Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Free Response Practice Questions Optics
Hochgeladen von
Ian StantonCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Free Response Practice Questions Optics
Hochgeladen von
Ian StantonCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Free Response Practice Questions : Optics
1. a. Light of a single wavelength is incident on a single slit of width w (w is a few wavelengths.) Sketch a graph of the
intensity as a function of position for the pattern formed on a distant screen.
b.
Repeat for the case in which there are two slits. The slits are of width w and are separated by a distance d
(d >> w). Sketch a graph of the intensity as a function of position for the pattern formed on a distant screen.
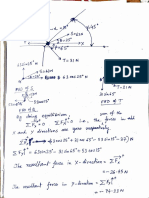
2. Light consisting of two wavelengths,
a = 4.4 x 107 meter and b = 5.5 x 107 meter, is
incident normally on a barrier with two slits separated
by a distance d. The intensity distribution is
measured along a plane that is a distance
L = 0.85 meter from the slits as shown above. The
movable detector contains a photoelectric cell whose
position y is measured from the central maximum.
The first-order maximum for the longer wavelength
b occurs at y = 1.2 x 102 meter.
a.
Determine the slit separation d.
b. At what position, Ya, does the first-order maximum occur for the shorter wavelength a?
Free Response Practice Questions : Optics
3. An object of height 1 centimeter is placed 6 centimeters to the left of a converging lens whose focal length is 8
centimeters, as shown on the diagram above.
(a) Calculate the position of the image. Is it to the left or right of the lens? Is it real or virtual?
(b) Calculate the size of the image. Is it upright or inverted?
(c) On the diagram, locate the image by ray tracing.
(d) What simple optical instrument uses this sort of object-image relationship?
4. The surface of a glass plate (index of refraction n3 =
1.50) is coated with a transparent thin film (index of
refraction n2 = 1.25). A beam of monochromatic light of
wavelength 6.0 x 10 7 meter traveling in air (index of
refraction n1 = 1.00) is incident normally on surface S1 as
shown. The beam is partially transmitted and partially
reflected.
a.
Calculate the frequency of the light.
b.
Calculate the wavelength of the light in the thin film.
The beam of light in the film is then partially reflected and partially transmitted at surface S 2
c. Calculate the minimum thickness d1 of the film such that the resultant intensity of the light reflected back into the air is
a minimum.
d. Calculate the minimum nonzero thickness d2 of the film such that the resultant intensity of the light reflected back into
the air is a maximum.
Free Response Practice Questions : Optics
Answers
1.
2.
a) m B = d x / L (1) (5.5x107) = d (1.2x102) / (0.85)
d = 3.9x105 m
b) m a = d x / L (1) (4.4x107) = (3.9x105) x / (0.85)
x = 9.6x103 m
3.
a)
1/f = 1/do + 1/di 1/8 = 1/6 + 1/di di = 24 cm, left of lens, virtual
b) M = di / do
M = (24) / 6 = +4 M = hi / ho 4 = hi / 1 cm hi = 4 cm, upright
c)
d) Magnifying glass, or telescope / microscope.
4.
a) c = f 3x108 = f (6x107) f = 5x1014 Hz.
b) n1 1 = n2 2
(1) (6x107) = (1.25) = 4.8x107 m = 480 nm
c) The light is traveling to progressively more dense materials, so undergoes phase shifts at both boundaries S 1 and S2
essentially canceling out this phase shift (from flips). To get minimum intensity (destructive), the total phase shift from
traveling in the film should be film so the film thickness should film = 480 nm = 120 nm
d) Based on the same analysis above. To get maximum intensity (constructive) the total phase shift from traveling in the film
should be 1 film, so the film thickness should be film = 480 nm = 240 nm
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Calc2 Final Exam Study GuideDokument2 SeitenCalc2 Final Exam Study GuideIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedDokument3 SeitenCalculus Cheat Sheet Integrals ReducedShahnaz GazalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clash Royale Cheats Master BlackbookDokument41 SeitenClash Royale Cheats Master BlackbookIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art Criticism Four StepsDokument4 SeitenArt Criticism Four StepsIan Stanton100% (1)
- Green Chemistry Pogil Activity Sum13Dokument2 SeitenGreen Chemistry Pogil Activity Sum13Ian StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Study GuideDokument4 SeitenUnit 7 Study GuideIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDokument5 SeitenCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralshyd arnes100% (5)
- Art History Survey II Course OverviewDokument5 SeitenArt History Survey II Course OverviewIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13a-Waves and Optics MC Practice Problems - Section C Geometric OpticsDokument19 Seiten13a-Waves and Optics MC Practice Problems - Section C Geometric OpticsIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SatireDokument18 SeitenSatireIan Stanton100% (2)
- Elections and CampaignsDokument12 SeitenElections and CampaignsIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congress and Public OpinionDokument7 SeitenCongress and Public OpinionIan Stanton25% (4)
- Apg&P Unit II Ch. 8 Elections & Campaigns Reading QuestionsDokument4 SeitenApg&P Unit II Ch. 8 Elections & Campaigns Reading QuestionsIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apg&P Unit II Ch. 8 Elections & Campaigns Reading QuestionsDokument4 SeitenApg&P Unit II Ch. 8 Elections & Campaigns Reading QuestionsIan StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Dokument16 SeitenReview For Unit 3 - Chapter 3 Part 2: Sin Xisthesameas (Sinx) Know The Unit Circle!!Ian StantonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- NCP 1014Dokument24 SeitenNCP 1014rodricaldasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bicycle Repair ManualDokument162 SeitenBicycle Repair Manualrazvancc89% (9)
- An Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Dokument5 SeitenAn Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Johnas DalusongNoch keine Bewertungen
- ¿Cómo Hacerlo?: Dr. Jorge Ramírez Medina, Dr. Guillermo Granados Ruíz EGADE Business SchoolDokument17 Seiten¿Cómo Hacerlo?: Dr. Jorge Ramírez Medina, Dr. Guillermo Granados Ruíz EGADE Business Schoolgalter6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Delivered Voided Application (Surrender Instrument) Returned To at - Sik - Hata Nation of Yamasee MoorsDokument20 SeitenDelivered Voided Application (Surrender Instrument) Returned To at - Sik - Hata Nation of Yamasee MoorsMARK MENO©™Noch keine Bewertungen
- Renal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaDokument9 SeitenRenal Angina Index in Pediatric Septic Patients As A Predictor of Acute Kidney Injury in Remote AreaFarhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evolution of The Fire SprinklerDokument11 SeitenEvolution of The Fire SprinklerPedro DudesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManupptDokument65 SeitenManupptKrishanarju VenkatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ZSL National Red List of Nepal's Birds Volume 2Dokument636 SeitenZSL National Red List of Nepal's Birds Volume 2Tushita LamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WaidhanDokument86 SeitenWaidhanPatel Nitesh OadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2. Green finance and sustainable development in EuropeDokument15 Seiten2. Green finance and sustainable development in Europengocanhhlee.11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Section V - Contract Adminstration Procedures Major BuildingsDokument13 SeitenSection V - Contract Adminstration Procedures Major BuildingsAyodele Oluwaseyi DinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME1001, ME1004, ME1005 - Basic Mech+Graphics+Workshop Pract.Dokument6 SeitenME1001, ME1004, ME1005 - Basic Mech+Graphics+Workshop Pract.Mayank AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analisis Efektivitas Inklusi Keuangan Di BMT Syariah Riyal: PendahuluanDokument25 SeitenAnalisis Efektivitas Inklusi Keuangan Di BMT Syariah Riyal: PendahuluanEma Rina SafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07-02-2023 MS QLNDokument3 Seiten07-02-2023 MS QLNSummaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caring Seedlings TLE Weekly PlanDokument3 SeitenCaring Seedlings TLE Weekly PlanMarjorie RaymundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1Dokument2 SeitenKunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1anirbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin On Socket Healing After Mandibular Third Molar ExtractionsDokument10 SeitenEfficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin On Socket Healing After Mandibular Third Molar Extractionsxiaoxin zhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- As Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Dokument7 SeitenAs Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Anonymous fFKqcYNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLTW: Digital Electronics Syllabus For Mrs. Yusufi: Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and DigitalDokument5 SeitenPLTW: Digital Electronics Syllabus For Mrs. Yusufi: Unit 1: Fundamentals of Analog and DigitalTriston DurbinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education Region IV-A Business Plan GuideDokument4 SeitenDepartment of Education Region IV-A Business Plan GuideSEAN DANIEL AGUARESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flap System RiginDokument12 SeitenFlap System RiginHarold Reyes100% (1)
- World MultipleDokument271 SeitenWorld MultipleatrkpoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS 704 Socio-Emotional and Moral Development in Middle ChildhoodDokument25 SeitenCS 704 Socio-Emotional and Moral Development in Middle ChildhoodPatricia PamintuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- LADY BroshureDokument2 SeitenLADY BroshureMcGabi GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vaje 3 - Macionis in PlummerDokument2 SeitenVaje 3 - Macionis in PlummerLazar DjondricNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finimpianti Power EngDokument2 SeitenFinimpianti Power EngJosip GrlicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1Dokument11 SeitenSri Dwi Mutiara-Jurnal CRSS OSNE 1sri dwi mutiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DodupukegakobemavasevuDokument3 SeitenDodupukegakobemavasevuMartian SamaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsDokument1 SeiteMaklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination Detailsaccung manNoch keine Bewertungen