Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Natural Enemies Poster PDF
Hochgeladen von
AgusNurjayaFaizOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Natural Enemies Poster PDF
Hochgeladen von
AgusNurjayaFaizCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Meet the Beneficials:
Natural Enemies of Garden Pests
Predators
hunt, attack, and kill their prey.
Encourage these natural enemies by avoiding
pesticides that kill them; choosing plants that provide
them pollen, nectar, and shelter; and keeping ants out
of pest infested plants. Common predators that eat
garden pests are pictured below.
Convergent lady beetles prefer to eat aphids but sometimes eat whiteflies and other soft-bodied insects.
Shown here are the adult (left), larva (center), and cluster of eggs (right).
Green lacewing adults eat
nectar and pollen. Some species
also eat insects.
Green lacewing larvae feed on
mites, eggs, and small insects,
especially aphids.
Green lacewing eggs are laid on
slender stalks in groups (as shown
here) or individually.
Predaceous ground beetle adults
stalk soil-dwelling insects, such as
cutworms and root maggots.
Predaceous ground beetle larvae
live on soil and in litter, feeding on
almost any invertebrate.
Assassin bugs attack almost any
insect.
Pirate bugs attack mites and any
tiny insect, especially thrips.
Damsel bugs are predaceous on
a wide variety of small insects.
Soldier beetle adults eat mostly
aphids; their larvae are soil-dwelling.
Spiders, including this crab
spider, attack all types of insects.
Some parasites attack insect eggs,
such as the Trissolcus species wasp.
Parasitized aphids die and turn
into crusty mummies that can
be black or beige. The hole in
the mummy at left indicates a
parasite has emerged. The aphid
in the middle is healthy.
Parasites
Syrphid fly (flower fly, hover fly)
adults eat pollen and nectar.
Syrphid fly larvae eat mostly
aphids but also soft-bodied insects.
Sixspotted thrips attack mostly
mites.
Western predatory mites attack
pest mites.
Adults of predatory wasps,
such as this paper wasp, prey on
caterpillars and other insects.
Praying mantids dont control
pests, because they eat both
beneficials and pests.
Visit the Natural Enemies Gallery
at www.ipm.ucdavis.edu
for more information!
Natural Enemies poster_TAKE 6_gold.indd 1
live and
feed in or on a larger
animal (host). Nearly
all insect pests have
at least one parasite
that attacks them.
Insects that parasitize
other invertebrates
(sometimes called
parasitoids) are parasitic
only in their immature
stages and kill their
host just as they reach
maturity. Most insect
parasites are hostspecific wasps or flies,
and many are so small
that often you wont see
them. An adult parasite
can lay eggs in hundreds
of host individuals
with a resulting quick
reduction in pest
numbers.
The blackish scale insects have
wasp larvae developing within.
Caterpillar parasites include the
Hyposoter exiguae wasp.
Aphid parasite life cycle: The
adult lays an egg in an aphid. The
egg hatches into a larva that feeds
inside. After killing the aphid, the
wasp larva pupates then emerges
as a wasp.
PHOTOS: J. K. CLARK
Statewide Integrated Pest Management Program
5/17/11 2:38 PM
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 10-Hydroponics System PDFDokument28 Seiten10-Hydroponics System PDFAgusNurjayaFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
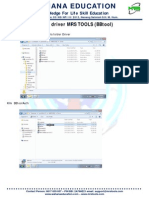
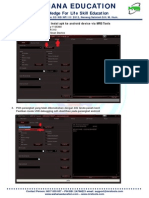
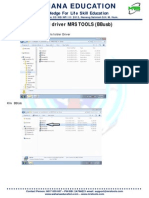
- 8.install Driver MRS TOOLS (BBtool)Dokument4 Seiten8.install Driver MRS TOOLS (BBtool)MRS TOOLSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsooft Publisher 2013 Brochure Free PDF Template PDFDokument49 SeitenMicrosooft Publisher 2013 Brochure Free PDF Template PDFAgusNurjayaFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquaculture development in South Sumatra open watersDokument15 SeitenAquaculture development in South Sumatra open watersrierNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2007-1S72 1f1s7460e1 PDFDokument62 Seiten2007-1S72 1f1s7460e1 PDFAgusNurjayaFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
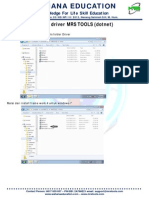
- 6.install Driver MRS TOOLS (Dotnet)Dokument3 Seiten6.install Driver MRS TOOLS (Dotnet)MRS TOOLSNoch keine Bewertungen
- R8 GT Wing - Install Instructions - MASTERDokument13 SeitenR8 GT Wing - Install Instructions - MASTERohshafiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surround ToolsDokument93 SeitenSurround ToolsVivek SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18.install Game APK With Mrstools 2.3 FATHDokument2 Seiten18.install Game APK With Mrstools 2.3 FATHMRS TOOLSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.install MRS TOOLS V 2.1 RebuildDokument4 Seiten2.install MRS TOOLS V 2.1 RebuildMRS TOOLSNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3install Driver MRS TOOLS BBusb PDFDokument5 Seiten3install Driver MRS TOOLS BBusb PDFAgusNurjayaFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Jupiter-Z1 1l1dy460e1 PDFDokument63 Seiten2012 Jupiter-Z1 1l1dy460e1 PDFAgusNurjayaFaiz100% (1)
- Lagenda Z 110 New Jupiterz - 1e2p2460e1Dokument62 SeitenLagenda Z 110 New Jupiterz - 1e2p2460e1Hasroy Lagenda83% (23)
- 2003-5TL1 1C5TL460E1 Mio2003Dokument53 Seiten2003-5TL1 1C5TL460E1 Mio2003js_maxwell50% (2)
- MIO Sporty Catalog PartsDokument52 SeitenMIO Sporty Catalog PartsAngga Chumie Bernadi81% (16)
- 2013 VIXION 1M1PA460EA Rev PDFDokument68 Seiten2013 VIXION 1M1PA460EA Rev PDFAgusNurjayaFaiz100% (1)
- Employee Year Austria Brazil Canada France Germany Mexico UK USADokument2 SeitenEmployee Year Austria Brazil Canada France Germany Mexico UK USARajat PaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 45P3 Byson 1m45p460e1 PDFDokument62 Seiten2012 45P3 Byson 1m45p460e1 PDFAgusNurjayaFaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Anna Rochester (1942) - LENIN On The Agrarian Question PDFDokument223 SeitenAnna Rochester (1942) - LENIN On The Agrarian Question PDFHoyoung ChungNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHG Models India PDFDokument10 SeitenSHG Models India PDFdolly100% (1)
- Tongue TwisterDokument13 SeitenTongue Twisteraatynn77Noch keine Bewertungen
- l3 Preview Readings Final s13Dokument8 Seitenl3 Preview Readings Final s13api-147406171Noch keine Bewertungen
- Experiencing TextilesDokument32 SeitenExperiencing TextilesBhavya Arun PakkanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NABARD Grade A - Agriculture & Rural Development - Set 5Dokument4 SeitenNABARD Grade A - Agriculture & Rural Development - Set 5Prakash BabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Conversion of Agricultural Land Into Built SurfacesDokument6 SeitenThe Conversion of Agricultural Land Into Built Surfacesstoica_ramona_5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final ProjectDokument13 SeitenFinal Projectapi-249539201Noch keine Bewertungen
- SWOT Analysis of ZTBLDokument10 SeitenSWOT Analysis of ZTBLMoieenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2000 Calorie Meal PlanDokument5 Seiten2000 Calorie Meal PlanChris Theberge98% (58)
- Codex Alimentarius PDFDokument255 SeitenCodex Alimentarius PDFFlavio SoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Grade 2Dokument5 SeitenScience Grade 2Roland Garcia Pelagio Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Seed Listing CatalogDokument20 SeitenSeed Listing CataloglilithblackthorneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Navdanya Visitor GuideDokument29 SeitenNavdanya Visitor GuideevergreenmanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Heirloom Rice Recipe CalendarDokument38 Seiten2016 Heirloom Rice Recipe CalendarsososolalalaiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caroli FoodDokument12 SeitenCaroli FoodFloriantheGreatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Induction of Lactation in Crossbred CattleDokument12 SeitenInduction of Lactation in Crossbred CattleDr. MANOJ SHARMA100% (3)
- 1 To 3Dokument49 Seiten1 To 3Vikki NandeshwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dipping TanksDokument8 SeitenDipping TanksSaid Ahmed SalemNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicroFinance and Women's Empowerment in Africa PDFDokument28 SeitenMicroFinance and Women's Empowerment in Africa PDFattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Electricity Tariff Fy2015-16Dokument8 SeitenAP Electricity Tariff Fy2015-16somnath250477Noch keine Bewertungen
- Academic Question Paper Test 3 PDFDokument21 SeitenAcademic Question Paper Test 3 PDFRam SnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chodosh Guide 15-16 Final-ADokument81 SeitenChodosh Guide 15-16 Final-AshasdafNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSFSTDokument127 SeitenBSFSTRajesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poultry Beyond 2023Dokument19 SeitenPoultry Beyond 2023Uday PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- AguilarDokument7 SeitenAguilarLovely CarbonelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Ideas 13th Edition Miller Heeren Hornsby Test BankDokument46 SeitenMathematical Ideas 13th Edition Miller Heeren Hornsby Test Bankdavid100% (24)
- Envi 118 - Principles in Watershed Management (Chapter IV)Dokument17 SeitenEnvi 118 - Principles in Watershed Management (Chapter IV)Gilbert D. ManongsongNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC Organic Vegetable Production Leading To Organic Agriculture Production NC IIDokument53 SeitenCBC Organic Vegetable Production Leading To Organic Agriculture Production NC IIJapet J100% (2)
- Management Oil Palm (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq.) Nursery in Bangun Bandar Estate, North SumateraDokument8 SeitenManagement Oil Palm (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq.) Nursery in Bangun Bandar Estate, North SumateraWendy JuliansyahNoch keine Bewertungen