Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
(Juan Ramirez) Accounting For Atives Advance (BookFi - Org) (1) 38
Hochgeladen von
Jasmeet0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten1 SeiteThe regression analysis method uses historical market rates to assess the correlation between changes in the fair value of the hedged item and hedging instrument. It involves three steps: 1) obtaining observations of the variables, 2) performing a regression to estimate a linear equation and statistics, 3) analyzing the statistics to determine if the hedge is highly effective.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
[Juan Ramirez] Accounting for Atives Advance(BookFi.org) (1) 38
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe regression analysis method uses historical market rates to assess the correlation between changes in the fair value of the hedged item and hedging instrument. It involves three steps: 1) obtaining observations of the variables, 2) performing a regression to estimate a linear equation and statistics, 3) analyzing the statistics to determine if the hedge is highly effective.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten1 Seite(Juan Ramirez) Accounting For Atives Advance (BookFi - Org) (1) 38
Hochgeladen von
JasmeetThe regression analysis method uses historical market rates to assess the correlation between changes in the fair value of the hedged item and hedging instrument. It involves three steps: 1) obtaining observations of the variables, 2) performing a regression to estimate a linear equation and statistics, 3) analyzing the statistics to determine if the hedge is highly effective.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
22
Accounting for Derivatives
Obtain X,Y
observations
from historical
rates
Perform regression:
Estimate linear
equation and
statistics
Analyse statistics
and determine if
hedge is highly
effective
Figure 1.9 Stages of the Regression Analysis Method.
1.9.3 The Regression Analysis Method
The regression analysis method is the most commonly used method in prospective tests, when
the critical terms method cannot be used. The idea is to analyse the behaviour of the hedging
relationship using historical market rates. Regression analysis is a statistical technique that
assesses the level of correlation between one variable (the dependent variable) and one or
more other variables (known as independent variables). In the context of hedge effectiveness
testing, the primary objective is to determine if changes in fair value of the hedged item and
the hedging instrument attributable to a particular risk were highly correlated in the past and,
thus, supportive of the assertion that there will be a high degree of offset in changes in fair
value of the hedged item and the hedging instrument in the future. The regression analysis is
a process that can be divided into three major steps, as shown in Figure 1.9.
The first step in the regression analysis is to obtain the inputs to the analysis: the X and
Y observations. Figure 1.10 outlines this process. This step is quite complex and requires a
computer program to perform it. The idea is to go back to a specific date (the simulation period
start date), assume that the hedge relationship started on that date and observe the behaviour
of the hedging relationship using the historical market data of the simulation period. The
simulation period ends on a date such that the term of the simulation is equal to the term of
the actual hedge. This process is repeated several times.
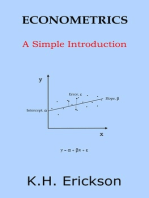
The second step of the regression analysis is to plot the values of the X and Y variables
and to estimate a best fitting line. A pictorial representation of the variables in the standard
regression equation is illustrated in Figure 1.11.
Regression analysis uses the least squares method to fit a line through the set of X and Y
observations. This technique determines the slope and intercept of the line that minimises the
size of the squared differences between the actual Y observations and the predicted Y values.
The linear equation estimated is commonly expressed as:
Y = + * X + , where
X: Change in fair value (or cash flow) of the hedging instrument attributable to the risk
to be hedged
Y: Change in fair value (or cash flow) of the hedged item attributable to the risk to be
hedged
: The intercept (where the line crosses the Y axis)
: The slope of the line
: The random error term
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Math (Regression Theory)Dokument31 SeitenMath (Regression Theory)Alina BorysenkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression PDFDokument16 SeitenRegression PDFadhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Juan Ramirez) Accounting For Atives Advance (BookFi - Org) (1) 40Dokument1 Seite(Juan Ramirez) Accounting For Atives Advance (BookFi - Org) (1) 40JasmeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predictive Modelling Using Linear Regression: © Analy Datalab Inc., 2016. All Rights ReservedDokument16 SeitenPredictive Modelling Using Linear Regression: © Analy Datalab Inc., 2016. All Rights ReservedABHISHEK V SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empirical Evidence On Volatility EstimatorsDokument38 SeitenEmpirical Evidence On Volatility EstimatorsAnonymous pb0lJ4n5jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 ECON NOTESDokument8 SeitenChapter 4 ECON NOTESMarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Regression ModelsDokument42 SeitenLinear Regression ModelsNomonde NatashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-III (Data Analytics)Dokument15 SeitenUnit-III (Data Analytics)bhavya.shivani1473Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Regression AnalysisDokument7 SeitenAn Introduction To Regression AnalysisNipun GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 003-Forecasting Techniques DetailedDokument20 Seiten003-Forecasting Techniques DetailedJahanzaib ButtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 5 MS 08 CorrelationDokument13 SeitenBlock 5 MS 08 CorrelationHarish PadmanabanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Prediction of Resistance and Support Levels - School of (PDFDrive)Dokument18 SeitenOptimal Prediction of Resistance and Support Levels - School of (PDFDrive)chandansingh45Noch keine Bewertungen
- ArunRangrejDokument5 SeitenArunRangrejArun RangrejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Credit Correlation - A GuideDokument36 SeitenCredit Correlation - A GuideVishal MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- RegressionDokument14 SeitenRegressionAndleeb RazzaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix (MTE 3105)Dokument10 SeitenAppendix (MTE 3105)Blaine TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensors Quality ManagementDokument7 SeitenSensors Quality Managementselinasimpson0201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Levenbach Causal2017Dokument15 SeitenLevenbach Causal2017Jenna GrantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Event Study FINISHDokument10 SeitenEvent Study FINISHharoonkhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business StatisticsDokument48 SeitenBusiness Statisticskragul780Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIt-3 TYDokument67 SeitenUNIt-3 TYPrathmesh Mane DeshmukhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Stock Market PredictionDokument6 SeitenSynopsis Stock Market PredictionSantoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Quality ManagementDokument7 SeitenConstruction Quality Managementselinasimpson0401Noch keine Bewertungen
- IntrinsicPricesOfRisk TrucLe LibreDokument11 SeitenIntrinsicPricesOfRisk TrucLe LibreMuhammad A. NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- A VAR Model As Risk Management ToolDokument15 SeitenA VAR Model As Risk Management Toolnamnh0307Noch keine Bewertungen
- Risks: Multiscale Analysis of The Predictability of Stock ReturnsDokument15 SeitenRisks: Multiscale Analysis of The Predictability of Stock ReturnsNguyen Hoai ThuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management EducationDokument7 SeitenQuality Management Educationselinasimpson2001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management CompanyDokument7 SeitenQuality Management Companyselinasimpson1301Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chpter 4 emDokument27 SeitenChpter 4 emMuhammad Hanief Al-KautsarNoch keine Bewertungen
- From Implied To Spot Volatilities: Valdo DurrlemanDokument21 SeitenFrom Implied To Spot Volatilities: Valdo DurrlemanginovainmonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBNR 06-GoovaertsDokument3 SeitenIBNR 06-GoovaertsdariotrajtenbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Value at Risk and Its Method of CalculationsDokument4 SeitenValue at Risk and Its Method of CalculationskoghillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Property ManagementDokument7 SeitenQuality Property Managementselinasimpson0101Noch keine Bewertungen
- Expected Monetary Value (EMV) Calculation StepsDokument4 SeitenExpected Monetary Value (EMV) Calculation StepsApurva JawadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estimation of Risk-Neutral Density SurfacesDokument35 SeitenEstimation of Risk-Neutral Density SurfacesdfdosreisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bayesian EstimatorDokument29 SeitenBayesian Estimatorossama123456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pom - Forecasting TechniquesDokument13 SeitenPom - Forecasting TechniquesSuganya SelvarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Other Useful Material For Project Management QualityDokument7 SeitenOther Useful Material For Project Management Qualityselinasimpson0401Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management TemplateDokument7 SeitenQuality Management Templateselinasimpson1201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Science Interview Preparation (30 Days of Interview Preparation)Dokument18 SeitenData Science Interview Preparation (30 Days of Interview Preparation)Satyavaraprasad BallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus QaDokument5 SeitenBus QaSaker AbdullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Econometrics ProjectDokument17 SeitenEconometrics ProjectAkash ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management DepartmentDokument7 SeitenQuality Management Departmentselinasimpson1201Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2Dokument38 SeitenLesson 219M647 - SRIRAM ANoch keine Bewertungen
- P Vs QDokument8 SeitenP Vs QRyan DavisNoch keine Bewertungen
- MAFS5220 Final Reserach ProjectDokument29 SeitenMAFS5220 Final Reserach ProjectyhuangaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Inference in Financial and Insurance Mathematics with RVon EverandStatistical Inference in Financial and Insurance Mathematics with RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Quality Management DefinitionDokument7 SeitenProject Quality Management Definitionselinasimpson1001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management IntroductionDokument7 SeitenQuality Management Introductionselinasimpson321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maximum Entropy Distribution of Stock Price FluctuationsDokument29 SeitenMaximum Entropy Distribution of Stock Price FluctuationsQfS1ahlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ba CH - 3Dokument37 SeitenBa CH - 3Naga RohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Home Quality ManagementDokument7 SeitenHome Quality Managementselinasimpson361Noch keine Bewertungen
- Model Estimation and ApplicationDokument40 SeitenModel Estimation and ApplicationlycancapitalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regression Analysis 2Dokument7 SeitenRegression Analysis 2Md Raihan AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Management PostersDokument7 SeitenQuality Management Postersselinasimpson2901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evans - Analytics2e - PPT - 07 and 08Dokument49 SeitenEvans - Analytics2e - PPT - 07 and 08MY LE HO TIEUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meucci 2011 - The PrayerDokument29 SeitenMeucci 2011 - The PrayershuuchuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditional Value-At-Risk: Aspects of Modeling and EstimationDokument22 SeitenConditional Value-At-Risk: Aspects of Modeling and EstimationYuri SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ ProblemsDokument7 SeitenMCQ ProblemsAfzal Ahmad100% (1)
- Gpa Calculator - Wec Wah Cantt-2Dokument5 SeitenGpa Calculator - Wec Wah Cantt-2FahadNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSRN Id2425048Dokument12 SeitenSSRN Id2425048sirj0_hnNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMW 103Dokument3 SeitenMMW 103Sean Virgines DueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter TestDokument9 SeitenChapter TestkokonyinyichitchitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staff 20and 20teaching 20assignment 20changes 20letter 20to 20parentsDokument1 SeiteStaff 20and 20teaching 20assignment 20changes 20letter 20to 20parentsapi-295573149Noch keine Bewertungen
- Detailed Lesson Plan DivisionDokument12 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan DivisionDarlin Shane SanguirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refiners High School: MathematicsDokument5 SeitenRefiners High School: MathematicsGabriel OnalekeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lecture Series: Time: 2 HrsDokument12 SeitenPhysics Lecture Series: Time: 2 HrsRohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthetic Division ReviewDokument3 SeitenSynthetic Division ReviewLailah Rose AngkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 41-42 Quadratic Optimal ControlDokument22 SeitenLecture 41-42 Quadratic Optimal ControlVeena Divya KrishnappaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 10 - Q2 - Module 5Dokument16 SeitenMath 10 - Q2 - Module 5Mark Glenn NadelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.10.3 Use of Solution of Linear Equation and Coefficient of A Power in Expansions To Find The Number of Ways of DistributionDokument50 Seiten7.10.3 Use of Solution of Linear Equation and Coefficient of A Power in Expansions To Find The Number of Ways of Distributionsanjayb1976gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5-Static EquilibriumDokument31 Seiten5-Static EquilibriumKnowledgeIsTruePowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adding Numbers in ExcelDokument3 SeitenAdding Numbers in ExcelFafunso AbiodunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometry III Section 3 - Harmonic IdentitiesDokument3 SeitenTrigonometry III Section 3 - Harmonic IdentitiesYiChuan ShaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wardova Metoda Od WardaDokument10 SeitenWardova Metoda Od WardaStarý DonorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning SyllabusDokument1 SeiteMachine Learning SyllabusmrameshmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Must Solve 100 Programs Part 5 - 10Dokument11 SeitenMust Solve 100 Programs Part 5 - 10Poojith Kodavaluru100% (1)
- Matrices - Ch. 1.8, 1.10Dokument36 SeitenMatrices - Ch. 1.8, 1.10Bryan PenfoundNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7: Systems of Linear Equations in Two or More VariablesDokument6 SeitenModule 7: Systems of Linear Equations in Two or More VariablesmoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inequality 4Dokument10 SeitenInequality 4Aarif AnsariNoch keine Bewertungen
- LCS Lab 5Dokument3 SeitenLCS Lab 5SaRosh RaeesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calc Medic Unit 4 Guided Notes AP Daily Videos - AP Precalculus - Calc MedicDokument20 SeitenCalc Medic Unit 4 Guided Notes AP Daily Videos - AP Precalculus - Calc Medicdevaden000Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 H2 Prelim Compilation (Complex Numbers)Dokument16 Seiten2018 H2 Prelim Compilation (Complex Numbers)toh tim lamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic - Minima and MaximaDokument11 SeitenTopic - Minima and MaximaMike OxlongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 4Dokument4 SeitenMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 4Ashmal ShazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grobler AJ Chapter4Dokument14 SeitenGrobler AJ Chapter4hieuhuech1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Derivatives Cylindrical Coordinates - RheaDokument8 SeitenVector Derivatives Cylindrical Coordinates - RheaSubhashisGhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQL DatatypeDokument7 SeitenSQL Datatypetesting engNoch keine Bewertungen