Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ibe c0 v1
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed AbbasOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ibe c0 v1
Hochgeladen von
Mohamed AbbasCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
Quality Manual
of the
INSPECTION BODY FOR
EMISSION INVENTORIES
at the
Umweltbundesamt GmbH, Environment Agency Austria
Spittelauer Lnde 5
1090 Wien, Austria
http://www.umweltbundesamt.at
2nd, completely revised edition
Author / Revison
Function
QR
Date
Signature
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
1/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
Summary on changes compared to previous version:
Im Vergleich zu IBEE C0:
nderung Name, Abkrzung und Ttigkeitsbereich (Ausschluss Register)
nderung Abkrzung EMEP GB
Content:
0 PREAMBLE
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
CONTENTOFQUALITYMANUAL
MATRIXISO/IEC17020ANDQUALITYMANUAL
LISTOFQUALITYANDTECHNICALPROCEDURES(EXCEPTSOPS)
TERMS,DEFINITIONSANDABBREVATIONS
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
4
5
7
8
2/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
PREAMBLE
The Environment Agency Austria has been entrusted by law with the preparation of
Austrias emission. Strict and binding guidelines have been set up by the international
community to ensure fairness and effectiveness within the system, and to contribute to
the achievement of the overall goal, which is to lower anthropogenic pressures on
Earth and to preserve the environment.
Besides strict compliance with these guidelines, absolute reliability of emission inventories is necessary for the functioning of the system. This can only be achieved by ensuring strict independence and impartiality.
To fulfill this task, the Inspection Body for Emission Inventories has been established
by and within the Environment Agency Austria.
A basic QA/QC system is obligatory for emission inventory compilers; the Environment
Agency Austria, aware of the importance of impartiality, has implemented an even
more sophisticated quality management system (in line with ISO/IEC 17020 Conformity
assessment General criteria for the operation of various types of bodies performing
inspection). Accreditation against this standard requires, in addition to an effective
QMS, personnel of high competence and compliance with impartiality and independence requirements.
In 2005, the berwachungsstelle Emissionsbilanzen (Inspection Body for Emission
Inventories) was first granted accreditation in line with ISO/IEC 17020, which was renewed at the beginning of 2011. Following a recommendation of the accreditation audit
to streamline the documentation of the management system, a completely revised
quality manual was produced; in the course of this work the revision of ISO/IEC 17020
was taken into account, the new manual being more user-friendly and providing an improved presentation of requirements relating to reporting obligations in the context of
emission inventories.
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
3/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
0.1
Content of Quality Manual
1 ORGANISATION
1.1 THEENVIRONMENTAGENCYAUSTRIAGMBH
1.2 LEGALIDENTIFIKATION
1.3 LIABILITYINSURANCE
1.4 ANNUALACCOUNTS
1.5 INSPECTIONBODYFOREMISSIONINVENTORIES
1.5.1 QUALITYMANAGEMENTSYSTEM
1.5.2 PERSONNEL
1.5.3 INTEGRATIONINTOTHEHIERARCHICALSTRUCTUREOFTHEENVIRONMENTALAGENCYAUSTRIA
1.5.4 TECHNICALMANAGER,AUTHORISEDSIGNATORIES
1.5.5 FACILITIESANDEQUIPMENT
1.6 IMPARTIALITYANDINDEPENDENCE
1.7 CONFIDENTIALITY
1.8 TERMSANDCONDITIONSOFTHEIBE
2
2
2
3
3
3
4
4
5
5
5
6
7
2 MANAGEMENTPROZESSES
2.1 QUALITYPOLICY
2.2 QUALITYREPRESENTATIVE
2.3 PERSONNEL
2.4 INTERNALCOMMUNICATION
2.5 DOCUMENTATIONOFTHEQMS
2.6 MANAGEMENTREVIEW
2.7 INTERNALAUDITS
2.8 CORRECTIVEANDPREVENTIVEACTIONS
2.9 COOPERATIONWITHTHEACCREDITATIONBODY
2.10 OTHERCOOPERATION
2
3
4
4
5
6
6
6
6
7
3 TECHNICALPROCESSES
3.1 INSPECTIONMETHODSANDPROCEDURES
3.2 DATASUPPLIERS
3.3 INSPECTIONRECORDS
3.4 SPECIFICQAPROCEDURESANDQCPROCEDURES
3.5 INSPECTIONREPORTSANDINSPECTIONCERTIFICATES
3.6 SUBCONTRACTING
3.7 CONTRACTS
3.8 CONFIDENTIALITY
3.9 DATASECURITYANDINTEGRITY
3.10 COMPLAINTSANDAPPEALS
2
2
2
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
4/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
0.2 Matrix ISO/IEC 17020 and quality manual
EN ISO/IEC 17020:2004
IBE Quality Manual
3 Administrative requirements
IBE C1.1, IBE C1.5.1, IBE C3.7,
IBE C1.3, IBE C1.4
4 Independence, impartiality and integrity
IBE C1.6
5 Confidentiality
IBE C2.6, IBE C3.8
6 Organization and management
IBE C1.5
7 Quality system
IBE C1.5.1, IBE C2, IBE Q2, IBE Q3
8 Personnel
IBE C1.5.2, IBE C2.3
9 Facilities and equipment
IBE C1.5.5
10 Inspection methods and procedures
IBE C3.1
11 Handling inspection items and samples
Not relevant
12 Inspection records
IBE C2.5, IBE Q2
13 Inspection reports and inspection certificates
IBE C3.5
14 Subcontracting
IBE C3.6
15 Complaints and appeals
IBE C2.8, IBE Q3.4
16 Cooperation
IBE C2.9, IBE C2.10
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
5/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
EN ISO/IEC 17020:DRAFT 2011 (Stage 40.60)
IBE Quality Manual
4 General requirements
4.1 Impartiality
IBE C1.6
4.2 Confidentiality
IBE C2.6, IBE C3.8
5 Structural requirements
IBE C1.5
6 Resource requirements
6.1 Personnel
IBE C1.5.2, IBE C2.3
6.2 Facilities and equipment
IBE C1.5.5
6.3 Subcontracting
IBE C3
7 Process requirements
7.1 Inspection methods and procedures
IBE C3
7.2 Handling inspection items and samples
Not relevant
7.3 Inspection records
IBE C2.5, IBE Q2
7.4 Inspection reports and inspection certificates
IBE C3
7.5 Complaints and appeals
IBE C2.8, IBE Q3
7.6 Complaints and appeals procedure
IBE Q3
8 Management system requirements
8.1 General
IBE C1.4.1
8.2 General management system
IBE C2.1, IBE C2.2, IBE C2.5
8.3 Control of documents
IBE C2.5, IBE Q2
8.4 Control of records
IBE C2.5, IBE Q2
8.5 Management review
IBE C2.6, IBE Q3
8.6 Internal audits
IBE C2.7, IBE Q3
8.7 Corrective actions
IBE C2.8, IBE Q3
8.8 Preventive actions
IBE C2.8, IBE Q3
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
6/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
0.3
List of quality and technical procedures (except SOPs)
Quality procedures:
IBE Q1 Personnel
IBE Q2 Documents and records
IBE Q3 Review and improvements
EMI Q1 Emission inventories
EMI Q2 Subcontracts (german)
Technical procedures:
EMI T1 Data management (german)
EMI T2 Uncertainties (german)
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
7/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
0.4
Terms, definitions and abbrevations
Term
Definition
Abbr.
IBE general
Inspection Body for Emission Inventories;
IBE
Abbreviation is used for general QMS documents, relevant to
all personnel and tasks of the IBE.
inspection
Emission
ventory
Inspection under the terms of ISO/IEC 17020; for the IBE inspection activities are the preparation of the emission inventory following SOPs
in-
Inventory of emissions (and removals) of air pollutants pursuant to the relevant specifications and guidelines (in particular
the guidelines of the IPCC and the LRTAP GPG).
EMI
Used in this manual to specify technical procedures.
Functions of the IBE
Head
IBE
of
the
Quality representative
Technical manager of the IBE (Gesamtverantwortlicher technischer Leiter gem 19 (1) AkkG: Inspektionsstellenleitung)
Member of top management who has the responsibility and
authority to ensure that processes and procedures needed for
the management system are established, implemented and
maintained, and to report to top management on the performance of the management system and any need for improvement.
HI
QR
Inspector
Staff member performing inspections
Staff member
personnel of the IBE, is appointed to different functions of the
IBE
SM
Staff emissions
Inspector appointed to EMI with the overall responsibility for a
CRF/NFR category (also referred to as sector expert).
SE
Project
ager
Function within the IBE: Project manager for one task of the
IBE
PM
Data manager
Function within the IBE: Data manager (for one task) of the
IBE
DM
Report coordinator
Function within the IBE: coordinator of a report of the IBE
RC
man-
QMS of the IBE
documentation
Used in this manual related to the documentation of the QMS,
i.e. comprises all documents:
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
8/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
document
Used in this manual related to the documentation of the QMS,
i.e. the quality manual and quality and technical procedures.
record
Used in this manual for an physical or electronic document
(paper or file) containing evidence of actions or results that
have been performed or prepared following the procedures
defined in this quality manual.
Implementation
audit
Type of Internal audit at the IBE testing the implementation of
its QMS
Conformity audit
Type of Internal audit at the IBE testing the conformity of its
QMS with the requirements of the ISO/IEC 17020 and the
AkkG
Chapter of the quality manual
Quality procedure
Definition of procedures for QM activities of the IBE
Technical procedure
Definition of procedures for activities supporting the tasks of
the IBE, e.g. data management
Standard operating procedure issued by the IBE for estimating
emissions (or removals)
SOP
Wildcard for filenames for a date e.g.: Jan11
DATE
Wildcard for filenames for a four digit year date
YEAR
Wildcard for consecutive numbers
X or XX
Wildcard for filenames for a name with no further specifications
NAME
Definitions from 2006 Guidelines
Quality objectives
A key component of a QA/QC plan [implementation at the IBE
is the quality manual] is the list of data quality objectives,
against which an inventory can be measured in a review. Data
quality objectives are concrete targets to be achieved in the
inventory preparation. They should be appropriate, realistic
(taking national circumstances into account) and allow for an
improvement of the inventory. Where possible, data quality
objectives should be measurable. Such data quality objectives
may be based upon and refined from the inventory principles.
Inventory principles
Transparency, Accuracy, Consistency (internal consistency as
well as time series consistency), Completeness, Comparability, [= TACCC] Timeliness and Improvement
Transparency
Transparency means that the assumptions and methodologies
used for an inventory should be clearly explained to facilitate
replication and assessment of the inventory by users of the
reported information. The transparency of inventories is fun-
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
TACCC
9/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
damental to the success of the process for the communication
and consideration of information.
Accuracy
Accuracy is a relative measure of the exactness of an emission or removal estimate. Estimates should be accurate in the
sense that they are systematically neither over nor under true
emissions or removals, as far as can be judged, and that uncertainties are reduced as far as practicable. Appropriate
methodologies conforming to guidance on good practices
should be used to promote accuracy in inventories.
Completeness
Completeness means that an inventory covers all sources and
sinks and gases included in the IPCC Guidelines for the full
geographic coverage in addition to other existing relevant
source/sink categories which are specific to individual countries (and therefore may not be included in the IPCC Guidelines).
Consistency
Consistency means that an inventory should be internally consistent in all its elements over a period of years. An inventory
is consistent if the same methodologies are used for the base
year and all subsequent years and if consistent data sets are
used to estimate emissions or removals from sources or sinks.
An inventory using different methodologies for different years
can be considered to be consistent if it has been estimated in
a transparent manner taking into account the guidance in Volume 1 on good practice in time series consistency.
Comparability
Comparability means that estimates of emissions and removals reported by Parties in inventories should be comparable
among Parties. For this purpose, Parties should use the
agreed methodologies and formats.
Timeliness
Conforming to the reporting requirements on time
Improvement
Improving the inventory in terms of the inventory principles.
Emissions
(Removals)
The release (removal) of air pollutants to the atmosphere over
a specified area and period of time.
Source (Sink)
Any process, activity or mechanism of release (removal). Notation in the final stages of reporting is the positive (+) (negative (-)) sign.
Uncertainty
Lack of knowledge of the true value of a variable that can be
described as a probability density function characterizing the
range and likelihood of possible values. Uncertainty depends
on the analysts state of knowledge, which in turn depends on
the quality and quantity of applicable data as well as
knowledge of underlying processes and inference methods.
Validation
Validation is the establishment of sound approach and foundation.
In the context of emission inventories, validation involves
checking to ensure that the inventory has been compiled cor-
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
10/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
rectly in line with reporting instructions and guidelines. It
checks the internal consistency of the inventory. The legal use
of validation is to give an official confirmation or approval of an
act or product.
Verification
Verification refers to the collection of activities and procedures
that can be followed during the planning and development, or
after completion of an inventory that can help to establish its
reliability for the intended applications of that inventory.
Typically, methods external to the inventory are used to check
the truth of the inventory, including comparisons with estimates made by other bodies or with emission and uptake
measurements determined from atmospheric concentrations
or concentration gradients of these gases.
Good Practice
Good Practice is a set of procedures intended to ensure that
greenhouse gas inventories are accurate in the sense that
they are systematically neither over nor underestimates so far
as can be judged, and that uncertainties are reduced so far as
possible.
Good Practice covers choice of estimation methods appropriate to national circumstances, quality assurance and quality
control at the national level, quantification of uncertainties and
data archiving and reporting to promote transparency.
Legal requirements
IPCC
lines
Guide-
Guidelines of the IPCC for estimating emissions (and removals) of greenhouse gases:
IPCC GL
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Revised 1996
IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories.
1997. Edited by J.T. Houghton, L.G. Meira Filho, B. Lim, K.
Tranton, I. Mamaty, Y. Bonduki, D.J. Griggs and B.A.
Callander. [rev. 1996 IPCC Guidelines]
IPCC
Good
Practice Guidance
Guidelines of the IPCC for good practice of estimating emissions (and removals) of greenhouse gases:
GPG
Good Practice Guidance and Uncertainty Management in National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. The Intergovernmental
Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), 2000.
Separate volume of the GPG for LULUCF:
Good Practice Guidance for Land Use, Land-Use Change and
Forestry, The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(IPCC), 2003.
LULUCF
GPG
IPCC
2006
Guidelines
Guidelines of the IPCC issued 2006 (revision of the IPCC
guidelines and the IPCC GPG)
2006 GL
EMEP Guidebook
EMEP/EEA air pollutant emission inventory guidebook
2009, prepared by the UNECE/EMEP Task Force on Emissions Inventories and Projections, published by European Environment
Agency
(Technical
report
No
9/2009,
EMEP GB
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
11/12
INSPECTIONBODYFOR
EMISSIONINVENTORIES
QUALITY MANUAL: IBE C0 Preamble
http://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/emep-eea-emissioninventory-guidebook-2009) (formerly referred to as the EMEP
CORINAIR emission inventory guidebook)
Environmental
Control Act
Umweltkontrollgesetz: Bundesgesetz ber die Umweltkontrolle und die Einrichtung einer Umweltbundesamt Gesellschaft mit beschrnkter Haftung, BGBl. I Nr. 152/1998
UKG
Austrian
Accreditation Law
Akkreditierungsgesetz: Bundesgesetz ber die Akkreditierung von Prf-, berwachungs- und Zertifizierungsstellen idF.,
BGBl. I Nr. 468/1999
AkkG
Emissionshchstmengen-Gesetzt Luft: Bundesgesetz ber
nationale Emissionshchstmengen fr bestimmte Luftschadstoffe, BGBl. I Nr. 34/2003
EG-L
EU
GHG
Monitoring
Mechanism
Council Decision No 280/2004/EC concerning a mechanism
for monitoring Community greenhouse gas emissions and for
implementing the Kyoto Protocol
EU MM
Implementing
Provisions
Commission Decision 2005/166/EC laying down rules for implementing Council Decision No 280/2004/EC
NEC Directive
Directive 2001/81/EC of the European Parliament and of the
Council of 23 October 2001 on national emissions ceilings
OTHER
eligibility
Permission for a party to the Kyoto protocol to participate in
the Kyoto Mechanisms
adjustment
Adjustment of emissions or removals by the review team
(made if the original estimate is not in line with the guidelines)
Review
cess)
External reviews by UNFCCC, UNECE or the EC
(pro-
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
COP
Conference of the Parties of the UNFCCC; agrees on rules
regarding implementation of the UNFCCC.
MOP
Meeting of the Parties to the Kyoto Protocol; agrees on rules
for implementing the Kyoto Protocol
Party
UNFCCC
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
IPCC
European Commission
EC
United Nations Economic Commission for Europe
UNECE
Convention on Long-range Transboundary Air Pollution
LRTAP
Country that has ratified a convention or protocol.
IBE_C0_v1.01 21.02.2012 12:22:00
12/12
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Iso Iec 17025 2017Dokument2 SeitenIso Iec 17025 2017esivaks2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Changes To ISO/IEC17021:2011 & ISO/IEC 19011:2011: AOQ QueenslandDokument54 SeitenChanges To ISO/IEC17021:2011 & ISO/IEC 19011:2011: AOQ QueenslandRidwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 9001 Audit Trail: A Practical Guide to Process Auditing Following an Audit TrailVon EverandIso 9001 Audit Trail: A Practical Guide to Process Auditing Following an Audit TrailBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- ISO-IEC 20000 Foundation Exam Sample Paper Rationale - January 2014Dokument15 SeitenISO-IEC 20000 Foundation Exam Sample Paper Rationale - January 2014chiwaicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nabl 160Dokument10 SeitenNabl 160Dr. Manikandan PalanisamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA InductionDokument3 SeitenQA InductionaszlizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecl - 1 Essco Quality SystemDokument8 SeitenEcl - 1 Essco Quality SystemGlobal QualityNoch keine Bewertungen
- PR16 Procedure On Internal System AuditingDokument2 SeitenPR16 Procedure On Internal System AuditingShahariar ShahadatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nabl 015Dokument24 SeitenNabl 015rangaramanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO-CASCO - ISO-IEC 17020, Conformity Assessment - Requirements For The Operation of Various Types of Bodies Performing InspectionDokument37 SeitenISO-CASCO - ISO-IEC 17020, Conformity Assessment - Requirements For The Operation of Various Types of Bodies Performing InspectionKatherine chirinosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 17025 Clause Wise ChangesDokument10 SeitenISO 17025 Clause Wise ChangesaasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 20000 (Service Management)Dokument4 SeitenISO 20000 (Service Management)billmin1110% (1)
- EXAMPLE Audit ReportDokument21 SeitenEXAMPLE Audit ReportLainhatanhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual - CMTDokument138 SeitenManual - CMTReama QumsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOH PMS-OPES Reference Table For TOTDokument958 SeitenDOH PMS-OPES Reference Table For TOTKaren May Garzota100% (1)
- ISO - IEC 17065 Presentation by Jim MunroDokument110 SeitenISO - IEC 17065 Presentation by Jim MunroRashedul Habib100% (1)
- DMC Quality ManualDokument58 SeitenDMC Quality ManualDMINFRANoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 9001correlation MatricesDokument7 SeitenISO 9001correlation MatricesSyv Consultores AsociadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- QA Manual Rev6Dokument44 SeitenQA Manual Rev6shifa100% (1)
- Comprehensive Clean RoomDokument4 SeitenComprehensive Clean RoomLucila Figueroa GalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Manual: Document No.: QM-01 Revision No.: 6Dokument45 SeitenQuality Manual: Document No.: QM-01 Revision No.: 6zae nuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementation of ISO:IEC 17020-2012Dokument14 SeitenImplementation of ISO:IEC 17020-2012Kin Kwan100% (3)
- I9000 1 94Dokument28 SeitenI9000 1 94shganesh81Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 17065Dokument66 SeitenPresentation 17065cperez2205100% (1)
- 2.1 EMS LA Delegate Manual - CoverDokument4 Seiten2.1 EMS LA Delegate Manual - CoverAli AlamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso Iec 17021 2011 OverviewDokument27 SeitenIso Iec 17021 2011 OverviewDimitris KatsierisNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 9001correlation MatricesDokument9 SeitenISO 9001correlation Matricesrgopinath3102Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Assurance Plan For WattsDokument30 SeitenQuality Assurance Plan For Wattsamit rajput100% (1)
- CL 5313 17021-1 Requirement Matrix-1458-5Dokument6 SeitenCL 5313 17021-1 Requirement Matrix-1458-5Noor Muddassir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso-17020 ISO - Manual-DocumentsDokument8 SeitenIso-17020 ISO - Manual-DocumentsPratik RamavatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 02 CDokument4 SeitenAssignment 02 CAjit K GNoch keine Bewertungen
- KI Quality Manual Rev. D 12-28-2012Dokument35 SeitenKI Quality Manual Rev. D 12-28-2012kzl009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Production: Eco Beauty Wholesale & LabsDokument12 SeitenProduction: Eco Beauty Wholesale & LabsMj AndresNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Interpretation and Implementation of Srps Iso/Iec 17021 StandardsDokument10 SeitenThe Interpretation and Implementation of Srps Iso/Iec 17021 StandardsBenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spec 9 Ed 06 May 2014 (Latest)Dokument76 SeitenSpec 9 Ed 06 May 2014 (Latest)P Sandana Nara100% (2)
- ISO 9001correlation MatricesDokument9 SeitenISO 9001correlation MatricesPirvu ValentinNoch keine Bewertungen
- IATF 16949 - 2016 ITALIANO - Da SitoDokument22 SeitenIATF 16949 - 2016 ITALIANO - Da Sitolucaturra69Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 17025 Requirements Testing Calibration LaboratoriesDokument12 SeitenIso 17025 Requirements Testing Calibration LaboratoriesOswaldo SperandioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Manual CalibrationDokument30 SeitenQuality Manual CalibrationsaidvaretNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO 17021 Manual DocumentationDokument9 SeitenISO 17021 Manual DocumentationSunil Arora67% (3)
- ISO 19011 ComaprisonsDokument10 SeitenISO 19011 ComaprisonsMYMAILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Correlation Matrices Between ISO 9001 2008 and ISO 9001 2015Dokument7 SeitenCorrelation Matrices Between ISO 9001 2008 and ISO 9001 2015Wewey NuestroNoch keine Bewertungen
- QM - Quality ManualDokument46 SeitenQM - Quality ManualRaajha MunibathiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Walker Presentation - IsO 17000 Process Models 2013 08 15Dokument9 SeitenA Walker Presentation - IsO 17000 Process Models 2013 08 15ediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 17025 Requirements Testing Calibration LaboratoriesDokument17 SeitenIso 17025 Requirements Testing Calibration Laboratoriesedgar gulden100% (5)
- ISO 19011 - 2018 WhitepaperDokument14 SeitenISO 19011 - 2018 WhitepaperJORGE MEJIA100% (1)
- 2005 L A B Guidance Document Rev 2 PDFDokument47 Seiten2005 L A B Guidance Document Rev 2 PDFTony SinambelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Review Agenda and Minutes1Dokument7 SeitenManagement Review Agenda and Minutes1sadbad660% (5)
- NABL 160 - Guide Preparing A Quality Manual PDFDokument61 SeitenNABL 160 - Guide Preparing A Quality Manual PDFzilangamba_s453567% (3)
- LSS 2013sept11 QIF Presentation Whats New in ISO 15189 (2012)Dokument38 SeitenLSS 2013sept11 QIF Presentation Whats New in ISO 15189 (2012)horia96Noch keine Bewertungen
- IMS IA - Exam PaperDokument15 SeitenIMS IA - Exam PaperujuabhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso Iec 17021 2011 OverviewDokument27 SeitenIso Iec 17021 2011 OverviewAlex Ramadhan SabananyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISO20000 DocumentDokument43 SeitenISO20000 Documentvijayalakshmis76100% (2)
- Report Writing in EnvironmentDokument8 SeitenReport Writing in EnvironmentFred Raphael IlomoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CL 5313 17021-1 Requirements Matrix-1458-3Dokument6 SeitenCL 5313 17021-1 Requirements Matrix-1458-3Amaro AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing Service Quality based on ISO/IEC 20000: A Management GuideVon EverandImplementing Service Quality based on ISO/IEC 20000: A Management GuideBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Remote Audit: From Planning to ImplementationVon EverandRemote Audit: From Planning to ImplementationBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Guid For Open Top Container (Equipment Inspection) 28Dokument1 SeiteGuid For Open Top Container (Equipment Inspection) 28Mohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guid For Open Top Container (Equipment Inspection) PDFDokument44 SeitenGuid For Open Top Container (Equipment Inspection) PDFMohamed Abbas50% (2)
- Detail A: OnesubseaDokument1 SeiteDetail A: OnesubseaMohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
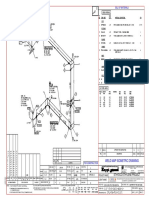
- Weld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsDokument1 SeiteWeld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsMohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
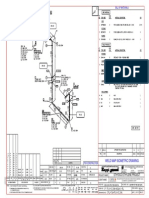
- Weld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsDokument1 SeiteWeld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsMohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
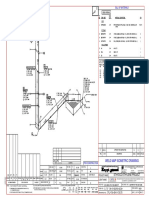
- Weld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsDokument1 SeiteWeld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsMohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsDokument1 SeiteWeld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsMohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsDokument1 SeiteWeld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsMohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsDokument1 SeiteWeld Map Isometric Drawing: Bill of MaterialsMohamed AbbasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DENR Nat'l Air Quality Status Report FADokument58 SeitenDENR Nat'l Air Quality Status Report FAcharles_0814Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report Final - Training ProgramDokument14 SeitenReport Final - Training Programanju goelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Method Calculating Marine Vessel EmissionDokument80 SeitenReview Method Calculating Marine Vessel EmissiondpossNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.a.3.a Aviation - Annex 1 - Master Emisisons Calculator - 2023 - Protected - v1.3Dokument11 Seiten1.a.3.a Aviation - Annex 1 - Master Emisisons Calculator - 2023 - Protected - v1.3alaaawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Volume 2 - EnergyDokument319 SeitenGuidelines For National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Volume 2 - EnergyEduardo VillacrésNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emissions Factors ToolkitDokument28 SeitenEmissions Factors ToolkitAhmed Abd El RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction - To - EEA - EMEP Guidebook2023 - TH AL 23 005 EN NDokument30 SeitenIntroduction - To - EEA - EMEP Guidebook2023 - TH AL 23 005 EN NAlexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combustion in ManufacturingDokument40 SeitenCombustion in ManufacturingVILLAINZ83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emb Annual Report For Cy 2016 PDFDokument50 SeitenEmb Annual Report For Cy 2016 PDFGeo DeryxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metodologia de Estimacion de Emisiones Vehiculares: Atmospheric EmissionsDokument18 SeitenMetodologia de Estimacion de Emisiones Vehiculares: Atmospheric EmissionsLuis Eduardo MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Category Title NFR: EMEP/EEA Air Pollutant Emission Inventory Guidebook 2019Dokument81 SeitenCategory Title NFR: EMEP/EEA Air Pollutant Emission Inventory Guidebook 2019GMNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.a.5.b Construction and Demolition GB2013Dokument8 Seiten2.a.5.b Construction and Demolition GB2013Tudor GeorgetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is An Emission Inventory?Dokument8 SeitenWhat Is An Emission Inventory?Mohammed S M AlghamdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission CalculationsDokument97 SeitenEmission CalculationsVIJAY MOHAN DAVE100% (4)
- Nether Land - Emission IntentoryDokument282 SeitenNether Land - Emission IntentoryHalil Ibrahim HacıoğluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Snap NomenklaturaDokument10 SeitenSnap NomenklaturaNejra KarovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mumbai ReportDokument515 SeitenMumbai ReportShailesh RathodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission InventoryDokument26 SeitenEmission InventoryDiniAryaP.NingrumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 3 23 9 12 47tapchi-Dhdn-So12 (97) .2015-Color-WebDokument128 Seiten2016 3 23 9 12 47tapchi-Dhdn-So12 (97) .2015-Color-WebThọ Nguyễn Văn100% (1)
- Emission Estimate Methodology For Maritime NavigationDokument12 SeitenEmission Estimate Methodology For Maritime NavigationdenizinakNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSE Environmental StandardsDokument150 SeitenGSE Environmental StandardsChick ChockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fagbeja Et Al 2017-Challenges Opportunities Emissions Inventory Niger DeltaDokument24 SeitenFagbeja Et Al 2017-Challenges Opportunities Emissions Inventory Niger DeltareninbabaskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission InventoryDokument47 SeitenEmission InventoryHsu MeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission CalculationDokument2 SeitenEmission CalculationSenthilkumar PragasamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AtmosphereDokument17 SeitenAtmosphereSunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Quality ManagementDokument80 SeitenAir Quality ManagementSarah AphirtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Emissions Inventory ReportDokument21 SeitenAir Emissions Inventory ReportMohammed Al MujainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENV30Dokument52 SeitenENV30Volca CmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- A.1 EMEP-EEA Guidebook Introduction 2019Dokument26 SeitenA.1 EMEP-EEA Guidebook Introduction 2019Walter LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploration Production TransportDokument28 SeitenExploration Production TransportafroznishatNoch keine Bewertungen