Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Channel
Hochgeladen von
PradeepCool0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten1 Seitechannel..
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
TXT, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenchannel..
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als TXT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
10 Ansichten1 SeiteChannel
Hochgeladen von
PradeepCoolchannel..
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als TXT, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel or channe
l, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logic
al connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel. A channel is us
ed to convey an information signal, for example a digital bit stream, from one o
r several senders (or transmitters) to one or several receivers. A channel has a
certain capacity for transmitting information, often measured by its bandwidth
in Hz or its data rate in bits per second.
Communicating data from one location to another requires some form of pathway or
medium. These pathways, called communication channels, use two types of media:
cable (twisted-pair wire, cable, and fiber-optic cable) and broadcast (microwave
, satellite, radio, and infrared). Cable or wire line media use physical wires o
f cables to transmit data and information. Twisted-pair wire and coaxial cables
are made of copper, and fiber-optic cable is made of glass.
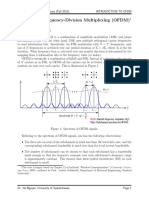
Digital channel models[edit]
In a digital channel model, the transmitted message is modelled as a digital sig
nal
Examples of digital channel models are:
Binary symmetric channel (BSC), a discrete memoryless channel with a certain bit
error probability
Binary bursty bit error channel model, a channel "with memory"
Binary erasure channel (BEC), a discrete channel with a certain bit error detect
ion (erasure) probability
Packet erasure channel, where packets are lost with a certain packet loss probab
ility or packet error rate
Arbitrarily varying channel (AVC), where the behavior and state of the channel c
an change randomly
Analog channel models[edit]
In an analog channel model, the transmitted message is modelled as an analog sig
nal. The model can be a linear or non-linear, time-continuous or time-discrete (
sampled), memoryless or dynamic (resulting in burst errors), time-invariant or t
ime-variant (also resulting in burst errors), baseband, passband (RF signal mode
l), real-valued or complex-valued signal model. The model may reflect the follow
ing channel impairments:
Types of communications channels[edit]
Digital (discrete) or analog (continuous) channel
Baseband and passband channel
Transmission medium, for example a fibre channel
Multiplexed channel
Computer network virtual channel
Simplex communication, duplex communication or half duplex communication channel
Return channel
Uplink or downlink (upstream or downstream channel)
Broadcast channel, unicast channel or multicast channel
hese are examples of commonly used channel capacity and performance measures:
Spectral bandwidth in Hertz
Symbol rate in baud, pulses/s or symbols/s
Digital bandwidth bit/s measures: gross bit rate (signalling rate), net bit rate
(information rate), channel capacity, and maximum throughput
Channel utilization
Link spectral efficiency
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Electronic Communications PDFDokument366 SeitenElectronic Communications PDFcongquy nguyen100% (1)
- Perc Comms 1Dokument9 SeitenPerc Comms 1Oliver Molitas100% (1)
- UMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFDokument63 SeitenUMTS LOG File Analysis & Optimization 1 PDFMahamadou Ousseini Barkiré100% (1)
- Television and Video Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDokument7 SeitenTelevision and Video Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bluetooth: ObjectiveDokument8 SeitenBluetooth: ObjectivePradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attachment B Mammo Room Floor PlanDokument1 SeiteAttachment B Mammo Room Floor PlanPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTMFDokument5 SeitenDTMFPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reed SwitchDokument4 SeitenReed SwitchPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- BT24 DatasheetDokument21 SeitenBT24 DatasheetPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- DS1621Dokument4 SeitenDS1621PradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Admission Prospectus AMITYDokument59 SeitenAdmission Prospectus AMITYAmit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Current Affairs PDF October 2015Dokument3 SeitenCurrent Affairs PDF October 2015PradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webcam 100208163119 Phpapp02Dokument8 SeitenWebcam 100208163119 Phpapp02PradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Boundary Agreement: HistoricalDokument2 SeitenLand Boundary Agreement: HistoricalPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- India and The WorldDokument24 SeitenIndia and The WorldPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Refugee Crisis: How It BeganDokument3 SeitenEuropean Refugee Crisis: How It BeganPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart City Mission: Why India Needs Smart Cities'?Dokument3 SeitenSmart City Mission: Why India Needs Smart Cities'?PradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- CoverDokument24 SeitenCoverPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- History:: Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface in Embedded SystemsDokument12 SeitenHistory:: Controller Area Network (CAN) Interface in Embedded SystemsPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- India and The WorldDokument24 SeitenIndia and The WorldPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC)Dokument3 SeitenNational Judicial Appointments Commission (NJAC)PradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormatDokument1 SeiteFormatPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- DtmfdocDokument40 SeitenDtmfdoc11090482Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3.6 Fire SensorDokument1 Seite3.6 Fire SensorPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awards & HonoursDokument19 SeitenAwards & HonoursPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1351147280Dokument30 Seiten1351147280lapogkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st June - 15 JuneDokument19 Seiten1st June - 15 JunePradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart City Mission: Why India Needs Smart Cities'?Dokument3 SeitenSmart City Mission: Why India Needs Smart Cities'?PradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- DTMFDokument5 SeitenDTMFPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol SensorDokument5 SeitenAlcohol SensorPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- BT24 DatasheetDokument21 SeitenBT24 DatasheetPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Land Acquisition Bill: What Is Land Acquisition and Which Laws Govern It?Dokument3 SeitenLand Acquisition Bill: What Is Land Acquisition and Which Laws Govern It?PradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Awards & HonoursDokument19 SeitenAwards & HonoursPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Refugee Crisis: How It BeganDokument3 SeitenEuropean Refugee Crisis: How It BeganPradeepCoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Format For Subject Specific ViewsDokument2 SeitenFormat For Subject Specific Viewsలక్ష్మీ సుబ్రహ్మణ్యం పుల్లెలNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ant Cab GSM Frequency BandGSM FREQUENCY BANDDokument120 SeitenAnt Cab GSM Frequency BandGSM FREQUENCY BANDJosue JeremieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cluster 10 ReportDokument224 SeitenCluster 10 ReportNino BongoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DX410 Beltpack WirelessHeadset DatasheetDokument2 SeitenDX410 Beltpack WirelessHeadset DatasheetDavid RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antenna: OutlineDokument32 SeitenAntenna: OutlineLuis CrespoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apstar 2R at 76Dokument22 SeitenApstar 2R at 76shahidacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discovery 2 MY00 - Alpine 7576R In-Car Entertainment Alpine (LRL0352ENG - 2nd Ed)Dokument24 SeitenDiscovery 2 MY00 - Alpine 7576R In-Car Entertainment Alpine (LRL0352ENG - 2nd Ed)Riahi RezegNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cellular Ommunication ObjectivesDokument2 SeitenCellular Ommunication Objectivesvictor kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass MediaDokument14 SeitenMass MediaJipson Abraham100% (3)
- Grand Opening InvitationDokument13 SeitenGrand Opening InvitationRica Mae Satsatin VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adi CB Manual Intek M-790 - SMDokument61 SeitenAdi CB Manual Intek M-790 - SMbiotekyNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Television in IndiaDokument16 SeitenHistory of Television in IndiaBalamurali KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Communication SyllabusDokument1 SeiteDigital Communication SyllabusVarun BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Ofdm Ieee 802 11a PDFDokument13 SeitenExercise Ofdm Ieee 802 11a PDFmhaabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrum Management & MonitoringDokument26 SeitenSpectrum Management & MonitoringsebghatandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BD387-VHF UHF Digital Signal Boosters DH14 Generic-FiplexDokument3 SeitenBD387-VHF UHF Digital Signal Boosters DH14 Generic-Fiplexculeros1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - AM ReceptionDokument43 SeitenChapter 5 - AM ReceptionmenchieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industry Analysis of TV Networks in The PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenIndustry Analysis of TV Networks in The PhilippinesEdgar BongatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 8Dokument3 SeitenSheet 8Ayman ElAshmawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument30 SeitenChapter 4Tausif Javed100% (1)
- Alex Rozier ResumeDokument2 SeitenAlex Rozier ResumealexmrozierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valuue Added Services in Radio BroadcastingDokument41 SeitenValuue Added Services in Radio Broadcastingtravel longNoch keine Bewertungen
- Layers and Codings v6-1Dokument29 SeitenLayers and Codings v6-1Bojan SubasicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single - Sideband Communications Systems: # Definitions TermsDokument30 SeitenSingle - Sideband Communications Systems: # Definitions TermsRalph Reyes SantelicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samsung Ln46b650 Spec SheetDokument2 SeitenSamsung Ln46b650 Spec SheetkenwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angle Modulation: What We Know Is Not Much. What We Do Not Know Is Immense. P. S. de LaplaceDokument79 SeitenAngle Modulation: What We Know Is Not Much. What We Do Not Know Is Immense. P. S. de LaplaceZoha AkramNoch keine Bewertungen