Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bio Review
Hochgeladen von
Myy TranOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bio Review
Hochgeladen von
Myy TranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
BiologyReviewChapter132015
Chapter1
science:systematicstudyofthenaturalworld
scientificmethod:observation,hypothesis,procedure,data,results,conclusion
errorbars:showtherangeofdataorthestandarddeviation
standarddeviation:spreadofdataaroundthemeanmeasureshowwidelyspreadthevaluesinasetof
dataare.
Gaussiancurve:normaldistributionmostvaluesareclosetothemeanandonlyafewvalueswillbe
farfromit
ttest:comparestwosetsofdataandindicatedtheprobabilitythatthetwosetsareessentiallythesame
Chapter2CellTheory
1665RobertHookediscoveredandnamedstructurescells
celltheory:1.alllivingorganismarecomposedofcells,andtheproductofcells
2.cellsarethesmallestunitsoflife
3.cellsonlycomefrompreexistingcells
functionsoflife:metabolism
response
growth
reproduction
homeostasis
nutrition
measurements:micrometer(m)1106ofametre
nanometer(nm)1109ofametre
eukaryoticcell:10100106ofametre
prokaryoticcell:15106ofametre
magnifiedsize=realsizexmagnification
volume:proportionaltotherateacellproducesheat/wasteandconsumesresources
volumeincreasemorerapidlythanthesurfacearea
surfacearea:proportionaltotheuptakeofresourcesandremovalofheat/wastegoesviathecell
membrane
todealwiththeincreaseofvolume:needtoincreasethesurfaceareabyprotruding
extensionorbyflatteningthecell
emergentproperties:organismcanachievemoreifitworktogetherwithotherorganismthanwhateach
cellcouldachieveindividuallyAKAteamwork
euchromatin:lightgreyrepresentsgenesthatareused
heterochromatin:darkgreyrepresentsgenesthatareNOTused
stemcells:unspecialisedcellstotipotenttogethertheycanbepluripotent
pluripotent:notfixedastodevelopmentalpotentialitiescapableof
differentiatingintooneofmanycelltypes
totipotent:capableofdevelopingintoacompleteorganismordifferentiating
intoanyofitscellsortissues
differentfromnormalcells
1. areundifferentiatednotspecialisedintoacertaintypeofcell,asaresultall(ormost)oftheir
genescanstillbeexpressed
2. selfsustaining
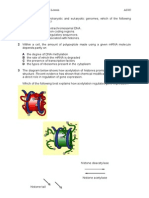
ProkaryoticCells
cellwall:madeofproteinsugar(plantsaremadeofcellulose)givescellshape,protectfromexternal
damage,preventburstingifcelltakesupalotofwater,anchorspiliandflagella
plasmamembrane:controlswhichmaterialsenterandleaveselectivelypermeable
cytoplasm:fluidthatcontainenzymesthatcontrolmetabolicreactionsincell
pili:thinproteintubes,foundoutsideofplasmamembrane
attachmentpili(fimbriae)
conjugationpili(sexpili):longerthanfimbriae,playroleinbacterialconjugation,buildbridge
betweencytoplasmsoftwobacterialcellsandallowplasmidtobetransferredfromonebacterialcellto
another
flagella:longthreadlike,madeofprotein,attachedtocellsurface,allowbacteriatomoveinfluid
environment
ribosome:consistsofRNAandproteinskeyroleinproteinsynthesis(translation)prokaryotic
ribosomesare70S,eukaryoticribosomesare80S
nucleoidregion:containsDNA
binaryfission:startswithDNAreplicationseparationoftwocircularstrandsofDNAtoeithersideof
cellcytokinesisdividescellsintotwocellgrowstofullsize
EukaryoticCells
similartoprokaryoticcellsinorganelles
roughendoplasmicreticulum:membranewithribosomesattached.RERmakesproteinsthatare
exportedviaexocytosisinordertobeusedoutsideofthecellsiteofproteinsynthesis
lysosome:containshydrolyticenzymes(lysozymescanbreakdownsubstancesincell)fuesewith
anddigestoldcellorganellesandmaterialtakeninviaendocytosiscanburstandcauseautolysisofa
cell
golgi:extensivenetworkincellintercellulartransportprocessandpackageofprotein
mitochondrion:linkreactionandthekrebscycletakeplaceinmatrixelectrontransportchainfoundon
cristaeofinnermembraneinvolvedinreleaseofenergyfromorganicmolecules
nucleus:largestcellorganellecontainsDNAcontrolsactivityofellbytranscribingcertaingenesand
notothers
features
similarities
differences
differences
prokaryotes
eukaryotes
geneticmaterials
DNA
nakedDNA
associatedwithproteins
circular
linear
foundincytoplasm
encloseinnuclearenvelope
proteinsynthesis
ribosomes
70S
80S
respiration
nomitochondriabutusesplasma
membraneandmesosomes
mitochondria
ultrastructure
internalmembranes
nointernalmembrane
compartmentalisecellintoareas
withdifferentfunctions
CellMembrane
names:fluidmosaicmodel,phospholipid,bilayer,plasmamembrane,
phospholipidmolecule:phosphateheadpolarandhydrophilicand2fattyacidtailsnonpolarand
hydrophobic
membranejob:keepcellcontentseparatefromtheoutsidesothatthecellcanhaveahigherorlower
concentration,semipermeable
proteins:integralproteins:foundbetweenphospholipidmoleculeshalfoutsidemembranehalfinside
peripheralprotein:foundoutsideofmembraneinteractwiththephosphateheadsmaynotbe
permanentlyassociatedwiththemembrane
proteinsthathascarbohydrategroupattachedtothemcalled:glycoproteins
containcholesterolbetweenfattyacidtailsreducesfluidityandpermeability
functions:
1. hormonebindingsites:hormonestransportedbybloodwillonlyactoncellsthathavethe
appropriateproteinreceptorontheoutsideoftheirmembrane
2. immobilisedenzymes:enzymesarrangesintosystemsinordertomakeiteasierforasequence
ofreactionstooccur
3. celladhesive:integralproteinscanstickoutandbindtospecificproteinmoleculesinadjacent
cellsortheycanbindtoanextracellularmatrix
4. celltocellcommunication:directcontactbetweenmembraneproteinsofadjacentcellsoria
signalslikehormonesorneurotransmitters
5. channelsforpassivetransport:allowsmallproteinstoentercellwithoutenergybeingused
6. pumpsforactivetransport:pumpinnervecell,usingATPtotransport
diffusion:movementofgasorliquidparticlesfromaregionofhighconcentrationtoaregionoflow
concentrationpassivetransport
osmosis:waterdiffusionpassivetransport
activetransport:requiresATP,moveparticlesagainstconcentrationgradient(lowtohigh)
passivetransport:requiresnoATP,moveparticlesdownconcentrationgradient(hightolow)
transportproteins:AKAcarrierproteinsmoveparticlesin/outmembrane
endocytosis:processcelltakesupasubstancebysurroundingitwiththemembraneneedATP,takes
upsubstancebecauseitistoopolarand/ortoolarge
pinocytosis:celldrinking
phagocytosis:celleating
exocytosis:reverseofendocytosismaterialsbeingremovedfromcells
CellDivision
cellstage:1.mitosis:processofnucleardivision
2.cytokinesis:physicaldivisionofcell
3.stageG1:cellgrowthandincreaseinorganelles
4.stageS:synthesisofDNA,replicationofDNA
5.stageG2:preparationformitosis,mitochondriaandchloroplastincreasethemost.
stageG1,SG2areinterphase,averyactiveperiodinlifeofacell,DNAtranscription
andtranslationandreplicationoccur
tumourrepressorgenes:produceproteinsinhibitscelldivision
protooncogenes:genesproduceproteinsstimulategrowthandcelldivision
toremovetumours:1.surgicalremoval
2.radiation
3.chemo
mitosis:1.prophase:chromosomesvisiblecentriolesmovetooppositepolesspindleformsnucleolus
invisiblenuclearmembranedisappearchromosomeshave2identicalsisterchromatidsheldtogether
bycentromere
2.metaphase:chromosomesmovetoequatorspindleattachtocentromeres
3.anaphase:centromeresseparatechromatidsseparateandmovetooppositepolesnowcall
chromosomes
4.telophase:spindlesdisappearcentriolesreplicatenuclearmembraneappearnucleolus
visiblechromosomesarechromatids
zygote:fertilizedegg
Chapter3ChemicalElementsandWater
elements:puresubstancesthatcannotbebrokendownanyfurther,theirparticlesareatom
molecules:atomcombinechemically
compound:substanceoftwoormoreelements
livingthinconsistofcompoundscontainingcarbon
elementsinlivingorganisms:O(65%)C(19%)H(10%)N(3%)
element
role:prokaryotes
plants
animals
sulfur
usechemicalreactionwithsulfuras
sourceofenergy
produceaminoacids
proteincontainsulfur
sameasplants
phosphorus
areofphosphategroupinATPand
same
same
DNA
calcium
maintainingcellstructureandmovement componentofcellwalls
andcellmembrane
strongbonesrelease
neurotransmitterintosynapsewhen
nervemessagearebeingtransmitted
iron
anaerobicbacteriausechemicalreaction
withironassourceofenergy
formationofchlorophyll
foundinredbloodcell,helpoxygen
transport
sodium
helpflagellum
insomeplantsithelpbind creatingactionpotentialinneurons
CO2forphotosynthesis
andaidglucosetransportacross
membrane
propertiesofwater:latentheatofvaporizationtakesinalotofenergytogofromliquidtogas
goodsolvent
cohesiveandadhesive
Carbohydrates,LipidandProteins
carbohydrates:containC,H,O
monosaccharidesaresimplesugarthencomesdisaccharidesandpolysaccharides
condensationreaction:produceswateroppositeishydrolysis
glucose+glucose maltose+water(right=condensation)
monosaccharides:
disaccharides
polysaccharides
1. glucose
1.maltose
starch
2. fructose
2.sucrose
glycogen
3. galactose
3.lactose
cellulose
sourceofenergy,produceATP
lipids:fatscondensationreactionbetweenglyceroland3fattyacids
unsaturatedoneormoredoublebondsbetweencarbonmolecules
saturatednodouble
glycerol+3fattyacid triglyceride+3water(right=condensation)
functions:storeenergy,thermalinsulationmakesupcellmembrane
proteins:polypeptidesarelongchainsofaminoacid
4differentgroupsattachedtocentralCatom1.aminegroupNH2
2.(carboxylic)acidgroupCOOH
3.simpleH
4.Rgrouphasdifferentaminoacids
aminoacid1+aminoacid2 dipeptide+water(right=condensation)
DNAstructure
DNA(deoxyribonucleicacid):storeinnucleus
RNA(ribonucleicacid):storeincytoplasm
buildingblocksarenucleotides
form:pentosesugar,phosphate,organicbase
sugar:RNAriboseDNAdeoxyribose
phosphate:H3PO4
organicbase:AKAnitrogenousbaseadenine,cytosine,thymine,guanine,uracil
AgoeswithT,CgoeswithG
AandGarepurinesbigringsC,T,andUarepyrimidines
sugarandphosphatearebackboneofDNA,RNAandorganicbaseistheladder
DNamoleculescoil10nucleotidescompleteoneturnofthehelix
DNAreplication
helicase:unzipDNA
polymerase:fromoldstrandwithnewstrands(semiconservation)
TranscriptionandTranslation
RNA: ribosomalRNA(rRNA)majorcomponentofribosomes
transferRNA(tRNA)carriesaminoacidstomRNA
messengerRNA(mRNA)asequenceofnucleotidesthatdeterminestheprimarysequenceof
polypeptide
transcription:RNAproducefromDNAtemplate
translation:assemblyofapolypeptideinasequencebytheorderofnucleotidesinmRNA
codons:3nucleotidesthattellswhichaminoacidtotake
introns:noncodingsectionsofanRNAtranscript,ortheDNAencodingit,thataresplicedoutbefore
theRNAmoleculeistranslatedintoaprotein
exons:anynucleotidesequenceencodedbyagenethatremainspresentwithinthefinalmatureRNA
productofthatgeneafterintronshavebeenremovedbyRNAsplicing
Enzymes
enzyme:proteinmoleculethatacceleratesaspecificchemicalreaction
theyarecatalystsitspeedsupareactionwithoutchangingitinanyotherway,helpreach
equilibriumfaster
lockandkeymodel
factorsaffectenzymeactivity:
1. temperatureoptimumtemp.37Cdenaturedabove60C
2. pHdependsonenzyme,(pepsinatpH2,trypsinatpH8)
3. concentrationofsubstratereactionwillgofasterifthesubstrateismore
concentrated
denaturation:structuralchangeinaproteinresultsinalossofitsbiologicalproperties(hightempand
extremepHcandenatureit)
cellrespiration
cellrespiration:controlreleaseofenergyfromorganiccompoundsincelltoformATPcantakeplace
inpresence/absenceofoxygen
glycolysis:breakdownofonemoleculeglucoseintotwomoleculeofpyruvatewithasmallnetyieldof
ATPtakeplaceincytoplasmandDOESNOTrequireoxygen
Photosynthesis
lightenergyconvertedtochemicalenergy
CO2+H2O+sunlight+chlorophyll=C6H12O6
sunlightandwavelengths
plantsaregreenbecausegreeniscausedbythepresenceofthepigmentchlorophyll,foundin
chloroplastanditreflectsoffthegreencolorandabsorbsalloftheothercolors
lightdependentstage:lightenergyisusedtosplitwatermolecules(photolysis)intohydrogenionsand
oxygenandelectrons,alsoproducesATP
lightindependentstage:H+andATPinlightdependentstageareusedtofixCO2tomakeorganic
molecules
ATP(adenosinetriphosphate)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Systematic: How Systems Biology Is Transforming Modern MedicineVon EverandSystematic: How Systems Biology Is Transforming Modern MedicineNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB - Biology 2009 Syllabus (Almost Complete Set of Notes)Dokument117 SeitenIB - Biology 2009 Syllabus (Almost Complete Set of Notes)Cristen100% (24)
- Notes On CellsDokument11 SeitenNotes On Cellsritu_mishh9983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 2 Cells NotesDokument8 SeitenTopic 2 Cells NotesCharmaine ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module BIO IIDokument7 SeitenModule BIO IIBrandon DacanayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio11 First LE ReviewerDokument9 SeitenBio11 First LE ReviewerFREE ARTICLESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept 1.2 Biological Systems Are Much More Than The Sum of Their PartsDokument8 SeitenConcept 1.2 Biological Systems Are Much More Than The Sum of Their PartsAriel VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology: Building Blocks of LifeDokument874 SeitenCell Biology: Building Blocks of LifeSıla DenizNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB BiologyDokument33 SeitenIB BiologySalina LamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthetic Biology PrimerDokument73 SeitenSynthetic Biology PrimerTorniqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3A: Understanding Cell StructureDokument22 SeitenModule 3A: Understanding Cell StructureDiane Balaba OsingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell TheoryDokument39 SeitenCell TheoryNethra SasikumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology SL - Working With DataDokument68 SeitenIB Biology SL - Working With DataShelley Lima100% (1)
- IB Biology Core Syllabus NotesDokument31 SeitenIB Biology Core Syllabus NotesKashish Doshi100% (1)
- Cell Cycle and Cancer LabDokument4 SeitenCell Cycle and Cancer LabRich20% (5)
- Introduction To World of BiologyDokument61 SeitenIntroduction To World of BiologyBio SciencesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honors Biology Semester 1 Review: Unit 1 Intro, Food PoisoningDokument7 SeitenHonors Biology Semester 1 Review: Unit 1 Intro, Food PoisoningSaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Biology Notes - 21 Cell TheoryDokument3 SeitenIB Biology Notes - 21 Cell TheoryJohn Philip D. NapalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sir Cholo 1Dokument2 SeitenSir Cholo 1api-247316176Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science: How Do We Define Science?: ScientiaDokument9 SeitenScience: How Do We Define Science?: ScientiaAlice Del Rosario CabanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 01 What Is BiologyDokument40 SeitenModule 01 What Is Biologyrrro0orrrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3 wK-SheetDokument14 SeitenLesson 3 wK-Sheetmaha1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Summary: 1 The Science of BiologyDokument3 SeitenChapter Summary: 1 The Science of BiologyJoanne TolopiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SL Biology Syllabus NotesDokument52 SeitenSL Biology Syllabus NotesRyel MuchunkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell CultureDokument6 SeitenCell CultureWael OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To BiologyDokument31 SeitenIntroduction To BiologyIrene JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Botany Notes: 004 Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenBotany Notes: 004 Chapter 1humanupgrade60% (5)
- Biology: 2.1.1 Outline Cell TheoryDokument21 SeitenBiology: 2.1.1 Outline Cell TheorycaseygoingNoch keine Bewertungen
- CK-12 Biology Advanced Concepts Answer Key Chapter 3 Cell Biology (AdvancedDokument29 SeitenCK-12 Biology Advanced Concepts Answer Key Chapter 3 Cell Biology (AdvancedMargie OpayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoology 232 NotesDokument36 SeitenZoology 232 NotesKevinNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Dokument14 SeitenGeneral Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Kerala MekuriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Dokument14 SeitenGeneral Biology: L.COL. Negash Teame (MSC)Kerala MekuriyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOL 1115 1. Tree of LifeDokument12 SeitenBIOL 1115 1. Tree of Lifeanaaneja805Noch keine Bewertungen
- modcan ١Dokument25 Seitenmodcan ١fahembajashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Guide To Vce Unit 1 BiologyDokument8 SeitenStudent Guide To Vce Unit 1 Biologyapi-348068677Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology FundamentalsDokument61 SeitenCell Biology FundamentalsVarsha DuraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology - Chapter 1 Discussion AnswersDokument3 SeitenAP Biology - Chapter 1 Discussion Answersangel91me6371100% (8)
- Unit 4Dokument14 SeitenUnit 4Yitbarek TesfayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Lab Explores Cell Cycle and CancerDokument4 SeitenVirtual Lab Explores Cell Cycle and CancerFarrenheit IsidroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03-Virtual Mitosis and Cancer LabDokument4 Seiten03-Virtual Mitosis and Cancer LabPeter Allen GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advancing Toxicity Testing Methods For The 21 CenturyDokument49 SeitenAdvancing Toxicity Testing Methods For The 21 CenturynataleebellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology, Cytology, Embryology. 3rd Semester. Exam QuestionsDokument30 SeitenHistology, Cytology, Embryology. 3rd Semester. Exam QuestionsIzabella MonteiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Science of BiologyDokument5 SeitenThe Science of Biologysimelanepamela0Noch keine Bewertungen
- DESAIN PENELITIAN HEWAN COBA BIOMOLEKULER & IMUNOLOGIDokument56 SeitenDESAIN PENELITIAN HEWAN COBA BIOMOLEKULER & IMUNOLOGIFarizka Dwinda HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biological Testing of BiomaterialsDokument92 SeitenBiological Testing of BiomaterialsShazia Rehman100% (1)
- Unit 4 Bio G_11Dokument65 SeitenUnit 4 Bio G_11daalee1997Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Viability AssayDokument6 SeitenCell Viability AssayChristian Jayvon LalunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Modern Biology NotesDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Modern Biology NotescateNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 01Dokument5 SeitenCH 01Casimiro Piedras del Rio100% (1)
- Assignment Cell BiologyDokument4 SeitenAssignment Cell BiologyLegends FunanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryDokument8 SeitenBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryEstebanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology: An Introduction to Cell Structure and FunctionDokument119 SeitenCell Biology: An Introduction to Cell Structure and FunctionAdrianMiranda100% (1)
- Biology Definitions & TheoriesDokument4 SeitenBiology Definitions & TheoriesMohammed EljackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Module 1 CombinedDokument10 SeitenUnit 1 Module 1 Combinedapi-293001217Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology SL NotesDokument51 SeitenBiology SL NotesBasma EnbehNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Cell Overview: History of Cell Theory and Modern Cell TheoryDokument15 SeitenThe Cell Overview: History of Cell Theory and Modern Cell TheoryBenson Aquitania AlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: Biology: Exploring LifeDokument5 SeitenChapter 1: Biology: Exploring LifeThalia Lau100% (1)
- Observing MitosisDokument20 SeitenObserving MitosisTootsie90% (21)
- Ignou MSCDFSM PaperDokument3 SeitenIgnou MSCDFSM Paper??Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Hypotonic SolutionDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Hypotonic SolutionC Six Nor AzwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation - One CDXDokument43 SeitenFoundation - One CDXWenju QianNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCOP and CATH DatabaseDokument22 SeitenSCOP and CATH DatabaseAishwarya Dharan100% (3)
- Genetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila Part 1 - Basics of Drosophila EmbryogenesisDokument28 SeitenGenetics of Axis Specification in Drosophila Part 1 - Basics of Drosophila Embryogenesisrheen77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis - Simple English Wikipedia The Free EncyclopediaDokument3 SeitenPhotosynthesis - Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopediaapi-253604375Noch keine Bewertungen
- Philippine Children's Medical Center: Covid-19 Testing Laboratory Molecular Pathology Result FormDokument1 SeitePhilippine Children's Medical Center: Covid-19 Testing Laboratory Molecular Pathology Result FormRica RegorisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDC 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)Dokument80 SeitenCDC 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)Oui AnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetic Organization HandoutDokument8 SeitenGenetic Organization HandoutConnorNoch keine Bewertungen
- THT5Dokument5 SeitenTHT5Marc Exequiel CatamioNoch keine Bewertungen
- MethodsDokument12 SeitenMethodsMohammad_Islam87Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pgem-T and Pgem-T Easy Vector Systems ProtocolDokument29 SeitenPgem-T and Pgem-T Easy Vector Systems ProtocolAprilia Isma DenilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annealing Oligonucleotides Protocol - IDTDokument3 SeitenAnnealing Oligonucleotides Protocol - IDTBenedikt EngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulletin 6060Dokument2 SeitenBulletin 6060Muni SwamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pierce Chapter 2Dokument30 SeitenPierce Chapter 2Sarah HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute Pitch: Prevalence, Ethnic Variation, and Estimation of The Genetic ComponentDokument18 SeitenAbsolute Pitch: Prevalence, Ethnic Variation, and Estimation of The Genetic Componenttonylee24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Reconstitution of protein transport between Golgi compartmentsDokument33 SeitenReconstitution of protein transport between Golgi compartmentsJessieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Directorate General of Drug Administration: SL Name of The Pharmaceutical Address Location Licence No. Present StatusDokument2 SeitenDirectorate General of Drug Administration: SL Name of The Pharmaceutical Address Location Licence No. Present StatusAnamika SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SA To Vol Ratio ALONG WithDokument7 SeitenSA To Vol Ratio ALONG WithJames SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aasim PresentationDokument11 SeitenAasim PresentationUmairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personalised Medicine in PsychiatryDokument58 SeitenPersonalised Medicine in PsychiatryAttaullah khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KARYOTYPE CHROMOSOME ANALYSISDokument15 SeitenKARYOTYPE CHROMOSOME ANALYSISMustafa Khandgawi0% (1)
- Mendel S Genes Molecular Characterization - 2011Dokument8 SeitenMendel S Genes Molecular Characterization - 2011MARIA DE LOS ANGELES ORTIZ CRUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Dokument8 SeitenLecture COPEG Qns (Last Lect)Wesley TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Midterm Examihation, I (Ovember: PUC RrorDokument2 SeitenMidterm Examihation, I (Ovember: PUC Rrorjäšħwâñtħ rNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDA Reissues EUA for Lagevrio to Treat COVID-19Dokument12 SeitenFDA Reissues EUA for Lagevrio to Treat COVID-19ivethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcript2021feb05 DCM 2017 71788Dokument5 SeitenTranscript2021feb05 DCM 2017 71788ElvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biotech PDFDokument34 SeitenBiotech PDFSelvakapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument4 SeitenChapter 7ram sunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2018 BMB - Molecular Biology at The Cutting Edge - A Review On CRISPR-CAS9 For UndergradsDokument11 Seiten2018 BMB - Molecular Biology at The Cutting Edge - A Review On CRISPR-CAS9 For UndergradsAline LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondVon EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyVon EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)
- Masterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeVon EverandMasterminds: Genius, DNA, and the Quest to Rewrite LifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldVon EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessVon Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (33)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindVon EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (93)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesVon EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (396)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceVon EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (515)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildVon EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (44)
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesVon EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (347)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesVon EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (51)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceVon EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (632)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorVon EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsVon EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Mitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfVon EverandMitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (98)
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesVon EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (55)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowVon EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (389)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsVon EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceVon EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsVon EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2083)
- Unthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsVon EverandUnthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceVon EverandThe Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (45)
- Awkward: The Science of Why We're Socially Awkward and Why That's AwesomeVon EverandAwkward: The Science of Why We're Socially Awkward and Why That's AwesomeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (22)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageVon EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (40)
- Summary of Robert M. Sapolsky's DeterminedVon EverandSummary of Robert M. Sapolsky's DeterminedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)