Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Factor, K, Pressure, Loss, Flow, Rate, Local, Head, Hydraulic
Hochgeladen von
bmspragueOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Factor, K, Pressure, Loss, Flow, Rate, Local, Head, Hydraulic
Hochgeladen von
bmspragueCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
factor, k, pressure, loss, flow, rate, local, head, hydraulic
Calculation of the singular pressure losses on hydraulic networks. Dynamic pressure, tables of the coefficients K (modules of pressure
loss), evaluation of the singular pressure loss.
French site
| Home | Thematic | Tables | Programs | Library | Download | Links | Contact | Forum |
_You are in the heading
Mon Apr 13 2015 11:22:38 GMT-0600 (Mountain Daylight Time)
--
Local pressure loss
Thematic
Quotation
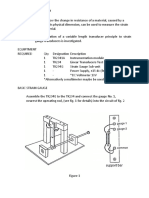
Local pressure loss calculation
Margin
Hydraulic
Linear pressure
loss
The local pressure losses corresponding by the valves and fittings in the hydraulic networks are expressed by the
following relation:
Local pressure
loss
Compressible
fluids
No circular duct
Thermal
Thermal fluid
flow
Pipe sizing
steam
Dps = local pressure loss in Pa
p = density of the fluid in kg/m3
V = rate of flow in m/s
K = coefficient depend on the nature of local resistance
= Dynamic pressure of the fluid.
Control valves
Orifice plate
Pumps
The local pressure losses are classified in 2 categories:
Ventilators
Gas
Fuel gas
Those which are with constant value whatever the diameter of the network used, such as the changes of
section (reductions, inlets and outlets of the pipes)
Those which vary according to the diameter of networks, whose pressure loss is due primarily by friction
and turbulence occurring such as for example in a valve.
K-factor with constant value
It should be noted that the following values all are established according to the smallest diameter.
This value can be converted on the largest diameter by (dlarge/dlitle)4.
Changement de section
- Rduction concentrique - largissement d1/d2 = 0.90
0.026
- Rduction concentrique - largissement d1/d2 = 0.80
0.13
- Rduction concentrique - largissement d1/d2 = 0.75
0.16
- Rduction concentrique - largissement d1/d2 = 0.67
0.28
- Rduction concentrique - largissement d1/d2 = 0.50
0.5
- Rduction concentrique rtrcissement d1/d2 = 0.90
0.008
- Rduction concentrique - rtrcissement d1/d2 = 0.80
0.041
- Rduction concentrique - rtrcissement d1/d2 = 0.75
0.049
- Rduction concentrique - rtrcissement d1/d2 = 0.67
0.085
- Rduction concentrique - rtrcissement d1/d2 = 0.50
0.16
Entre et sortie conduite
- Entre conduite de niveau - r/d = 0.00 (angle vif)
0.5
- Entre conduite de niveau - r/d = 0.02
0.28
- Entre conduite de niveau - r/d = 0.04
0.24
http://www.thermexcel.com/english/ressourc/pdclocal.htm[4/13/2015 11:23:26 AM]
factor, k, pressure, loss, flow, rate, local, head, hydraulic
- Entre conduite de niveau - r/d = 0.06
0.15
- Entre conduite de niveau - r/d = 0.10
0.09
- Entre conduite de niveau - r/d > 0.15 (bien arrondie)
0.04
- Entre conduite saillante
0.78
- Sortie canalisation
Divers
Comptage (Consulter normalement le fabricant)
- Compteur disque (K : 3,4 10)
10
- Compteur rotatif
10
- Compteur piston
15
- Compteur turbine (K : 5 7.5)
7.5
Branchement radiateurs y/c robinetterie
- Piquage sur rseaux aller et retour, radiateur, robinetterie
Ensemble chaudire y/c robinetterie
15
- entre et sortie chaudire y/c changements brusques de sections, entre et sortie,
vanne, tuyauterie de drivation, piquage, du vase d'expansion (8 12)
Tronon entre 2 piquages
12
- sans variation de section
1.5
- avec variation de section
3.5
K-factor depend on the diameter used
This calculation must be carried out separately for each pipe size, using the appropriate velocity within that pipe
section.
Evaluation of local pressure loss
The singular pressure losses are expressed by:
Conversely, it is possible to know the value of K according to the pressure loss (read on an abacus)
V = Rate of flow in m/s
DPs = Pressure loss in Pa
p = Density of the fluid in kg/m3 (depends on the temperature)
K = coefficient depend on the nature of local resistance
Last update: 04/13/2015 11:22:38
Copyright 2003-2014 - ThermExcel - All Rights Reserved
http://www.thermexcel.com/english/ressourc/pdclocal.htm[4/13/2015 11:23:26 AM]
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Mass Model For Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines: July 2017Dokument21 SeitenA Mass Model For Liquid Propellant Rocket Engines: July 2017Đinh Quốc TríNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimization and Sizing For Propulsion System of Liquid Rocket Using Genetic AlgorithmDokument7 SeitenOptimization and Sizing For Propulsion System of Liquid Rocket Using Genetic AlgorithmspetNoch keine Bewertungen
- RocketWeightsRohrschneiderR 8900Dokument229 SeitenRocketWeightsRohrschneiderR 8900wgabler2001455Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manuscrit These Balesdent 2011Dokument252 SeitenManuscrit These Balesdent 2011bmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of A Mass Estimating Relationship Database For Launch Vehicle Conceptual DesignDokument229 SeitenDevelopment of A Mass Estimating Relationship Database For Launch Vehicle Conceptual DesignbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace Science TechnologyDokument16 SeitenAerospace Science TechnologybmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doekhie Et Al. - A Computer-Based Tool For Preliminary Design and Performance Assessment of Continuous Detonation Wave EnginesDokument14 SeitenDoekhie Et Al. - A Computer-Based Tool For Preliminary Design and Performance Assessment of Continuous Detonation Wave EnginesbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- NASA TM-107473 Comparison of High Aspect Ratio CoolingDokument13 SeitenNASA TM-107473 Comparison of High Aspect Ratio CoolingbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulator R40Dokument2 SeitenRegulator R40bmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modeling and Simulation of Launch Vehicles Using Object-Oriented Programming: Impact of The Engine Parameters On The Launcher PerformanceDokument13 SeitenModeling and Simulation of Launch Vehicles Using Object-Oriented Programming: Impact of The Engine Parameters On The Launcher PerformancebmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Microwave SuperconductivityDokument32 SeitenFundamentals of Microwave SuperconductivitybmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 791S16L08 MERsxDokument45 Seiten791S16L08 MERsxbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Estimating Relationships For Liquid Rocket Engines: Extended AbstractDokument3 SeitenMass Estimating Relationships For Liquid Rocket Engines: Extended AbstractbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Space Systems Cost ModelingDokument43 SeitenSpace Systems Cost ModelingErickGarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NASA TP-1998-208530 Reusable Rocket Engine Operability Modeling and AnalysisDokument91 SeitenNASA TP-1998-208530 Reusable Rocket Engine Operability Modeling and AnalysisbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIAA 2001-4619 A Study of Air Launch Methods For RLVsDokument16 SeitenAIAA 2001-4619 A Study of Air Launch Methods For RLVsbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen Storage Using Lightweight TanksDokument19 SeitenHydrogen Storage Using Lightweight Tanksbmsprague100% (1)
- Naca RM E58b25Dokument18 SeitenNaca RM E58b25bmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIAA-2002-5220 Progress in The Design of A Reusable Launch Vehicle StageDokument11 SeitenAIAA-2002-5220 Progress in The Design of A Reusable Launch Vehicle StagebmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- MMGH 10.1.1.120.9455Dokument176 SeitenMMGH 10.1.1.120.9455bmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spacecraft StructuresDokument38 SeitenSpacecraft StructuresBahtiar Setiawan100% (1)
- AIAA-2003-7057 Technical Development Perspective of Reusable Booster StagesDokument11 SeitenAIAA-2003-7057 Technical Development Perspective of Reusable Booster StagesbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009gfd0001308 200gfgf8049065Dokument28 Seiten2009gfd0001308 200gfgf8049065bmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- NASA CR - 1998-208958 - 3D CharacteristicsDokument8 SeitenNASA CR - 1998-208958 - 3D CharacteristicsbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2D and 3D Method of Characteristic Tools For Complex Nozzle DevelopmentDokument42 Seiten2D and 3D Method of Characteristic Tools For Complex Nozzle DevelopmentbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficiency Analysis of An Aerospike Nozzle: Dipak J. Choudhari, Uday V. AsolekarDokument5 SeitenEfficiency Analysis of An Aerospike Nozzle: Dipak J. Choudhari, Uday V. AsolekarAswith R ShenoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To TurbomachineryDokument66 SeitenIntroduction To TurbomachineryJeff SimpsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stabilization of Abi 00 Cox DDokument100 SeitenStabilization of Abi 00 Cox DbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Methods in Gas DynamicsDokument171 SeitenNumerical Methods in Gas DynamicsbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stabilization of Abi 00 Cox DDokument100 SeitenStabilization of Abi 00 Cox DbmspragueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Dimensional AnalysisDokument16 SeitenDimensional AnalysisChara ZerihunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module22 - Consequence Analysis - Effect ModelDokument52 SeitenModule22 - Consequence Analysis - Effect ModelMinh ThưNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transmission Syn FE 75W-90 A 0410Dokument1 SeiteTransmission Syn FE 75W-90 A 0410Fer EmilNoch keine Bewertungen
- ML12142A123Dokument58 SeitenML12142A123Mohammed RiyaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of INdustrial ControlDokument5 SeitenFundamentals of INdustrial ControlKirtikumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Fields & Waves: MD Abu Ismail Siddique Lecturer Ete, RuetDokument60 SeitenElectromagnetic Fields & Waves: MD Abu Ismail Siddique Lecturer Ete, RuetSmshihab ShararNoch keine Bewertungen
- B SafeunitDokument4 SeitenB SafeunitSabariyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Supplee's ParadoxDokument3 SeitenSupplee's Paradoxperception888Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mhf4u Unit 5Dokument14 SeitenMhf4u Unit 5bennn666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Control (Switch) - Test 01-03-2010Dokument9 SeitenSpeed Control (Switch) - Test 01-03-2010harikrishnanpd3327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dell 1815dn Service Manual PDFDokument150 SeitenDell 1815dn Service Manual PDFHugo Manuel Sánchez MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurements and Instrumentation Unit 1Dokument62 SeitenMeasurements and Instrumentation Unit 1R. Jhansirani83% (6)
- 3516BDokument392 Seiten3516Bmuhammad arif95% (22)
- Earth and Life Science Copy (Repaired)Dokument39 SeitenEarth and Life Science Copy (Repaired)Aaron Manuel MunarNoch keine Bewertungen
- James Wilberding-Plotinus' Cosmology - A Study of Ennead II.1 (40) - Text, Translation, and Commentary (2006) PDFDokument281 SeitenJames Wilberding-Plotinus' Cosmology - A Study of Ennead II.1 (40) - Text, Translation, and Commentary (2006) PDFRobert BrennerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Waves and Particles According To Classical PhysicsDokument8 Seiten1.1 Waves and Particles According To Classical PhysicsLUCKY KUSHWAHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Report Sample 5Dokument35 SeitenInternship Report Sample 5SUMIT KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC O& M City Mall Version 1.0Dokument12 SeitenAC O& M City Mall Version 1.0yewminyun6098Noch keine Bewertungen
- Astm E0169 16Dokument6 SeitenAstm E0169 16archanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herschel 400 2 Log BookDokument29 SeitenHerschel 400 2 Log BookEveraldo FaustinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- C-05 April - May-2012Dokument30 SeitenC-05 April - May-2012John SandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strain GuageDokument6 SeitenStrain GuageChristian EspanolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1757 Nursing Foundation Question BankDokument11 Seiten1757 Nursing Foundation Question BankSovon Samanta100% (1)
- Lecture 1 U & DDokument33 SeitenLecture 1 U & DMr DrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Least Learned Competencies With Interventions ConductedDokument2 SeitenList of Least Learned Competencies With Interventions ConductedGerry Chel-Nunez Awa-Laurente Aga100% (1)
- Theory AssignmentDokument12 SeitenTheory Assignmentfahadfadi48Noch keine Bewertungen
- C184 E037bDokument48 SeitenC184 E037bNeyda Flores VasquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMQ 75m-Min - 1500mm (SK92372.1AD-IEC90-90LP)Dokument2 SeitenBMQ 75m-Min - 1500mm (SK92372.1AD-IEC90-90LP)YeisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New Fatigue Damage Accumulation Rating Life Model of Ball Bearings Under Vibration LoadDokument11 SeitenA New Fatigue Damage Accumulation Rating Life Model of Ball Bearings Under Vibration LoadAlbertoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Construction Design (ULS Only)Dokument93 SeitenComposite Construction Design (ULS Only)CawanNeroMiranio100% (1)