Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ex2 Glucocorticoids: Study Online at
Hochgeladen von
JohnBedaLatawanMalecdanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ex2 Glucocorticoids: Study Online at
Hochgeladen von
JohnBedaLatawanMalecdanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ex2 Glucocorticoids
Study online at quizlet.com/_8qqss
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
Elevated potassium
raises production of
___
Aldosterone
20.
GCRc is bound to ___
in cytoplasm, which
acts to ___
HSP (Heat shock Protein;
Chaperone), anchors GCRc to
cytoplasm
Aldosterone regulates
what transporters in
the distal convoluted
tubule?
Na/Cl symporter, Na/K ATPase
21.
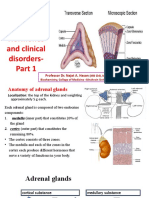
Adrenal cortex
produces which
hormones?
cortisol, aldosterone, androgens
adrenal medula
produces ___
epinephrine, norepinephrine
Cl exites the
basolateral membrane
of the distal
convuluted tubule via
___
Cl Channel
zona reticularis
produces
androgens
steps to produce
aldosterone
cholesterol, pregnenolone,
progesterone, aldosterone
Aldosterone also helps
control ___, ___,
____
Sweat, GI tract, Salivary glands.
Electrolyte and water balance
steps to produce
cortisol
cholesterol, pregnenolone,
progesterone OR 17-OHpregnenolone, 17-OHprogesterone, cortisol
Aldosterone acts on a
____
nuclear receptor
aldosterone is a ___,
made in the ___
mineralcorticoid, zona
glomerulosa (outer section)
steps to make
androgens
cholesterol, pregnenolone, 17-OHprogesterone OR 17-OHpregnenolone, androgens
Aldosterone increases
___
Na resorption, K secretion, water
retension (BP)
In the kidney,
aldosterone ___, and
___
phosphorylates an amiloride
sensitive Na channel, and
upregulates Na/K/ATPase
In the collecting
tubule, aldosterone
actions are ___
More Na channels, Na/K/ATPase,
change in permability of tight
junctions
GC are also
stimulated by ADH
and CRH?
true????
AIP is ___
Aldosterone induced porteins
Aldosterone affects
channels by ___
more trancript/translate, and also
inserts them into the membrane
29.
ACTH is a ___
Growth Factor
Aldosterone also
affects the
mitochondria
30.
Excess ACTH causes
Adrenal Hyperplasia
Insufficient ACTH
causes
Atrophy of the inner cotex
body makes tons more
___ than ___
GC than MC
Cortisol circulates
___
protein bound
what is the name of
the enzyme that
converts cortisol to
cortisone?
11-Beta-Hydroxysteroid
dehydrogenase
When GC binds GCRc,
GCRc forms ___, and
recruites ____
dimer, activators or repressors
in the collecting ducts,
aldosterone ___
upregulates Na channels, Na/Cl
symporter, Na/K ATPase
34.
GCRc bindes to ___
after forming dimer
GRE
Cortisol is a ___,
made in the ____
glucocorticoid, zona fasciculata
35.
surfactant proteins
are ___ in lung by GC
upregulated
Cortisol causes ____
increased Blood Sugar, decreaed
immune system, increased fat,
protein, carb metabolism,
decreased bone formation
36.
GC-RC coactivators
are
CBP/TRB (activators, repressors)
Cortisol is converted
to cortisone in the ___
Gut, Kidney, Salivary, Sweat
glands. So MC rules here
can overide enzyme by
___
giving large doses of GC that also
have MC activity
GC Rc resides where
when empty
cytoplasm
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
27.
28.
31.
32.
33.
37.
38.
39.
40.
41.
42.
43.
44.
45.
46.
47.
48.
49.
repression 1
steps
GCRc complex blocks other transcription
promoting factors from binding to their
promotor regions. In this scheme. GCGCRc
is bound to the "wrong" promotor, instead of
binding to a GRE like it is supposed to.
are K+
channels
upregulated
by
Aldoserone?
no
Na/K/ATPase
are found
where?
everywhere in the tubule. All of them are
upregeulated by Aldosterone, everywhere
repression II
GCGCRc travels to the nucleus but doesn't
dimerize. Instead it forms a complex by
binding with other transcription factors.
These factors can no longer bind to
promotor that it should have bound to
50.
51.
52.
GC are usually
used to
suppress ___
inflammation
in the liver, GC
will
increase gluconeogenesis (for needed
energy), and glycogen storage (for
conserving extra for later), increase protein
synthesis for these
In striated
muscle, GC
increases ___
protein catabolism for making glucose
In adipose
tissue, GC
increases ___
lipolysis for making glucose
in bone and
skin, GC will
__
decrease Ca uptake in the gut, inhibit
calcitonin, enhance oseoclastic activity,
inhibit osteoblastic activity, decrease protein
synthesis
which fat is
the most
active?
viceral
GC will make
you hyper or
hypocalcemic?
hyer, by inhibiting Vit D, decreases bone
density
under chronic
stress, GC will
make you
develop more fat, not full osteoporosis, more
blood glucose
Prolonged
doses of GC
does what to
the gland?
How to adjust
dose?
adrophies (Adrenal Cortex), taper the dose
53.
54.
55.
56.
57.
58.
59.
60.
61.
62.
63.
Cortisol
suppresses ___
CRH, ACTH, Immune System
(lymphocytes, Macrophages, Monocytes,
Neutrophils)
Which
inflammation
factors does GC
repress?
IL-1,2,6, TNF-alpha
which chemicals
stimulate the
hypothalamus to
secrete CRH?
Ach, 5-HT, NE
Which chemicals
suppress
Hypothalamus
CRH secretion?
NE, GABA
Which
inflammation
factorss increase
Cortisol?
IL-1,2,6, TNF-alpha
Cushings is a
result of
excess cortisol
High blood
pressure is a
result of
excess aldosterone
cardiac
remodeling is
caused by
aldosterone, high blood pressue, by
direct action
aldosterone
antagonists treat
___ and prevent
___
high BP, deleterious cardiac remodeling
How does GC
inhibit
Macrophages
and monocytes?
Phospholipase A2 is inhibited, limiting
the supply of arachadonic acid, which
suppresses COX enzymes.
When
Macrophages
and monocytes
are inhibited,
___
no prostoglandins or leukotriens are
produced; acute phase reactants,
including some compliment compontnes
are reduced. Turns down pain.
GC inhibits
endothelial cells
by ____
Reducing the expression of adhesion
molecules
reducing the
expression of
adhesion
molecules results
in
no homing or concentrating of
leukocytes at infection sites.
GC inhibits
Basophils by ___
inhibiting histamine production by
suppression of IGF dependant role
GC inhibits Lyphocytes by ___
inhibiting cytokine production, by limiting chemotaxis or the expansion of immune cells by IL-2,
IL-6
giving pregnant mom GC during
pregnancy will stimulate
fetal surfactant gene
addison's disease is a result of
___
cortisol or aldosteron deficiency
tumor in zona fisticulada will
cause ___
excess cortisol
vasoactive mediators are effected
by __, and makes ___
aldosterone excess, vaculature more sensetive to ANGII, and catecholamines (negative effect)
69.
Signs of Cushings Syndrome
Increased susceptibility to infection, fat redistribution, peripheral muscle wasting, Skin thinning,
Increased bruising, Hypertesnio, Bone loss, buffalo hump, moon face
70.
Symptoms of Addison's disease
Can't make MC or GC, volume contraction, don't retain sodium, Na is excreeting, hyponeutremic,
low volume
71.
primary addison's disease is
adrenal deffect, need surgical removal
Secondary and tertiary addison's
disease are
defect in pituitary (2ndary) or hypothalamus (tertiary)
64.
65.
66.
67.
68.
72.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Kortizol FizyolojiDokument5 SeitenKortizol FizyolojiVedat KacarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenocorticosteroids: Adrenal GlandDokument51 SeitenAdrenocorticosteroids: Adrenal Glandكسلان اكتب اسميNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdrenocorticosteroidsDokument64 SeitenAdrenocorticosteroidsGeraldine Marie SalvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration of Cellular Responses To Multiple Signaling Pathways: Insulin ActionDokument12 SeitenIntegration of Cellular Responses To Multiple Signaling Pathways: Insulin ActionThu NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Gland: Adrenal Cortex Adrenal MedullaDokument25 SeitenAdrenal Gland: Adrenal Cortex Adrenal MedullaMohammed JeelaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenocortical HormonesDokument46 SeitenAdrenocortical HormoneschayChay gapolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormones of The Adrenal Cortex 1-13Dokument47 SeitenHormones of The Adrenal Cortex 1-13abstabs50% (2)
- Adrenal Notes - EndocrineDokument6 SeitenAdrenal Notes - Endocrinekep1313Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDokument18 SeitenAdrenal Gland: Structure, Hormones and Clinical Disorders-: Professor Dr. Najat A. HasanDrFarah Emad Ali100% (1)
- Chap3 The Adrenal GlandDokument20 SeitenChap3 The Adrenal GlandSharon GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Glands 2018 - 2019Dokument32 SeitenAdrenal Glands 2018 - 2019Bianca BiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis FCRDokument10 SeitenGlycolysis and Gluconeogenesis FCRMesut OzilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipid Metabolism L3+4Dokument50 SeitenLipid Metabolism L3+4bgj9cddvxhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Week 2Dokument38 SeitenCarbohydrate Metabolism Week 2shadaalnaas657Noch keine Bewertungen
- UWorld Cards July 14Dokument7 SeitenUWorld Cards July 14smian08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Gland - DR CokerDokument59 SeitenAdrenal Gland - DR CokerIshaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNE Biochem 1005 Practice QuestionsDokument4 SeitenUNE Biochem 1005 Practice QuestionselelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics in Diseases of Adrenal GlandsDokument7 SeitenBasics in Diseases of Adrenal GlandsFrancis ChegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem 2Dokument5 SeitenBiochem 2D MacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioch CL 7. Enzime Utilizate in Diagnostic 20-21 (R+e)Dokument44 SeitenBioch CL 7. Enzime Utilizate in Diagnostic 20-21 (R+e)Andrea ModestieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hal 106-108Dokument6 SeitenHal 106-108Dirgantari PademmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Control Within The Body: Presented byDokument20 SeitenAdrenal Control Within The Body: Presented byhumnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Cortex HormonesDokument21 SeitenAdrenal Cortex HormonesAaa JjjjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenocortical HormonesDokument5 SeitenAdrenocortical HormonesHala RezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENDO 22 SCL Data Interpretation of Adrenocortical DysfunctionDokument41 SeitenENDO 22 SCL Data Interpretation of Adrenocortical DysfunctionNazreen sofia HazleenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS)Dokument36 SeitenDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS)Ismail GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corticosteroid Physiology and Principles of Therapy PDFDokument6 SeitenCorticosteroid Physiology and Principles of Therapy PDFTriawan AdinataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiotonic Drugs Revised DheryanDokument16 SeitenCardiotonic Drugs Revised Dheryanlinnet17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gluconeogenesis InhibitorDokument4 SeitenGluconeogenesis InhibitorLinhNguyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal GlandDokument46 SeitenAdrenal GlandhSANNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Diabet Curs 1 STEFANADokument34 Seiten3 Diabet Curs 1 STEFANAAnda Madalina ZahariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of The Adrenal Gland: DR Nyein Nyein Wai Associate ProfessorDokument42 SeitenPhysiology of The Adrenal Gland: DR Nyein Nyein Wai Associate ProfessorAzizan HannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activation of Protein Kinase C in Glomerular Cells in DiabetesDokument8 SeitenActivation of Protein Kinase C in Glomerular Cells in DiabetesOwen BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steroidni HormoniDokument45 SeitenSteroidni Hormoniivan12sdNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMF1 2015 Exam ReviewDokument19 SeitenBMF1 2015 Exam ReviewTyler KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism of Adrenal SteroidsDokument15 SeitenMetabolism of Adrenal SteroidsRahmawati RdnNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProstaglandinsDokument29 SeitenProstaglandinsNarasimha MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 78 - Adrenocortical HormonesDokument8 Seiten78 - Adrenocortical Hormonesmanjitashet4049Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolic Aspect of CVSDokument25 SeitenMetabolic Aspect of CVSsamar yousif mohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist: A. B. C. D. eDokument18 SeitenChecklist: A. B. C. D. eHoanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 003Dokument358 Seiten003Gordana UzelacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperglycemia As An Effect of Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Intra-Operative Glucose ManagementDokument6 SeitenHyperglycemia As An Effect of Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Intra-Operative Glucose ManagementMuhammad RizqiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biosynthesis of Cortisol Ics-2Dokument3 SeitenBiosynthesis of Cortisol Ics-2Kate Alyssa CatonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingDokument10 SeitenSynthesis of Eicosanoids and SignalingCLEMENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- GluconeogenEZ Control of Blood GlucoseDokument1 SeiteGluconeogenEZ Control of Blood GlucosebirlikteyizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 21 - Responding To The Cellular EnvironmentDokument29 SeitenChapter 21 - Responding To The Cellular EnvironmentRebecca Long HeiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostaglandi: Bhumika Sharma Bms IiiyearDokument29 SeitenProstaglandi: Bhumika Sharma Bms IiiyearQamar QamarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6-Adrenocortical Hormones PancreaseDokument47 Seiten6-Adrenocortical Hormones Pancreasetmqt2fbnzgNoch keine Bewertungen
- CorticosteroidsDokument36 SeitenCorticosteroidsAbdur RafayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry MCQsDokument21 SeitenBiochemistry MCQsnikteshgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry - 230204 - 191022Dokument41 SeitenBiochemistry - 230204 - 191022DRJS 74Noch keine Bewertungen
- DkaDokument38 SeitenDkaHam SotheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control of Intermediary Metabolism: D. C. Mikulecky Dept. PhysiologyDokument21 SeitenControl of Intermediary Metabolism: D. C. Mikulecky Dept. Physiology4127297Noch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal & KortisolDokument47 SeitenAdrenal & KortisolPrisca AngelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39Dokument94 Seiten1-Adrenocorticosteroids Chapter39hamidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormon AdrenalDokument76 SeitenHormon AdrenalgitafazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caffeine Blocks SREBP2Dokument17 SeitenCaffeine Blocks SREBP2Javier ArellanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperglycemia Crisis: Dr. Netty NurnaningtyasDokument34 SeitenHyperglycemia Crisis: Dr. Netty Nurnaningtyasnetty nurnaningtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Glands - Cortex - Dr. Gagare DBDokument28 SeitenAdrenal Glands - Cortex - Dr. Gagare DBkehigeh812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Groundbreaking ProgramDokument1 SeiteGroundbreaking ProgramJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Did Rizal Develop His Nationalist AspirationsDokument3 SeitenHow Did Rizal Develop His Nationalist AspirationsJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Burns: Dr. Shiara Ortiz-Pujols Burn Fellow NC Jaycee Burn CenterDokument75 SeitenPathophysiology of Burns: Dr. Shiara Ortiz-Pujols Burn Fellow NC Jaycee Burn CenterJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Local Anesthetics: Richard D. Minshall, PHD Tobias Piegeler, MDDokument40 SeitenLocal Anesthetics: Richard D. Minshall, PHD Tobias Piegeler, MDJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding My Benefits: Pre - Auth@Dokument2 SeitenUnderstanding My Benefits: Pre - Auth@Jonelle Morris-DawkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 Safety and Health at WorkDokument42 SeitenModule 5 Safety and Health at Workdoidoi80% (5)
- Dunkin DonutsDokument2 SeitenDunkin DonutszerpthederpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coca Cola Fairlife CaseDokument4 SeitenCoca Cola Fairlife Caseapi-315994561Noch keine Bewertungen
- WEEK 2 ILP Grade 4Dokument5 SeitenWEEK 2 ILP Grade 4jean arriolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MENTAL HEALTH NURSING ExamDokument5 SeitenMENTAL HEALTH NURSING ExamSurkhali BipanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Clinical SkillsDokument376 SeitenPsychiatric Clinical SkillsSamuel Agunbiade100% (5)
- Avocado Production in The PhilippinesDokument20 SeitenAvocado Production in The Philippinescutieaiko100% (1)
- PHIL 125: Practical Logic: University of Alberta Sam Hillier, Fall 2013Dokument12 SeitenPHIL 125: Practical Logic: University of Alberta Sam Hillier, Fall 2013Harry WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diastasis Recti Ebook DownloadDokument19 SeitenDiastasis Recti Ebook DownloadMertcan DamatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartDokument2 SeitenSelective, Differential, & Enriched Media Lab ChartFrankiesgirl6yr100% (6)
- Neurobiologic Theories and PsychopharmacologyDokument2 SeitenNeurobiologic Theories and Psychopharmacologymyer pasandalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diet's CardDokument8 SeitenDiet's CardJORGE ATRIANONoch keine Bewertungen
- The Barrier To Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice Among Novice TherapistsDokument11 SeitenThe Barrier To Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice Among Novice TherapistsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume 3Dokument2 SeitenResume 3api-458753728Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Adult Psychodiagnostic Chart 2012 1.7 PDFDokument3 SeitenThe Adult Psychodiagnostic Chart 2012 1.7 PDFMF LeblancNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head StartDokument49 SeitenHead StartDavid BernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intrathecal Antibiotic Administration Procedure (Paediatrics)Dokument9 SeitenIntrathecal Antibiotic Administration Procedure (Paediatrics)Abu Azzam Al-HadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCL-81 Product Sheet - VeroDokument5 SeitenCCL-81 Product Sheet - VeroKrishnan KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1PE 4 Q3 Answer Sheet March 2024Dokument3 Seiten1PE 4 Q3 Answer Sheet March 2024Chid CabanesasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knee Pain and The Internal Arts: Correct Alignment (Standing)Dokument7 SeitenKnee Pain and The Internal Arts: Correct Alignment (Standing)Gabriel PedrozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Essay On ObesityDokument6 SeitenShort Essay On ObesityLisa Wong100% (1)
- Branksome Hall Asia Code of ConductDokument9 SeitenBranksome Hall Asia Code of Conductapi-246218373Noch keine Bewertungen
- Baby Led-WeaningDokument7 SeitenBaby Led-WeaningsophieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philo Final SummativeDokument2 SeitenPhilo Final SummativeFobe Lpt NudaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumor AngiogenesisDokument35 SeitenTumor AngiogenesisDoni Mirza KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hearing Handicap Inventory For The Elderly (HHIE)Dokument5 SeitenHearing Handicap Inventory For The Elderly (HHIE)Is GutiérrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hygienic Design Food IndustryDokument19 SeitenHygienic Design Food IndustryLinaArev H100% (1)
- Centrifugal ChillerDokument24 SeitenCentrifugal ChillerARUL SANKARANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Thesis 22Dokument66 SeitenFinal Thesis 22AdombireNoch keine Bewertungen