is usually brackish because of its high salt content. Known as saline soil, it can cause damage to and stall plant growth,
impede germination, and cause difficulties in irrigation.
The salinity is due to the buildup of soluble salts in the rhizospherehigh salt contents prevent water uptake by plants, leading to drought stress.
Its easy enough to test if you have saline soil. Youll probably see a white layer coating the surface of the soil, your plants are growing poorly, and theyre
suffering from leaf tip burn, especially on young leaves.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Proclamation No. 1105Dokument2 SeitenProclamation No. 1105Marian TudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proclamation No. 1105Dokument2 SeitenProclamation No. 1105Marian TudNoch keine Bewertungen
- AutoCAD Keyboard Shortcuts 2012Dokument6 SeitenAutoCAD Keyboard Shortcuts 2012Ali SoewarnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article III, Philippines ConstitutionDokument2 SeitenArticle III, Philippines ConstitutionWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental PollutionDokument5 SeitenEnvironmental PollutionWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
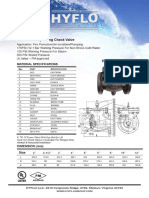
- Hyflo - Check Valve Swing TypeDokument1 SeiteHyflo - Check Valve Swing TypeWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- E 120 14 PDFDokument20 SeitenE 120 14 PDFGia Minh Tieu TuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACI Standard BendDokument8 SeitenACI Standard Bends.skumar1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Globe Sprinkler CompanyDokument20 SeitenGlobe Sprinkler CompanyWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superior Pipes LaunchDokument2 SeitenSuperior Pipes LaunchWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shakespeare's Seven Ages of ManDokument4 SeitenShakespeare's Seven Ages of ManWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excuse LetterDokument1 SeiteExcuse LetterWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case AnalysisDokument3 SeitenCase AnalysisWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlkenesDokument19 SeitenAlkenesWinard Wantog100% (1)
- Simple Crock Pot SpicyDokument3 SeitenSimple Crock Pot SpicyWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design ElementDokument16 SeitenDesign ElementWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Areolar Connective Tissue LPOMPODokument7 SeitenAreolar Connective Tissue LPOMPOWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlkenesDokument19 SeitenAlkenesWinard Wantog100% (1)
- Christian Chordbook PDFDokument132 SeitenChristian Chordbook PDFDenise Holland84% (19)
- Secondary Growth 2Dokument3 SeitenSecondary Growth 2Winard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disaster Nursing HandoutDokument3 SeitenDisaster Nursing HandoutWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atmospheric CirculationDokument6 SeitenAtmospheric CirculationWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Service Training ProgramDokument1 SeiteNational Service Training ProgramWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Ways To Measure Your PresentationDokument24 Seiten4 Ways To Measure Your PresentationWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phil Health P.W.P.Dokument14 SeitenPhil Health P.W.P.Winard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Septic Tank BuildersDokument49 SeitenSeptic Tank BuildersWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical ParasitologyDokument4 SeitenClinical ParasitologyWinard WantogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Updated Climate Change in The PhilippinesDokument91 SeitenUpdated Climate Change in The PhilippinesWinard Wantog100% (1)
- Board of Civil Engineering Exam ScopeDokument8 SeitenBoard of Civil Engineering Exam ScopeMANDARAW93% (14)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Environment Has Always Been An International Problem Because Government Are Not Imposing Harsh Punishments Against OffendresDokument3 SeitenEnvironment Has Always Been An International Problem Because Government Are Not Imposing Harsh Punishments Against OffendresColor hubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Emergency PamphletDokument52 SeitenClimate Emergency PamphletClimate CampaignerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Exam, 1Dokument5 SeitenPaper Exam, 1Saeed StriderNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Future Without Plastic Waste Through Sustainability and CircularityDokument1 SeiteA Future Without Plastic Waste Through Sustainability and CircularityRishi VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lotek NetworkDokument15 SeitenLotek NetworkbinukirubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- C40 Cities (2021) Creating Local Green Jobs in South AfricaDokument7 SeitenC40 Cities (2021) Creating Local Green Jobs in South AfricalucianaleisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE-402: Irrigation Engineering: 8 Semester (4 Year) Civil Engineering Spring 2021Dokument23 SeitenCE-402: Irrigation Engineering: 8 Semester (4 Year) Civil Engineering Spring 2021SajadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity and Assessment Plan: Name: Grade Level NGSS Performance Expectation: 2-LS4-1Dokument5 SeitenActivity and Assessment Plan: Name: Grade Level NGSS Performance Expectation: 2-LS4-1api-506353226Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isc2 2Dokument8 SeitenIsc2 2BalkanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bài giảng Day 02.2 3Dokument7 SeitenBài giảng Day 02.2 3Uyên Nguyễn ThụcNoch keine Bewertungen
- How biodiversity contributes to ecosystem sustainabilityDokument27 SeitenHow biodiversity contributes to ecosystem sustainabilityLey Domingo Villafuerte GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neighbourhood CPPDokument2 SeitenNeighbourhood CPPsalimdido didoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Global Warming Affects Our PlanetDokument15 SeitenHow Global Warming Affects Our PlanetNeel Sumariaa0% (1)
- IP Springfield Mill Fact SheetDokument1 SeiteIP Springfield Mill Fact SheetSinclair Broadcast Group - EugeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS Current Affairs - Water Crisis NOTESDokument2 SeitenCSS Current Affairs - Water Crisis NOTESHassaan AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elevating Sustainability Through PT Astra Agro's 2021 ReportDokument192 SeitenElevating Sustainability Through PT Astra Agro's 2021 ReportQamar UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deforestation Facts and Information PDFDokument4 SeitenDeforestation Facts and Information PDFYasir100% (1)
- Anatomy of Tropical StormDokument40 SeitenAnatomy of Tropical StormJeford Lazo Tabarino ApostolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jensen e HaiseDokument3 SeitenJensen e HaiseArthur SuassunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 009 PPT in Food Web and Food ChainDokument33 Seiten009 PPT in Food Web and Food ChainMary Grace G. CatubiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar on Natural Resources ManagementDokument18 SeitenSeminar on Natural Resources ManagementSwapnil RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Vincent College of Cabuyao: Barangay Mamatid, Cabuyao City, LagunaDokument2 SeitenSt. Vincent College of Cabuyao: Barangay Mamatid, Cabuyao City, LagunaMacaraeg NicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Science in Project and Facility Management With Honours (BPFM)Dokument22 SeitenBachelor of Science in Project and Facility Management With Honours (BPFM)Muhammad AdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental ChampionDokument1 SeiteEnvironmental Championbuloy377Noch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Circulation Patterns and LinksDokument63 SeitenClimate Circulation Patterns and LinksPugar Septia GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diatom Index for Pampean RiversDokument9 SeitenDiatom Index for Pampean RiversApolinaVunoimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Plan Literature ReviewDokument2 SeitenSite Plan Literature ReviewRamavath BharathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biodiversity and BioprospectingDokument44 SeitenBiodiversity and BioprospectingmberensteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Selangor Dam EIADokument17 SeitenThe Selangor Dam EIAaja_zaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Life Science - Q2 - Mod15 - Biotic Potential and Environmental Resistance - Version1Dokument19 SeitenEarth and Life Science - Q2 - Mod15 - Biotic Potential and Environmental Resistance - Version1Glenda Astodillo100% (2)