Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency 2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
Hochgeladen von
Christopher AuOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency 2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
Hochgeladen von
Christopher AuCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
2.
10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
Work
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
1.
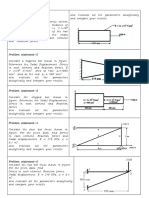
Work done by a constant force is given by the product of the force and the distance moved
in (parallel) the direction of the force.
2.
The unit of Nm(Newton metre) or J(Joule).
3.
Work is a scalar quantity.
4.
Formula
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
When the direction of force and motion are same, = 0o, therefore cos = 1
Work done,W=Fs
Example:
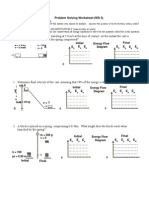
A force of 50 N acts on the block at the angle shown in
the diagram. The block moves a horizontal distance of
3.0 m. Calculate the work being done by the force.
Example:
Diagram above shows a 10N force is
pulling a metal. The friction between
the block and the floor is 5N. If the
distance travelled by the metal block is
2m, find
1. the work done by the pulling force
2. the work done by the frictional force
Energy
1.
2.
Energy is defined as the capacity to do work.
Work is done when energy is converted from one form to another.
3.
The unit of work is Nm or Joule(J)
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational potential energy is the
energy stored in an object as the result
of its vertical position (i.e., height).
Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic potential energy is the
energy stored in elastic materials
as the result of their stretching or
compressing.
Equation of Kinetic Energy
Is the energy that a body in motion.
Example
Determine the kinetic energy of a 2000-kg bus that is moving with a speed of 35.0 m/s.
Power
Power is the rate at which work is done, which means
how fast a work is done.
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
1) Ep=Ek (Potential Energy = Kinetic Energy)
2) Energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can be transformed from one to form to another, but the
total kinetic energy in a system is constant.
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
Air
Conditioner
1. Switch off the air conditioner when not in use.
2. Buy the air conditioner with suitable capacity according
to the room size.
3. Close all the doors and windows of the room to avoid the
cool air in the room from flowing out.
Refrigerator
1. Always remember to close the door of refrigerator.
2. Open the refrigerator only when necessarily.
3. Always keep the cooling coil clean.
4. Defrost the refrigerator regularly.
5.
Choose the refrigerator with capacity suitable for the family size.
2.10 Work, Power, Energy, Efficiency
2.11 Power Efficiency 100%
6.
Refrigerator of large capacity is more efficient compare with refirgerator of small capacity.
Lamp or Light Bulb
1.
Use fluorecent bulb rather than incandescent bulb. Fluorescent bulbs are much more efficient than
incandescent bulbs.
2.
Use a lamp with reflector so that more light is directed towards thr desirable place.
Washing Machine
1.
Use front-loading washing machine rather than top-loading wahing machine because it uses less
water and electricity.
2.
Use washing machine only when you have sufficient clothes to be washed. Try to avoid washing small
amount of clothes.
10
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ME359 FinalProjectDokument11 SeitenME359 FinalProjectAdeeb AisamuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesDokument44 SeitenModule 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesMarjorie Brondo100% (1)
- Module 5Dokument12 SeitenModule 5Gil Jerome II100% (1)
- Module in PhysicsDokument41 SeitenModule in PhysicsJeje NutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Teacher'sDokument10 SeitenForm 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (1)
- Module Sample Format For Math and ScienceDokument44 SeitenModule Sample Format For Math and Sciencetees cNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Student'sDokument10 SeitenForm 4 Physics Chapter 2.10-2.12 - Student'sPavithiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 101 Chapter 5: Üsküdar UniversityDokument85 SeitenChem 101 Chapter 5: Üsküdar UniversityNora Zor-elNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics: Chapter 3 Topic 3 AnswersDokument5 SeitenThermodynamics: Chapter 3 Topic 3 AnswersApril Galope OlaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Science Notes Ch11 WorkDokument8 Seiten09 Science Notes Ch11 WorkHarshJangidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elastic Potential EnergyDokument17 SeitenElastic Potential EnergyAlther AlitaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1-3 Problem Solving Worksheet-1Dokument2 Seiten1-3 Problem Solving Worksheet-1Samantha FineNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY104 Note-Taking Worksheet - Unit 2 Pg. 1Dokument7 SeitenPHY104 Note-Taking Worksheet - Unit 2 Pg. 1api-450969507Noch keine Bewertungen
- COVER PAGE (AutoRecovered)Dokument15 SeitenCOVER PAGE (AutoRecovered)Enigma YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1: Basic ThermodynamicsDokument277 SeitenUnit 1: Basic ThermodynamicsVinot NathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8-Work, Power and EnergyDokument6 SeitenChapter 8-Work, Power and EnergyLesther James CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 4 - 2 - PhysicsDokument18 SeitenUNIT 4 - 2 - PhysicsPpx XdNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power ADokument11 SeitenQB Topic 2 - 3 Work Energy Power AmarufinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bell Ringer: What Do You Think of When You Hear The Word (List at Least Three Items in Your Bell Ringer)Dokument28 SeitenBell Ringer: What Do You Think of When You Hear The Word (List at Least Three Items in Your Bell Ringer)MNM100% (1)
- 6 Work: Nsci-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Dokument8 Seiten6 Work: Nsci-6100 Physics For Engineers 1Yoo JungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penang Trial SPM 2013 Physics K2 Skema PDFDokument8 SeitenPenang Trial SPM 2013 Physics K2 Skema PDFbdy3372Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy and PowerDokument6 SeitenWork, Energy and Powerselar7347Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic Systems and EfficiencyDokument18 SeitenThermodynamic Systems and EfficiencyJack AndreasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Power Energy PDFDokument9 SeitenWork Power Energy PDFSalvadoRaulJr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- g481 1 3 1 Work and Energy ConservationDokument6 Seiteng481 1 3 1 Work and Energy Conservationapi-236179294Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesDokument44 SeitenModule 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesJudy Panguito Aralar100% (2)
- Exercices TP1 Enoncés enDokument2 SeitenExercices TP1 Enoncés enyassine kouraichiNoch keine Bewertungen
- J2006 - Termodinamik 1 - UNIT1Dokument16 SeitenJ2006 - Termodinamik 1 - UNIT1Amar ZalleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Sample Exam - For ES and LHDokument4 SeitenPhysics Sample Exam - For ES and LHNabil DoumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work EnergyDokument7 SeitenWork EnergyMysterious gamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work - Energy Theorem Problems With Solution - SankarDokument8 SeitenWork - Energy Theorem Problems With Solution - Sankarvasanthakumarsk17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy and EfficiencyDokument30 SeitenWork, Energy and EfficiencyLa JiejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project 2 - 3 + Project 3 - 1Dokument3 SeitenProject 2 - 3 + Project 3 - 1Phạm ChiếnNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY 103 Lecture 4Dokument32 SeitenPHY 103 Lecture 4NurudeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem StatementDokument3 SeitenProblem Statementeafz111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy and PowerDokument23 SeitenWork, Energy and Powervibgyorislight100% (1)
- Work Power and EnergyDokument29 SeitenWork Power and EnergyRuru pyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems For Finite Element Method: April 2019Dokument48 SeitenPractice Problems For Finite Element Method: April 2019emreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy & Power: Syllabus ObjectivesDokument40 SeitenWork, Energy & Power: Syllabus ObjectivesBrandly NyamapnziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eme 516Dokument11 SeitenEme 516VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 4 (Problems - Ch. 2) :: Solve The Following ProblemsDokument3 SeitenAssignment No. 4 (Problems - Ch. 2) :: Solve The Following ProblemsMohNajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Energy PowerDokument15 SeitenWork Energy PowerRaef AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elsayed PaperDokument7 SeitenElsayed PaperHassan MostafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 08 HomeworkDokument40 SeitenChapter 08 HomeworkFatboy9146% (24)
- Work Power and Energy Physics 10 PDFDokument46 SeitenWork Power and Energy Physics 10 PDFNorjiel BrandinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 101ah - Lesson 5Dokument8 SeitenPhysics 101ah - Lesson 5Ronald TantiadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermochemistry - Energy Flow and Chemical ChangeDokument6 SeitenThermochemistry - Energy Flow and Chemical ChangeRon Heindrix MaandigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems For Finite Element Method: April 2019Dokument48 SeitenPractice Problems For Finite Element Method: April 2019UrujMasoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- The First Law: Physical ChemistryDokument26 SeitenThe First Law: Physical ChemistryAnnaLynYepesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work, Energy, Power, and MachinesDokument46 SeitenWork, Energy, Power, and MachinesDee Doroin50% (2)
- Solved QP-Mechanics-Ktunote - in PDFDokument16 SeitenSolved QP-Mechanics-Ktunote - in PDFThaanya sNoch keine Bewertungen
- No.1Parctical PradeepDokument4 SeitenNo.1Parctical PradeepIssac MosaharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building Services and Technology Continuous Assessment 2 Portfolio of CalculationsDokument17 SeitenBuilding Services and Technology Continuous Assessment 2 Portfolio of Calculationsapi-380828333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work & EnergyDokument8 SeitenWork & EnergyOrlee Villafañe JrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 SpecificationDokument77 Seiten2011 Specificationapi-280482050Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Kirara PDFDokument13 SeitenSMK Kirara PDFChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- My HroDokument9 SeitenMy HroChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 PT3 KH Trial Seksyen 1 KT (Student Copy) PDFDokument14 Seiten2017 PT3 KH Trial Seksyen 1 KT (Student Copy) PDFChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pt3 English Special Programme: Date NameDokument4 SeitenPt3 English Special Programme: Date NameChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section D (40 Marks) ) (Time Suggested: 45 Minutes)Dokument3 SeitenSection D (40 Marks) ) (Time Suggested: 45 Minutes)Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sad I AmDokument2 SeitenSad I AmChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReporDokument16 SeitenReporChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM 2016 BK5 SJ PDFDokument14 SeitenSPM 2016 BK5 SJ PDFChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novel Moby DickDokument1 SeiteNovel Moby DickChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT3 15words StudentDokument4 SeitenPT3 15words StudentChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4003 CourseworkDokument5 Seiten4003 CourseworkChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 060 TMN Midah F4 PhysicsDokument4 Seiten060 TMN Midah F4 PhysicsChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10。5Dokument18 Seiten10。5Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5 Diffraction of WavesDokument21 Seiten1.5 Diffraction of WavesChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Answer IntensiveDokument9 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Answer IntensiveChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force 2.7.2.8Dokument16 SeitenForce 2.7.2.8Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnet 8.4Dokument11 SeitenElectromagnet 8.4Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Essay IntensiveDokument12 SeitenChapter 2 Essay IntensiveChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure 3.13.2Dokument12 SeitenPressure 3.13.2Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Forces and MotionDokument21 Seiten2 Forces and Motionriesya1206Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnet 8.1 StudentDokument14 SeitenElectromagnet 8.1 StudentChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force 2.10-2.12 StudentDokument15 SeitenForce 2.10-2.12 StudentChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric 7.5Dokument10 SeitenElectric 7.5Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnet 8.3Dokument11 SeitenElectromagnet 8.3Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force 2.10-2.12 StudentDokument15 SeitenForce 2.10-2.12 StudentChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnet 8.2 StudentDokument12 SeitenElectromagnet 8.2 StudentChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force 2.10-2.12Dokument15 SeitenForce 2.10-2.12Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Force 2.9 StudentDokument16 SeitenForce 2.9 StudentChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnet 8.1 StudentDokument14 SeitenElectromagnet 8.1 StudentChristopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnet 8.1Dokument14 SeitenElectromagnet 8.1Christopher AuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why CPVC Pipes FailDokument12 SeitenWhy CPVC Pipes FailNikita Kadam100% (1)
- Piston EffectDokument11 SeitenPiston EffectBK180Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q1 LAS 4 FABM2 12 Week 2 3Dokument7 SeitenQ1 LAS 4 FABM2 12 Week 2 3Flare ColterizoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS en Iso 11114-4-2005 (2007)Dokument30 SeitenBS en Iso 11114-4-2005 (2007)DanielVegaNeira100% (1)
- Freelance Contract AgreementDokument10 SeitenFreelance Contract AgreementGayathri Prajit100% (1)
- Lolcat - Linux Cat Command Make Rainbows & Unicorns - LinuxsecretsDokument1 SeiteLolcat - Linux Cat Command Make Rainbows & Unicorns - LinuxsecretsAli BadNoch keine Bewertungen
- DITS 2213 Final Exam OSDokument6 SeitenDITS 2213 Final Exam OSAmirul FaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12-24VDC Powered Ignition System: N N N N N N NDokument2 Seiten12-24VDC Powered Ignition System: N N N N N N NLeinner RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Post Bail For Your Temporary Liberty?Dokument5 SeitenHow To Post Bail For Your Temporary Liberty?Ruel Benjamin Bernaldez100% (1)
- Đo Nhiệt Độ LI-24ALW-SelectDokument4 SeitenĐo Nhiệt Độ LI-24ALW-SelectThang NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil & Grease CatalogDokument4 SeitenOil & Grease Catalogmanoj983@gmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 111a - Activity No. 2Dokument5 SeitenChem 111a - Activity No. 2MARY KATE FATIMA BAUTISTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Services and Facilities Matrix - Local Gov''tDokument2 SeitenBasic Services and Facilities Matrix - Local Gov''tMishi Liao100% (2)
- Beer Distribution Game - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument3 SeitenBeer Distribution Game - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSana BhittaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bearing SettlementDokument4 SeitenBearing SettlementBahaismail100% (1)
- Ruling The CountrysideDokument9 SeitenRuling The Countrysiderajesh duaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VMware SD WAN Google Cloud Platform Virtual Edge Deployment GuideDokument24 SeitenVMware SD WAN Google Cloud Platform Virtual Edge Deployment GuideJuan RojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBEC BPL System ArchitectureDokument2 SeitenIBEC BPL System ArchitectureAleksandar ConevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vibroscreen BrochureDokument12 SeitenVibroscreen BrochureVarun MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ass2 mkt1009Dokument11 SeitenAss2 mkt1009thang5423Noch keine Bewertungen
- IT 118 - SIA - Module 1Dokument9 SeitenIT 118 - SIA - Module 1Kim Zyrene DominoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Books Confirmation - Sem VII - 2020-2021 PDFDokument17 SeitenBooks Confirmation - Sem VII - 2020-2021 PDFRaj Kothari MNoch keine Bewertungen
- NF en 1317-5 In2Dokument23 SeitenNF en 1317-5 In2ArunNoch keine Bewertungen
- KACE SeDokument63 SeitenKACE SeAbdul RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 7Dokument18 SeitenTopic 7Anonymous 0fCNL9T0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity at Work - Safe Working Practices HSG85Dokument27 SeitenElectricity at Work - Safe Working Practices HSG85Sivakumar NatarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RICS APC Candidate Guide-Aug 2015-WEB PDFDokument24 SeitenRICS APC Candidate Guide-Aug 2015-WEB PDFLahiru WijethungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7 - Materials Management Configuration For Goods Receipts Reach - Ucf.eduDokument12 SeitenModule 7 - Materials Management Configuration For Goods Receipts Reach - Ucf.eduAjitabh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- WT Notes by Mohammed Ahmed PDFDokument11 SeitenWT Notes by Mohammed Ahmed PDFElavarasan MathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair of Small Household Appliances and Power ToolsDokument315 SeitenRepair of Small Household Appliances and Power ToolsahmadnawazjaswalNoch keine Bewertungen