Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
EN Waler
Hochgeladen von
vsnsfbOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EN Waler
Hochgeladen von
vsnsfbCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
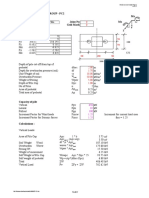
Steel member design (EN1993-1-1:2005)
In accordance with EN1993-1-1:2005 incorporating Corrigenda February 2006 and April 2009 and the recommended values
Section details
Section type;
UC 356x406x393 (BS4-1)
Steel grade;
S355
From table 3.1: Nominal values of yield strength fy and ultimate tensile strength fu for hot rolled structural steel
Nominal thickness of element;
t = max(tf, tw) = 49.2 mm
Nominal yield strength;
fy = 335 N/mm2
Nominal ultimate tensile strength;
fu = 470 N/mm2
Modulus of elasticity;
E = 210000 N/mm2
Partial factors - Section 6.1
Resistance of cross-sections;
M0 = 1.00
Resistance of members to instability;
M1 = 1.00
Resistance of tensile members to fracture;
M2 = 1.25
Lateral restraint
Distance between major axis restraints;
Ly = 5000 mm
Distance between minor axis restraints;
Lz = 2500 mm
Effective length factors
Effective length factor in major axis;
Ky = 0.700
Effective length factor in minor axis;
Kz = 0.700
Effective length factor for torsion;
KLT = 0.750
Classification of cross sections - Section 5.5
= [235 N/mm2 / fy] = 0.84
Internal compression parts subject to bending and compression - Table 5.2 (sheet 1 of 3)
Width of section;
c = d = 290.2 mm
= min([h / 2 + NEd / (2 tw fy) - (tf+ r)] / c, 1) = 0.771
c / tw = 11.3
Class 1
Outstand flanges - Table 5.2 (sheet 2 of 3)
Width of section;
c = (b - tw - 2 r) / 2 = 173 mm
c / tf = 4.2
Class 1
Section is class 1
Check shear - Section 6.2.6
Height of web;
hw = h - 2 tf = 320.6 mm
Shear area factor;
= 1.000
hw / tw < 72 /
Shear buckling resistance can be ignored
Design shear force parallel to z axis;
Vz,Ed = 2035 kN
Shear area - cl 6.2.6(3);
Av = max(A - 2 b tf + (tw + 2 r) tf, hw tw) =
Design shear resistance - cl 6.2.6(2);
Vc,z,Rd = Vpl,z,Rd = Av (fy / [3]) / M0 = 2516.3 kN
PASS - Design shear resistance exceeds design shear force
Combined bending, shear and axial force - Section 6.2.10
Reduction factor (6.2.10(3));
v = [(2 Vz,Ed / Vpl,z,Rd) - 1]2 = 0.381
Design shear force parallel to y axis;
Vy,Ed = 5 kN
Shear area - cl 6.2.6(3);
Av = max(2 b tf + (tw + 2 r) tf, A - (hw tw)) = 43050
Design shear resistance - cl 6.2.6(2);
Vc,y,Rd = Vpl,y,Rd = Av (fy / [3]) / M0 = 8326.4 kN
PASS - Design shear resistance exceeds design shear force
Check bending moment major (y-y) axis - Section 6.2.5
Design bending moment;
My,Ed = 1500 kNm
Design bending resistance moment - eq 6.13;
Mc,y,Rd = Mpl,y,Rd = W pl.y (1 - v) fy / M0 = 1704.3 kNm
Slenderness ratio for lateral torsional buckling
Correction factor - Table 6.6;
kc = 1
C1 = 1 / kc2 = 1
Curvature factor;
g = [1 - (Iz / Iy)] = 0.789
Poissons ratio;
= 0.3
Shear modulus;
G = E / [2 (1 + )] = 80769 N/mm2
Unrestrained length;
L = 0.75 Lz = 1875 mm
Elastic critical buckling moment;
Mcr = C1 2 E Iz / (L2 g) [Iw / Iz + L2 G It / (2 E Iz)] = 85759 kNm
Slenderness ratio for lateral torsional buckling;
LT
Limiting slenderness ratio;
LT,0
LT
<
LT,0
= [W pl.y fy / Mcr] = 0.179
= 0.4
- Lateral torsional buckling can be ignored
Design resistance for buckling - Section 6.3.2.1
Buckling curve - Table 6.5;
Imperfection factor - Table 6.3;
b
LT = 0.34
Correction factor for rolled sections;
= 0.75
LTB reduction determination factor;
LT = 0.5 [1 + LT (
LTB reduction factor - eq 6.57;
LT = min(1 / [LT + (
Modification factor;
f = min(1 - 0.5 (1 - kc) [1 - 2 (
Modified LTB reduction factor - eq 6.58;
LT,mod = min(LT / f, 1) = 1.000
Design buckling resistance moment - eq 6.55;
Mb,Rd = LT,mod W pl.y (1 - v) fy / M1 = 1704.3 kNm
PASS - Design buckling resistance moment exceeds design bending moment
LT
2
LT
LT,0
) +
2
LT
2
LT
] = 0.475
)], 1, 1 /
2
LT
) = 1.000
- 0.8) ], 1) = 1.000
2
LT
Check bending moment minor (z-z) axis - Section 6.2.5
Design bending moment;
Mz,Ed = 10 kNm
Design bending resistance moment - eq 6.13;
Mc,z,Rd = Mpl,z,Rd = W pl.z (1 - v) fy / M0 = 861 kNm
PASS - Design bending resistance moment exceeds design bending moment
Check compression - Section 6.2.4
Design compression force;
NEd = 1610 kN
Design resistance of section - eq 6.10;
Nc,Rd = Npl,Rd = A fy / M0 = 16769.3 kN
Slenderness ratio for major (y-y) axis buckling
Critical buckling length;
Lcr,y = Ly Ky = 3500 mm
Critical buckling force;
Ncr,y = 2 ESEC3 Iy / Lcr,y2 = 248067.9 kN
Slenderness ratio for buckling - eq 6.50;
= [A fy / Ncr,y] = 0.260
Design resistance for buckling - Section 6.3.1.1
Buckling curve - Table 6.2;
Imperfection factor - Table 6.1;
b
y = 0.34
Buckling reduction determination factor;
y = 0.5 [1 + y (
Buckling reduction factor - eq 6.49;
y = min(1 / [y + ( -
Design buckling resistance - eq 6.47;
Nb,y,Rd = y A fy / M1 = 16410.8 kN
- 0.2) +
2
y
2
y
2
y
] = 0.544
)], 1) = 0.979
PASS - Design buckling resistance exceeds design compression force
Slenderness ratio for minor (z-z) axis buckling
Critical buckling length;
Lcr,z = Lz Kz = 1750 mm
Critical buckling force;
Ncr,z = 2 ESEC3 Iz / Lcr,z2 = 374711.1 kN
Slenderness ratio for buckling - eq 6.50;
= [A fy / Ncr,z] = 0.212
Design resistance for buckling - Section 6.3.1.1
Buckling curve - Table 6.2;
Imperfection factor - Table 6.1;
c
z = 0.49
Buckling reduction determination factor;
z = 0.5 [1 + z (
Buckling reduction factor - eq 6.49;
z = min(1 / [z + ( -
Design buckling resistance - eq 6.47;
Nb,z,Rd = z A fy / M1 = 16670.5 kN
- 0.2) +
2
z
2
z
2
z
] = 0.525
)], 1) = 0.994
PASS - Design buckling resistance exceeds design compression force
Check torsional and torsional-flexural buckling - Section 6.3.1.4
Torsional buckling length factor;
KT = 0.70
Torsional buckling length;
Lcr,T = max(Ly, Lz) KT = 3500 mm
Distance from shear centre to centroid in y axis;
y0 = 0.0 mm
Distance from shear centre to centroid in z axis;
z0 = 0.0 mm
Radius of gyration;
i0 = [iy2 + iz2] = 200.9 mm
Elastic critical torsional buckling force;
Ncr,T = 1 / i02 [G It + 2 ESEC3 Iw / Lcr,T2] = 150333.9
Torsion factor;
T = 1 - (y0 / i0)2 = 1.000
Elastic critical torsional-flexural buckling force
Ncr,TF = Ncr,y / (2 T) [1 + Ncr,T / Ncr,y - [(1 - Ncr,T / Ncr,y)2 + 4 (y0 / i0)2 Ncr,T / Ncr,y]] = 150333.9 kN
Elastic critical buckling force;
Ncr = min(Ncr,T, Ncr,TF) = 150333.9 kN
Slenderness ratio for torsional buckling - eq 6.52;
= [A fy / Ncr] = 0.334
Design resistance for buckling - Section 6.3.1.1
Buckling curve - Table 6.2;
Imperfection factor - Table 6.1;
c
T = 0.49
Buckling reduction determination factor;
T = 0.5 [1 + T (
Buckling reduction factor - eq 6.49;
T = min(1 / [T + (T2 -
Design buckling resistance - eq 6.47;
Nb,T,Rd = T A fy / M1 = 15624.5 kN
- 0.2) +
2
T
] = 0.589
)], 1) = 0.932
2
T
PASS - Design buckling resistance exceeds design compression force
Biaxial bending - Section 6.2.9
Plastic moment resistance (y-y);
MN,y,Rd = Mpl,y,Rd = 2754.5 kNm
Plastic moment resistance (z-z);
MN,z,Rd = Mpl,z,Rd = 1391.5 kNm
Normal force to plastic resistance force ratio;
n = NEd / Npl,Rd = 0.10
Parameter introducing effect of biaxial bending;
bi = 2.00
Parameter introducing effect of biaxial bending;
bi = 5 n = 0.48
Interaction formula eq (6.41);
(My,Ed / MN,y,Rd)_bi + (Mz,Ed / MN,z,Rd)_bi = 0.390
PASS - Biaxial bending check is satisfied
Check combined bending and compression - Section 6.3.3
Cmy = 1.000
Equivalent uniform moment factors - Table B.3;
Cmz = 1.000
CmLT = 1.000
Interaction factors kij for members susceptible to torsional deformations - Table B.2
Characteristic moment resistance;
My,Rk = W pl.y fy = 2754.5 kNm
Characteristic moment resistance;
Mz,Rk = W pl.z fy = 1391.5 kNm
Characteristic resistance to normal force;
NRk = A fy = 16769.3 kN
Interaction factors;
kyy = Cmy [1 + min(
- 0.2, 0.8) NEd / (y NRk /
kzy = min(0.6 + z, 1 - 0.1
kzz = Cmz [1 + min(2
NEd / ((CmLT - 0.25)
- 0.6, 1.4) NEd / (z NRk
kyz = 0.6 kzz = 0.590
Interaction formulae - eq 6.61 & eq 6.62;
NEd / (y NRk / M1) + kyy My,Ed / (LT My,Rk / M1) + kyz Mz,Ed
NEd / (z NRk / M1) + kzy My,Ed / (LT My,Rk / M1) + kzz Mz,Ed
PASS - Combined bending and compression checks are satisfied
commended values
, hw tw) = 13010 mm2
- (hw tw)) = 43050 mm2
= 1704.3 kNm
2
LT
] = 0.475
1 /
2
LT
) = 1.000
- 0.8) ], 1) = 1.000
2
= 1704.3 kNm
Lcr,T2] = 150333.9 kN
/ (y NRk / M1)] = 1.006
((CmLT - 0.25) z NRk / M1)) = 0.812
NEd / (z NRk / M1)] = 0.983
) + kyz Mz,Ed / (Mz,Rk / M1) = 0.650
) + kzz Mz,Ed / (Mz,Rk / M1) = 0.546
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Weld Design BS 5950-1 (Ok)Dokument16 SeitenWeld Design BS 5950-1 (Ok)Zaido Al HalabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.shear Capacity of Steel Frame Member Rev 0.2Dokument22 Seiten9.shear Capacity of Steel Frame Member Rev 0.2WahidAgungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crack WidthDokument2 SeitenCrack Widthhabibur Rahman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bolt Design & Development LengthDokument3 SeitenBolt Design & Development LengthShamik ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eccentric Footing Design PDFDokument9 SeitenEccentric Footing Design PDFmsiddiq1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Axial Load Capacity For Deep Foundations Piles: Sand Input ResultsDokument8 SeitenAxial Load Capacity For Deep Foundations Piles: Sand Input Resultsacidrisamuel2656Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACI TSecDokument3 SeitenACI TSecمصطفى عبدالرحيمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dam I33Dokument47 SeitenDam I33Trung ConNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Design of Bracket: Load On Bracket Type LevelDokument4 Seiten1.0 Design of Bracket: Load On Bracket Type LeveldsureshcivilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 008 - Column Load AnalysisDokument17 Seiten008 - Column Load AnalysisVAIBHAVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slab Manual DesignDokument1 SeiteSlab Manual DesignAtul ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Long Wall: Tank Full and No Soil PressureDokument6 SeitenDesign of Long Wall: Tank Full and No Soil PressureAshoka YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metro Standard StructDwgs 080613Dokument41 SeitenMetro Standard StructDwgs 080613rpazbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Lacing: 2.5% of Axial Load Force in Each Lacing Bar (Flac)Dokument4 SeitenDesign of Lacing: 2.5% of Axial Load Force in Each Lacing Bar (Flac)Prasad SamantNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV DM 001 100dpiDokument58 SeitenCV DM 001 100dpighazi andonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEC Prog - Design of CorbelDokument4 SeitenJEC Prog - Design of CorbelAaron O'SullivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xxx-Type (H XM, B M) (Superstructure Type: PSC (Span 50m) ) : 1.design Condition 1.1 Type: 1.2 Foundation TypeDokument9 SeitenXxx-Type (H XM, B M) (Superstructure Type: PSC (Span 50m) ) : 1.design Condition 1.1 Type: 1.2 Foundation TypesudipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Footing-RgDokument101 SeitenCombined Footing-RgkumsbamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deflection For Cantilever Beam or Salb: Size B D FCK Fe E M.IDokument2 SeitenDeflection For Cantilever Beam or Salb: Size B D FCK Fe E M.IHemant SonawadekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultimate Moment Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Section To EN 1992-2 - Clause 6.1Dokument5 SeitenUltimate Moment Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Section To EN 1992-2 - Clause 6.1Randhir BharatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring Stiffnes CalculationDokument13 SeitenSpring Stiffnes Calculationyadav04_abhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Young's ModuleDokument12 SeitenYoung's Modulelazy catNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of RCC Footing As Per ACI 318 95 EdDokument2 SeitenDesign of RCC Footing As Per ACI 318 95 EdMaad Ahmed Al-MaroofNoch keine Bewertungen
- C Section PropertiesDokument2 SeitenC Section PropertiesnavinzhereNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wind Load Calculation Using EurocodeDokument3 SeitenWind Load Calculation Using EurocodeemmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementDokument32 SeitenShallow Foundation Design 2: SettlementPhanna MongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 ExamplesDokument8 SeitenChapter 13 ExamplesAnonymous kBl0u3nNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01-Retaining Wall Counterfort L ShapedDokument15 Seiten01-Retaining Wall Counterfort L ShapedBijendra Man Pradhan MRBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wildlife Crossing Design Based On AASHTO-17th & ACI 318-14Dokument1 SeiteWildlife Crossing Design Based On AASHTO-17th & ACI 318-14jklo12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation of Rss Building 3VIN 9 554 D1 S1 202 R0 Design of Foundations DataDokument56 SeitenDesign Calculation of Rss Building 3VIN 9 554 D1 S1 202 R0 Design of Foundations DataARUNKUMAR KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of 2 - Pile Group - Pc2 MX Design Data: Load Case 100 DL+LL Joint No MZ Grid Mark Column LoadDokument9 SeitenAnalysis of 2 - Pile Group - Pc2 MX Design Data: Load Case 100 DL+LL Joint No MZ Grid Mark Column LoadMythili BysaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACI BendDokument3 SeitenACI Bendمصطفى عبدالرحيمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thiet Ke Cot Composite - EC4. V1.0 (MS03)Dokument5 SeitenThiet Ke Cot Composite - EC4. V1.0 (MS03)luuvandong48xf396Noch keine Bewertungen
- Isolated FootingsDokument30 SeitenIsolated FootingsBanda 007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Crack WidthDokument6 SeitenCrack Widthnitin400Noch keine Bewertungen
- Loads For Supporting Beams: LX Ly UDL On SlabDokument6 SeitenLoads For Supporting Beams: LX Ly UDL On SlabAnonymous sfkedkymNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geotechnical Investigations of Mumbai-Pune ExpresswayDokument17 SeitenGeotechnical Investigations of Mumbai-Pune Expresswayblackberry7100gNoch keine Bewertungen
- Column Interaction DiagramDokument4 SeitenColumn Interaction DiagramAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PILE CAP PC1-FOUR Pile (IBL SHED)Dokument5 SeitenPILE CAP PC1-FOUR Pile (IBL SHED)vikas WaghmareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detail Estimate of RailingDokument5 SeitenDetail Estimate of Railingdebasispal78Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Dokument8 SeitenLateral Pile Capacity Caculation Using Broms's Method (Free Head Type)Mohammad Tawfiq WaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gardez - Khost Bridge No. 5 I - GIRDER 0.600 X 1.450 X 25.700 MDokument5 SeitenGardez - Khost Bridge No. 5 I - GIRDER 0.600 X 1.450 X 25.700 MBrian UrciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deck Slab DesignDokument19 SeitenDeck Slab DesignManvendra NigamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concentric Column: Design of Square/Rectangular Isolated FootingDokument21 SeitenConcentric Column: Design of Square/Rectangular Isolated FootingangeladolfoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHS With Concrete CalculationDokument23 SeitenCHS With Concrete CalculationYanfei JinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cladding& Runner DesignDokument1 SeiteCladding& Runner DesignDeepmalaJayeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culvert Design 1Dokument66 SeitenCulvert Design 1kanishkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chequred Plate CheckDokument2 SeitenChequred Plate Check_jessecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 41-Pile FoundationDokument56 Seiten41-Pile Foundationsharif uddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gusset BaseDokument2 SeitenGusset Basemanish mehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015-0075 1 5 KH Tann 3/20/2018 Dawson Deep Beam Formworks: 149b Selegie Road Singapore 188314Dokument6 Seiten2015-0075 1 5 KH Tann 3/20/2018 Dawson Deep Beam Formworks: 149b Selegie Road Singapore 188314jasekan.dcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monorail 0.5 TonDokument9 SeitenMonorail 0.5 TonAndreas HendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamic Earth PressureDokument2 SeitenDynamic Earth PressureMahadev D. BhandareNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-Design of Raft FoundationDokument2 Seiten5-Design of Raft FoundationheshamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZDokument5 SeitenEc9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZimotalpNoch keine Bewertungen
- TEDDS Calculation Version 3.0.09: - Section Is CompactDokument2 SeitenTEDDS Calculation Version 3.0.09: - Section Is CompactSupun Aravinda JayawardhaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS800 2007 Tee Detailed CalculationDokument5 SeitenIS800 2007 Tee Detailed CalculationVembuarasi VaithiyanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Column DesignDokument10 SeitenSteel Column DesignWazini D. IzaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.15 Swing Barrier v.1.0Dokument190 Seiten5.15 Swing Barrier v.1.0rfvz6sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ponniyin Selvan - SynopsisDokument5 SeitenPonniyin Selvan - Synopsisvsnsfb100% (1)
- Load Cases Circular ShaftsDokument1 SeiteLoad Cases Circular ShaftsvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- HouseDokument3 SeitenHousevsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fillet Welding Capacity in KNDokument2 SeitenFillet Welding Capacity in KNvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwall Force & DeflectionDokument1 SeiteDwall Force & DeflectionvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- For Reference Only (Confidential) : Ryobi Geotechnique International Pte LTDDokument8 SeitenFor Reference Only (Confidential) : Ryobi Geotechnique International Pte LTDvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Task List - 20150414Dokument10 SeitenDaily Task List - 20150414vsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corroded Bar Treatment 2Dokument1 SeiteCorroded Bar Treatment 2vsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bending Moment Shear ForceDokument3 SeitenBending Moment Shear ForcevsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
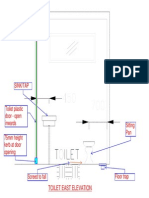
- Toilet East Elevation - SketchDokument1 SeiteToilet East Elevation - SketchvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corroded Bar TreatmentDokument1 SeiteCorroded Bar TreatmentvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steel Plate Gate DesignDokument5 SeitenSteel Plate Gate DesignvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist For PPEDokument1 SeiteChecklist For PPEvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corroded Bar Treatment2Dokument1 SeiteCorroded Bar Treatment2vsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pile C.width CalculatorDokument2 SeitenPile C.width CalculatorvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design CalculationDokument4 SeitenDesign CalculationvsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design CriteriaDokument4 SeitenDesign CriteriavsnsfbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tunnel LiningDokument3 SeitenTunnel Liningvsnsfb100% (1)
- Connections For Tilt Up WallsDokument46 SeitenConnections For Tilt Up WallsMichael James100% (1)
- Bhabha Student Front PagDokument7 SeitenBhabha Student Front PagimranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Popeye SpecificationsDokument436 SeitenPopeye Specificationspascal rosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material TestingDokument59 SeitenMaterial TestingWilliam Salazar100% (4)
- Introduction Power System ProtectionDokument110 SeitenIntroduction Power System ProtectionjameelahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDH Post Tensioned Concrete Design PDFDokument8 SeitenPDH Post Tensioned Concrete Design PDFabdulmananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shubham Shukla CVDokument4 SeitenShubham Shukla CVShubham ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV Rizzieri EnglishDokument6 SeitenCV Rizzieri EnglishGiampaoloRizzieriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid AssignmentDokument8 SeitenSolid AssignmentPaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sar EcDokument363 SeitenSar EcdhananjayslambNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ketentuan Detail Tulangan Pada Struktur Beton Bertulang - Yogyakarta - 14-15nov.20118 BW PDFDokument235 SeitenKetentuan Detail Tulangan Pada Struktur Beton Bertulang - Yogyakarta - 14-15nov.20118 BW PDFAris AriyadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Strengths of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Made Using Field-Demolished Concrete As AggregateDokument9 Seiten4 Strengths of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Made Using Field-Demolished Concrete As Aggregateget100% (2)
- Syllabus Signal and System IIDokument2 SeitenSyllabus Signal and System IIkuntjoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rectangular Concrete TanksDokument10 SeitenRectangular Concrete Tanksferchov_coNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Terkini 2016 / 2017Dokument1 SeiteResume Terkini 2016 / 2017syarul77% (13)
- CSR of WiproDokument26 SeitenCSR of WiproAshok Solanki79% (14)
- Clause For Seismic DesignDokument10 SeitenClause For Seismic DesignFarhanah Binti FaisalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Date Tested: Performance Check of Sieves With Designation Larger Than 4.75mm/no. 4 (ASTM E11)Dokument64 SeitenDate Tested: Performance Check of Sieves With Designation Larger Than 4.75mm/no. 4 (ASTM E11)Hamza MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robert Kavetsky Et Al - Energetic Systems and Nanotechnology - A Look AheadDokument10 SeitenRobert Kavetsky Et Al - Energetic Systems and Nanotechnology - A Look AheadSteemWheelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLAXIS - The-Spring-Constant-and-Soil-structure-Interaction PDFDokument16 SeitenPLAXIS - The-Spring-Constant-and-Soil-structure-Interaction PDFDedy KristiantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crossing Boundaries, Building Bridges - Comparing The History of Women Engineers, 1870s-1990sDokument310 SeitenCrossing Boundaries, Building Bridges - Comparing The History of Women Engineers, 1870s-1990sThaísReginaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caixa Gbox - DocDokument15 SeitenCaixa Gbox - Docsimao.bolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features: Measurement of Residual Stresses in Uoe-Saw Line PipesDokument5 SeitenFeatures: Measurement of Residual Stresses in Uoe-Saw Line PipesMaulana HendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Reality of Project Management Office For Construction PDFDokument8 SeitenThe Reality of Project Management Office For Construction PDFyveseoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat Fluids - Oils: Recommended UseDokument4 SeitenCat Fluids - Oils: Recommended UseAndrei Bleoju100% (2)
- The Application of Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)Dokument6 SeitenThe Application of Reliability Centered Maintenance (RCM)Ðian KpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Epoxy Coated & Glass Fiber Bamboo & Steel ReinforcedConcrete BeamsDokument7 SeitenAnalysis of Epoxy Coated & Glass Fiber Bamboo & Steel ReinforcedConcrete BeamsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cooper B Line Pipe HangersDokument332 SeitenCooper B Line Pipe HangersAhmed EmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algroup Enterprises - Company Profile 2014-1Dokument6 SeitenAlgroup Enterprises - Company Profile 2014-1Faquruddin AliNoch keine Bewertungen