Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lipids Worksheet
Hochgeladen von
Natalie PembertonCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lipids Worksheet
Hochgeladen von
Natalie PembertonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Natalie Pemberton-Parris00027917
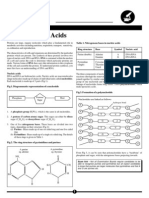
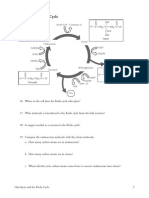
CHEM 121 Lipids Worksheet (53 marks)
1.
Some lipids are considered to be amphipathic because they have a polar and non-polar part.
2.
For a 12 carbon fatty acid, what is the value of n? 10
3.
Is the fatty acid in figure 1 a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid? Saturated
Figure 1
4.
Is a cis fatty acid saturated or unsaturated?
5.
Is a Trans fatty acid saturated or unsaturated?
6.
Listed below are three fatty acids:
Unsaturated
Unsaturated
18:2 cis 9, 12
18:0
18:2 Trans 9, 12
Write them in order of increasing melting point (Lowest Highest)
18:2 cis 9, 12-----> 18:2 Trans 9, 12 ----> 18:0
7.
Listed below are three fatty acids:
18:1 cis 9 oleic acid
18:2 cis 9, 12 linoleic acid
18:3 cis 9, 12, 15 -linolenic acid
Write them in order of decreasing melting point (Highest Lowest)
18:1 cis 9 oleic acid ---> 18:2 cis 9, 12 linoleic acid ---> 18:3 cis 9, 12, 15 a-linolenic acid
8.
(a) Draw the structure of the fatty acid 18:3 cis
9,12,15
(b) Rename the above fatty acid using the symbol
9.
18: 3 cis 3, 6, 9
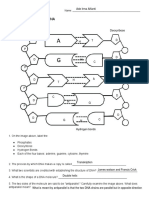
A glyceride is a molecule made from a linkage(s) between two other molecules. State the
names of those two molecules.
1. Glycerol
2. Fatty Acid
10.
Name the important linkage which is present within a glyceride.
Esther Linkage
11.
A diglyceride contains how many of the linkages mentioned in question 9 and 10.
1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids and 2 Esther linkages
12.
A Glycerophospholipids is made up of a one glycerol backbone, two fatty acids and a
phosphate group which is linked to a variable group.
13.
Name two important linkages present within a Glycerophospholipids
1. Ester Linkage
2. Phosphate Ester Linkage
14.
The Sphingolipids ceramide is formed between a sphingosine molecule and an N-linked fatty
acid molecule.
15.
The linkage formed from the reaction of the amino group on sphingosine and a carboxylic
group from another molecule is called an amide bond linkage.
16.
A cholesterol ester molecule is formed from a carboxylic group of the fatty acid molecule and a
hydroxyl group of a cholesterol.
17.
Describe the structure of a lipoprotein.
The core of these spherical particles contains primarily cholesteryl ester and triglyceride. These
insoluble molecules are surrounded by a coating of proteins and phospholipids that are
amphipathic; that is, they have both polar and nonpolar regions.
18.
What is the function of a lipoprotein?
Lipoproteins transport triglycerides, cholesterol and cholesteryl esters through the bloodstream.
19.
Lipoproteins are found traveling mainly through the bloodstream
20.
Chylomicrons transport mainly the lipid triglycerides
21.
Chylomicrons are produced in the small intestine
22.
What Apo lipoprotein does a nascent (newly-formed) chylomicron need to obtain in order for it
to be able to get rid of its main lipid content? Apo c-II
23.
From which other lipoprotein does the nascent chylomicron obtain the Apo lipoprotein in
question 22? HDLs
24.
What is the function of the Apo lipoprotein Apo C-II? (1mark)
Activates an enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) and return to HDLs
25.
What is the function of the Apo lipoprotein Apo E?
(1mark)
Apo E acts as a navigator to direct chylomicrons to the liver cells.
26.
Where is the Apo E receptor located?
27.
Where are VLDLs produced?
28.
VLDLs obtain Apo-C-II and Apo E from which other lipoprotein?
29.
How are VLDLs converted into IDLs?
(1 MARK)
Apo C-II activates the enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL). It then hydrolyzes triacylglycerol into
fatty acids and glycerol, thereby converting VLDLs into IDLs
30.
How are IDLs converted into LDLs?
(1 mark)
Apo C-II and some Apo E return to HDLs, thereby converting IDLs into LDLs
31.
Cholesterol is produced naturally in cells and so there is no need for LDLs to be too high.
a. Cholesterol is stored as cholesterol esters in cells
(1 mark)
b. Cholesterol is converted into its storage product in cells by the enzyme ACAT) (1mark)
c. High levels of LDLs can lead to which condition?
Atherosclerosis (1 mark)
32.
HDLs are released from the liver and small intestine. (2 marks)
33.
HDLs take up excess cholesterol from peripheral tissues, other lipoproteins and cell
membranes. (3 marks)
34.
The Apo lipoprotein Apo A1 is responsible for activating the enzyme PCAT present on HDLs.
What is the function of PCAT? To esterify cholesterol to cholesteryl esters. (1 mark)
(1 mark)
(1 mark)
On the cell membrane of the Liver cell
In the Liver
HDLs
35.
LDL lipoproteins can be modified by chemical reactions such as oxidations. Such modified
LDLs lead to the formation of what medical condition?
(1mark) Atherosclerosis
36.
Lipoprotein (a) is associated with what medical condition? Coronary artery disease (1 mark)
37.
Two factors that increase levels of Lipoprotein (a) are: (2 marks)
1. A diet high in trans-fatty acids
2. Genetics
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Central Dogma Review KEYDokument8 SeitenCentral Dogma Review KEYeula faith miracle andam0% (1)
- What Are CarbohydratesDokument36 SeitenWhat Are CarbohydratesPINNACLE CAFENoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Ecology Graph Worksheet - KEY PDFDokument4 SeitenPopulation Ecology Graph Worksheet - KEY PDFBinal DaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic AcidsDokument3 SeitenNucleic AcidsBio Sciences100% (2)
- Carbohydrates WorksheetDokument4 SeitenCarbohydrates WorksheetNatalie Pemberton86% (7)
- Chapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellDokument14 SeitenChapter 4: Chemical Composition in A CellEma FatimahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Cycle RegulationDokument23 SeitenCell Cycle RegulationShikhaj ArmaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Respiration WorksheetDokument3 SeitenCellular Respiration WorksheetKlit MejanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Great Plains Laboratory Clinician ManualDokument80 SeitenGreat Plains Laboratory Clinician ManualAnonymous DiWfMNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complications of PregnancyDokument40 SeitenComplications of PregnancyNatalie Pemberton100% (1)
- Review The Structure of DNA AdeDokument1 SeiteReview The Structure of DNA AdeADE IRMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet With ANSWERSDokument6 SeitenCell Membrane Coloring Worksheet With ANSWERSCortland Leslie100% (1)
- Why Animals Don't Get Heart Attacks - But People Do!Dokument13 SeitenWhy Animals Don't Get Heart Attacks - But People Do!selvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Metabo (IsmDokument8 SeitenIntro To Metabo (IsmManila MedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemical Basis of LifeDokument13 SeitenThe Chemical Basis of Lifezulfikarleghari100% (1)
- LIPIDS D PharmDokument65 SeitenLIPIDS D PharmMadhuri poulkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 McKee Enzyme KineticsDokument79 SeitenChapter 6 McKee Enzyme KineticsSuwahono, M.PdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 Biomolecules ReviewerDokument9 SeitenScience 10 Biomolecules ReviewerTasha Heart QuiambaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 7 - Sensory SystemDokument46 SeitenLab 7 - Sensory SystemNatalie Pemberton100% (1)
- Hunter's Spring Wildfit Back To SpringDokument9 SeitenHunter's Spring Wildfit Back To Springnorm.deslandesNoch keine Bewertungen
- OET ReadingDokument12 SeitenOET ReadingWarangkana89% (137)
- Cell Respiration Worksheet KEYDokument3 SeitenCell Respiration Worksheet KEYerikabeltranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turmeric ProjectDokument21 SeitenTurmeric ProjectNARESH WALIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Respiration NotesDokument10 SeitenCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- NEJM - Orion-10 and Orion-11 - 2020-03-18 ProtocolDokument598 SeitenNEJM - Orion-10 and Orion-11 - 2020-03-18 ProtocolMets FanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concentration of SolutionsDokument4 SeitenConcentration of SolutionsPRANAV BANSAL100% (1)
- Lec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCDokument12 SeitenLec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCJonah Micah MangacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krebs Cycle WorksheetDokument3 SeitenKrebs Cycle Worksheetapi-569197188100% (1)
- Pregnancy Discomforts/ Minor Disorders of Pregnancy:: Nausea and VomitingDokument5 SeitenPregnancy Discomforts/ Minor Disorders of Pregnancy:: Nausea and VomitingNatalie Pemberton100% (1)
- Glycolysis Krebscycle Practice Questions SCDokument2 SeitenGlycolysis Krebscycle Practice Questions SCapi-323720899Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Metabolism WorksheetDokument3 SeitenCarbohydrate Metabolism WorksheetNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipid Practice WorksheetDokument2 SeitenLipid Practice WorksheetDana FransenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 5 Reading WorksheetDokument3 SeitenChap 5 Reading WorksheetSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate - Lecture NotesDokument7 SeitenCarbohydrate - Lecture NotesKate Taylor100% (1)
- 13 Cellular Respiration-KEYDokument6 Seiten13 Cellular Respiration-KEYgilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - Metabolism & Bioenergetics (Part 2) PDFDokument69 SeitenChapter 2 - Metabolism & Bioenergetics (Part 2) PDFdarren100% (2)
- Biomolecule Test Review 2016 - KeyDokument6 SeitenBiomolecule Test Review 2016 - KeyVannyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Basis of LifeDokument38 SeitenChemical Basis of LifeFernadez RodisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis Worksheet 2 KeyDokument7 SeitenPhotosynthesis Worksheet 2 KeysarfarazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intracellular TransportDokument66 SeitenIntracellular Transportalvitakhoridatul100% (1)
- Feeder Pathways For GlycolysisDokument62 SeitenFeeder Pathways For GlycolysisAbdikafar AbdullahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Structure and FunctionDokument2 SeitenDNA Structure and FunctionAliza SaddalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2103 Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet KEYDokument6 Seiten2103 Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet KEYJM AlicbusanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipid Chemistry: BiochemistryDokument14 SeitenLipid Chemistry: BiochemistryManila Med0% (1)
- Biochemistry: CarbohydrateDokument10 SeitenBiochemistry: CarbohydrateAsif Hasan NiloyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Across Cell MembraneDokument38 SeitenTransport Across Cell MembraneViswadeep DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme and PH Simulation WorksheetDokument2 SeitenEnzyme and PH Simulation WorksheetPurePureMilkNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Worksheet #2Dokument2 SeitenDNA Worksheet #2JOYCE S. SAGANoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrates: Dr. V. PrabhakaranDokument50 SeitenCarbohydrates: Dr. V. PrabhakaranDesire ramsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 (The Fundamental Unit of Life) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Dokument22 SeitenUnit 5 (The Fundamental Unit of Life) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Nikhil SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryDokument16 SeitenBiomolecules: Biomolecules, Polymers, Chemistry in Everyday Life & Env. ChemistryIshanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate QuizDokument5 SeitenCarbohydrate QuizJoshua Bailey100% (2)
- Fa Lipid MetabDokument4 SeitenFa Lipid MetabJoy VergaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Lecture 15 Biological Membranes - 1Dokument27 SeitenBiochemistry Lecture 15 Biological Membranes - 1Professor Rakesh Sharma Biochemistry Lectures100% (1)
- Classification of Protein Based On CompositionDokument4 SeitenClassification of Protein Based On CompositionHambaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabolism of Ketone BodiesDokument38 SeitenMetabolism of Ketone BodiesJavedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism PDFDokument36 Seiten8 Carbohydrate Metabolism PDFDayne Ocampo-SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 5 Worksheet AnswersDokument5 SeitenWeek 5 Worksheet AnswersaskldhfdasjkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochemistry Notes For BoardsDokument35 SeitenBiochemistry Notes For BoardsUjjwal PyakurelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes WorksheetDokument2 SeitenEnzymes WorksheetNatalie Pemberton100% (1)
- B.3 - Lipid WorksheetDokument2 SeitenB.3 - Lipid WorksheetNadim KattanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDokument6 SeitenBio Molecule Review WorksheetMari LouNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProteinDokument16 SeitenProteinRosnadia RosliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of LipidsDokument18 SeitenClassification of LipidsD Kaur100% (1)
- STUDENT WORKSHEET HydrocarbonDokument5 SeitenSTUDENT WORKSHEET HydrocarbonFiryal Nabilah Q ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Genes ChromosomesDokument17 SeitenGenes Chromosomesapi-445198464Noch keine Bewertungen
- HtwoO and BufferDokument7 SeitenHtwoO and BufferManila MedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology WorksheetDokument2 SeitenBiology WorksheetAzariah Anuar100% (1)
- Notes C19 121Dokument21 SeitenNotes C19 121Uche KennethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipioprotein Lec11 PDFDokument44 SeitenLipioprotein Lec11 PDFحسن محمد سعيد جاسمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lipids Function and StructureDokument60 SeitenLipids Function and StructureIndra GunawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Drugs in The Institutions... AgenciesDokument6 SeitenManagement of Drugs in The Institutions... AgenciesNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction WorksheetDokument2 SeitenIntroduction WorksheetNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzymes WorksheetDokument2 SeitenEnzymes WorksheetNatalie Pemberton100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids WorksheetDokument4 SeitenNucleic Acids WorksheetNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amino Acids and Proteins WorksheetDokument2 SeitenAmino Acids and Proteins WorksheetNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Midsummer Night's DreamDokument59 SeitenA Midsummer Night's DreamLarissa A.Noch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Forms of ContraceptionDokument2 Seiten10 Forms of ContraceptionNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 6 - Nervous SystemDokument33 SeitenLab 6 - Nervous SystemNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 4 - The Skeletal SystemDokument38 SeitenLab 4 - The Skeletal SystemNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 - Organisation of The Human BodyDokument14 SeitenLab 1 - Organisation of The Human BodyNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 5 - Bones & JointsDokument20 SeitenLab 5 - Bones & JointsNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3 - Part 2 Tissues and The IntegumentaryDokument19 SeitenLab 3 - Part 2 Tissues and The IntegumentaryNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 3 - Part 1 Tissues and The IntegumentaryDokument28 SeitenLab 3 - Part 1 Tissues and The IntegumentaryNatalie PembertonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 2 - Microscopy and The CellDokument44 SeitenLab 2 - Microscopy and The CellNatalie Pemberton100% (1)
- Papaya Leaf ExtractDokument12 SeitenPapaya Leaf ExtractYamunaa ElencovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casestudy29 OpenabdomenDokument14 SeitenCasestudy29 Openabdomenapi-301118772100% (1)
- Use of Food Supplements As Nutricosmetics in Health and Fitness A Review - 2014Dokument14 SeitenUse of Food Supplements As Nutricosmetics in Health and Fitness A Review - 2014ranasoftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Simultaneous Administration of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Alkylbenzene Sulfonic Acid Salt in RatsDokument17 SeitenEffect of Simultaneous Administration of Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Alkylbenzene Sulfonic Acid Salt in RatsSh1vaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LDL Cholesterol (Direct) BXC0431 A25 A15Dokument2 SeitenLDL Cholesterol (Direct) BXC0431 A25 A15jef1234321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fatty Acid Catabolism PDFDokument25 SeitenFatty Acid Catabolism PDFLuceroLalaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sumit Kumar Lab ReportsDokument8 SeitenSumit Kumar Lab ReportssumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Name Value Unit Biological Ref Interval Biochemistry Liver Function Test (LFT)Dokument7 SeitenTest Name Value Unit Biological Ref Interval Biochemistry Liver Function Test (LFT)Himanshu GarkhelNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Endo Eval Exam IIDokument7 SeitenGI Endo Eval Exam IICraig Jesse B. LardizabalNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Stubborn Fat SolutionDokument50 SeitenThe Stubborn Fat SolutionMohamed Elkhder100% (2)
- Accucare Control SeraDokument2 SeitenAccucare Control SeraSubodhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concise Review: Importance of Probiotics Yogurt For Human Health ImprovementDokument6 SeitenConcise Review: Importance of Probiotics Yogurt For Human Health ImprovementIOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artigo Microbioma Intestinal e Redução Níveis ColesterolDokument16 SeitenArtigo Microbioma Intestinal e Redução Níveis ColesterolMaria Júlia CintraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cholesterol: Low Carbohydrate High Fat Diet PlanDokument44 SeitenCholesterol: Low Carbohydrate High Fat Diet PlanCylubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yan Sri MardadiDokument37 SeitenYan Sri Mardadika em jeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Savva2016 PDFDokument8 SeitenSavva2016 PDFHenry Rivero GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs) About Lipitor and CholesterolDokument8 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions (Faqs) About Lipitor and CholesterolAnurag DabralNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review 2.1. Shodhana A. Ayurvedic System of ShodhanaDokument93 SeitenLiterature Review 2.1. Shodhana A. Ayurvedic System of ShodhanasiesmannNoch keine Bewertungen
- EN GoBarley Antioxidants FinalDokument7 SeitenEN GoBarley Antioxidants FinalKamal UddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MBR 2019 - Biochemistry HandoutsDokument66 SeitenMBR 2019 - Biochemistry HandoutsEiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank DifficultDokument11 SeitenQuestion Bank DifficultkvmahadevNoch keine Bewertungen
- February 7 2013 Mount Ayr Record-NewsDokument16 SeitenFebruary 7 2013 Mount Ayr Record-NewsMountAyrRecordNewsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antihyperlipidemic AgentsDokument14 SeitenAntihyperlipidemic AgentsMerlin DineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population QuestionsDokument79 SeitenPopulation QuestionsBooNoch keine Bewertungen