Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Electromagnetic Induction Guide
Hochgeladen von
WOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Electromagnetic Induction Guide
Hochgeladen von
WCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 22
Electromagnetic
Induction
Induced Emf and Induced Current
There are a number of ways a magnetic field can be used to
generate an electric current.
It is the changing field that produces the current.
Induced Emf and Induced Current
The current in the coil is called the induced current because it is brought
about by a changing magnetic field.
Since a source emf is always needed to produce a current, the coil behaves
as if it were a source of emf. This emf is known as the induced emf.
Induced Emf and Induced Current
An emf can be induced by changing the
area of a coil in a constant magnetic field
In each example, both an emf and a current are induced because
the coil is part of a complete circuit. If the circuit were open, there
would be no induced current, but there would be an induced emf.
The phenomena of producing an induced emf with the aid of a
magnetic field is called electromagnetic induction.
Motional Emf
THE EMF INDUCED IN A MOVING CONDUCTOR
Each charge within the conductor
is moving and experiences a
magnetic force
F qvB
The separated charges on the
ends of the conductor give rise
to an induced emf, called a
motional emf.
Motional Emf
Motional emf when v, B,
and L are mutually
perpendicular
E vBL
Magnetic Flux
MOTIONAL EMF AND MAGNETIC FLUX
magnetic flux
BA
Magnetic Flux
o
E
t to
t
Magnetic Flux
GENERAL EXPRESSION FOR MAGNETIC FLUX
BA cos
Magnetic Flux
BA cos
Magnetic Flux
GRAPHICAL INTERPRETATION OF MAGNETIC FLUX
The magnetic flux is proportional
to the number of field lines that pass
through a surface.
Faradays Law of Electromagnetic Induction
FARADAYS LAW OF ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
The average emf induced in a coil of N loops is
N
E N
t
t to
SI Unit of Induced Emf: volt (V)
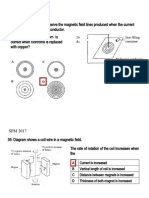
Lenzs Law
LENZS LAW
The induced emf resulting from a changing magnetic flux has a
polarity that leads to an induced current whose direction is such
that the induced magnetic field opposes the original flux change.
Reasoning Strategy
1. Determine whether the magnetic flux that penetrates the coil
is increasing or decreasing.
2. Find what the direction of the induced magnetic field must be
so that it can oppose the change influx by adding or subtracting
from the original field.
3. Use RHR-2 to determine the direction of the induced current.
Lenzs Law
Conceptual Example The Emf Produced by a Moving Magnet
A permanent magnet is approaching a
loop of wire. The external circuit consists
of a resistance. Find the direction of the
induced current and the polarity of
the induced emf.
Lenzs Law
Conceptual Example The Emf Produced
by a Moving Copper Ring.
There is a constant magnetic field directed
into the page in the shaded region. The field
is zero outside the shaded region. A copper
ring slides through the region.
For each of the five positions, determine whether
an induced current exists and, if so, find its
direction.
Applications of Electromagnetic Induction to the Reproduction of Sound
Applications of Electromagnetic Induction to the Reproduction of Sound
Applications of Electromagnetic Induction to the Reproduction of Sound
The Electric Generator
HOW A GENERATOR PRODUCES AND EMF
The Electric Generator
Emf induced in a rotating planar coil
E NAB sin t Eo sin t
2 f
The Electric Generator
E Eo sin t
The Electric Generator
THE ELECTRICAL ENERGY DELIVERED BY A GENERATOR
AND THE COUNTERTORQUE
When the generator is delivering current, there is a magnetic force
acting on the coils.
The Electric Generator
The magnetic force gives rise to a
countertorque that opposes the
rotational motion.
The Electric Generator
THE BACK EMF GENERATED BY AN ELECTRIC MOTOR
When a motor is operating, two sources of emf are present: (1) the
applied emf V that provides current to drive the motor, and (2) the
emf induced by the generator-like action of the rotating coil.
The Electric Generator
Consistent with Lenzs law, the induced emf acts to oppose the
applied emf and is called back emf.
V E
I
R
Transformers
A transformer is a device for increasing or decreasing an ac
voltage.
Es N s
Ep N p
t
Es N s
Ep N p
Transformers
Transformer
equation
Vs N s
Vp N p
Transformers
I s Vp N p
I p Vs N s
A transformer that steps up the voltage simultaneously steps
down the current, and a transformer that steps down the voltage
steps up the current.
Transformers
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Induction: How Changing Magnetic Fields Generate Electric CurrentsDokument17 SeitenInduction: How Changing Magnetic Fields Generate Electric Currentsbatraz79Noch keine Bewertungen
- p112 Lecture13 PDFDokument20 Seitenp112 Lecture13 PDFGauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ProjectDokument8 SeitenPhysics ProjectVanshika DariraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument8 SeitenElectromagnetic InductionSanjay GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedDokument9 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedStudies 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction: A Project By: Faraz ThakurDokument16 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction: A Project By: Faraz ThakurFaraz Thakur50% (2)
- Physics ProjectDokument15 SeitenPhysics ProjectDebkanti Gupta Bhaya0% (1)
- Chapter 3 EMIDokument52 SeitenChapter 3 EMIMayank MeghaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Apparatus and DevicesDokument24 SeitenElectrical Apparatus and DevicesMadelo, Allysa Mae, M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMI Important Questions-1Dokument13 SeitenEMI Important Questions-1SBU eduNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Unit 4 EM Original PDFDokument18 Seiten12 Unit 4 EM Original PDFSiva VijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iitm Diploma 1st Year FeeeDokument62 SeitenIitm Diploma 1st Year Feeeblackgoku1512007Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument23 SeitenUntitledArnab DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Physics 2 - LessonsDokument24 SeitenGeneral Physics 2 - LessonsAshley NicoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument18 SeitenElectromagnetic Inductionwakki 10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDokument3 SeitenPhysics Investigatory Projectsivansh shuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics TheoryDokument6 SeitenPhysics Theorylalit palNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eec Microproject 2Dokument4 SeitenEec Microproject 2Prathamesh PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument10 SeitenElectromagnetic InductionDeboprita BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Electromagnetic InductionDokument19 Seiten1 Electromagnetic InductiondbgareslNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mu PhysicsDokument12 SeitenMu PhysicsMONISHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch31&32 Electromagnetism SlidesDokument38 SeitenCh31&32 Electromagnetism SlidesVent101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction: Electro MagnetDokument8 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction: Electro MagnetAbdulRehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Electrical Engineering10ELE25Dokument78 SeitenBasic Electrical Engineering10ELE25jpsridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report on Electromagnetic InductionDokument8 SeitenProject Report on Electromagnetic Inductionthe best ofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction ExplainedDokument49 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction ExplainedthebestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy ProjectDokument18 SeitenPhy ProjectRohit rajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CertificateDokument17 SeitenCertificatecᴘcтԍᴀмιɴԍ YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter31 Faraday&LenzDokument25 SeitenChapter31 Faraday&Lenzmalini72Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH6 Formula SheetDokument11 SeitenCH6 Formula SheetNancy SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic InductonDokument12 SeitenElectromagnetic InductonAishwarya TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic InductionDokument11 SeitenElectromagnetic InductionblueegofxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dheeraj 1Dokument16 SeitenDheeraj 1dheeraj singhrajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Magnetic Induction Final 1Dokument52 SeitenChapter 5 Magnetic Induction Final 1Salve Marie DoratoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faraday Law of Induction, Induced Emf and Electric Field, Eddy CurrentDokument17 SeitenFaraday Law of Induction, Induced Emf and Electric Field, Eddy Currentzaini.iqbal761Noch keine Bewertungen
- 36 Faraday's Law of em Induction Version 1Dokument6 Seiten36 Faraday's Law of em Induction Version 1nidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction GuideDokument22 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction GuideKunal AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 12th ProjectDokument11 SeitenPhysics 12th ProjectVed RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 30 (1) .MagneticDokument29 SeitenChapter 30 (1) .MagneticOsama HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Machines AssignmentDokument95 SeitenElectrical Machines AssignmentNivedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction Chapter SummaryDokument15 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction Chapter SummaryBeverly PamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Induction ArmanDokument12 SeitenElectromagnetic Induction ArmanMalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 NotesDokument20 SeitenChapter 15 NotesMian EjazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairaneDokument18 SeitenPhysics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairanePrerana PorechaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3B Electromagnetic InductionDokument6 SeitenChapter 3B Electromagnetic InductionTaonga NhambiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Electromagnetic InductionDokument4 SeitenIntroduction to Electromagnetic InductionRajender ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module2 Lesson3Dokument5 SeitenModule2 Lesson3Jerald AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISC12 Physics Project668Dokument19 SeitenISC12 Physics Project668Ruhi BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.3 Electromagnetic InductionDokument117 Seiten8.3 Electromagnetic InductionPAKK20622 CHARLENE LIONG YAN TINGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii Electromagnetic PDFDokument19 SeitenPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek Class Xii Electromagnetic PDFDevang HandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectroMagnetic InductionDokument8 SeitenElectroMagnetic InductionRobin Singh100% (1)
- Physics ProjectDokument20 SeitenPhysics Projectblah68194Noch keine Bewertungen
- MOTOR-GENERATOR FUNDAMENTALSDokument9 SeitenMOTOR-GENERATOR FUNDAMENTALSzen anastacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 31 Faraday S LawDokument27 SeitenCHAPTER 31 Faraday S LawSattishZeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faraday's LawDokument5 SeitenFaraday's LawSyeda Rutab AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class-Xii-Electromagnetic InductionDokument19 SeitenClass-Xii-Electromagnetic Inductionjananisrinivasan46000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Self Induction and Mutual InductionDokument24 SeitenSelf Induction and Mutual InductionRavi Ranjan89% (9)
- Electomagnetic Induction:-Faraday's Law: Project ReportDokument17 SeitenElectomagnetic Induction:-Faraday's Law: Project ReportSushantSinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsVon EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- A New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Von EverandA New Approach to the Quantum Theory: Think Physics, #7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rizal The HeroDokument24 SeitenRizal The HeroRichard de la Cruz100% (1)
- DNA Extraction Whole BloodDokument27 SeitenDNA Extraction Whole BloodW0% (1)
- Ohms Law Problem 3Dokument9 SeitenOhms Law Problem 3WNoch keine Bewertungen
- UltimateBeginnerHandbookPigeonRacing PDFDokument21 SeitenUltimateBeginnerHandbookPigeonRacing PDFMartinPalmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theology of The BodyDokument5 SeitenTheology of The BodyWNoch keine Bewertungen
- JusticeDokument16 SeitenJusticeWNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFC On Human SexualityDokument2 SeitenCFC On Human SexualityW100% (1)
- Extracting Dna From Whole BloodDokument21 SeitenExtracting Dna From Whole BloodWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Percent Difference ErrorDokument1 SeitePercent Difference ErrorVanessa AlmeidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Social MissionDokument16 SeitenThe Social MissionWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 BDokument5 SeitenExperiment 1 BWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base PropertiesDokument5 SeitenAcid Base PropertiesWNoch keine Bewertungen
- L2b - Cytoskeleton PDFDokument7 SeitenL2b - Cytoskeleton PDFWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rosaceae (Rose Family) (Genus N-Z)Dokument29 SeitenRosaceae (Rose Family) (Genus N-Z)WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Dignity and Human RightsDokument7 SeitenHuman Dignity and Human RightsWilcen John V. Padolina100% (1)
- L2a - CytoplasmDokument6 SeitenL2a - CytoplasmWNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human WorkDokument12 SeitenThe Human WorkWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryolec Ch. 11Dokument4 SeitenEmbryolec Ch. 11WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Dignity and Human RightsDokument7 SeitenHuman Dignity and Human RightsWilcen John V. Padolina100% (1)
- Assess Environmental Impact Hydroelectric Power PlantDokument1 SeiteAssess Environmental Impact Hydroelectric Power PlantWNoch keine Bewertungen
- p6 GRP HWDokument1 Seitep6 GRP HWWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 4: Work, Energy and PowerDokument2 SeitenExperiment 4: Work, Energy and PowerW0% (2)
- 8 Rotational KinematicsDokument25 Seiten8 Rotational KinematicsWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revised Expt 5 Physics LabDokument10 SeitenRevised Expt 5 Physics LabWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expt 8 Act 3 and 5 & ApplicationsDokument5 SeitenExpt 8 Act 3 and 5 & ApplicationsWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adipose Tissue: - Cells (Fat Cells) of The Adipose Tissue - Very Wide DistributionDokument7 SeitenAdipose Tissue: - Cells (Fat Cells) of The Adipose Tissue - Very Wide DistributionWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relationship of Personal Growth Initiative With Self-EfficacyDokument12 SeitenRelationship of Personal Growth Initiative With Self-Efficacyeva pandanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fossil Watch Instructions EN US PDFDokument23 SeitenFossil Watch Instructions EN US PDFsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing The I C Bus: New Instructions For MCS-51 BASICDokument2 SeitenImplementing The I C Bus: New Instructions For MCS-51 BASICRadunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guna Memenuhi Tugas Matakuliah Pemrograman Aplikasi IndustriDokument12 SeitenGuna Memenuhi Tugas Matakuliah Pemrograman Aplikasi IndustriArif Nur RokhmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TLC 549Dokument19 SeitenTLC 549Farhana ImronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 850K XLT - WT - LGP Crawler Dozer 04 PDFDokument4 SeitenCase 850K XLT - WT - LGP Crawler Dozer 04 PDFEli EhmedliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photon Energy and WavelengthDokument20 SeitenPhoton Energy and WavelengthNeil Joseph LandinginNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPA Review School Philippines Final Exam GuideDokument14 SeitenCPA Review School Philippines Final Exam GuideAzureBlazeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Co2 Dragsters Research FolioDokument19 SeitenCo2 Dragsters Research Folioapi-299008285Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Technologies (IT)Dokument167 SeitenInternet Technologies (IT)Pramod GedamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tests of SignificanceDokument60 SeitenTests of SignificancegirmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bread and Pastry Production NC IIDokument88 SeitenBread and Pastry Production NC IIjhessica ibal50% (2)
- Fresh Water Generator On Ships 2Dokument16 SeitenFresh Water Generator On Ships 2Hamilton RamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Mittapalli College of EngineeringDokument41 SeitenSri Mittapalli College of EngineeringbrsreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TIRODA THERMAL DESIGN REPORTDokument38 SeitenTIRODA THERMAL DESIGN REPORTmithun46100% (2)
- Control LEDs, appliances via 16A AC dimmerDokument15 SeitenControl LEDs, appliances via 16A AC dimmerAlfhira KalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JJ512 - Pneumatic & Hydraulic-Chapter1Dokument51 SeitenJJ512 - Pneumatic & Hydraulic-Chapter1Udin Anuar100% (1)
- CURE Software PublishedDokument14 SeitenCURE Software PublishedMario GuedesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditional SentencesDokument14 SeitenConditional SentencesIvana StankovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTC3108 EnergyHarvestDokument3 SeitenLTC3108 EnergyHarvestliawyssbdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elance Service Manaual - Rev H PDFDokument94 SeitenElance Service Manaual - Rev H PDFJuanAguileraOlivo67% (3)
- Thomas L. SaatyDokument18 SeitenThomas L. SaatyliafaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of The Electromagnetic MethodDokument8 SeitenFundamentals of The Electromagnetic MethodEder VacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sedimentation Sanitary Engineering-Lecture4-2003Dokument41 SeitenSedimentation Sanitary Engineering-Lecture4-2003motuz adamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 3.11 Problem Statement: F I J I JDokument5 SeitenSolution 3.11 Problem Statement: F I J I JPandji Arie NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual: EEE434LDokument33 SeitenLab Manual: EEE434LAmanullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stats Form 4Dokument35 SeitenStats Form 4kirin19100% (2)
- Assignment Atomic Structure JH Sir-2611Dokument30 SeitenAssignment Atomic Structure JH Sir-2611Shivam KumarNoch keine Bewertungen