Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bioprocess Quiz
Hochgeladen von
VPrasarnth RaajCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bioprocess Quiz
Hochgeladen von
VPrasarnth RaajCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1. What is Bioprocessing?
A technique in which microorganisms, living cells, or their components are used as bio-catalyst to
produce a desired end product.
2. What are some disciplines related to bioprocessing?
o
Biochemistry
Microbiology
Genetics
Molecular Biology
Engineering
3. What the advantages of bioprocessing over chemical methods?
o
Complex organic molecules cant be produced by chemical means
Bioconversion has a higher yield
Operate at a lower temperature and pH
Isomeric compounds are easily excluded
Very Specific
4. What are the disadvantages of bioprocessing over chemical means?
o
Easily contaminated
Requires separation of wanted product
Results in biohazard waste
Relatively slow process (many steps)
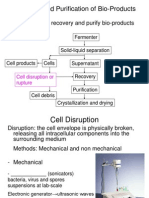
5. What are the steps in bioprocessing?
o
Preparation Stage
Raw Material
Substrates
Medium
Conversion State
Biocatalysts
Downstream processing
Volume production
Purification
Final Product processing
6. What are some cell types used in bioprocessing?
o
Bacteria (gram + and -)
Fungal
Mammalian
Plant
7. What are properties of an organism that is relevant for bioprocessing?
o
Nature of Strain (Pathogenicity, Toxin Production, Strain Stability)
Genetics
Cell Culture Shape, Size and Morphology
Cell membrane and transport system
Cell nutrition
Cell Growth Kinetics
Correlation between growth and product formation
Presence of regulatory enzymes
Activities of intracellular and extracellular proteases
8. What are enzymes?
o
Protein catalyst
Can be produced by bioprocessing
Affected by pH and Temperature
Very specific
Biodegradable
9. What are enzyme properties in bioprocessing?
o
Specificity- substrate range
Stability- effect of pH and temperature range
Solubility- medium for reaction, hydrophobic vs. hydrophillic
Structure, charge and size- for purification and recovery
10. What operations are involved in general bioprocessing?
o
Agitation and mixing
Heat transfer
Size reduction and enlargement
11. What is agitation?
Agitation is a process of mixing suspension of solids in a liquid to prevent chemical, physical and thermal
gradients.
12. What are two major causes of cell damage?
o
Hydrodynamic force or shear forces
Energy from bursting bubbles
13. What are 2 types of impellers?
o
Radial flow- not as efficient
Axial flow (used for animal cells) lifts cells from the bottom
14. What are the movement of mixers?
o
The entire container moves
Container is stationary with internal device rotating
A combination of the above two
15. Which has large surface area to unit volume ratio, a large or small reactor? Which require
addition of heat and which requires removal of heat?
o
Small reactors have large surface area and require addition of heat.
Large have small surface area and require removal of heat.
16. What is distillation?
It separates chemicals by the difference in how easily they vaporize
17. What is distillation categories based on?
o
System composition- Binary and Multicomponent distillation
Processing mode- continuous or batch
Processing Sequence
-Stripping- removing Light from heavy
-Recification- removing Heavy from Light
-Fractionation- removing by Strip/Recti at the same time
-Complex Fractionation- a combination of all methods
18. How do we reduce the size of cells?
o
Mills, roller, crushers
Tissue cutting, Homogenization, and Mincing or Extrusion
Microbial tissue breaking
19. What is the purpose of size enlargement?
o
Reduce direct contact
Render powder free flowing
Prevent caking or lumping
20. What are the methods for size enlargement?
o
Pressure compactment
Tumblers and mixer agglomeration
Spray dryers
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Downstream ProcessingDokument21 SeitenDownstream ProcessingNasir Ahmed YusufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec5.Recovery and Purification of Fermentation ProductsDokument26 SeitenLec5.Recovery and Purification of Fermentation Productsannaduraipillai50% (2)
- 2.25 Respiration H 2.28, 2.2.10Dokument22 Seiten2.25 Respiration H 2.28, 2.2.10George Oswald Junior CarringtonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 9 (PPT WaterDokument17 SeitenChapter - 9 (PPT Waterhabib panaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 15Dokument10 SeitenLecture 15Tejas MhaiskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03Dokument53 SeitenESTII 22 23 TP Lecture 03YaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- بيوتكنولوجيا البيئية- المحاضرة الثالثة2024Dokument37 Seitenبيوتكنولوجيا البيئية- المحاضرة الثالثة2024Nourhan SobhyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5-2Dokument27 SeitenUnit 5-2tejasribalsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 362 Introduction to Separation ProcessesDokument21 SeitenCH 362 Introduction to Separation ProcessesLohith LoliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTH 401 AssignmentDokument15 SeitenBTH 401 AssignmentMelissa lhingnunhoi SimteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovery and Purification of Bio-ProductsDokument26 SeitenRecovery and Purification of Bio-ProductsAmrie Iam100% (2)
- Introduction to Bioprocess FundamentalsDokument10 SeitenIntroduction to Bioprocess FundamentalsNaufal AdityasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Unit Process Removes Organic CompoundsDokument7 SeitenBiological Unit Process Removes Organic Compoundshimelhimel34Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Bioprocesses and Their ApplicationsDokument8 SeitenIntroduction to Bioprocesses and Their ApplicationsRavenSkullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Bioprocesses and Their ApplicationsDokument8 SeitenIntroduction to Bioprocesses and Their ApplicationsRavenSkullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Word MtoDokument7 SeitenWord MtoAvani TaiwadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioseperation 12Dokument47 SeitenBioseperation 12César D. Ybarra MeléndezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment On Effluent Treatment PlantDokument18 SeitenAssignment On Effluent Treatment PlantShahriar NewazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vortax MixerDokument7 SeitenVortax MixerHabib UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Introduction To Aerobic Treatment 1-9-06Dokument39 Seiten1 - Introduction To Aerobic Treatment 1-9-06Farah EL ShahawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHP 7-8Dokument37 SeitenCHP 7-8Nur AsiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy From BiomassDokument35 SeitenEnergy From BiomassSannidhi V. ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovery and Purification of Intracellular and Extra Cellular ProductsDokument25 SeitenRecovery and Purification of Intracellular and Extra Cellular ProductsGanesh V GaonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- O & M - S Brewing ETPDokument47 SeitenO & M - S Brewing ETPOmkar Bharankar100% (1)
- 9 Wastewater Treatment: Basic Processes of Water TreatmentDokument94 Seiten9 Wastewater Treatment: Basic Processes of Water TreatmentSayan BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Wastewater Treatment ProcessesDokument106 SeitenBiological Wastewater Treatment ProcessesFajaryan Wijananto100% (3)
- ASSINGMENT ON BIOLOGICAL ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant)Dokument15 SeitenASSINGMENT ON BIOLOGICAL ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant)tusharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supercritical Fluid ExtractionDokument8 SeitenSupercritical Fluid ExtractionAvani TaiwadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aims of Wastewater TreatmentDokument11 SeitenAims of Wastewater TreatmentParth ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject: Secondary Wastewater Treatment Biological Methods: Faculty of Engeneering ScienceDokument13 SeitenSubject: Secondary Wastewater Treatment Biological Methods: Faculty of Engeneering ScienceNenad Spiki VukomanovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- It's Not That Easy Bein' Green But It Is Essential For Life On Earth!Dokument36 SeitenIt's Not That Easy Bein' Green But It Is Essential For Life On Earth!Fathmath JameelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater Treatment Process OverviewDokument148 SeitenWastewater Treatment Process OverviewAilan TenGkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 1Dokument24 SeitenChap 1Yonas FekaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioreactor 2020 PPT PDFDokument76 SeitenBioreactor 2020 PPT PDFAbrar Ali Sitab100% (3)
- Stages of Downstream ProcessingDokument7 SeitenStages of Downstream ProcessingNitin KhodifadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 4: Heuristic of Process SynthesisDokument28 SeitenTopic 4: Heuristic of Process Synthesis伟铭Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Not On Biochemical EngineeringDokument81 SeitenA Not On Biochemical EngineeringSuleiman TaofeeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 - Class-Biomass Energy Conversion Technologies and Processes - Anaerobic DigestionDokument51 SeitenLecture 7 - Class-Biomass Energy Conversion Technologies and Processes - Anaerobic DigestionBenard KalamboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Wastewater TreatmentDokument70 SeitenIndustrial Wastewater TreatmentAudrius100% (3)
- Ee Mod2@Azdocuments - inDokument19 SeitenEe Mod2@Azdocuments - inmqrsr494Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bacteria Classifications and Usage For Wastewater TreatmentDokument43 SeitenBacteria Classifications and Usage For Wastewater TreatmentamaarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExamDokument9 SeitenExamDileepa NeranjanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yakob SDokument137 SeitenYakob SfiangliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effluent Treatment2Dokument14 SeitenEffluent Treatment2Mirza Md. Nazmus SakibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual SBUDokument19 SeitenLab Manual SBUSiti Anis IzzatieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4Dokument11 SeitenModule 4yiyiyi7699Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4a - Microbial MetabolismDokument29 SeitenChapter 4a - Microbial MetabolismNUR BAHIJATUL AKMAL BINTI MOHD ZUL KM-PelajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EST I 2 Chap4 Part2 TratAnaerobio v4Dokument38 SeitenEST I 2 Chap4 Part2 TratAnaerobio v4filipe.juneNoch keine Bewertungen
- FermentationDokument7 SeitenFermentationSyed D Kings'Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anaerobic TreatmentDokument61 SeitenAnaerobic TreatmentBalaji Lambo100% (1)
- Waste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementDokument27 SeitenWaste Water Treatment and Sludge ManagementSujith KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Wastewater TreatmentDokument72 SeitenFundamentals of Wastewater Treatmentanikamanal100% (3)
- Electricity From AlgaeDokument9 SeitenElectricity From AlgaeRaghamath KaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Environmental I AssDokument15 SeitenEnvironmental I AssAbel TayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Surfactant Based Sepn (Lec-5)Dokument16 SeitenChapter 3 - Surfactant Based Sepn (Lec-5)liyou eshetuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Processes for BioseparationsVon EverandEngineering Processes for BioseparationsLAURENCE R. WEATHERLEYBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Material-Microbes Interactions: Environmental Biotechnological PerspectiveVon EverandMaterial-Microbes Interactions: Environmental Biotechnological PerspectiveNabin AryalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotransfrmtns Prepartv Organic Chemistry: The Use of Isolated Enzymes and Whole Cell Systems in SynthesisVon EverandBiotransfrmtns Prepartv Organic Chemistry: The Use of Isolated Enzymes and Whole Cell Systems in SynthesisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mach CC App Form Jun16 Eng 20160629Dokument6 SeitenMach CC App Form Jun16 Eng 20160629ZulIzzamreeZolkepliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyundai AccentDokument10 SeitenHyundai AccentVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarDokument1 SeiteCarVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Map To CBJ OfficeDokument1 SeiteMap To CBJ OfficeVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Well Log Analysis - Introduction - Oct2013Dokument35 SeitenBasic Well Log Analysis - Introduction - Oct2013Jorge PirelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finaldissertation NoRestrictionDokument120 SeitenFinaldissertation NoRestrictionVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- C19115I2901Dokument1 SeiteC19115I2901VPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job satisfaction in human resource managementDokument102 SeitenJob satisfaction in human resource managementMed ElbanadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP PDS Con EngDokument3 SeitenHP PDS Con EngVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proton On The Road Price After Gst-20160215Dokument1 SeiteProton On The Road Price After Gst-20160215VPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windscreen Report Claim FormDokument3 SeitenWindscreen Report Claim FormVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- ResignationDokument1 SeiteResignationAlan KhorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pchardware StartecDokument1 SeitePchardware StartecVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 308 - November 2015 Version 29Dokument19 Seiten308 - November 2015 Version 29VPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 TH SOGCEDirectoryDokument40 Seiten4 TH SOGCEDirectoryVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajni and ManagementDokument12 SeitenRajni and ManagementVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 AccentDokument8 Seiten2011 AccentVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prototype Development To Test EOR Methods: Joana - Sanches@ist - Utl.ptDokument10 SeitenPrototype Development To Test EOR Methods: Joana - Sanches@ist - Utl.ptVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- British PetroleumDokument10 SeitenBritish PetroleumVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jadual Waktu MOG Semester 2, Sesi 2014.2015Dokument1 SeiteJadual Waktu MOG Semester 2, Sesi 2014.2015VPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- All It DesktopDokument4 SeitenAll It DesktopNatasya WillmoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCADokument1 SeiteLCAVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Assignment - UOP Q-Max Cumene Process (FULL)Dokument436 SeitenPetroleum Assignment - UOP Q-Max Cumene Process (FULL)VPrasarnth Raaj100% (12)
- List of Tables, Figures & Executive SummaryDokument4 SeitenList of Tables, Figures & Executive SummaryVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Milestone 5 Outline KC40203 2012Dokument1 SeiteMilestone 5 Outline KC40203 2012VPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Different Collection Efficiency Models For Venturi ScrubbersDokument10 SeitenComparison of Different Collection Efficiency Models For Venturi ScrubbersPassmore DubeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Petroleum Home Assignment OutlineDokument3 SeitenPetroleum Home Assignment OutlineVPrasarnth RaajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packed Tower AbsorberDokument58 SeitenPacked Tower AbsorberCelestino Montiel MaldonadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BK10110302-Shuler Problems PDFDokument13 SeitenBK10110302-Shuler Problems PDFVPrasarnth Raaj100% (2)
- Propeller Pin Crack InspectionDokument4 SeitenPropeller Pin Crack InspectionNicolás PiratovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Diesel-Photovoltaic Hybrid Power PlantDokument93 SeitenDesign Diesel-Photovoltaic Hybrid Power PlantDaniel Okere100% (1)
- Dynamometer - 1Dokument3 SeitenDynamometer - 1Vishal BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of 3PL and 4PL ContractsDokument8 SeitenAnalysis of 3PL and 4PL ContractsGoutham Krishna U BNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAP Demo ExercisesDokument34 SeitenMAP Demo ExercisesNancy HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fix Canon Pixma MP287 Printer Error CodesDokument7 SeitenFix Canon Pixma MP287 Printer Error CodesBen BennyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet CONTI SILENTSYNC ENDokument1 SeiteDatasheet CONTI SILENTSYNC ENViniciusNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB 4 Pole Contactor, 230V, 40ADokument1 SeiteABB 4 Pole Contactor, 230V, 40ASEERALANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limodor: Ventilation According To DIN 18017-3Dokument16 SeitenLimodor: Ventilation According To DIN 18017-3Petar BaricevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Richard GrisenthwaiteDokument25 SeitenRichard GrisenthwaitecaarthiyayiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bill of Quantities: Fifteen-Classrooms ADokument1 SeiteBill of Quantities: Fifteen-Classrooms AFritz NatividadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wire Rope and Material Properties GuideDokument100 SeitenWire Rope and Material Properties GuideReynald de VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- JeppView - LGSA (7 Charts)Dokument18 SeitenJeppView - LGSA (7 Charts)Roshan UppalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Omop Etl Template v4.0Dokument17 SeitenOmop Etl Template v4.0kartikb60100% (1)
- Hydraulic Cylinder Seal Kits: Quality With Value GuaranteedDokument16 SeitenHydraulic Cylinder Seal Kits: Quality With Value GuaranteedHenry GamboaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Torch Parts: T100 ConsumablesDokument2 SeitenMachine Torch Parts: T100 Consumablesبسام الاغبريNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determine Floating Body StabilityDokument11 SeitenDetermine Floating Body StabilityDember Paul100% (1)
- Astm c243 Withdrawn.31346Dokument4 SeitenAstm c243 Withdrawn.31346SilvioCarrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Alat TSMDokument2 SeitenDaftar Alat TSMagus ImawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Railway Signaling Concepts and DefinitionsDokument92 SeitenRailway Signaling Concepts and DefinitionsGopipavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statement of PurposeDokument2 SeitenStatement of PurposeAan DaisyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Readout (TRO) 2750 (Fan Made)Dokument106 SeitenTechnical Readout (TRO) 2750 (Fan Made)Mescalero100% (4)
- Jtm45plus Wiring DiagramDokument1 SeiteJtm45plus Wiring DiagramSarah Ladeira LucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital VLSI System Design Prof. Dr. S. Ramachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDokument30 SeitenDigital VLSI System Design Prof. Dr. S. Ramachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasPronadeep BoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- MVC Project Jarvis DatabaseDokument30 SeitenMVC Project Jarvis DatabaseSravan SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 253 MA Austenitic - High - Temperature - Grades - Datasheet PDFDokument12 Seiten253 MA Austenitic - High - Temperature - Grades - Datasheet PDFAbdulNoch keine Bewertungen
- MacBook Pro (13-Inch, Mid 2009) - Technical SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenMacBook Pro (13-Inch, Mid 2009) - Technical SpecificationsIndianOnRunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Tools Questions and Answers - GrindingDokument4 SeitenMachine Tools Questions and Answers - GrindingRohit GhulanavarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm C109-16Dokument10 SeitenAstm C109-16Travis TwaddellNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC200 Inverter Manual OverviewDokument239 SeitenAC200 Inverter Manual OverviewJuliana AndradeNoch keine Bewertungen