Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
MUSC 2610 Midterm Study Guide: Sound Principles
Hochgeladen von
Derrin LeeOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MUSC 2610 Midterm Study Guide: Sound Principles
Hochgeladen von
Derrin LeeCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
MUSC 2610
Midterm Study Guide
Fall 2013, Dr. Greene
The midterm exam (10/9/13) will cover the following terms and concepts.
SOUND PRINCIPLES
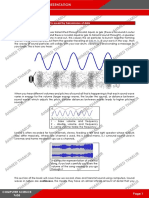
Propagation of sound in air-compression and refraction of air molecules being pushed in a wave
form
Conversion of sound into neural impulses- in the cochlea and the basilar membrane
Sound wave terms:
-
Cycle-one full compression in refraction
Period- the amount of time it takes to complete one cycle
Frequency- number of cycles per seconds in Hz
Amplitude- The maximum mediation of sound
Phase- The point along the waveform at any given moment
Threshold of audibility/pain- the lowest sound we can hear (0dB) the loudest sound we can hear
is (120dB)
Frequency range of human hearing- 20Hz to 20,000Htz
Pitch perception-how the ear hears a frequency
Loudness: the decibel-comparing how intense the sound actually is.
Equal Loudness (Fletcher-Munson) curve- A curve that shows where our perception of loudness
is
Amplitude envelope- ADSR (attack, Decay, Sustain, Release)
Sound production by:
-
Strings-The vibration of the spring after being plucked moves the air molecule to make a
sound
Reeds- vibrates against the mouth piece and allows air to flow and stop with each
vibration to make a sound
Flute- air is blown across the blow hole and the air goes in and out of the column
Brass- vibration of the lips produces the sound wave
FREQUENCY SPECIFICS
Spectrum-the frequency of a sound
Fundamental-the lowest frequency that defines pitch
Partials (harmonic and inharmonic) harmonic is integer multiples of the fundamentals and
inharmonic is non-integer multiples
Noise-random energy across the frequency spectrum; non periodic wave form
Timbre-The tone quality and color of a sound
STUDIO BASICS
Balanced and unbalanced cables-Balanced cables picks up less outside interference and
unbalanced does not
Mic level vs. line level- Mic level is a lower level from the mic; line level is use to boost the mic
level using a preamp
Transducer-Turns one form of energy to another
Dynamic microphone-Magnate in the coil and not very sensitive to sound
Condenser microphone-two plate system and is very sensitive to sound
Microphone directionality- cardioid shaped like a heart; omnidirectional picks up sound all
around; bidirectional picks up sound from two different ends
DIGITAL AUDIO
Analog vs. Digital- Analog is continuous sound and digital is a series of numbers in sound
ADC/DAC- audio to digital converter; digital to analog converter
Sample- measures the amplitude of sound given at an instant
Sampling rate- the number of samples per second
Bit depth-tell us the resolution of amplitude in a sample
CD standard (sampling rate and bit depth)-44.1kz is sampling rate and 16-bit is the bit depth
Trace the path of audio (in words and/or a drawing) from microphone to computer, and back out
to speakers. At each stage, indicate whether the signal is analog or digital.
Sound vibrations-electrical energy-ADC-digital-cpu-digital-DAC converter-electrical energysound analog wave
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- JBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementVon EverandJBL Audio Engineering for Sound ReinforcementBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Fundamentals of Sound Quality: Dr. Arunkumar M. SampathDokument32 SeitenFundamentals of Sound Quality: Dr. Arunkumar M. SampathsikmmmppsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sounds' Final Slide - PPSXDokument98 SeitenSounds' Final Slide - PPSXSHUBHI SHRIVASTAVANoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound / Audio: Multimedia FundamentalsDokument57 SeitenSound / Audio: Multimedia FundamentalsVivian GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUTC - Week2 Handout 2 PDFDokument6 SeitenMUTC - Week2 Handout 2 PDFLane TraversNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Sound and AudioDokument20 SeitenChapter 2 Sound and AudiorpNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 Digital Audio - Nuts and BoltsDokument52 Seiten04 Digital Audio - Nuts and BoltsKanad Kumar GhoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Audio - Nuts and BoltsDokument52 SeitenDigital Audio - Nuts and BoltsAthira KuttyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio Production Theory: School of Science and Humanities Department of Visual CommunicationDokument43 SeitenAudio Production Theory: School of Science and Humanities Department of Visual Communicationpiano&musicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPD - Public Address SystemDokument93 SeitenCPD - Public Address SystemThilina SarangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Description: Understanding Audio PhysicsDokument11 SeitenProject Description: Understanding Audio PhysicsAlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound MeasurementsDokument26 SeitenSound MeasurementsAnuraag SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ear Does Fourier AnalysisDokument14 SeitenEar Does Fourier AnalysisLuckySharma SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 (Audio)Dokument29 SeitenChapter 6 (Audio)Ain FarahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic of SoundDokument54 SeitenBasic of SoundRoslina Jaafar75% (4)
- Introduction To Noise: Department of Occupational Safety & Health, Ministry of Human ResourcesDokument41 SeitenIntroduction To Noise: Department of Occupational Safety & Health, Ministry of Human ResourcesShazana Mat TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPEG AudioDokument68 SeitenMPEG Audiocsivaranjani69Noch keine Bewertungen
- BIT3233/BIT32303 Audio Video Production: Azizan Bin Ismail Level 4, Pm9, FSKTM RPP04Dokument38 SeitenBIT3233/BIT32303 Audio Video Production: Azizan Bin Ismail Level 4, Pm9, FSKTM RPP04FasihahIdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of AudioDokument46 SeitenBasics of AudioSammy KipkosgeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH # 4 AudioDokument55 SeitenCH # 4 AudioHamza Nazir Hamza NazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recording, Eq & FX KeywordsDokument7 SeitenRecording, Eq & FX KeywordssimonballemusicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound Power, Sound Pressure, and Octave Bands Explained: 39 Series Engineering GuidelinesDokument3 SeitenSound Power, Sound Pressure, and Octave Bands Explained: 39 Series Engineering Guidelinesvj8584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Light NoteDokument39 SeitenLight NoteNur Amalina AzizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject:: Audio, Video & TV EngineeringDokument71 SeitenSubject:: Audio, Video & TV EngineeringNilesh KaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- AcousticsDokument56 SeitenAcousticsLorraine I. Jamero100% (1)
- Audio and Public Address SystemsDokument46 SeitenAudio and Public Address SystemsColesha BarukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HVAC Systems Noise ControlDokument109 SeitenHVAC Systems Noise ControlYaseen MallickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Noise Pollution Control: JD Waarachchige CH 4182Dokument85 SeitenIndustrial Noise Pollution Control: JD Waarachchige CH 4182Udya DevarajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MART 201 Final Exam Guide V.2Dokument3 SeitenMART 201 Final Exam Guide V.2qwewqwqwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ger 4248 Acoustic Terms Definitions General InformationDokument14 SeitenGer 4248 Acoustic Terms Definitions General InformationsipurmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Sound & AcoustDokument8 Seiten1 Sound & AcoustAayush BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building's Structure or The GroundDokument5 SeitenBuilding's Structure or The GroundPat GeronzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics Module 1Dokument33 SeitenAcoustics Module 1mariyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound Waves IIDokument68 SeitenSound Waves IIEng Bile LastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- AUDIO - Basic Sound Concepts: Name:Rani Mariya Joy Roll No:24 MCA20Dokument23 SeitenAUDIO - Basic Sound Concepts: Name:Rani Mariya Joy Roll No:24 MCA20Marianinu antonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics, Sound and Sound Properties: OutlineDokument25 SeitenAcoustics, Sound and Sound Properties: OutlineSHREYA LOHAKARENoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Hearing: DR BukanuDokument31 SeitenPhysiology of Hearing: DR BukanuJumanne JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Reviewer 1Dokument55 SeitenArchitectural Reviewer 1Joshua Mari Villaluna100% (2)
- Different Acoustic Terms: Arbu 3Dokument18 SeitenDifferent Acoustic Terms: Arbu 3Angel CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sound ReinforcementDokument43 SeitenSound Reinforcementshreya puthranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics Presentation1Dokument87 SeitenAcoustics Presentation1von kervy onradeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Music ProductionDokument2 SeitenModule 1 - Music ProductionYuki KannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audio Production 1Dokument7 SeitenAudio Production 1Sarah MbeweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar On AcousticsDokument39 SeitenSeminar On AcousticsPreethi HannahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Board Exam Reviewer: ElementsDokument6 SeitenArchitectural Board Exam Reviewer: ElementsCherry Ann Hernandez YamatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 - Physics of SoundDokument45 Seiten2 - Physics of Soundlala silangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speech Chapter 4Dokument41 SeitenSpeech Chapter 4ai20152023Noch keine Bewertungen
- AcousticsDokument56 SeitenAcousticsRidhuGahalotRdgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review of Sound IntensityDokument4 SeitenLiterature Review of Sound Intensityfvffv0x7100% (1)
- Lect 4Dokument14 SeitenLect 4mahmoudelshemy968Noch keine Bewertungen
- Architectural Acoustics - ReviewersDokument5 SeitenArchitectural Acoustics - ReviewersMarc Gregory Queral OlanioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1.3 SoundDokument10 Seiten1.1.3 SoundGamer ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ear Does Fourier AnalysisDokument6 SeitenEar Does Fourier AnalysisLuckySharma SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimedia Digital AudioDokument7 SeitenMultimedia Digital AudioMohammed Abdel Khaleq DwikatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acoustics 4-30-09Dokument115 SeitenAcoustics 4-30-09vdchaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is SoundDokument22 SeitenWhat Is SoundAbigail de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6-Audio Basics FileType MP3ComprDokument145 Seiten6-Audio Basics FileType MP3Comprعلی احمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule 10-02Dokument6 SeitenSchedule 10-02Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- To Go Menu Final December 2019Dokument2 SeitenTo Go Menu Final December 2019Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume-For St. Mark Word-1Dokument3 SeitenResume-For St. Mark Word-1Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2120 T SCHMWF Spring 2010 RDokument2 Seiten2120 T SCHMWF Spring 2010 RDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05a KEYBOARD SPLITDokument4 Seiten05a KEYBOARD SPLITDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derrin Lee Resume Work 2018Dokument3 SeitenDerrin Lee Resume Work 2018Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Print PreviewDokument4 SeitenPrint PreviewDerrin Lee100% (1)
- Derrin Lee 509 Pebble Creek Cir. Antioch, TN 37013 (901) 254-3399 CellDokument3 SeitenDerrin Lee 509 Pebble Creek Cir. Antioch, TN 37013 (901) 254-3399 CellDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derrin Lee 2020 ResumeDokument3 SeitenDerrin Lee 2020 ResumeDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Order of Service Morning Service First Anniversary Day Dec 9Dokument1 SeiteOrder of Service Morning Service First Anniversary Day Dec 9Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Pop FinalDokument12 SeitenHistory of Pop FinalDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Music Ministry Propsal BudgetDokument6 SeitenMusic Ministry Propsal BudgetDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teddy C.Dokument1 SeiteTeddy C.Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quincy JonesDokument5 SeitenQuincy JonesDerrin Lee100% (1)
- Maliki Leavell-Murphy - 6TH Grade History Ancient Egypt EssayDokument2 SeitenMaliki Leavell-Murphy - 6TH Grade History Ancient Egypt EssayDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form9A Color ApplicationDokument28 SeitenForm9A Color ApplicationDerrin Lee100% (1)
- Thursday, May 8, 10:10-12:10: Multiple-Choices, Short-Answer, Essay QuestionsDokument4 SeitenThursday, May 8, 10:10-12:10: Multiple-Choices, Short-Answer, Essay QuestionsDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- American History PaperDokument5 SeitenAmerican History PaperDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Recording Business RevisedDokument6 SeitenThe Recording Business RevisedDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resident - Ministry EvaluationSpring 2014Dokument2 SeitenResident - Ministry EvaluationSpring 2014Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- W.E.B. Dubois: Dubois: Sociologist, Philosopher, Black Leader)Dokument3 SeitenW.E.B. Dubois: Dubois: Sociologist, Philosopher, Black Leader)Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Etheridge KnightDokument8 SeitenEtheridge KnightDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUSC 2610 Midterm Study Guide: Sound PrinciplesDokument4 SeitenMUSC 2610 Midterm Study Guide: Sound PrinciplesDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap6 AnswersDokument2 SeitenChap6 AnswersDerrin Lee50% (2)
- Derrin Lee 3500 John A. Merritt Blvd. Nashville TN, 37209 P.O. Box 6018 (901) 254-3399 Cell (901) 942-4509 HomeDokument3 SeitenDerrin Lee 3500 John A. Merritt Blvd. Nashville TN, 37209 P.O. Box 6018 (901) 254-3399 Cell (901) 942-4509 HomeDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap5 AnswersDokument2 SeitenChap5 AnswersDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of Pop FinalDokument12 SeitenHistory of Pop FinalDerrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap3 AnswersDokument2 SeitenChap3 AnswersDerrin Lee0% (1)
- MUSC 3385 History of Popular Music CH 1: Themes and Streams of American Popular Music, Pp. 1 - 19Dokument2 SeitenMUSC 3385 History of Popular Music CH 1: Themes and Streams of American Popular Music, Pp. 1 - 19Derrin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bài 1: Fill in The Blank With Present Simple, Present Continuous or Past SimpleDokument6 SeitenBài 1: Fill in The Blank With Present Simple, Present Continuous or Past SimplePhương Anh Đỗ NgọcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caeneus and PoseidonDokument77 SeitenCaeneus and PoseidonSabrina CareyNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of DiamondsDokument21 SeitenHistory of Diamondssilvernitrate1953Noch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility Study of Creating Spaces For Cultural Tourism Under The Floating Market Concept at Nong Han Lake, Sakon Nakhon, ThailandDokument5 SeitenFeasibility Study of Creating Spaces For Cultural Tourism Under The Floating Market Concept at Nong Han Lake, Sakon Nakhon, ThailandInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Notes Unit-1 (Network Operating System) : Session: 2021-22Dokument17 SeitenLecture Notes Unit-1 (Network Operating System) : Session: 2021-22Pradeep BediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xu 2020Dokument11 SeitenXu 2020Marco A. R. JimenesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 520l0553 PDFDokument52 Seiten520l0553 PDFVasil TsvetanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrionDokument22 SeitenPrionAnushkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site AnalysisDokument20 SeitenSite AnalysisCarlo RosaioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management Science - Lecture 2Dokument9 SeitenManagement Science - Lecture 2Nicole SallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beauty Therapy Thesis SampleDokument8 SeitenBeauty Therapy Thesis Samplerachelvalenzuelaglendale100% (2)
- Saberon StratMan2Dokument3 SeitenSaberon StratMan2paredesladyheart18Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vital Judo Throwing TechniquesDokument193 SeitenVital Judo Throwing TechniquesJuan Jose Opazo Carvajal100% (1)
- Static CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsDokument19 SeitenStatic CMOS and Dynamic CircuitsAbhijna MaiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement - Refrigerant PipingDokument7 SeitenMethod Statement - Refrigerant PipingGirithar M SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pnbcontr0223en (Web)Dokument308 SeitenPnbcontr0223en (Web)James GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oplan Tumbler ProposalDokument3 SeitenOplan Tumbler ProposalKay Tuppil ManzanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paintings of Juan LunaDokument39 SeitenPaintings of Juan LunaMiss MellowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cot 3Dokument16 SeitenCot 3jaycel cynthiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Q2) Electrochemistry 29th JulyDokument21 Seiten(Q2) Electrochemistry 29th JulySupritam KunduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fractal Audio Footswitch Functions Guide PDFDokument22 SeitenFractal Audio Footswitch Functions Guide PDFerikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFDokument9 Seiten1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFIfwat ThaqifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Order,+ERC+Case+No.+2014 174+RCDokument9 SeitenOrder,+ERC+Case+No.+2014 174+RCCoii Yee Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sarason ComplexFunctionTheory PDFDokument177 SeitenSarason ComplexFunctionTheory PDFYanfan ChenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0707-Passive VoiceDokument6 Seiten0707-Passive VoiceKhôi TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facility Systems, Ground Support Systems, and Ground Support EquipmentDokument97 SeitenFacility Systems, Ground Support Systems, and Ground Support EquipmentSree288Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bams 1st Rachna Sharir Joints and Their Classification 16-05-2020Dokument15 SeitenBams 1st Rachna Sharir Joints and Their Classification 16-05-2020Sanjana SajjanarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigerant Solutions: Refrigerant Retrofit For Existing R22 EquipmentDokument2 SeitenRefrigerant Solutions: Refrigerant Retrofit For Existing R22 EquipmentpriyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Dust Technology Seminar ReportDokument32 SeitenSmart Dust Technology Seminar ReportSushan Upadhyay67% (3)
- Boil-Off Gas CalculationsDokument14 SeitenBoil-Off Gas CalculationsAlberto100% (1)