Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Biology Unit 1 Revision
Hochgeladen von
zainabOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Biology Unit 1 Revision
Hochgeladen von
zainabCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
May 21, 2013
As Biology
Just in Time Revision
Unit 1
May 21, 2013
Don't Worry if you've
never seen the topic!!
May 21, 2013
Practical Questions
- Variables and how to measure
- Safety
- Repeats
- Control
May 21, 2013
Longer Questions
- Check the Command Words
- Answer the question (not
what you think it says)!
- Bullet Points are OK
- Make at least 4 points
- Use keywords
- Don't repeat the question.
May 21, 2013
DNA Structure
May 21, 2013
DNA Replication
1. Helicase unwinds the DNA forming the replication fork.
2. New nucleotides diffuse into the fork and hydrogen bind
with their complementary partners
3. DNA Polymerase joins the nucleotides together forming
the new sugar phosphate backbone
May 21, 2013
DNA - Conservative / semiconservative replication
Meselson and Stahls experiments involved growing
bacteria in culture media containing either heavy nitrogen
(15N) or light nitrogen (14N). The DNA was then
extracted from the bacteria. The DNA was then analysed:
May 21, 2013
{1 / 2} molecules shown with
one light and one heavy strand
{1 / 2} molecules shown with
two light strands;
May 21, 2013
DNA vs RNA
May 21, 2013
mRNA vs tRNA
May 21, 2013
DNA vs RNA
May 21, 2013
Protein Synthesis
1) Transcription
2) Translation
May 21, 2013
Protein Synthesis
1) Transcription
2) Translation
May 21, 2013
Protein Synthesis
1) Transcription
2) Translation
May 21, 2013
The Genetic Code
May 21, 2013
Double vs Single
Circulation
May 21, 2013
Gaseous Exchange insects
May 21, 2013
Gaseous Exchange
- Fish
May 21, 2013
Gaseous Exchange
- single celled
organisms
May 21, 2013
Cardiac Cycle
Label this diagram!
May 21, 2013
Cardiac Cycle
On the diagram, draw arrows to show the
flow of blood into and through the right
side of the heart during one beat of the
heart.
May 21, 2013
1. SAN sends a wave of electrical activity
(depolarization) around the walls of the
atria.
2. A ring of insulating tissue blocks the wave
from passing into the ventricles.
3. The AVN conducts the wave into the
Ventricles slowly, which gives the ventricles
time to fill.
4. The Purkinje fibres are fast-conducting and
take the wave to the apex of the heart first,
so the ventricles contract bottom upwards.
May 21, 2013
0 - 0.2s - Atrial Systole The atria contract, atrial pressure rises
&blood is pushed from atria --> ventricles
0.2
- 0.3s rises
- Ventricular
Systole
Theand
ventricles
contract,
ventricular
pressure
above atrial
pressure
the cuspid
valves
shut;
Ventricular pressure rises, but no blood leaves
the heart yet! When ventricular pressure rises above pressure in the
arteries the semi-lunar valves open Blood leaves the heart
0.3 - 0.4s - Diastole The ventricles relax. Ventricular pressure falls
and when pressure in the arteries > ventricular pressure the semilunar valves shut
0.4 - 0.7s - Diastole The entire heart is relaxed. The cuspid valves
open (4) and both atria and ventricles fill with blood.
May 21, 2013
Blood Vessels
May 21, 2013
Blood Vessels
May 21, 2013
Blood Clo/ng
1. Platelets are
activated by
substances
released by the
damaged artery wall
2. Platelets become
sticky and form a
platelet plug on the
surface of the
atheroma
3. Platelet plus
releases chemicals
which activate
thromboplastin
4. Thromboplastin
initiates the clotting
cascade
May 21, 2013
The clotting cascade
May 21, 2013
Plasma Cell Membrane
Structure
May 21, 2013
Transport Across membranes
May 21, 2013
Transport Across membranes
Active Transport
May 21, 2013
Transport Across membranes
Active Transport
May 21, 2013
Transport Across membranes
Active Transport
May 21, 2013
Amino Acid Structure
May 21, 2013
May 21, 2013
Protein Structure
May 21, 2013
Protein Structure
Explain the importance of the primary structure of an
enzyme to its function.
ANSWERS:
1. Primary structure determines 3D folding
2. Types of A.A. / bonds
3. Position of A.A. determines position of bonds
4. Shape / position/ of active site determined
by position of A.A.
5. Shape of active site being correct to bind to
substrate
May 21, 2013
Proteins
ANSWERS:
May 21, 2013
Enzymes
biological catalyst & activation energy.
May 21, 2013
Fats & Oils
Triglycerides are either fats or oils. They are
made from the elements C, H & O only.
1 x glycerol
3 x fatty acid
May 21, 2013
Esterification
A condensation reaction which causes an
ester bond to form between the fatty acid and
the glycerol
hydroxyl group carboxyl group
(-COOH)
(-OH)
This happens 3 times to join the 3 fatty acids
to the glycerol molecule
May 21, 2013
Saturated triglycerides have no
C=C bonds in them.
They form fats.
Unsaturated triglycerides DO have
C=C bonds in them.
They form oils.
May 21, 2013
Lipid structures - omega
3 & omega 6
Describe omega 3.
How is it different to omega 6?
Why are they so named?
May 21, 2013
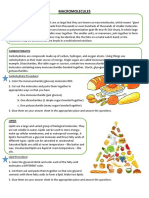
Carbohydrates - Saccarides
Made of: Carbon, Hydrogen and
Oxygen
Monosaccharides 1 sugar molecule
Disaccharides 2 sugar molecules joined
Polysaccharides many sugar molecules
barley
sugar cane
milk
May 21, 2013
Carbohydrates different structures of glucose
Spot the difference?!
May 21, 2013
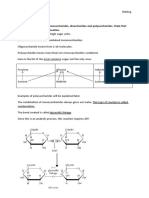
Carbohydrates condensation reactions:
a-glucose
a-glucose
maltose
May 21, 2013
May 21, 2013
maltose
Carbohydrates hydrolysis reactions:
+
a-glucose
a-glucose
May 21, 2013
Carbohydrates - polysaccharides
May 21, 2013
Carbohydrates - starch
a1-4 bonds between 3 glucose molecules.
Made from 2 molecules - Amylose & Amylopectin
Found in Amyloplasts (starch grains) inside plant
cells for energy storage
Insoluble, so no osmotic effect in tissues
Amylose has no branches (1-4 GB only), so
access to glucose is slow
Amylopectin has some branches (both 1-4 & 1-6
GB)
May 21, 2013
Carbohydrates - starch
Amylose
Amylose coiled structure
/ compact ideal for
storage!
Amylopectin side branches
allow enzymes
which break
down the
molecule to get
to bonds easily.
Means
GLUCOSE CAN
BE RELEASED
QUICKLY!
Unbranched
Amylopectin
branched
May 21, 2013
Carbohydrates - glycogen
1. Made from Poly ( Glucose).
2. Found in muscle and liver cells for energy
storage
3. Insoluble, so no osmotic effect in issues
4. Lots of branches (i.e. 1-6 GB present),
which allows quick access to glucose
5. Compact shape, so good for storage
May 21, 2013
Carbohydrates - cellulose
1. Made from Poly ( Glucose).
2. Main component of cell walls as it is a very
strong
structural molecule
3. Insoluble for obvious reasons!
4. Cellulose has no branches (i.e. 1-4 GB only),
so adjacent cellulose chains line up close
5. Hydrogen bonds form between adjacent
chains, creating very strong cellulose fibrils
May 21, 2013
Water structure - as a dipolar molecule
Water molecules are polar
H = Positively charged (+)
O = Negatively charged (-)
This allows them to form Hydrogen
Bonds with other water molecules. This
gives water some useful properties;
May 21, 2013
Lungs
May 21, 2013
Reasons for not
getting a valid
conclusion
- other variables are present or need
considering
- no information available about other
variables
May 21, 2013
Correlation
vs
Causal Link
Causation: when a change in
one variable is responsible for a
change in another variable
Correlation: when a change in
one variable is reflected by a
change in the other
May 21, 2013
Using the information in the graph...
May 21, 2013
Using the information in the graph ...
May 21, 2013
Using the information in the graph, describe the
effect of storage time on the vitamin C content
of the camu-camu fruit.
May 21, 2013
Using the information in the table ...
Using the data in the table, what is the evidence that drug S
is safe for people to take
Using the information in the table, describe the effect
that temperature has on the permeability of the
membranes of the beetroot cells.
May 21, 2013
Genetics
May 21, 2013
Distinguish between the terms allele and
gene; homozygous; recessive allele
Pedigree diagrams
May 21, 2013
Drawing Genetic diagrams
Parents
Phenotype:
Parents
Genotype:
Gametes
Genotype:
Zygotes
Genotype:
Zygotes
Phenotype:
May 21, 2013
May 21, 2013
Genetically Inherited
Diseases
May 21, 2013
May 21, 2013
May 21, 2013
Genetic Screening
May 21, 2013
Vectors
May 21, 2013
Genetic Screening
May 21, 2013
Multiple choice - don't
leave blank!!
Explain
Describe
May 21, 2013
Compare!
May 21, 2013
Describe an experiment questions
Include all variables (IV, DV, CV)
Include any relevant safety measures
How to maintain DV (e.g. water bath)
Reference to {range / at least 5} of IV
Appropriate controlled variable named
Reference to repeats / replicates
Include equipment / procedures to use
Reference to comparison of volumes
May 21, 2013
(QWC - Spelling of technical
terms must be correct and the
answer must be organised in
a logical sequence)
May 21, 2013
CVD
Not smoking
Increase exercise
Improvements to diet (e.g. reduce salt,
reduce saturated fat, increase fibre)
Maintaining appropriate weight
Reduced alcohol consumption
Reducing stress
Use of medication e.g. statins,
May 21, 2013
CVD
Not smoking
Increase exercise
Improvements to diet (e.g. reduce salt,
reduce saturated fat, increase fibre)
Maintaining appropriate weight
Reduced alcohol consumption
Reducing stress
Use of medication e.g. statins,
May 21, 2013
CVD
May 21, 2013
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Edexcel Biology As Revision NotesDokument67 SeitenEdexcel Biology As Revision Notesgrimmy96100% (1)
- Carbohydrates: Notes in BiologyDokument3 SeitenCarbohydrates: Notes in BiologyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- MetabolismDokument85 SeitenMetabolismkjgbitoon00125Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Kepentingan Air kepada Benda HidupDokument12 Seiten5 Kepentingan Air kepada Benda HidupIsmaliza IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW5 - Biochem Friday MorningDokument2 SeitenHW5 - Biochem Friday Morningnghanie02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Q4 Science 10 Module 2Dokument26 SeitenQ4 Science 10 Module 2Francine Alburo75% (4)
- 3.3 Carbohydrates PolysaccharidesDokument45 Seiten3.3 Carbohydrates PolysaccharidesPratika MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary General BiologyDokument8 SeitenSummary General BiologyquenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1 AsDokument156 SeitenPaper 1 As18salawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Macromolecules Cut and Paste 2Dokument5 SeitenMacromolecules Cut and Paste 2Crazy BasketballNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1: Carbohydrates: Sugar in Its Many FormsDokument10 Seiten5.1: Carbohydrates: Sugar in Its Many Formsjudy ann calibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Biology AS Revision NotesDokument67 SeitenEdexcel Biology AS Revision NotesTim Filtness95% (184)
- Carbohydrates: MonosaccharidesDokument4 SeitenCarbohydrates: MonosaccharidesMafalda CalheirosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Questions Cellular Biology 211Dokument6 SeitenDiscussion Questions Cellular Biology 211nigNoch keine Bewertungen
- 159 PolysaccharidesDokument4 Seiten159 PolysaccharidesHAMZAHwozERE100% (2)
- Carbs: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides & PolysaccharidesDokument6 SeitenCarbs: Monosaccharides, Disaccharides & PolysaccharidesJada HartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 A 2 AfcDokument8 Seiten1 A 2 AfcMahina WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Unit 2: M Ce LlsDokument2 SeitenBiology Unit 2: M Ce LlsRory PatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity No. 5 - I Scream For Ice CreamDokument5 SeitenActivity No. 5 - I Scream For Ice CreamReynalyn AbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- S2 Answer to the questions Units 2 and 3Dokument7 SeitenS2 Answer to the questions Units 2 and 3Official HYVIX ツNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1.01MC BiochemDokument6 SeitenModule 1.01MC BiochemCesar L. Laspiñas IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role of The Carbohydrates in Plasmatic MembranDokument26 SeitenThe Role of The Carbohydrates in Plasmatic Membranmadwinyi skeptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Von EverandAQA Biology Unit 1: Revision Notes: myrevisionnotes, #1Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- 04 CarbohydratesDokument10 Seiten04 CarbohydratesAlbert MuswewemombeNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA AS Biology 3.1.2 CarbohydratesDokument11 SeitenAQA AS Biology 3.1.2 CarbohydratesChryssa EconomouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eoc ReviewDokument33 SeitenEoc Reviewapi-237316144Noch keine Bewertungen
- Amylase Enzyme ThesisDokument6 SeitenAmylase Enzyme Thesischristinajohnsonanchorage100% (2)
- 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Carbohydrates PDFDokument4 Seiten1.1, 1.2, 1.3 Carbohydrates PDFshahbazhu006Noch keine Bewertungen
- AFN 3209 - CARBOHYDRATE IntroductionDokument5 SeitenAFN 3209 - CARBOHYDRATE IntroductionieunicemuthengiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gluten-free and casein-free diet effects on autismDokument12 SeitenGluten-free and casein-free diet effects on autismMimbel WimbelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Javascript The Web Warrior Series 6Th Edition Vodnik Gosselin 1305078446 9781305078444.docx Full Chapter PDFDokument25 SeitenSolution Manual For Javascript The Web Warrior Series 6Th Edition Vodnik Gosselin 1305078446 9781305078444.docx Full Chapter PDFpatricia.rice235100% (13)
- Biological MoleculesDokument31 SeitenBiological MoleculesEmy AnkrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Diffusion & Permeability - Teacher VersionDokument9 SeitenCell Diffusion & Permeability - Teacher VersionTeachLABScINoch keine Bewertungen
- CARBOHYDRATESDokument41 SeitenCARBOHYDRATESLorine LowrioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20Dokument20 SeitenTopic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20lisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen: How Disaccharides Are Formed?Dokument3 SeitenCarbon Hydrogen Oxygen: How Disaccharides Are Formed?Kalina VieleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen: How Disaccharides Are Formed?Dokument3 SeitenCarbon Hydrogen Oxygen: How Disaccharides Are Formed?Kalina VieleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept 10Dokument6 SeitenConcept 10Faustinalyn ConcepcionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Grid BookletDokument12 SeitenBasic Grid BookletSue Martin100% (6)
- Biochemistry Activities and ExercisesDokument13 SeitenBiochemistry Activities and ExercisesIel FedericoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolyDokument2 SeitenPolyapi-296833859Noch keine Bewertungen
- CH 08 - BioDokument44 SeitenCH 08 - Bioklopos1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 | Biological Macromolecules: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic AcidsDokument35 SeitenChapter 3 | Biological Macromolecules: Carbs, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic AcidsMarkus EvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology A-Level: Module 1: Biological MoleculesDokument13 SeitenBiology A-Level: Module 1: Biological MoleculesHK Nova ChiuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarbohydratesDokument35 SeitenCarbohydratesJaezean Jules B. GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Structure, Processes, and Reproduction, Third EditionVon EverandCell Structure, Processes, and Reproduction, Third EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIDokument30 SeitenLesson 3 - 1A2-3 Carbohydrates I & IIAlex SmirnovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 10 General Tests For CHODokument5 SeitenActivity 10 General Tests For CHOShekinah CamachoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inherited Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism - Glycogen Storage Diseases and Deficiencies of Monosaccharide MetabolismVon EverandInherited Disorders of Carbohydrate Metabolism - Glycogen Storage Diseases and Deficiencies of Monosaccharide MetabolismNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsVon EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jumpstarters for the Human Body, Grades 4 - 8Von EverandJumpstarters for the Human Body, Grades 4 - 8Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsVon EverandA-level Sciences Revision Boxset: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Nso Class11 PDFDokument11 SeitenNso Class11 PDFsanjayagrawal70-1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Cycle Events & PhasesDokument12 SeitenCardiac Cycle Events & Phasesanupam manu100% (1)
- FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY PPT DD Fix2Dokument43 SeitenFETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY PPT DD Fix2PAOGI UNAND100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemDokument17 SeitenAnatomy of The Digestive System and Circulatory SystemRafael Quieta Claro Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- International Health Olympiad Reference Book Juniors PDFDokument188 SeitenInternational Health Olympiad Reference Book Juniors PDFRajesh KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHF PathophysiologyDokument4 SeitenCHF PathophysiologyVirtudazo JessaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesia For Kasai ProcedureDokument2 SeitenAnesthesia For Kasai ProcedureBayu Residewanto PutroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiogenic Shock and Pulmonary EdemaDokument41 SeitenCardiogenic Shock and Pulmonary EdemaChristian Gallardo, MD100% (7)
- Instruction Manual ECP-TIDokument35 SeitenInstruction Manual ECP-TIBryanJermyHendrik100% (1)
- Edexcel Biology GCSE Topic 8 Notes on Exchange and Transport in AnimalsDokument10 SeitenEdexcel Biology GCSE Topic 8 Notes on Exchange and Transport in AnimalsLei LavinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quintinitarosalyn Module 1-Wk1respiratory SystemDokument35 SeitenQuintinitarosalyn Module 1-Wk1respiratory Systemrosalyn quintinita60% (5)
- Cardiovascular Disease in Small Animal Medicine (VetBooks - Ir) PDFDokument397 SeitenCardiovascular Disease in Small Animal Medicine (VetBooks - Ir) PDFGrisel Leal GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Review of Cardiovascular SystemDokument19 SeitenI Review of Cardiovascular SystemJoe TincilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Full Length Paper-2 (Student Copy)Dokument15 Seiten02 Full Length Paper-2 (Student Copy)jawaidaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmosis Acute Coronary SyndromesDokument5 SeitenOsmosis Acute Coronary Syndromesvalentinabil3Noch keine Bewertungen
- G9-Q1-LAS ScienceDokument14 SeitenG9-Q1-LAS ScienceLiomer Zabala-Mubo CredoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Function TestsDokument40 SeitenCardiac Function TestsAkua Konama AttakoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LessonplanDokument3 SeitenLessonplan=paul=Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHEST X-RAY Presentation CVSDokument45 SeitenCHEST X-RAY Presentation CVSNorsafrini Rita Ahmad100% (1)
- Ayurveda Q&A - Detoxification Therapy Cures Fungal Infection - Sify HealthDokument12 SeitenAyurveda Q&A - Detoxification Therapy Cures Fungal Infection - Sify Healthsanti_1976Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hurst Pathophysiology-Ch01 986x PDFDokument42 SeitenHurst Pathophysiology-Ch01 986x PDFeng78ineNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Heart Diagram and Pathway of Blood ActivityDokument4 SeitenThe Heart Diagram and Pathway of Blood Activityapi-233736029Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ECG Interpretation MWDokument211 SeitenBasic ECG Interpretation MWLorelie AsisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoDokument157 SeitenSimple Nursing Medical Surgical - CompletoRenato Bandeira100% (4)
- IB Biology HL: 6.2 The Blood System - Human PhysiologyDokument12 SeitenIB Biology HL: 6.2 The Blood System - Human PhysiologypetraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Heart MuscleDokument31 Seiten9 Heart Muscleshoeb4uNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Perfect Answer Biology Revision Guide - Edexcel IGCSE 9-1 - 1st EditionDokument36 SeitenThe Perfect Answer Biology Revision Guide - Edexcel IGCSE 9-1 - 1st EditionKevir Man85% (13)
- NBME 26 Questions Version PDFDokument203 SeitenNBME 26 Questions Version PDFRakulNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCRN CardiacDokument39 SeitenCCRN CardiacMike100% (5)
- BiologyDokument80 SeitenBiologyAmp100% (6)