Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Aldehydes and Ketones: Results
Hochgeladen von
Stephanie Joy EscalaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Aldehydes and Ketones: Results
Hochgeladen von
Stephanie Joy EscalaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
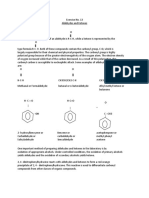
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
RESULTS
Table 1. General Test for Carbonyl Compounds (Aldehydes and Ketones):
Nucleophilic Addition of 2,4-DNPH
Description of Product
(Phenylhydrazone)
Carbonyl
Compound
Test
Response
(+/-)
Chem
Rxn
Formaldehyde
Benzaldehyde
Acetone
Chemical Equations:
1a
1b
1c
+ H 2O
Table 2. General Test for Aldehydes: Oxidation by Tollens Reagent
General Equation:
Carbonyl
Compound
Formaldehyde
Description of Resulting Mixture
Ag mirror was formed; Clear solution
Test
Response
(+/-)
Che
m
Rxn
2a
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
Benzaldehyde
Formation of emulsion; Dirty white solution
2b
Acetone
No Ag mirror formed; Clear solution
2c
Chemical Equations:
2a
2b
NO REACTION
2c
No reaction
Table 3. General Test for Aliphatic Aldehydes: Oxidation by Fehlings Reagent
General Equation:
Test
Response
(+/-)
Chem
Rxn
Carbonyl
Compound
Description of Resulting Mixture
Formaldehyde
Blue solution Brick red precipitate was
formed
3a
Benzaldehyde
Lighter blue No precipitate formed
3b
Acetone
Dark blue solution No precipitate formed
3c
Chemical Equations:
3a
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
3b
2C6H6CHO + NaOH C6H6CH2OH +C6H6COONa
3c
No reaction
Table 4. Preservative Action of Formaldehyde
Protein
Sample
Description of Sample
Description of Sample
in Hot Water
Untreated
gelatin sheet
Did not dissolve in water
Gelatin sheet
treated with
H2C=O
Dissolved in water
Solubil
ity in
H2O
(+/-)
+
Table 5. Oxidation by KMnO4
Test
Response
(+/-)
Chem
Rxn
Carbonyl
Compound
Description of Resulting Mixture
Formaldehyde
Pink solution Yellow solution with red
precipitate
5a
Acetone
Pink solution
5b
Chemical Equations:
5a
5C6H6CHO + 2KMnO4 + 6H+ 5C6H6COOH +2Mn2+ + 3H2O + 2K+
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
5b
CH3COCH3 + KMnO4 No reaction
Table 6. Test for CH3C=O or methyl ketone group in carbonyl compound: Iodoform
Test
Carbonyl
Compound
Description of Resulting Mixture
Test
Response
(+/-)
Chem
Rxn
Formaldehyde
Brown solution White precipitate
6a
Acetone
Clear solution with white precipitate
6b
Chemical Equations:
6a
+ I2 + OH- No reaction
+ I2 + OH- No reaction
6b
DISCUSSION
This experiment is all about performing tests in order to know whether which
of the following compounds are aldehydes and which are ketones.
In the general test for Carbonyl compounds, 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine was
used. Aldehydes and ketones react with a number of nitrogen containing compounds
through nucleophilic addition and subsequent loss of water to give products that
havea carbon nitrogen double bond. The color of the hydrazone precipitate formed is
often a guide to the amount f conjugation in the original aldehyde or ketone.
Unconjugated ketones such as cyclohexanone often give a yellow solid, while
conjugated ketones such as acetophenone give orange to red solids. Compounds
which are highly conjugated give red solids. 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine already was
orange-red itself; thus the color must be judged with caution. There were three test
tubes prepared, each one for a different test compounds; one for formaldehyde, one
for benzaldehyde and one for acetone. Each of the three test tubes was already
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
containing mL of 95% ethanol and a drop of each test compound was added to
each of which it is assigned. The test tube with
Second was the Tollens test which is the general test for Aldehydes.
Aldehydes are very easily oxidized to yield carboxylic acid or their salts if the reaction
is done in basic media. Since ketones are not readily oxidized, this test is a useful
method of differentiating between aldehydes and ketones. The solution used in this
test was an ammoniacal silver hydroxide solution which is a very mild oxidizing agent.
When the reaction is positive, a silver mirror sometimes is formed on the test tube
which is resulted from the reduction of the silver ion to metallic silver. Ordinary
ketones do not give a positive result in this test. Again, there were three test tubes
prepared, each for the different test compounds. Each test tube was occupied with
1mL of Tollens solution. A drop of each test compound were added to each assigned
test tube. The test tube with formaldehyde and Tollenssolution reacted positively and
formed a silver mirror, while the test tubes with bezaldehyde and acetone didnt react
positively. There was an emulsion formed in the test tube with benzaldehyde while
the test tube with acetone didnt show any reaction at all.
Third was the general test for Aliphatic Aldehydes or the Fehlings test. There
were two solutions used for this test; the Fehlings A, which was a blue aqueous
solution of copper(II) sulfate, and the Fehlings B, which was a clear and colorless
solution of aqueous potassium sodium tartate and a strong alkali. The formation of
brick-red precipitate of cuprous oxide indicates the positivity and indicates that the
compound is an aldehyde. There were three test tubes prepared, each for each
assigned test compound. Each test tube contains a half mL of the Fehlings A solution
and another half of the Fehlings B. A drop of each solution was added to each test
tube. Then each was warmed in a water bath. Only the test tube with the test
compound formaldehyde reacted positively, with a colored blue solution and brick-red
precipitate. The two other test tubes with benzaldehyde and acetone, respectively,
were also blue in color but didnt produce any precipitate.
Next was the oxidation by KMnO4, Potassium permanganate is a strong
oxidizing agent used to test the presence of an aldehyde or a ketone. If the
compound present is an aldehyde, it will be readily oxidized by the potassium
permanganate into a carboxylic acid due to the presence of the hydrogen
atom bonded to the carbonyl group. If the compound present is a ketone, it is
generally not oxidized by potassium permanganate, unless in extreme
conditions such as the presence of heat. If KMnO 4 is able to oxidize the
ketone, a cleavage mixture of two carboxylic acids would be present in the
solution. The result when 5 drops of 0.0002M KMnO4 to formaldehyde is a pink
solution. It was then acidified by dilute H2SO4, there was a red precipitate. On
the other hand, there was no reaction when acetone is used. Theoretically,
formaldehyde, benzaldehyde and cyclohexanone would positive results, since
they would be oxidized by potassium permanganate to form brown
manganese dioxide. On the other hand, acetone is not expected to produce a
positive result for potassium permanganate.
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
The test for methyl ketone group or the Iodoform test was the last test
performed. Methyl ketones can be distinguished from other ketones by their reaction
with iodine in a basic solution to yield iodoform (CH 3I) as a yellow colored precipitate.
However, acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) will also form iodoform under the same conditions.
Alcohols of the type described are easily oxidized to methyl ketones under the
conditions of the iodoform reaction. Two test tubes were prepared and occupied with
a solution of formaldehyde and acetone (5 drops of each compound with 2 mL water).
Five drops of I2 solution and a few drops of NaOH were added until the brown solution
was discharged. It was then warmed in water bath. After the water bath, the
formaldehyde solution with I2 and a few drops of NaOH was still brown in color and
produced some white precipitate. However, the acetone solution changed its solution
color from brown to white and like the formaldehyde solution, the acetone solution
produced some white precipitate.
References:
1. http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/carbonyls/oxidation.html
2. http://www.wikipremed.com/03_organicmechanisms.php?
mch_code=030208_030
3. http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/carbonyls/addelim.html
4. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fehling's_solution
Abstract
A qualitative analysis of aldehydes and ketones was conducted in the
experiment. Four test samples, namely acetone, formaldehyde and
benzaldehyde were used in the experiment. Various parameters regarding the
physical properties of aldehydes and ketones were determined using tests
such
as
the
oxidation
with
potassium
permanganate,
2,4dinitrophenylhydrazine test, Tollens test, Fehlings test, iodoform test and
action of formaldehyde on protein substances. The objectives of the
experiment were met since the physical properties of the aldehydes and
ketones were observed using the tests. However, some experimental results
deviated from the theoretical one, such as the non-oxidation of formaldehyde
with potassium permanganate. These unforeseen errors and deviations in the
result of the experiment can be attributed to the impurities that may have
altered the original result. The experiment would be very helpful in
establishing the identity of a certain unknown compound.
Conclusion
The objectives of the experiment were met after the experiment. This is
due to the fact that the physical properties of aldehydes and ketones were
observed using the four test samples. However, some unexpected results
were recorded, such as the non-oxidation of formaldehyde in potassium
permanganate and the negative results of acetone and formaldehyde.
The deviations of the experimental results from the theoretical one may be
attributed to the impurities present in some of the samples. These impurities
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
present may have hindered any reaction, or produced a new reaction which
may be the reason why the results deviated from the expected one.
In order to avoid the confusion in determining whether the compound is an
aldehyde or a ketone, it is recommended to conduct additional tests that
would better establish the identity of a certain compound
Procedure
A.
a. General Test for Carbonyl Compounds
1. 1 drop of the test compound was added in a test tube containing mL of
95% ethanol.
2. mL of 2,4-DNPH was added next.
3. Shaked and stand for few minutes.
b. Tollens Test
1. 1 mL of Tollens solution was transferred in a clean test tube.
2. 1 drop of test compound was then added.
3. Mixed and warmed in a water bath.
c. Fehlings Test
1. 1 drop of the test compound was added to a test tube containing mL of
Fehlings A and Fehlings B.
2. Mixed and warmed in a water bath.
B.
d. Action of Formaldehyde on Protein Substances
1. 2 mL of formaldehyde was mixed with 2 mL water in a small test tube.
2. Shaked.
3. Strip of gelatin sheet was divided into two.
4. strip of a gelatin sheet was dipped into the solution.
5. The sheet was removed.
6. Solubility was tested.
e. Oxidation by KMnO4
1. mL of formaldehyde was added to a test tube with 5 drops of 0.0002M
KMnO4.
2. Acidified with a few drops of dilute H2SO4.
3. Mixed.
f. Iodoform Test
1. Solutions of formaldehyde and acetone was made.
2. 5 drops of I2 solution was added and then dilute NaOH solution.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Aldehydes and Ketones Individual Laboratory ReportDokument12 SeitenAldehydes and Ketones Individual Laboratory ReportBernard Jomari Blancada Razote91% (64)
- Ace T AldehydeDokument5 SeitenAce T AldehydeAlfa FallurinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsDokument8 SeitenExperiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - & Carbonyl-Containing CompoundsPatricia Isabel Tayag100% (7)
- Brady's Tests Can Be Used To Qualitatively Detect The Carbonyl Functionality of ADokument6 SeitenBrady's Tests Can Be Used To Qualitatively Detect The Carbonyl Functionality of AEdon EduinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separation of The Colored Pigments Found in MalunggayDokument9 SeitenSeparation of The Colored Pigments Found in MalunggayZxyl BasilioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalDokument31 SeitenTest For Aldehyde/Ketone: Course No. Chem 222/ 122 Course Name: Organic Chemistry SessionalHasan RabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 9 Formal ReportDokument5 SeitenExperiment 9 Formal ReportTrishaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDokument7 SeitenClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Louise MondonedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 5352688982180245339Dokument11 Seiten2 5352688982180245339حسين محمد مطرود كاظمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Test For Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing Compound ReferenceDokument6 SeitenClassification Test For Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing Compound ReferenceErica OcheaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing Compounds AutosavedDokument9 SeitenClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing Compounds AutosavedCamille OngchuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment #8: Aldehydes and KetonesDokument12 SeitenExperiment #8: Aldehydes and Ketonesamrhkmh100% (1)
- Classification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsDokument7 SeitenClassification of Carbonyl and Hydroxyl Containing CompoundsSamantha Hope SyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 9 Title: Aldehyde and Ketones: Characterization of An Unknown ObjectiveDokument7 SeitenExperiment 9 Title: Aldehyde and Ketones: Characterization of An Unknown ObjectiveKristinne Daenielle GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- AldehydesDokument9 SeitenAldehydesNadine Jamih100% (2)
- Organic Chemical Tests (A2)Dokument3 SeitenOrganic Chemical Tests (A2)Kevin The Chemistry TutorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesDokument7 SeitenCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and KetonesLynde Claire Dilag100% (1)
- Notes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIDokument52 SeitenNotes On "ORGANIC CHEMISTRY" CBSE Class XIIMahesh AdhikariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehyde and KetonesDokument7 SeitenCarbonyl Compounds Aldehyde and KetonesJason Raquin Roque100% (1)
- Qualitative Analysis of Functional GroupsDokument8 SeitenQualitative Analysis of Functional GroupsMohamed Mohammed100% (1)
- CH102 Lab 5 Aldehydes and Ketones PDFDokument10 SeitenCH102 Lab 5 Aldehydes and Ketones PDFAnonymous caERsANoch keine Bewertungen
- Labreport 8 OrganicDokument12 SeitenLabreport 8 OrganicHajarul AjiehahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 8A Formal ReportDokument4 SeitenExperiment 8A Formal ReportEj RempilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- GROUP 3 - LABORATORY REPORT 5 - Compounds With Carbonyl GroupsDokument26 SeitenGROUP 3 - LABORATORY REPORT 5 - Compounds With Carbonyl GroupsJESSIE FREDRICK DALANIELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Test Expt 9Dokument9 SeitenClassification Test Expt 9Francia PalinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDokument5 SeitenClassification Tests For Hydroxyl and Carbonyl Containing CompoundsAcener Padua100% (1)
- Experiment 2-Aldehydes & Ketones: Fall 2021Dokument6 SeitenExperiment 2-Aldehydes & Ketones: Fall 2021atat2002Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 8ADokument74 SeitenExpt 8APearl Azucena100% (3)
- Aldehydes and Ketones: I. Abstract The Main Purpose of This Experiment Was To Determine The Reactions of Aldehydes andDokument5 SeitenAldehydes and Ketones: I. Abstract The Main Purpose of This Experiment Was To Determine The Reactions of Aldehydes andJoseph DenoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Laboratory AssignmentDokument44 SeitenPre Laboratory AssignmentJr Montero100% (3)
- Files-3-Lecture Notes CHEM-303 (Classification Tests)Dokument56 SeitenFiles-3-Lecture Notes CHEM-303 (Classification Tests)mmiliyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Lab 6Dokument19 SeitenOrganic Lab 6badirmhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem-No.-13 2Dokument5 SeitenChem-No.-13 2ho laNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Qualitative Analysis Aldehydes and KetonesDokument4 SeitenOrganic Qualitative Analysis Aldehydes and KetonesNitty MeYa50% (2)
- FM7 Labreport 2Dokument12 SeitenFM7 Labreport 2Jei y’allNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEsts For UnsaturationDokument16 SeitenTEsts For UnsaturationMahrishiShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl Carbonyl Containing CompoundsDokument8 SeitenExperiment 9 Classification Tests For Hydroxyl Carbonyl Containing CompoundsLovelyrabbit26Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compound-2Dokument20 SeitenCarbonyl Compound-2fishindasea00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab ReportDokument5 SeitenLab ReportAllan PinkertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDokument44 SeitenReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- What Are Carbonyl CompoundsDokument14 SeitenWhat Are Carbonyl CompoundsThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Tests For Carbonyl and Hydroxyl GroupsDokument10 SeitenClassification Tests For Carbonyl and Hydroxyl GroupsJennifer HerediaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12Dokument6 Seiten12NathaLie Sta ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6-283gDokument11 SeitenLab 6-283gAnonymous 4KuItFhNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Positive Result Is A Red-Orange Precipitate of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazoneDokument3 SeitenA Positive Result Is A Red-Orange Precipitate of 2,4-DinitrophenylhydrazoneBianca Del RosarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17Dokument28 SeitenReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones: Learning Activity No. 17angeline medallo100% (1)
- CHM1024 Report 5: Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesDokument14 SeitenCHM1024 Report 5: Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesAkmal Adib Fadzil96% (98)
- Reactions of Aldehydes and KetonesDokument7 SeitenReactions of Aldehydes and Ketones门门Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl CompoundsDokument40 SeitenCarbonyl CompoundsMiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- C C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CDokument5 SeitenC C C C C C CCC: CCC C C CCCCCCCC C C CCCC CCCCC CC CCC CC C CCC CCC CC CCCCC C CCC C CCCC CCC C CCCCCC CShan TiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldhyde Ketone AcidDokument30 SeitenAldhyde Ketone AcidSamratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Lab 6 chm207Dokument2 SeitenDiscussion Lab 6 chm2072023300959Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem31.1 Finals NotesDokument8 SeitenChem31.1 Finals NotesElla YapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Organic Chemistry (Experiment 7) Lim Wey LoonDokument24 SeitenLab Report Organic Chemistry (Experiment 7) Lim Wey LoonWEY LOON LIMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueDokument28 SeitenAldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids: Presented by GROUP 4 Psych 1-A Pacto Maribao Miranda Nalaunan NiqueMissy NalaunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Tests For Hydroxyl - and Carbonyl - Containing CompoundsDokument6 SeitenClassification Tests For Hydroxyl - and Carbonyl - Containing CompoundsShaira Jhann L. Rosales50% (2)
- The Cerric Nitrate Test: Shows Positive Test ForDokument9 SeitenThe Cerric Nitrate Test: Shows Positive Test ForPraveen KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Paper Exp 7Dokument6 SeitenScientific Paper Exp 7Brent TenorioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herbal MedicineDokument33 SeitenHerbal MedicineStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCLEXnotesDokument20 SeitenNCLEXnotesStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procedures and Diagnostics - 025003Dokument6 SeitenProcedures and Diagnostics - 025003Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids - Electrolyte - 022244Dokument20 SeitenFluids - Electrolyte - 022244Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VS - Labs - 030730Dokument12 SeitenVS - Labs - 030730Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MaternalDokument5 SeitenMaternalStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV1Dokument10 SeitenCV1Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLG IV TherapyDokument10 SeitenTLG IV TherapyStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLG SuctioningDokument5 SeitenTLG SuctioningStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JustificationDokument2 SeitenJustificationStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA Case StudyDokument3 SeitenCA Case StudyStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biblio CPDokument2 SeitenBiblio CPStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SuctioningDokument11 SeitenSuctioningStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM107ESCALADokument3 SeitenNCM107ESCALAStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument2 SeitenAbstractStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final (Translated - Nabila Dipatuan)Dokument12 SeitenFinal (Translated - Nabila Dipatuan)Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA2Dokument5 SeitenCA2Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Chapter 1 The ProblemDokument17 SeitenFinal Chapter 1 The ProblemStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Chapter 2 RRLDokument17 SeitenFinal Chapter 2 RRLStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV1Dokument10 SeitenCV1Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pallia by MMDokument3 SeitenPallia by MMStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insect Sting - Concept MapDokument2 SeitenInsect Sting - Concept MapStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WitDokument2 SeitenWitStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV1Dokument10 SeitenCV1Stephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Chapter 3 MethodologyDokument31 SeitenFinal Chapter 3 MethodologyStephanie Joy Escala100% (3)
- CPDokument3 SeitenCPStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research ShizDokument2 SeitenResearch ShizStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLG - PostopDokument3 SeitenTLG - PostopStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative PathophysiologyDokument4 SeitenNarrative PathophysiologyStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument1 SeiteAbstractStephanie Joy EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastomers Chemical Compatibility CharDokument12 SeitenElastomers Chemical Compatibility CharsubrataNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Acjc CH h2 p1 PrelimDokument19 Seiten2012 Acjc CH h2 p1 Prelimetud3clNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section Module1 - ExerSheetDokument3 SeitenSection Module1 - ExerSheetArnel FelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus For Bachelor of Science (Biotechnology, Chemistry, Botany) Academic Year (2012)Dokument62 SeitenSyllabus For Bachelor of Science (Biotechnology, Chemistry, Botany) Academic Year (2012)rutwickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Dokument7 SeitenGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks: BackgroundDokument14 SeitenThe Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks: BackgroundGrad OanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klucel HPC BookletDokument26 SeitenKlucel HPC BookletΜανωλης ΛοιζοςNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering of HalogenasesDokument123 SeitenEngineering of HalogenasesNick PapasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Growth Processes: Transpiration, Photosynthesis, and RespirationDokument12 SeitenPlant Growth Processes: Transpiration, Photosynthesis, and RespirationAbhilash ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Conversion of Carboxylic Acids To KetonesDokument5 SeitenThe Conversion of Carboxylic Acids To KetonesKybernetikumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shri AMM Urugappa Hettiar Esearch Entre: M C R CDokument8 SeitenShri AMM Urugappa Hettiar Esearch Entre: M C R CSenthil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biogeochemical CycleDokument22 SeitenBiogeochemical CycleFrncesca MacalindongNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRB Silanes Presentation PDFDokument48 SeitenBRB Silanes Presentation PDFgokhanyaparNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEB USP Glyphosate Pesticide Beer and Wine REPORT 022619Dokument23 SeitenWEB USP Glyphosate Pesticide Beer and Wine REPORT 022619LaRepublica DigitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Singapore SDS Techtrol Gold IIIDokument10 SeitenSingapore SDS Techtrol Gold IIIBrender VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- En - Silcoset 152 TDS - 2Dokument1 SeiteEn - Silcoset 152 TDS - 2Андрей МошкинNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ethylene BasicsDokument53 SeitenEthylene Basicskingcobra008100% (5)
- Ascorbic Acid EstimationDokument1 SeiteAscorbic Acid EstimationMahamud Hasan PrinceNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Damage and RepairDokument23 SeitenDNA Damage and RepairbadrhashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument4 SeitenPDFLaboratorio InkctechNoch keine Bewertungen
- AlcoholDokument20 SeitenAlcoholhahahahahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste Recycling and Application Possibilities: A ReviewDokument9 SeitenPolyethylene Terephthalate Waste Recycling and Application Possibilities: A ReviewGabriel AparicioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hespiridin PDFDokument4 SeitenHespiridin PDFanon_753148412Noch keine Bewertungen
- Milk Powder and Cream PowderDokument5 SeitenMilk Powder and Cream PowderNat TangsuphoomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phytochemical Analysis of Plant ExtractsDokument23 SeitenPhytochemical Analysis of Plant ExtractsjaninasuzetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Utilization of Waste Plastic Water Bottle As A Modifier For Asphalt Mixture PropertiesDokument20 Seiten2015 Utilization of Waste Plastic Water Bottle As A Modifier For Asphalt Mixture PropertiesKhalil ZaaimiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0005.Dokument10 SeitenWa0005.samarkhatri300Noch keine Bewertungen
- VectorDokument43 SeitenVectorRohini KeshavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State PolymerizationDokument28 SeitenSolid State PolymerizationDarkLugiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Format of Unit Plan/Scheme of Work: A Learner Can Explain 1. Biology 8th Ed by Campbell and ReeceDokument19 SeitenFormat of Unit Plan/Scheme of Work: A Learner Can Explain 1. Biology 8th Ed by Campbell and ReeceMutaganda Ami fideleNoch keine Bewertungen